Instructions for use BICARD-LF
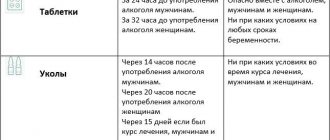
The effectiveness and tolerability of bisoprolol may be affected by concomitant use of other medications. This interaction may also occur if there is a short period of time between medications. The patient should inform the doctor about taking other medications, including medications purchased without a prescription.
Combinations not recommended
Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil, and to a lesser extent diltiazem:
- inhibitory effect on myocardial contractile function and AV conductivity. IV administration of verapamil can lead to severe arterial hypotension and AV blockade in patients taking beta-blockers.
Antihypertensive drugs with a central mechanism of action (clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine, rilmenidine):
- coadministration may result in worsening heart failure. During combination therapy, abrupt discontinuation of these drugs may increase the risk of reflex hypertension.
Combinations requiring special caution
When used simultaneously with class I antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin, flecainide, propafenone), the inhibitory effect on AV conductivity and myocardial contractile function may be enhanced.
Calcium antagonists such as dihydropyridine (for example, nifedipine, felodipine, amlodiline) may increase the risk of arterial hypotension. The possibility of increased negative inotropic effects in patients with heart failure cannot be ruled out.
Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, amiodarone) may enhance the inhibitory effect on AV conduction.
When used together with parasympathomimetics, it is possible to increase AV conduction time and increase the risk of bradycardia.
When used simultaneously with local beta-blockers (for example, those contained in eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma), the effect of bisoprolol may be enhanced.
Bisoprolol enhances the effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs. Symptoms of hypoglycemia may be masked. Such an interaction is most likely when using non-selective beta-blockers.
When using anesthetic agents while taking bisoprolol, the risk of myocardial function depression and arterial hypotension increases.
Cardiac glycosides (digitalis preparations) can reduce heart rate and increase AV conduction time.
NSAIDs may weaken the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol.
When using beta-sympathomimetics (for example, isoprenaline, dobutamine) in combination with bisoprol, the therapeutic effect of both drugs may be reduced.
When bisoprolol is combined with adrenomimetics that affect α- and β-adrenergic receptors (for example, norepinephrine, epinephrine), it is possible to enhance the vasoconstrictor effects caused by the action on α-adrenergic receptors, which leads to an increase in blood pressure. Such an interaction is more likely when using non-selective beta-blockers.
Antihypertensive drugs, as well as other drugs with a possible antihypertensive effect (for example, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazines), can enhance the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol.
Combinations to Consider
Mefloquine may increase the risk of bradycardia.
MAO inhibitors (except MAO B inhibitors) may enhance the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers. Concomitant use may also lead to the development of a hypertensive crisis.
Genferon supp 250 thousand IU N10 (Biocard)
GENFERON® is a combination drug, the effect of which is determined by the components included in its composition. Has local and systemic effects. The composition of the drug Genferon® includes recombinant human interferon alpha-2b, produced by a strain of the bacterium Escherichia coli, into which the human interferon alpha-2b gene was introduced using genetic engineering methods. Interferon alpha-2b has antiviral, immunomodulatory, antiproliferative and antibacterial effects. The antiviral effect is mediated by the activation of a number of intracellular enzymes that inhibit viral replication. The immunomodulatory effect is manifested, first of all, by enhancing cell-mediated reactions of the immune system, which increases the effectiveness of the immune response against viruses, intracellular parasites and cells that have undergone tumor transformation. This is achieved through the activation of CD8+ T killer cells, NK cells (natural killer cells), increased differentiation of B lymphocytes and their production of antibodies, activation of the monocyte-macrophage system and phagocytosis, as well as increased expression of molecules of the major histocompatibility complex type I, which increases the likelihood recognition of infected cells by cells of the immune system. Activation under the influence of interferon of leukocytes contained in all layers of the mucous membrane ensures their active participation in the elimination of pathological foci; in addition, due to the influence of interferon, restoration of the production of secretory immunoglobulin A is achieved. The antibacterial effect is mediated by reactions of the immune system, enhanced under the influence of interferon. Taurine helps normalize metabolic processes and tissue regeneration, has membrane-stabilizing and immunomodulatory effects. Being a strong antioxidant, taurine directly interacts with reactive oxygen species, the excessive accumulation of which contributes to the development of pathological processes. Taurine helps maintain the biological activity of interferon, enhancing the therapeutic effect of the drug. Benzocaine (anesthetic) is a local anesthetic. Reduces the permeability of the cell membrane to sodium ions, displaces calcium ions from receptors located on the inner surface of the membrane, and blocks the conduction of nerve impulses. Prevents the occurrence of pain impulses at the endings of sensory nerves and their conduction along nerve fibers. It has an exclusively local effect, without being absorbed into the systemic
Mechanism of action of Bicard
The active component of Bicard belongs to the group of beta blockers (beta adrenergic receptor blockers). Bicard is used for the treatment of hypertension and stable angina, and with other medications for the treatment of chronic heart failure.
