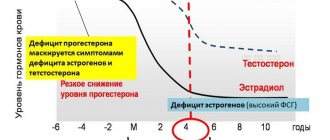
Testosterone is an androgen (a steroidal male sex hormone) that is produced in small quantities in a woman’s body. It takes part in the regulation of metabolism and affects reproductive function.
Physiological changes in testosterone concentration are observed during puberty, pregnancy and menopause. Pathological causes of hormonal imbalance are severe damage to organs and systems, diseases of the endocrine glands, and tumor formations.
One of the most common female hormonal problems is an increase in testosterone levels in the body. The official name of the disease is hyperandrogenism.
Testosterone hormone levels play an important role in a woman's health. Deviation from the norm of this indicator should be a signal for immediate action.
What are hormones?
The content of the article
A hormone is a chemical substance. It is secreted by one tissue and travels with body fluids to affect other tissues of the body. Essentially, hormones are “chemical messengers.” Many hormones, especially those that affect growth and behavior, are important for both men and women.
The amounts and levels of hormones change daily. The sex hormones, estrogen and testosterone, are secreted in short bursts—pulses—that vary from hour to hour and even minute to minute.
The release of the hormone varies between night and daytime and from one stage of the menstrual cycle to the next.
Testosterone in men and infertility
Here's what testosterone levels affect in men:
- responsible for the formation of male-type genital organs;
- promotes muscle growth;
- improves heart condition;
- increases calcium deposition in bones;
- responsible for the structure of the larynx and the entire body according to the male type;
- is the main cause of specific male behavior and mental reactions;
- forms the appearance of hair and adipose tissue strictly in certain places;
- promote sperm production.
Both low and high testosterone levels can be to blame for infertility. In the second case, testosterone suppresses the production of LH, which increases the production of follicle-stimulating hormone. This inhibits sperm division.
What is estrogen?
Estrogen is a class of related hormones that includes estriol, estradiol, and estrone.
Estriol is produced from the placenta during pregnancy. It is the main sex hormone in pregnant women. It is formed from developing ovarian follicles.
Estradiol is responsible for female characteristics and sexual functioning. In addition, estradiol is important for bone health in women. Changes in estradiol levels contribute to the development of most gynecological problems, including endometriosis, fibroids and even female cancers.
Estrone is widely distributed throughout the body. This is the main estrogen present after menopause.
Men's health center in Kirov
You can get a consultation with a urologist and urologist-andrologist in Kirov at the NAEDINE Clinic. The clinic has technologies, equipment and personnel to successfully identify and solve problems of the male reproductive system:
- ultrasound examination, including transrectal ultrasound (TRUS);
- laboratory diagnostics, incl. PCR, ELISA, hormones, biochemistry, andoflor;
- radio wave surgery and other minimally invasive methods;
- highly qualified urologists and andrologists with extensive clinical experience.
- 5 programs for diagnosing men's health
Make an appointment with a urologist by phone in Kirov: (8332) 32-7777 or through the form on the website
Why do estrogen levels drop?
Why do estrogen levels drop?
There are many reasons why estrogen levels drop, including:
- hypogonadism;
- hypopituitarism;
- disruption of pregnancy (estriol);
- perimenopause and menopause (estradiol);
- polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS);
- anorexia nervosa (eating disorder);
- extreme exercise or training;
- medications that block estrogen, such as clomiphene.
Additionally, women experience low estrogen levels immediately after childbirth, as well as during breastfeeding.
Medicines that affect testosterone levels
As mentioned earlier, certain medications used in the treatment of certain diseases can lead to a decrease in testosterone concentrations. These medications include:
- used for arterial hypertension - prazosin, reserpine, beta-blockers, clonidine;
- affecting the heart - verapamil, antiarrhythmic drugs, digoxil;
- affecting the gastrointestinal tract - ranitidine, cerucal;
- diuretics – hypotazid, chlorthalidone, veroshpiron;
- affecting the central nervous system - sedatives, antidepressants, amphetamines.
It is unacceptable for a patient to decide to self-prescribe medications. This should be done by a doctor, taking into account the possible negative consequences and impact on sexual function.
Do estrogen levels drop during menopause?
Yes. Estrogen levels drop during menopause. This is a natural condition for all women between the ages of 40 and 55. Also, a decrease in estrogen levels can occur suddenly in young women who have had their ovaries removed, leading to what is called surgical menopause.
Perimenopause is the transition period before menopause. At this stage, the first natural decline in estrogen levels and other physiological changes begin. Women going through perimenopause may experience weight gain along with other menopausal symptoms. For example, they may have irregular periods, hot flashes, and vaginal dryness.
On average, menopause occurs at age 51. When this happens, a woman's body produces less estrogen and progesterone. Declining estrogen levels during menopause can cause unpleasant symptoms, including:
- tides;
- night sweats;
- vaginal dryness or itching;
- loss of libido or sex drive.
Some women begin to act up. This may or may not be related to estrogen loss. Lower estrogen levels may also increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and osteoporosis.
Signs of testosterone deficiency
The importance of testosterone cannot be understated. It affects the condition of the body, and therefore its lack can lead to extremely adverse consequences. You can suspect a hormone deficiency based on the following symptoms:
- deterioration of attention, decrease in concentration;
- decrease or disappearance of libido;
- erection problems;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased strength, decreased muscle mass;
- reduction in the size of the prostate gland and testicles (they acquire a soft consistency);
- hot flashes;
- decreased level of red blood cells, causing anemia;
- brittle bones (osteoporosis);
- infertility caused by a decrease in sperm count.
