Methylfolate: folic acid
Methylfolate is nothing more than one of the most biologically active forms of folic acid (vitamin B9). As is known, folic acid plays a very important role for human health, but in its pure form it is unable to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (the barrier between the circulatory and central nervous systems). Only after a number of transformations, under the influence of special enzymes, this acid is transformed into more accessible forms of folate, including methylfolate . However, these metabolic processes do not occur in the same way for everyone. Some people have mutations in certain genes (for example, MTHFR), which impair the adequate conversion of vitamin B9 into a bioavailable form. In other words, they absorb folic acid very poorly or not at all. It is in such cases that drugs with methylfolate are especially relevant. Unlike folic acid, it is easily absorbed into the circulatory system and consumed by cells. An important advantage of using methylfolate is that in this case there is no risk of accumulation of unchanged folate in the blood, and it itself does not pose a toxic danger to the body.
Folic acid. Instructions for use.
Doctors at our clinic consider pregnancy, including that resulting from an IVF program, as a normal physiological condition. We do not recommend taking dietary supplements and multivitamins during pregnancy planning if the woman is eating adequately. Gynecologists and reproductive specialists have a special attitude towards folic acid. Let's look at the most common questions that patients ask during their appointments. What is folic acid and what is it eaten with?
The name comes from the Latin word "folium" - leaf. Folic acid is part of the B group of vitamins. Vitamin B9 includes a group of compounds - folic acid, folacin, folates. This is a water-soluble vitamin, so overdose is almost impossible.
Easily destroyed by cooking and exposure to light. So, when cooking vegetables and meat, the loss of folic acid reaches 70-90%, and when frying meat - 95%, when boiling eggs - 50%. Folic acid is found in fresh vegetables (beans, spinach, tomatoes), as well as in the liver and kidneys of animals. In the human body it is formed by intestinal microflora. Additional intake of bifidobacteria helps to increase the synthesis of folic acid in the large intestine. Alcohol abuse and smoking reduce the synthesis and absorption of folic acid.
How does folic acid work?
Once in the human body, folic acid enters the liver, and in the presence of ascorbic acid, under the action of the enzyme reductase, it is converted into its active form - tetrahydrofolate.
Why do we need folic acid?
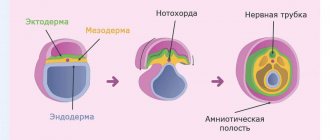
The body needs folic acid at any period of a person’s life, as it is necessary for the normal formation of blood cells and is involved in the synthesis of amino acids and nucleic acids (the basis for the formation of cells of all tissues). In the process of planning pregnancy, folic acid is necessary not only for women, but also for men. The main indicator of men's health is the condition of sperm, and their synthesis simply requires nucleic acids and protein. With a decrease in folate concentration, sperm synthesis is disrupted, their concentration and the percentage of morphologically normal forms decrease. The importance of vitamin B9 during pregnancy is difficult to overestimate, because in the first 12 weeks it is responsible for the correct formation of the neural tube of the fetus, which begins approximately 14-20 days from the moment of conception. The nervous tissue of the fetus consists of cells that are very actively dividing. And for normal, proper division, folic acid is necessary.
Taking folic acid daily when planning pregnancy and up to 12 weeks reduces the risk of developing neural tube defects by 72%!
How much, when and how to take folic acid?
In Europe, it is recommended that all women and men of childbearing age take folic acid, taking into account the possibility of unplanned pregnancy. According to Russian recommendations, you need to start taking folic acid three months before your planned pregnancy.
For most women and men, the recommended daily dose is 400 mcg, regardless of the fact of food intake. The only thing is that strong tea accelerates the removal of folic acid from the body.
Folic acid intake should be continued during pregnancy up to 12 weeks at a dose of 400 mcg/day.
When should you increase the daily dose of the drug?
An increase in the daily dose to 5 mg is justified only in the case of taking anticonvulsants, antacids (drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice), and sulfonamides. These drugs reduce the absorption of folic acid. The dose also increases if you have diabetes or celiac disease (impaired digestion and absorption).
If you have had a termination of pregnancy for medical reasons due to pathologies of fetal development or you have an established diagnosis of miscarriage, then increasing the dose will be quite justified.
What happens if there is a lack of folic acid?
Even short-term folic acid deficiency can lead to serious long-term consequences. The most common pathologies are hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the brain), anencephaly (complete or partial absence of the cerebral hemispheres, cranial vault bones and soft tissues), spina bifida, cerebral hernia, delayed physical and mental development, and premature birth.
Is excess folic acid dangerous?
Yes, it's dangerous.
Long-term use of folic acid in large doses may mask the symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia.
Folic acid salts can accumulate in the body, causing vomiting, stomach upset, nervousness and insomnia.
Excessive doses of folic acid increase the likelihood of autism in a child by 2.5 times. Malignant cells belong to the group of rapidly dividing cells and also require folic acid. In conditions of excess folic acid, antitumor immunity decreases.