Active ingredients from the beta blocker group bind to beta receptors in the heart. As a result, the hormone adrenaline can no longer dock with them, and the effect does not appear. Adrenaline increases cardiac output and blood pressure.
Bicard
Taking Bicard causes the heart to beat slower and less powerfully, and lowers blood pressure. The heart consumes less energy and oxygen, which alleviates the symptoms of angina: difficulty breathing and chest pain.
Pharmacokinetics of Bicard
After oral administration, Bicard is rapidly absorbed. Has a bioavailability of 90%. Doses ranging from 10 to 100 mg result in maximum blood concentrations after 3 hours. The half-life is 10 to 11 hours, with half of the substance excreted unchanged through the kidneys and the rest eliminated through the liver.
Side effects of Bicard
Administration of Bicard causes adverse reactions. Headache, dizziness, sensory disturbances, fatigue and weakness are common.
The following side effects may sometimes occur:
- Confusion, mood swings, depression and sleep disorders.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
- Muscle weakness and joint disease.
- Rash and itchy skin.
- Slow heartbeat, impaired heart function, and decreased blood pressure with changes in body position.
- Rave.
- Nervous discomfort.
- High blood pressure.
- AV block.
- Increased myocardial failure with fluid retention or difficulty breathing.
- Anorexia.
- Abdominal cramps.
- Muscle weakness.
- Cramps.
- Allergic skin reactions (redness, itching, mild rash, urticaria).
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Lipid disorders.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation and stomach pain.
In very rare cases, taking Bicard causes a decrease in tear secretion, an increase in blood lipid concentrations, respiratory disorders, hyperhidrosis of the limbs, erectile dysfunction and weight gain.
Contraindications to the use of Bicard
Bisoprolol is not used for certain diseases. Often a contraindication may be hypersensitivity to Bicard components. Other contraindications:
- Severe or underestimated forms of myocardial failure.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Cardiac conduction disorders.
- Lung diseases: severe bronchial asthma or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Low blood pressure.
- Malignant adrenal tumor.
- Late stage of intermittent claudication or Raynaud's phenomenon.
- Acidosis.
Pay special attention to patients with diabetes, psoriasis, impaired liver or kidney function, Prinzmetal's angina, slow heart rate (bradycardia), hyperthyroidism, and atrial-to-ventricular conduction disorders. Patients who become desensitized should take bisoprolol after a careful risk/benefit assessment by their healthcare provider.
Myocardial failure of the last stage
Bicard during pregnancy
During pregnancy, Bicard can only be used if the doctor considers treatment absolutely necessary. There is still no reliable data on how Bicard works during pregnancy. However, there are signs that it may cross the placental barrier and therefore may cause growth disorders in the baby.
Last trimester of pregnancy
Do not use during lactation. In animal studies, the drug passes into breast milk. If treatment is necessary, the child should be weaned from breastfeeding. Children should not be treated with bisoprolol because there is no clinical data regarding the safety of the drug in this age group.
Indications for use of Bicard
In medical practice, beta-blockers are used for diseases of the cardiovascular system. The main list of diseases for which Bicard is used:
- With hyperthyroidism, only with an increase in heart rate (tachycardia). A special case is thyrotoxic crisis, a complication of hyperthyroidism that is caused by infections or iodinated contrast agents. Bicard suppresses the formation of active thyroid hormones, counteracts the symptoms of restlessness and anxiety that occur with the disease.
- In case of circulatory disorders in the heart - coronary heart disease - and after heart attacks, Bicard is used to reduce the heart rate. Thanks to this, the heart does less work and consumes less oxygen. Many of the beta blockers are used to replace Bicard.
- Cardiac arrhythmias, in which the heart rate increases (atrial fibrillation).
- For liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension, propranolol is used, less often - bisoprolol. These two beta blockers reduce pressure in the portal vein, causing the blood vessels in this area to dilate.
Hyperthyroidism – increased thyroid function
Bicard LF tablets: what is the combination drug with beta blockers taken for?
Beta blockers are available as combination medications. Scientists combine beta blockers with dehydrating agents (hydrochlorothiazide, HCT). Such drugs are useful in the treatment of essential hypertension because HCT lowers blood pressure. Used for moderate to severe heart failure if there is edema.