There are several types of acids that are essential for the human body and are widely used by both cosmetologists and doctors. Ascorbine, nicotine, folic acid - these names are always heard, and everyone knows them well. But there are also some substances that are not so well known, and their invaluable health effects are difficult to assess. Lipoic acid is very popular for regulating metabolic processes in the body. This drug is beneficial for the metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates, and also helps control cholesterol levels. Therefore, it is used in the treatment of diabetes, liver cirrhosis, excess body weight, atherosclerosis, and is also widely used by people professionally involved in sports, as it is one of the safest supplements.
Useful properties for women
Alpha lipoic (or thioctic) acid is also called vitamin N. It is a kind of antioxidant that protects cells from free radicals, which prevents the process of premature aging. And these are not all the miraculous properties. Lipoic acid has incredible benefits for women:
- Improves the health of the cardiovascular, digestive and endocrine systems.
- Increases immunity.
- Improves reproductive function, helps normalize the menstrual cycle.
- Reduces the need to eat, which is so important in the fight against excess weight.
- The substance is often used to treat ailments such as diabetes.
Healthy Origins, Alpha Lipoic Acid, 600 mg, 150 Capsules
RUB 1,753
More details
Medicines with alpha lipoic acid are prescribed for certain purposes:
- removal of harmful substances from the body;
- normalization of all metabolic processes;
- impaired liver function;
- maintaining acceptable cholesterol levels;
- diabetes;
- detoxification after poisoning.
Interesting to know! When used correctly, lipoic acid slows down the breakdown of proteins and accelerates cell recovery. Therefore, drugs with this substance are popular not only among women, but also among bodybuilders.
What women need lipoic acid for is found deep in the cells of the body. The substance cleanses and rejuvenates us - these are the main advantages, which is a good reason not to neglect taking alpha-lipoic acid.
Side effects
In some situations, the occurrence of headaches and allergies cannot be ruled out.
Similar symptoms may appear as the indicated dose increases. If any of these symptoms occur, you should quickly stop taking LC and visit a doctor.
Thus, before using the medicine you need to carefully read the instructions. It is worth buying alpha acid from trusted manufacturers. It is best to rely on stores that specialize in nutrition for athletes.
Indications for use
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) supplements are prescribed in a number of cases:
- After 40 and 50 years. With age, vital processes in the body slow down, which leads to a weakening of the immune and other important systems. Vit. N cleanses the blood of harmful substances and speeds up metabolic processes.
- In order to maintain normal functioning of the endocrine system. The acid regulates the production of thyroid hormones, which forms the thyroid gland.
- For disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. The substance normalizes the digestion process and liver function. It also accelerates the breakdown of fats, which helps in the fight against excess weight.
- Acid is good for brain activity. Antioxidant properties help improve memory and alertness, especially in older people.
- For liver diseases. In order for as few compounds dangerous to the body as possible to settle in the liver, it is necessary to cleanse it. Vitamin N copes with this task perfectly. Deficiency of the enzyme causes significant harm to liver functions.
- Alpha-lipoic acid is useful for restoring strength. The fact is that the compounds are involved in the formation of cellular energy.
- In order to protect against free radicals, which is significant for women's health.
- To regulate blood sugar levels. Antioxidants cleanse the blood, which helps burn sugar.
- For disorders of the central nervous system. Organic compounds neutralize the effects of the oxidation process.
- Thioctic acid provides invaluable benefits to the cardiovascular system. The properties of the substance prevent heart attack, eliminate pain symptoms in blood vessels and protect tissues from the harm of the oxidative process.
- Antioxidants are used for youthful skin. The substance is drunk simultaneously with probiotics for the beauty of the facial dermis. The result is the smoothing of wrinkles, the removal of irritation, redness, rashes, as well as smoothness and elasticity.
Alpha lipoic acid can also be taken for cosmetic purposes, as well as for weight loss and when planning a child.
Vitamin N is universal - it breaks down perfectly with both water and fats.
Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and ALA
The role of oxidative stress has been deeply studied in experimental diabetes models and in patients with diabetes mellitus. Increased glucose levels in people with diabetes lead to an increase in advanced glycation end products (AGEs). This process, defined as auto-oxidative glycolysis, is considered to be the main cause of increased free radical production in diabetic patients [31]. In addition, autooxidative glycolysis may be responsible for reducing the availability and activity of antioxidant enzymes. Fructose, the level of which increases, serves as an additional source of AGE precursors. The damaging effect of accumulated AGEs is due to their binding to specific nerve fiber sheath receptors and activation of nuclear factor B (NF-B). One of the effects of NF-xB is to stimulate the release of substances that impair blood flow, such as endothelin-1 [15, 16]. In contrast, antioxidants inhibit NF-xB. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress promotes the programmed death of Schwann cells, which is an additional pathogenetic factor in the development of diabetic neuropathy. For example, when glucose is added to a culture of dorsal root ganglion cells, the frequency of programmed death of Schwann cells increases [19]. Free radicals disrupt the activity of cellular structures, including the endothelium, causing endoneurial hypoxia and accelerating the development of neuropathy.
ALA is a fatty acid that is found in every cell of the human body. ALA is formed naturally in the body and is chemically defined as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid (C8H14O2S2). In humans, ALA is synthesized in the liver and other tissues. Additional sources of ALA are foods. It is found in red meat, liver, green vegetables, potatoes, and yeast. The endogenous level of ALA in healthy people is 1-25 ng/ml [34]. But its synthesis decreases with age, as well as in people with chronic diseases, including diabetes and its complications, such as diabetic neuropathy.
This acid plays a critical role in the process of converting glucose into energy. At the same time, ALA is a powerful lipophilic antioxidant, the effectiveness of which has been proven, including in vitro [22]. The main effect of acid is the absorption of various reactive oxidized substances. ALA is a universal antioxidant because it is both water- and fat-soluble. This property provides the advantage of ALA in the protection of various forms of oxidative stress, in particular, intracellular protection. An additional benefit of ALA is its synergistic interaction with other antioxidants, including vitamins C and E. In addition, ALA is involved in the recycling of other antioxidants, such as vitamins C, E and glutathione. For example, ALA may be involved in the regeneration reactions of vitamin C and glutathione [21]. Glutathione is a major non-enzymatic defense mechanism that can directly react with free radicals to destroy them and is part of the glutathione peroxidase enzyme system. Together with ALA, glutathione plays an important role in various cellular redox reactions. An additional effect of ALA is the stimulation of nerve growth factor and, accordingly, fiber regeneration [20]. The natural form of ALA consists of an R-isomer, but the synthetic form is a racemic mixture of two isomers, the R- and S-form. Both isomers have different potentials. The R-form has greater potential for glucose utilization, while the S-form exhibits better affinity for glutathione reductase. Antioxidants may protect against glycemia-induced nerve dysfunction or improve diabetic neuropathy.
The uniqueness of ALA as an antioxidant lies in the following properties: 1) the ability to directly eliminate free radicals; 2) the ability to regenerate endogenous antioxidants, such as glutathione, vitamins E and C; 3) the ability to reduce the production of free radicals due to metal chelate activity.
Dosage of lipoic acid per day
Attention! Before using medications, consult your doctor. Also, do not forget to read the instructions, which clearly state the intake standards.
Table 2. Daily dose of vitamin N
| Category | Prevention, mg | Treatment, mg |
| Women | 25—100 | 300—600 |
| Pregnant | — | up to 75 |
| Men | 25—100 | 300—600 |
| Athletes | 100—200 | 150—250 |
For children under 18 years of age, drugs containing ALA may only be prescribed for therapeutic purposes. The approximate dose is 25 mg per day.
The maximum limit per day is 600 mg.
Application for women 40+
In the female body after 40 years, reserves of antioxidants are depleted, which weakens the protective functions against free radicals. All this provokes a loss of strength and youth. With age, harmful substances accumulate in important organs. In this case, the need for lipoic acid increases, so it is recommended to take at least 60-100 mg per day.
And in the presence of certain diseases (Alzheimer's, diabetes, etc.), the dosage is increased to 600 mg (at the discretion of the doctor).
Also, drugs are prescribed for problems in the field of gynecology: to normalize the menstrual cycle and alleviate the symptoms of menopause.