By following simple recommendations for taking folic acid, you influence the health of your unborn child!
Methylfolate: composition
As already mentioned, methylfolate is part of the folate group - various forms of water-soluble folic acid. These compounds are not synthesized by the body and come from food or in the form of dietary supplements. Sources of folate are:
- legumes,
- green leafy vegetables,
- liver,
- egg yolk,
- citrus.
However, most of these folates are not metabolically active compounds. In order to participate in metabolic processes, they need to undergo a complex transformation process and only methylfolate easily penetrates the central nervous system.
Genetic polymorphisms and folate metabolism
Genetic variations (polymorphisms)* in the human genome occur frequently and, in some cases, can lead to the production of proteins with altered biological activity. Several such polymorphisms have been identified in genes encoding proteins involved in folate metabolism. As noted above, metabolic processes that require the transfer of methyl groups are regulated by the MTHFR enzyme. In the United States, approximately 60% of the population are intermediate folate metabolizers or carriers of the heterozygous form of the MTHFR enzyme gene polymorphism [8], and up to 25% of certain population groups are carriers of the homozygous form of these genetic variations [5]. These polymorphisms interfere, to varying degrees, with the conversion of folate to its active form, L-methylfolate. For example, individuals with poor folate metabolism are carriers of the homozygous common genotype 677C->T of the MTHFR gene and exhibit approximately 30% of the enzyme activity of wild-type (CC) individuals, while carriers of the heterozygous form of this polymorphism have approximately 65% of the activity. enzyme in wild-type individuals [9]. With another genotype variant, 1298A->C, of the MTHFR gene, carriers of the homozygous form may exhibit reduced catalytic activity of the enzyme, amounting to up to 68% of the activity characteristic of individuals with the wild type [10]. Given the high prevalence of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms in the population and the problems associated with reduced enzyme activity and correspondingly less bioavailable L-methylfolate, new research in this area has begun to focus on L-methylfolate supplementation rather than supplemental FA supplementation. means of preventing pathologies associated with folate deficiency.
Methylfolate: properties
Since methylfolate is a form of folic acid, it has the same properties as folic acid:
- participates in the formation of nitric oxide from arginine;
- controls the level of homocysteine in blood plasma;
- influences the efficiency of neural transmitters and is responsible for cognitive functions;
- plays a significant role in the process of physiological division and growth of all cells in the body.
Thus, methylfolate is a very promising drug for the prevention and treatment of various diseases, including psychosomatic disorders and depression.
In addition, methylfolate , unlike folic acid, has the ability to restore endothelial cell function in patients with hypercholesterolemia, a genetic disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood.
Additional benefits of taking folic acid
In addition to the prevention of neural tube defects, additional FC intake before and after conception has another beneficial effect - the prevention of congenital heart diseases and oral clefts [42–45], as well as preterm birth (as discussed above). The mechanisms by which FA exerts a preventive effect against the development of structural abnormalities in the fetus are unknown, but may involve the regulation of homocysteine metabolism [46].
Some researchers have concluded that taking FA may have additional beneficial effects on pregnancy outcome. This line of research arose as epidemiological studies showed that exposure to PK antagonists during pregnancy is associated with significantly higher rates of placenta-related pregnancy complications [47–50]. PK antagonists represent a wide range of drugs used for a variety of clinical indications, including the treatment of epilepsy, mood disorders and urinary tract infections.
PK antagonists can be divided into two groups: a) DHFR inhibitors (for example, sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim), which block the conversion of folate to its more active metabolites (see figure); b) other PK antagonists, which are a group consisting mainly of anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone and carbamazepine), but also including otilonium bromide (an antispasmodic drug containing low doses of phenobarbital) and cholestyramine.
One study noted that exposure to DHFR inhibitors (n = 12,546) or other FC antagonists (n = 1,565) during pregnancy was associated with an increased risk of developing preeclampsia (adjusted odds ratio [OR] = 1.52, 95% CI – 1.39–1.66), severe preeclampsia (OR = 1.77, 95% CI – 1.38–2.28), placental abruption (OR = 1.32, 95% CI – 1.12–1 .57), intrauterine growth restriction < 10th percentile (OR = 1.07; 95% CI – 1.01–1.13), intrauterine growth restriction < 3rd percentile (OR = 1.22; 95% CI – 1.11–1.34) and fetal death (OR = 1.35, 95% CI – 1.07–1.70) [49]. These adverse events have one thing in common: they all result from problems with implantation and placental formation that occur early in pregnancy. Since FA has been shown to regulate trophoblast invasion [51], there is a biological possibility that folate deficiency may interfere with early placental development, leading to pregnancy complications later in pregnancy.