Also, a decrease in testosterone concentration affects the psycho-emotional state of a man, leading to depressed mood, blues, and depression.
Why do estrogen levels increase?
During puberty, estrogen levels increase - this is normal. This hormone promotes changes in the body of a young girl. For example, it plays a role in breast development, a more mature figure, fuller thighs, and the growth of pubic and armpit hair.
In addition, high estrogen levels are observed:
- in overweight women;
- during a healthy pregnancy;
- for tumors of the ovaries or adrenal glands.
Certain medications may increase estrogen levels, such as steroid medications, ampicillin, estrogen-containing medications, phenothiazines, and tetracyclines.
Reasons for increased testosterone in the female body
The hormone testosterone in women is increased: the reasons for this can be very diverse, but the main place among them is given to:
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- taking certain medications;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet of women;
- vegetarian lifestyle - absence of meat and fish in the diet;
- presence of a tumor in the body;
- heredity;
- pregnancy status;
- menopause;
- ovulation.
What happens when testosterone levels rise or fall?
What happens when testosterone levels rise or fall?
If the body produces too much testosterone, the patient may have irregular or absent periods. There may also be more body hair. Some women with high testosterone levels experience baldness. Other possible effects include acne, clitoral enlargement, increased muscle mass, and deepening of the voice.
High testosterone levels can also lead to infertility and are commonly seen in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is an endocrine disorder that sometimes occurs in women of childbearing age. Women with PCOS have symptoms similar to those caused by high testosterone levels.
These include:
- obesity;
- apple-shaped body;
- excess or thinning hair;
- acne;
- menstrual irregularities.
PCOS leads to the following changes:
- higher levels of circulating male hormones;
- insulin resistance;
- Carbohydrate intolerance - a condition in which you tend to gain weight;
- low levels of HDL - “good” cholesterol;
- elevated triglycerides;
- high LDL - “bad” cholesterol;
- obesity;
- high blood pressure.
As women with PCOS age, the presence of these risk factors increases their risk of heart disease.
During menopause, women experience a decrease in testosterone levels. This decrease may be due to decreased libido. Some findings suggest that testosterone replacement therapy may improve sexual function in some perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Testosterone replacement is not recommended for women with breast or uterine cancer. Treatment may also increase the chance of heart disease and liver disease. Therefore, specialists are careful when prescribing such drugs.
Preparation for the procedure
Like any planned study, a blood test for testosterone should be carried out outside of acute viral and bacterial diseases, no earlier than two weeks after recovery.
Taking certain medications may affect test results; It is necessary to discuss with your doctor the list of medications used, and perhaps discontinue some of them in consultation with your doctor.
Blood collection should be done in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of overnight fasting. Drinking water is allowed. On the eve of the study, it is recommended to exclude significant physical and emotional stress and alcohol consumption. It is not recommended to smoke at least one hour before the test.
For women, the test is usually carried out 2-4 days after the start of menstruation, unless other conditions are recommended by the attending physician.
References
- Dedov, I. I. Endocrinology: textbook / 2nd ed., revised. and additional - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2013. - 432 p. — ISBN: 978-5-9704-2535-1.
- Kronberg, M. Reproductive endocrinology: textbook. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. - 416 p. — ISBN: 978-5-91713-029-3, 978-1-4160-2911-3.
- Tkachuk, V. A. Introduction to molecular endocrinology. Reception and intracellular signaling / ed. V. A. Tkachuk - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2021. - 240 p. — ISBN 978-5-9704-4264-7.
- Khera, M. Testosterone Therapies, 2021. - Vol. 43(2). — P. 185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2016.01.004.
How to determine testosterone deficiency
Laboratory testing can determine testosterone levels. To do this, you need to take a blood test in the morning (from 7:00 to 11:00). It is during this period of the day that the hormone reaches its maximum levels. Additionally, an analysis for LH, sex hormone binding protein and a number of other studies are required, which the doctor prescribes on an individual basis. In addition, a specialist is able to suspect a deviation in testosterone production based on clinical signs.
There is also a questionnaire designed for a man to self-assess the level of male sex hormones. He needs to honestly answer a number of questions:
- Is there a decrease in sexual desire, lack of desire to perform sexual acts, or a decrease in pleasure from sexual contact?
- Has growth decreased?
- Has your stamina and physical strength decreased?
- Do you have an irresistible urge to sleep after lunch?
- Do you feel like your enjoyment of life has decreased and that all the best things in life have already passed?
- Has the quality of erections deteriorated?
- Has your performance decreased?
- Has your usual energy and activity decreased?
- Have you become uncharacteristically irritable and/or unexplainedly sad?
- Has your ability to participate in sports become worse recently?
Androgen deficiency is possible if the answers to any three questions or questions 1 and 6 are positive.
Complexes with this research
Male confidence Prostate cancer risk assessment and testosterone level control RUB 1,190 Composition
Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening RUB 11,960 Composition
Check-up No. 1 for children and adolescents Annual preventive examination program RUB 10,950 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Men's check-up No. 1 RUB 18,570
- Female hormones. Follicular phase RUB 5,930
- Fitness monitoring 6,780 RUR
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 33,710
- Male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 13,300