Interesting to know! Although alpha lipoic acid is called vitamin N, it is not a vitamin.
For wrinkles
The positive results of antioxidants are especially evident in adulthood, when the body begins to urgently need ALA. Therefore, most women after 40 years of age prefer cosmetics enriched with lipoic acid.
Such cosmetics have superior properties: smoothes wrinkles, gives elasticity, beautiful color, fights pigment spots and reduces circles under the eyes.
For infertility
Lipoic acid has long been popular in gynecology. It is prescribed to both partners at the planning stage of the baby. The drug is especially popular for IVF. In men, LA improves the quality of semen, and in women, the ability to conceive.
Lipoic acid is not always beneficial during pregnancy. The fact is that the substance suppresses iron levels, which interferes with maintaining hemoglobin levels. Therefore, in order to avoid anemia, it is advisable to use LA before pregnancy, and not during pregnancy. However, the drug can be prescribed in a minimum dose for therapeutic purposes - at the discretion of the doctor.
Interesting fact! Western neurology specialists prescribe up to 600 mg of ALA per day to adult patients. This prevents disruption of brain activity due to age.
ALC in clinical practice
ALA was first used for therapeutic purposes in 1966 in Germany for the treatment of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy and cirrhosis of the liver. The basis for this was data on low ALA levels in this category of patients [9]. In addition, in experimental models of diabetes, ALA was found to improve blood circulation and signal conduction along the nerve [11]. Over decades of use of ALA, numerous evidence has accumulated regarding the effectiveness of this drug against the symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy [30]. At the same time, it was noted to be well tolerated.
ALA is the drug of choice for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy
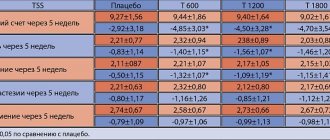
Major evidence-based studies on the effectiveness and safety of ALA for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy were conducted in the 1990s. The first large study, ALADIN I-III [36], examined three different dosages of ALA. The ALADIN I study included 328 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. They received intravenous LA at doses of 1200 mg, 600 mg, 100 mg, or placebo for 3 weeks. Improvement in symptoms of 30% or more was observed in 71% of patients receiving 1200 mg ALA per day; in 82% of patients receiving 600 mg ALA per day; in 65% of patients receiving 100 mg ALA per day; in 58% of patients receiving placebo. The ALADIN II study analyzed the results of 65 patients who received two doses of ALA tablets (600 or 1200 mg per day) or placebo for over 2 years. There was strong evidence of clinical improvement in neuropathy symptoms. The main indicator of the severity of diabetic polyneuropathy was the Total Symptom Score (TSS), which allowed us to determine the intensity and frequency during the last 24 hours of the main positive neuropathic symptoms, such as shooting pain, burning, numbness and paresthesia. Based on these positive results, the ALADIN III trial was designed to test the hypothesis of the effectiveness of a short course of intravenous ALA followed by a long course of ALA tablets for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy [36]. In this study, patients received 600 or 1200 mg of ALA per day for 3 weeks, followed by a tablet form of 1800 mg per day for 6 months. The results obtained showed a steady trend towards a decrease in the severity of pain, without reaching a degree of statistical significance.
In the ORPIL study [15], in which patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus received ALA at a dose of 1800 mg per day, a significant improvement in endoneurial function was found after 3 weeks of treatment. The SYDNEY study [7, 36] demonstrated the effect of ALA on the sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy. It included patients with stable diabetes complicated by sensorimotor neuropathy. They were prescribed intravenous administration of 600 mg ALA or placebo 5 days a week, for a total of 14 infusions. After treatment, there was a significant (p<0.001) improvement in the TSS scale mentioned above. In addition to a rapid improvement in sensory symptoms, a reduction in the processes of degeneration of nerve fibers was observed. The authors concluded that ALA can be successfully used to treat sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy.