Methylfolate: homocysteine
According to scientists, the most important merit of methylfolate is its ability to influence the amount of the amino acid homocysteine (methionine metabolic product) in the body. More than 80 studies show that increased homocysteine levels are fraught with an increase in the number of free radicals and the development of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke, heart attack, hemorrhage and thrombosis. In addition, deviations in quantitative homocysteine levels can negatively affect the health of pregnant women and lead to irreversible consequences for the fetus. The main role in controlling the level of this amino acid in the body belongs to three vitamins: vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folic acid, but it is the latter in the form of methylfolate that is most effective.
Risks associated with taking high doses of folate
Although it has been shown that supplementation with FA in doses above physiological levels may have beneficial effects on pregnant women and the fetus as described above, the potential risks associated with taking high doses of folate must still be considered. First, supplemental folate may mask a vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia), so care must be taken, especially with sensitive individuals, not to miss this diagnosis. Questions have also been raised about the potential adverse effects of unmetabolized synthetic FA in relation to cancer, depression and cognitive impairment [52]. Given these concerns, initial evidence suggests that supplementation with L-methylfolate rather than FA may reduce these risks [53].
Methylfolate: during pregnancy
Today methylfolate , along with magnesium and vitamin A, is increasingly recommended during pregnancy as a preventative measure against the development of intrauterine fetal malformations. We are talking, first of all, about neural tube defects, the incidence of which on average in Russia is approximately 0.5%. This congenital malformation is one of the causes of child mortality and disability, so the main medical task is to prevent such disorders.
Studies show that additional consumption of folic acid a month before and a month after conception reduces the risk of developing this defect by 60-100%, since this vitamin plays a critical role in the formation of the vascular bed of the placenta. In addition, folic acid prevents the occurrence of other congenital defects, such as heart defects and underdevelopment of limbs.
On top of this, a lack of folate during pregnancy often leads to premature birth and low birth weight of newborns.
Thus, folic acid is one of the most important nutrients for the proper intrauterine development of a child.
Meanwhile, according to statistics, recently, among women with difficult pregnancies, cases of MTHFR gene defect are becoming more common. The use of regular folic acid in this case is ineffective, therefore, to compensate for its deficiency, it is more advisable to use methylfolate .
Indications for the use of metafolin supplements
For more than 70 years, scientists have extensively studied all the benefits and possible harms of metafolin. Many RCTs and meta-analyses confirm that taking the substance from supplements is completely safe. Severe deficiency of vitamin B9 is extremely rare; this happens in case of intestinal dysfunction (due to illness or other reasons). But minor shortages are common. The main symptoms that suggest a deficiency of the substance are:
- Deterioration in sleep quality;
- Depressive states and worsening mood;
- More pronounced mood swings and emotional instability during PMS in women;
- Increased weakness, lethargy and drowsiness;
- Frequent headaches that occur for no apparent reason;
- Deterioration of skin health, dullness and appearance of skin defects;
- Deterioration of hair health, acceleration of baldness;
- Numbness in the limbs.
The substance is usually prescribed by a doctor. Given how beneficial metafolin is for women, it is recommended to take two courses per year to prevent deficiency. In this case, a doctor's prescription is not required.
Methylfolate: dietary supplement
According to numerous studies, modern people consume significantly less folate than necessary. methylfolate help fill this deficiency . Pharmaceutical companies offer a wide selection of such drugs, and they can be either single-component or complex, with the addition of B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin D3 and other nutrients.
Methylfolate: capsules
The most popular form of vitamin preparations, including methylfolate , are traditionally capsules.
Enlarge picture
- An example of such a product is “Methyl Folate” (400 mcg, 60 capsules) from Jarrow Formulas . It is manufactured using Quatrefolic fourth-generation folate production technology, which provides a more stable and highly concentrated biological compound. This form of folate is necessary for people who, due to any hereditary metabolic abnormalities or psychological factors, have impaired transformation of folic acid. This dietary supplement provides support for the nervous and cardiovascular systems, improves cell division, and reduces the risk of having children with spinal cord and brain defects.
Directions for use: Take 1 capsule daily with food.
Enlarge picture
- Among complex food supplements with methyl phtholate , “B-Right” vitamins (100 capsules) from the same company Jarrow Formulas . methylfolate itself , as a fourth generation form of folic acid, this optimized complex includes a number of B vitamins in high concentrations, namely:
- thiamine (vitamin B1),
- riboflavin (vitamin B2),
- niacin (vitamin B3),
- choline (vitamin B4),
- vitamin B5,
- pantethine (vitamin B5 derivative),
- vitamin B6,
- biotin,
- vitamin B12,
- inositol
Directions for use: Take 1 capsule daily, preferably with meals or as directed by a healthcare practitioner.