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, which is found in 25% of patients, is also known to be a severe complication of diabetes. This neuropathy is characterized by a reduction in cardiovascular rate variability (HR) and is associated with an increased risk of mortality in patients with diabetes. Of great interest in this regard is the DEKAN study [35], which assessed the effectiveness of a 4-month course of ALA at a dose of 800 mg per day. An improvement in heart rate variability was found compared to placebo. There has also been evidence of the benefit of long-term oral ALA for the treatment of both diabetic sensorimotor neuropathy (600-1800 mg per day) and cardiac autonomic neuropathy (800 mg per day). In addition, the effectiveness of a combined course (600 mg per day intravenously for 10 days followed by taking a tablet form of 600 mg per day for 50 days) was established in patients with various forms of autonomic neuropathy [35]. At the same time, there was a regression of symptoms of diabetic enteropathy, a decrease in complaints of dizziness and (or) instability in a standing position, and an improvement in sexual function. The data obtained allowed the authors to conclude that ALA is effective in the treatment of various forms of diabetic autonomic neuropathy.
In 2004, data from a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials ALADIN I, ALADIN III, SYDNEY and NATHAN II, which included over 1000 patients, were published [38]. Convincing data were obtained that after 3 weeks of intravenous administration of ALA at a dose of 600 mg, a positive effect was observed in more than 50% of patients. It was noted that improvement was observed both in terms of positive neuropathic symptoms and neurological deficits.
A daily dose of 600 mg in tablet form showed the optimal balance of safety and effectiveness [39] (SYDNEY II study), while using a daily dose of 1200 mg, moderate nausea occurred in 21% of patients, which is higher than in the ALADIN I clinical trial (15%) and ALADIN II (7%), in which the dose was similar.
Post-marketing observations confirmed the highly safe profile of ALA [37].
The results of the clinical studies made it possible to formulate an algorithm for the treatment of diabetic patients with diabetic polyneuropathy with intravenous administration of ALA. Treatment begins with intravenous administration of ALA in a single dose of 600 mg for 14-15 days. Subsequently, tablet forms are used.
Russian neurologists and endocrinologists, who have domestic and foreign injectable and tablet ALA preparations, have also accumulated extensive clinical experience in the use of ALA for diabetic neuropathy. Among the domestically produced drugs, the drug thiolepta stands out, effective against diabetic and alcoholic neuropathy [5]. A corresponding comparative study [2] showed that the use of thiolepta at a dose of 600 mg per day (2 tablets of 300 mg once) for 2 months, in addition to basic therapy that maintains euglycemia, provides a more pronounced tendency to regression of symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy compared with patients receiving only basic therapy: by the end of treatment, the severity of symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy was less in the main group of patients compared to the control group; there was also a disappearance of neurological symptoms according to the TSS scale in 30% of patients (in the control group, neurological symptoms persisted); An electroneuromyographic study revealed a statistically insignificant (p>0.05) tendency towards a more pronounced increase in the speed of impulse conduction along the sensory and motor nerves, as well as the amplitudes of motor and sensory responses in the main group.
Additional possibilities for using ALA
From the above it is clear that the main indication for the use of ALA is diabetes mellitus and complications associated with impaired glucose metabolism, including not only neuropathy, but also cataracts. Additionally, it can be noted that ALA helps reduce the dependence of diabetic patients on insulin.
Due to its properties, ALA can be used for medicinal purposes and for a number of other diseases. From the data we present below, it is clear that for some diseases certain therapeutic results have already been obtained, while for others only the prerequisites for the use of ALA are still being considered.
ALC and compression ischemic radiculopathy
In animal models (compression of the rat sciatic nerve), the protective effect of ALA in reducing oxidative stress in traumatic damage to the nerve fiber has been proven [32]. These data may provide a basis for the use of ALA in the treatment of back pain associated with radiculopathy. The most common cause of radiculopathy and radicular pain is lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Damage to the nerve fiber depends on the duration of the compression. A sequential pattern of axonal degeneration and myelin degradation and subsequent rapid regeneration is characteristic of peripheral nerve injury. An undeniable fact is that free radical levels increase after tissue damage. Increased production of free radicals under conditions of ineffective balance of cellular antioxidant systems leads to additional direct damage to cell membrane phospholipids, mitochondria, and cellular proteins. Superoxide dismutase is one of the protective systems that protects cells from damage associated with exposure to free radicals. Superoxide dismutase belongs to the family of metatalloproteinases. It catalyzes the dismutation of free radicals, the end products of which are water and hydrogen peroxide, the latter being neutralized due to the activity of catalase. An experimental model of damaged nerve fiber showed an increase in the activity of superoxide dismutase and catalase, which may be a response that levels oxidative stress. Despite the lack of complete understanding of the subtle mechanisms of nerve fiber damage, the evidence available to date is sufficient to suggest that ALA may enhance the antioxidant protection of damaged fibers.