TOP 5 supplements in the form of 5-MTHF
Folates should not only be taken by pregnant women; they are recommended during the preconception stage for both potential parents. Sufficient folate content eliminates miscarriages and minimizes the likelihood of premature birth, eliminates delays in fetal development, and also improves the quality of seminal material in men. Adequate consumption of folates minimizes the risks of developing cancer pathologies, has a beneficial effect on the mucous membranes, and promotes their rapid recovery. A sufficient level of folate also has a positive effect on other intraorganic structures, improves the condition of the skin, hair, etc. We can highlight the TOP 5 folic acid supplements in the form of metafolin.
Fully Active Folate 800, Doctor¢s Best (USA)
Doctor's Best, Active Folate 800, 800 mcg, 60 Veggie Caps
713 rub.
More details
The package of the drug contains 60 capsules of the drug containing 800 mcg of the active substance - methyltetrahydrofolate. The auxiliary composition is represented by microcrystalline cellulose and vegetarian capsule (modified cellulose). The drug has many advantages:
- Participated in scientific research.
- Recommended for pregnant women as it ensures healthy fetal development.
- Contains the folate form of folic acid – Quatrefolic.
- This is a vegetarian, gluten-free and GMO-free dietary supplement.
This is the best bioactive form of B9 with Quatrefolic. It is recommended to take 1 capsule per day, preferably between meals or according to the regimen recommended by your doctor. Taking metafolin according to the instructions ensures the healthy development of the fetal spine and brain. In adults, folate supplementation helps support brain function and emotional health. The drug is absorbed in the small intestine, which ensures better folate absorption. There is a similar drug from the same manufacturer and with the same name, the only difference is in the dosage, which is 400 mcg of methylfolate, and 90 capsules are placed in a jar.
Methyl Folate, Now Foods (USA)
Now Foods, Methyl Folate, 1,000 mcg, 90 Tablets
968 rub.
More details
The drug belongs to dietary supplements based on natural active methylfolate. Additional composition is represented by cellulose and vegetable stearic acid, silica. The package contains 90 or 120 tablets containing 1000 or 5000 mcg of the active ingredient. The tool has a number of features:
- does not contain animal components, vegetarian product;
- enriched with Co-enzyme B vitamin;
- characterized by increased bioavailability;
- no GMOs;
- passed the necessary studies and has quality guarantees.
You need to take the dietary supplement with food, one tablet once a day. The drug is intended exclusively for adult patients. When taken by the elderly or those who have problems absorbing B12, it is necessary to monitor the level of this vitamin in the body. Reviews of methylfolate prove its effectiveness. Users claim that vitamins are easy to take, they do not cause discomfort, do not leave an aftertaste, are easy to swallow, and test results return to normal after 2-3 weeks of taking them.
Optimized Folate, Life Extension (USA)
Life Extension, Optimized Folate, 100 mcg, 100 Veggie Tablets
869 rub.
More details
This is optimized folic acid or methylfolate in the metabolically active form of methyl acid. The package contains 100 tablets containing 1000 mcg of active ingredient each. Auxiliary components are: MCC, silica, dicalcium phosphate, stearic acid and croscarmellose sodium, vegetable stearate.
Optimized folate is a non-GMO dietary supplement. Take 1 tablet per day according to the instructions or according to the regimen recommended by the doctor. Patients are often advised to take a similar form of methylfolate throughout pregnancy, but they should still avoid self-medication and consult their doctors first.
The supplement has several different dosages. In addition to the described option, you can buy a pack of 30 tablets with a dosage of 5000 mcg of metafolin (methylfolate) each. A pronounced result, as confirmed by laboratory tests, is observed after a couple of weeks of use, but to complete the course you need to finish the package. If necessary, your doctor will prescribe additional methylfolate.
5-MTHF, Thorne Research (USA)
Thorne Research, 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate, 1 mg, 60 Capsules
RUB 1,615
More details
Dietary supplement based on the active form of folate. The package contains 30 or 60 capsules containing 1, 5 or 15 mg of the active ingredient. Excipients: MCC, hypromellose, silicon dioxide and leucine. According to the instructions, you should take 1-3 capsules. per day. Pregnant women should definitely consult a doctor about taking this form of B9.
5-MTHF dietary supplement provides cardiovascular health, supports nervous system functions, helps maintain excellent psycho-emotional health and is beneficial for fetal development. Prescribed to patients who have problems absorbing regular folic acid.
The supplement is indicated for pregnant women and women preparing to conceive. It provides the full content of vitamin B9 in the first trimester of gestation, when the body of the mother and the embryo especially needs it. Folic acid in this form helps normalize homocysteine levels, preventing many of the adverse effects associated with an excess of this amino acid.
QuatreActiv Folate, Allergy Research Group (USA)
Allergy Research Group, QuatreActiv 4th Generation Phtholate 5-MTHF, 90 Capsules
RUB 1,481
More details
Hypoallergenic food supplement based on folate or folic acid in the form of fourth generation Quatrefolic. Excipients are: MCC, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, l-leucine. The package contains 90 capsules with the main active substance 5-MTHF.
- The instructions recommend taking the supplement one capsule 1-2 times a day or according to the regimen recommended by the doctor.
- Each capsule contains 500 mcg of 5-MTHF.
- The capsules do not contain GMOs or components of animal origin.
- The product is completely vegetarian.
- Take only on the advice of a specialist.
- The supplement is especially recommended for the treatment of chronic fatigue and depressive conditions, degenerative changes in the peripheral nervous system, as well as for maintaining cardiovascular structures and brain activity.
Pregnant patients should undergo preliminary examination before taking QuatreActiv Folate supplement, since self-medication may lead to unpredictable consequences. Only a doctor can choose the safest regimen for taking methylfolate, as well as determine the optimal duration of therapy.
Methylfolate: Solgar 400 mcg tablets
Enlarge picture
- One of the best dietary supplements with methylfolate are “Folate” tablets (666 mcg, 100 pcs) from the famous American manufacturer Solgar . The active folate in the form of metafolin contained in each tablet helps support heart and nervous system health, as well as the formation of red blood cells.
Recommendations for use: take 1 tablet 2 times a day, preferably with food.
Folic acid and the prevention of preterm birth
Premature birth, that is, birth occurring before 37 weeks of gestation, is a complication in 12.5% of all births in the United States. It is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in newborns. Premature infants are at risk of developing sudden complications from respiratory, gastrointestinal, immune, and central nervous systems, as well as long-term motor, cognitive, and neurobehavioral sequelae, resulting in the societal cost of preterm birth exceeding $26 billion per year in the United States alone [25]. Preterm birth is a syndrome rather than a diagnosis because the etiology of preterm birth is varied.About 20% of preterm births are iatrogenic and are performed for maternal or fetal indications, including intrauterine growth restriction, preeclampsia, placenta previa, and disappointing fetal findings.
births in the United States. It is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in newborns. Premature infants are at risk of developing sudden complications from respiratory, gastrointestinal, immune, and central nervous systems, as well as long-term motor, cognitive, and neurobehavioral sequelae, resulting in the societal cost of preterm birth exceeding $26 billion per year in the United States alone [25]. Preterm birth is a syndrome rather than a diagnosis because the etiology of preterm birth is varied.About 20% of preterm births are iatrogenic and are performed for maternal or fetal indications, including intrauterine growth restriction, preeclampsia, placenta previa, and disappointing fetal findings.
Although the causes of the remaining 80% of preterm births are not yet fully understood, four main pathophysiological mechanisms have been described: • premature activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis; • intrauterine infection/inflammation; • decidual bleeding (placental abruption); • pathological distension of the uterus [26].
Treatment of preterm birth is primarily aimed at inhibiting uterine contractions, but this does not reduce the incidence of preterm birth or improve the outcome for the newborn [27]. Given this therapeutic nihilism, more attention has been paid to prevention. Folic acid is one of the drugs being studied to prevent preterm birth in women at both low and high risk of preterm birth.
Epidemiological data
There is indirect evidence to suggest that folate may indeed have a significant effect on timing of labor. In observational studies, shorter gestational age was associated with low serum folate levels [6, 28] and the fact that no FA supplementation was given during pregnancy [29]. Early intervention studies focused on multiple micronutrient supplements and showed significant reductions in pregnancy complications, including low birth weight, small size for gestational age, and maternal anemia. [30–33]. These studies were underpowered to demonstrate differences in preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, or placental abruption. Interestingly, these differences become less significant when comparing multimicronutrient supplements with a supplement containing only iron/FA [29]. This allows us to conclude that these elements are the most important.
Subsequent studies indicate that supplemental FC alone may protect against the risk of preterm birth without increasing the risk of miscarriage, structural abnormalities, multiple pregnancies, or stillbirths [29, 34–36]. The largest such study is a secondary analysis of the FASTER prospective observational study conducted in the United States from 1999 to 2002. [36]. This secondary analysis included data from 34,480 women with singleton pregnancies beginning in the first trimester who delivered between 20 and 42 weeks of gestation. Spontaneous preterm birth was defined as delivery between 20 and 36 weeks of gestation in the absence of medical or obstetric complications or indications. Pregnancies that ended in elective termination or stillbirth, and pregnancies with chromosomal or structural abnormalities in the fetus were excluded from the study. At the initial stage of inclusion in the study in the first trimester of pregnancy, all participants were asked questions about their diet, specifically about the dose and duration of taking FC.
In this group, compared with those not taking FA supplementation, preconception and postconception supplementation for ≥ 1 year was associated with a significant reduction in spontaneous preterm birth (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.22, 95% confidence interval [CI] – 0.08–0.61; p = 0.004 for deliveries at 20–28 weeks; RR = 0.45, 95% CI, 0.24–0.83; p = 0.010 for deliveries at 28–32 weeks th week). The authors concluded that folate supplementation before and after conception reduces the risk of spontaneous preterm birth and that this causal association is strong, specific, dose-dependent, consistent with data from other studies, biologically plausible, and remains essentially unchanged after adjustment for potential confounders. factors [36].