Recent studies by M. Ranieri et al. [27] showed the effectiveness of ALC against such clinical symptoms as pain, paresthesia, hypoesthesia in patients with compressive radiculopathy due to disc-radicular conflict. These authors found the beneficial effects of ALA when evaluating the effectiveness of the adjunctive use of a combination of ALA and gamma-linolenic acid in a 6-week rehabilitation program in patients with discogenic radiculopathy compared with a similar group of patients treated only as part of a rehabilitation program. Additional benefits of antioxidant therapy have been demonstrated not only in terms of pain reduction, but also in associated functional impairment, assessed on a number of well-known scales, including improvement in quality of life [17].
ALA and alcoholic neuropathy
. Antioxidant therapy is considered as one of the possible ways to treat the toxic effects of alcohol on the nervous system. Although there are a lot of publications on the proven therapeutic effect of ALC in diabetic polyneuropathy, studies on the effectiveness of ALC in alcoholic polyneuropathy (AP) are still rare.
I.A. Sklar et al. [4] found that ALC is effective in 70% of patients with AP; it affects sensory and motor symptoms and also has a positive effect on painful and paresthetic manifestations of AP that are painful for patients. E.A. Kovrazhkina et al. [3], when analyzing the effectiveness and tolerability of ALA in AP in comparison with thiamine, found that ALA was significantly more effective than vitamin B1 in both clinical and electrophysiological parameters.
Treatment of ALA for AP can be considered etiotropic, since the drug affects one of the main etiological factors in the formation of polyneuropathy in chronic alcoholism - oxidative stress. In addition, there is evidence [26] of a direct effective effect of ALA on ethanol-mediated neurotoxicity in vivo
.
ALC and vibration disease
. The main symptoms of vibration disease include vascular disorders, manifested by disturbances of peripheral circulation, changes in capillary tone, disruption of general hemodynamics, as well as the development of autonomic-sensory polyneuropathy of the extremities. In this case, ischemia of the endoneurium triggers oxidative stress processes, which play an important role in damage to the nerve fiber. All this is a sufficient basis for the use of antioxidant therapy, in particular ALA, for the treatment of vibration disease.
The corresponding study was carried out by V.G. Artamonova and E.L. Lashina [1]: thiolept was used in a comparative open randomized study at a dose of 600 mg per day (course duration 21 days) for the treatment of vibration disease with autonomic-sensory polyneuropathy. The additional introduction of thiolepta into therapy led to a decrease in the frequency of subjective complaints of patients, a persistent decrease in relapses of pain in the extremities, and a decrease in the frequency of vasospasm attacks. In the group of patients receiving thiolept, there was a significant positive dynamics (p<0.05) of electrophysiological parameters testing the state of the nerve fiber. After treatment, an increase in the speed of propagation of excitation along motor and sensory fibers was observed.
ALA and immunodeficiency virus
.
There are certain experimental grounds for the use of ALA drugs in HIV-infected individuals. For example, it has been shown that ALA significantly (30-70%) increases glutathione in HIV-infected people. This may be important for hepatocyte recovery, since the immunodeficiency virus induces glutathione deficiency [13]. Moreover, ALA inhibits viral replication during acute and chronic periods of cell infection. In vitro
, ALA exhibits a synergistic antiviral effect with azathiaprine. This combination results in stronger inhibition of viral replication than either drug alone [8]. Separate studies have shown that ALA reduces the activity and invasive ability of the HIV gene.