Recent evidence suggests that the duration of FC supplementation may be as important as the dose. In the large prospective cohort study mentioned above [36], the risk of spontaneous preterm birth was inversely related to the duration of FA supplementation and was lowest for women who reported taking FA supplementation for more than a year before conception.
Biological probability
If FC supplementation is indeed associated with a reduced risk of preterm birth, then what is the mechanism? This issue is complicated by the fact that very little is known about the molecular mechanisms responsible for the onset of labor in humans, both timely and premature, not to mention the ways to maintain a pregnancy complicated by preterm labor. It is becoming clear that many cases of preterm birth are associated with a pathological inflammatory response, which can be triggered by intrauterine infection or bleeding [22]. Folate is known to be important for normal immune function. People with folate deficiency, for example, have dysfunction of both cellular and humoral immunity [37]. In addition, in people with folate deficiency, polymorphonuclear leukocytes have reduced phagocytic and bactericidal abilities, which increases their susceptibility to infections such as asymptomatic bacteriuria [38]. Supplementation containing FA has been shown to improve immune function in these individuals and reduce circulating biomarkers of inflammation, including alpha-1-acid glycoprotein and C-reactive protein [39].
Several genetic variations in key genes involved in folate metabolism have recently been described to confer an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. One such variant involves the loss of the 19th base pair (bp) in the DHFR gene [40], which is an important enzyme in the folate metabolic cascade because, as discussed above, ingested folate must be completely reduced before further metabolism can occur. The DHFR 19 base pair deletion allele interferes with folate metabolism and transport of reduced folates across the placenta.
Another example of a sequence variation in the SHMT1 (serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1) gene is known as the SHMT1(1420)T variant. It results in decreased transcriptional activity of VHMT1 and is associated with an increased risk of spontaneous preterm birth. This effect was most pronounced among patients with low FA intake [41].
Findings like these raise the possibility that even women with “adequate” folate intake may be at risk for preterm birth if they carry a particular genetic variation. It is currently unknown whether these women would benefit from taking a supplement containing higher doses of FA or taking an L-methylfolate supplement directly.
Methylfolate: analogues
Methylfolate is a unique compound of its kind, so it has no absolute analogues. However, in terms of their ability to influence homocysteine levels in the body, there are dietary supplements with similar effects. First of all, we are talking about B vitamins and, above all, folic acid. With normal metabolism, preparations of this vitamin do an excellent job and can be recommended as a measure to maintain adequate homocysteine levels, like methylfolate .
Enlarge picture
- Solgar are excellent for replenishing folic acid . This company is one of the oldest of its kind. Since 1947, it has been producing high-quality and environmentally friendly products, the effectiveness of which cannot be doubted. This drug is recommended for maintaining heart and vascular health, strengthening the nervous system, successfully bearing a child, reducing homocysteine in the blood and the formation of red blood cells.
Recommendations for use: take 1-2 tablets per day, preferably with food.
Not long ago it was discovered that it is possible to lower homocysteine levels with the help of Omega-3.
Enlarge picture
- For this you can use Omega-3 capsules (1000 mg, 180 capsules) from Now Foods . They are made from natural fish oil that meets the strictest GMP quality control standards. Each capsule contains 120 mg of docosahexaenoic acid and 180 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid.
Directions for use: Take 2 capsules twice daily with food.
Which form do you prefer?
We have already described above what kind of vitamin this is – methylfolate. But it has many forms, so it may be difficult to choose a drug:
- Methylfolate. This form is the most active. The use of L-methylfolate is most preferable for people who have the MTHFR mutation. But there are people who suffer from intolerance to methylated forms. Folin acid is more suitable for these people instead of methylfolates.
- Folinic acid is also a type of folate, but it does not require reduction and the participation of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. Sometimes experts recommend the combined use of methylfolate and folinic acid, especially if there is a B12 deficiency. Sometimes its transformation is also prevented by gene mutations, but it does not increase homocysteine and does not hide B12 deficiency.
When assessing the difference between these forms, it is important to consider the side effects that may occur with their use. They have virtually no differences and manifest themselves in the form of rashes or excessive irritability, as well as sleep disorders. When taking folic acid, strict monitoring is necessary in the presence of bipolar affective disorders; the drug can also provoke muscle pain. And folinic acid provokes the development of side effects much less frequently and has a mild antidepressant and calming effect, which is the main difference between these drugs.
If no adverse reactions occur, then experts recommend combining folates from natural products or other sources at the same time. If there are adverse reactions, you will have to choose an individual regimen for taking B9, adding various amino acids or vitamin components.