ALA and skin aging
. There are suggestions [24] that ALA can promote the elimination of damaged collagen and have a preventive effect on the processes of protein glycolysis, which prevent premature aging and skin damage (23). Clinically, ALA has advantages over vitamins C and E for symptoms such as improved skin color, tone, and texture. It is no coincidence that ALA is traditionally included in creams whose action is aimed at improving skin texture and reducing pores and wrinkles.
ALA and the cardiovascular system
. Oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) with the formation of free radicals contributes to the deposition of cholesterol in the arterial wall, which is associated with atherosclerosis. Since 1992, studies have been published demonstrating the synergistic effect of ALA with vitamins C and E against free radical oxidation of LDL. Clinical studies confirm the ability of ALA to reduce ischemia and reperfusion damage to the heart muscle and brain [10].
ALA and treatment of multiple sclerosis
. Many researchers believe that oxidative damage may play a large role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Using a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice, the effectiveness of ALA was proven in reducing the clinical symptoms of encephalomyelitis (effectiveness between 23 and 100%), reducing inflammatory processes, demyelination and loss of axons in the spinal cord. It is assumed that the effectiveness of ALA is associated with inhibition of lymphocyte transport across the blood-brain barrier and, possibly, with inhibition of metalloproteinases [18]. However, consideration of ALA as a potential drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis still needs to be explored.
Possibilities of ALA for the treatment of olfactory impairment
. Usually, a violation of the sense of smell is associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract.
One study [14] found an improvement in post-viral olfactory dysfunction under the influence of a course (4.5 months) of ALA at a dose of 600 mg per day in approximately 60% of patients.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
. When considering the causes of chronic fatigue syndrome, some researchers suggest a possible role for changes in free radical levels. This naturally suggests the possibility of using antioxidant therapy. Such a study was conducted by Canadian clinicians who established the positive effect of ALA and other antioxidants in the treatment of the syndrome in question [17].
Potential of ALA in the prevention of drug toxicity
. Neuropathy can be a dose-limited side effect of drugs used in the treatment of life-threatening conditions such as cancer and HIV infection. We are talking primarily about cytostatics, which often cause axonal sensorimotor neuropathy, or, less commonly, damage to small fibers in some patients [23]. Cytostatic drug-induced neuropathy can be acute or chronic. Symptoms of acute neuropathy appear during or a short period after a course of therapy with drugs containing platinum. Chronic neuropathy can occur weeks or months after chemotherapy. The prognosis of drug-induced neuropathies is poor, and in some patients the symptoms remain irreversible. Some antiviral drugs may also cause sensory neuropathy.
Recently, publications have appeared on the beneficial effect of ALA in neuropathies induced by cytostatics. Thus, C. Gedlicka et al. [12] patients with cytostatic-induced neuropathy were prescribed during the next course of ALC at a dose of 600 mg intravenously for 3-5 weeks, and then 1800 mg in tablet form until the symptoms of neuropathy resolved, for a maximum of 6 months. The average duration of treatment was 2 months. Improvement in neuropathy symptoms was observed after an average of 4 weeks of treatment. The authors conclude that the preventive use of ALA in combination with cytostatics is useful for the treatment and prevention of damage to the peripheral nervous system. The benefits of preventive use of the tablet form of ALA (1800 mg per day, three times a day) for at least 24 weeks were confirmed in a special randomized trial [25]. A positive effect of ALC has been established [6] in reducing the risk of cardiotoxicity of cytostatics: for example, taking ALA 5 days before and 2 days after doxybicin injection leads to a clinically significant reduction in plasma creatine phosphokinase and lactate dehydrogenase.
How to take for weight loss
Alpha lipoic acid is not intended specifically for weight loss. However, the enzyme has tremendous benefits in weight loss. All thanks to its properties:
- Decreased appetite. Lipoic acid regulates blood sugar levels, thereby reducing the need for food. With the help of acid, dieting becomes more comfortable.
- Removing toxins and waste. Thanks to cleansing, your well-being improves, which makes it easier to withstand physical activity.
- Improving carbohydrate metabolism. Strength for physical activity appears and the process of burning reserves accelerates.
The drug is taken before training or immediately after exercise. The daily norm is up to 100 mg.
Watch the video for more details:
Lipoic acid for weight loss. USING lipoic acid for weight loss