Methylfolate: instructions
methylfolate supplements , be sure to follow the recommendations in the supplement instructions. The concentration of the active substance in different drugs can vary widely, and since an overdose of folates can have extremely adverse consequences, this information should be treated very carefully.
Methylfolate: how to take
Enlarge image
In order for medications with methylfolate to be exclusively beneficial, you need to know how to take them correctly. The dosage of such supplements depends on how much active substance is contained in one tablet or capsule. In most cases, metafolin is available in dosages of 200 mcg or 400 mcg.
According to experts, the preventative daily dose of methylfolate for an adult is 200-400 mcg. During pregnancy, the daily norm increases to 600-800 mcg. In order to reduce homocysteine levels, it is recommended to take about 800-1000 mcg of metafolin per day. Methylfolate consumed with food.
Best Metafolin Supplements
There are not many manufacturers that produce metafolin. Most often, large brands produce folic acid, which is inferior in bioavailability. The highest quality and effective supplements with metafolin are produced by the Solgar brand. The company produces supplements in various packaging and dosages that suit any purpose of administration:
- Solgar Folate as Metafolin 400 mcg is an optimal preventative supplement for men and women;
- Solgar Folate Metafolin 666 mcg is a good option for women and men who are planning a pregnancy;
- Solgar Folate as Metafolin 800 mcg - usually prescribed by doctors during pregnancy. For a preventive course of treatment, such an amount of the substance is not required;
- Solgar Folate 1333 mcg as Metafolin is the highest dosage per serving supplement in the Solgar line. Usually prescribed in cases where increased amounts of vitamin B9 are needed during pregnancy. It can also be prescribed in the later stages of pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage.
Methylfolate: reviews
Enlarge image
Reviews of methylfolate are mostly positive. We are mainly talking about the ability of this compound to affect the amount of homocysteine in the blood of pregnant women. People taking methylfolate for neurological reasons note a significant improvement in their condition - attacks of depression and anxiety disappear, and sleep improves. In general, medications containing methylfolate are well tolerated and do not cause any side effects.
Folic acid and anemia prevention
An increase in blood volume resulting from increased plasma and red blood cell volume is a normal physiological change during pregnancy. Although the mother's blood becomes more plasma than red blood cells, the increase in red blood cell volume is also significant and averages about 450 ml [21]. Due to the increase in plasma volume, hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit usually decrease slightly during pregnancy. However, although the average hemoglobin concentration is 12.5 g/dL, about 5% of women have anemia with hemoglobin concentrations below 11.0 g/dL (Table 2) [22].
. Hemoglobin concentrations in 85 healthy women with proven iron stores.
Erythropoiesis is the process by which red blood cells are formed in the hematopoietic tissue of the bone marrow. Among other things, active erythropoiesis requires adequate supplies of three key nutrients: folate, cobalamin (vitamin B12), and iron. Although full detail of the role of these nutrients in erythropoiesis is beyond the scope of this review, it is important to understand that the reaction in normal erythropoiesis that involves both folate and vitamin B12 is the transfer of a methyl group from L-methylfolate to homocysteine by methylcobalamin to regenerate methionine [23]. Therefore, low levels of folate and/or vitamin B12 are likely to cause anemia. For example, in a recent retrospective analysis of anemia in pregnancy by Bentley et al., pregnant women were prescribed a prenatal nutritional therapy supplemented with 1.13 mg L-methylfolate in addition to 0.4 mg FA and 500–1000 μg vitamin B12 (high level folate, high vitamin B12) and compared with pregnant women prescribed standard prenatal vitamins containing only 0.8–1.0 mg FA and 0–12 μg vitamin B12 (low folate, low vitamin B12) [24] . Women receiving high folate and vitamin B12 supplementation had significantly higher hemoglobin levels at delivery (11.8 versus 10.7 g/dL; p = 0.001) than the control group receiving standard prenatal vitamins. It remains to be determined in the future how these results will translate into prospective randomized trials and what effect direct L-methylfolate supplementation will have on other folate-related pathways.
Methylfolate: price
The price of methylfolate is slightly higher than folic acid. This is explained by the fact that the production technology of this drug is much more complex. However, it is fair to note that methylfolate is much more effective than regular folic acid, and therefore its price is well justified. In order not to overpay for nutritional supplements, it is best to use an online store that cooperates directly with manufacturers. The most famous and reliable of them is the site below. Here you can buy not only methylfolate , but also a lot of other less common, but very useful supplements, for example, coenzyme Q10, hyaluronic acid, fat burners, benfotiamine and methylsulfonylmethane at a price several times lower than in Russian online pharmacies.
TOP 3 supplements based on synthetic folic acid
Regular synthetic folic acid, as mentioned above, brings much less benefit to the body, therefore, if you have the opportunity to buy methylfolate, it is better to give preference to this particular type of substance. Yes, the price of methylfolate is slightly higher than supplements with a synthetic component, but it is safer and more effective, eliminating the accumulation of excess homocysteine and unmetabolized folic acid. Among the many additives with regular Folic Acid, three of the best can be identified; they are worth considering in more detail.
Folic Acid, Solgar (USA)
Solgar, Folic Acid, 800 mcg, 250 Tablets
897 rub.
More details
The supplement contains synthetic folic acid in amounts of 400 and 800 mcg in each tablet. There are a total of 250 tablets in the bottle. The main component is Folic Acid, and the auxiliary components are represented by MCC and vegetable stearic acid, silicon dioxide. The drug has proven itself well among patients and has a number of features:
- It has been successfully operating on the market for more than 70 years.
- Does not contain dairy products. Gluten or wheat components.
- It is a bioactive supplement that can be successfully taken by vegetarians.
- A kosher product, that is, it falls under the requirements of proper nutrition.
- Recommended for maintaining the functioning of the cardiovascular system, to ensure full intrauterine fetal development. If a pregnant woman’s body has sufficient levels of metabolized folic acid, then the risk of giving birth to a child with nervous system, brain or spinal defects is minimized.
The dietary supplement is intended for adult patients only. The tablets should be taken with food, one tablet per day. If necessary, the doctor adjusts the dosage and dosage regimen at his own discretion. It is recommended to take Folic Acid only after consulting a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable.
Detailed review
Folic acid, Sundown Naturals (USA)
Sundown Naturals, Folic Acid, 400 mcg, 350 Tablets
266 rub.
More details
Another popular dietary supplement among patients, which has proven itself well, as proven by customer reviews. The drug is sold in a dosage of 400 mcg/350 tablets or 800 mcg/100 tablets. The main component is Folic Acid, auxiliary components are calcium carbonate and vegetable cellulose, vegetable magnesium stearate and silica. Features of the supplement from Sundown Naturals (USA):
- The vitamin supplement is excellent for maintaining the activity of the vascular system, heart, and brain structures.
- Contains no dairy ingredients, gluten, lactose or GMOs, artificial flavors, preservatives or any non-natural colors.
- Suitable for vegetarians.
- When taken by pregnant women, it reduces the risk of having a child with vertebral or brain abnormalities.
You need to take 1-2 tablets per day as recommended by your doctor. It is better to combine the intake with food to ensure more active absorption of the components.
Folic Acid, 21st Century (USA)
21st Century, Folic Acid, 400 mcg, 250 Tablets
230 rub.
More details
21st Century's synthetic folic acid supplement comes in tablets packaged in 250/400 mcg or 180/800 mcg bottles. The auxiliary composition contains substances such as maltodextrin and croscarmellose sodium, cellulose and stearic acid, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 1000 mcg of the active ingredient.
Advantages of the product from 21st Century:
- vitamin supplement to support heart health;
- contains no gluten;
- the drug has been laboratory tested and has quality guarantees;
- The tablets are small and easy to swallow;
- contains essential vitamin B9, necessary for humans;
- has mostly positive reviews;
- Contains no dyes, preservatives, additives, yeast or sugar.
You should take one tablet per day with food. You should take folic acid only as directed by your doctor. It is especially important to first consult with a specialist for persons with any pathologies, as well as for nursing or pregnant women.
Methylfolate: buy
Here is such a large assortment of forms, dosages and manufacturers of methylfolate :
Buy Methylfolate and Metafolin capsules!
1. You can buy methylfolate at a low price and with guaranteed high quality in the famous American online organic store iHerb, so beloved by residents of Russia and the CIS (purchase in rubles, hryvnia, etc., reviews in Russian for each supplement). 2. Detailed step-by-step instructions for placing an order (very simple): How to place an order on iHerb! 3. When ordering, you can use a promotional code for iHerb! You will get a $5 discount for new customers and 5% for “old” customers (without ADDITIONAL DISCOUNTS), as well as profitable Promotions up to 60%! We definitely recommend that you take advantage of it; on your second order, you can also count on discounts or get some of your funds back through the best cashback services, which will try to return interest on purchases to already low prices! Look through the latest discount offers, for example, a Yandex Market promotional code for a discount will help when buying children's goods, working Litres promotional codes will help you buy books cheaper, and also promotional codes for Ozone will make goods and food for children cheaper! 4. Detailed articles about the intricacies of delivery and payment: iHerb payment and iHerb delivery!
Photo source: iHerb.com
methylfolate help you ? Your feedback is very important for new buyers!
Where to buy drugs
You can buy folic acid or folate supplements at your local pharmacy, online stores, or on iHerb. The price range is quite wide, so choosing the best option is not easy.
The lowest prices for folic acid are in the well-known online store iHerb. From other sellers the cost will be 30-50% higher. You can check it yourself.
There is a discount of up to 10% on iHerb using this promotional code:
AGK4375
Activate
The promotional code is activated in the cart after adding the 1st product and is valid only for the 1st order.