How does the disease manifest? Signs of liver problems
- External manifestations
- Internal manifestations
The liver is the largest gland in the human body, so its diseases have a serious impact on overall health. At the same time, it is very sensitive and extremely susceptible to various disorders. Doctors often hear the complaint “I have pain in the liver area.” But can the liver itself hurt and what sensations does a person experience when various diseases appear?
General information
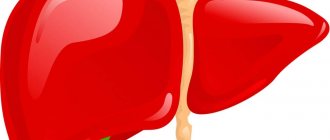
The liver is one of the most important organs of the human body, which is a glandular formation. How much does a human liver weigh? Its mass reaches one and a half kilograms, thanks to which it performs many vital functions, which we will talk about a little later.
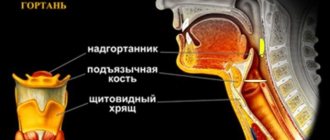
The gland is located in the right hypochondrium, so it is here that the organ is palpated to assess its size, density and outline.
Now we will more accurately describe where the liver is located. The location of the liver in a person depends to some extent on his age. So, in an adult it is located in the right hypochondrium, and slightly extends beyond the border of the midline of the abdomen. In children, the gland occupies most of the abdominal cavity.
The upper border of the liver is at the level of the cartilage of the 5th rib, when assessed along the midclavicular line. Moving along the liver to the left side, we reach the xiphoid process of the sternum, then we head to the cartilage of the 6th rib. The lower border runs along the edge of the costal arch. The gland touches the diaphragm from above, the abdominal wall from the front, and the spinal column, aorta and esophagus from the back. To the left of the gland are organs such as the stomach and duodenum.
The location of the human liver is mesoperitoneal. It is customary to speak of such an arrangement when the organ is not surrounded on all sides by the peritoneum. The physiological structure of the liver does not have compactions, deformations, or additional neoplasms. It is represented by a homogeneous fabric with a small grain size. The edges of the organ are even and the surface is smooth.
The gland has bile ducts and blood vessels. The liver contains hepatocytes (liver cells), which ensure the functioning of the organ and the body as a whole.
Vitamins
All fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K, etc.) are absorbed into the intestinal walls only in the presence of bile acids secreted by the liver. Some vitamins (A, B1, P, E, K, PP, etc.) are deposited by the liver. Many of them are involved in chemical reactions occurring in the liver (B1, B2, B5, B12, C, K, etc.). Some vitamins are activated in the liver, undergoing phosphorication there (B1, B2, B6, choline, etc.). Without phosphorus residues, these vitamins are completely inactive and often the normal vitamin balance in the body depends more on the normal state of the liver than on the sufficient intake of one or another vitamin in the body. As we can see, both fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins can be deposited in the liver; only the time of deposition of fat-soluble vitamins, of course, is disproportionately longer than that of water-soluble vitamins.
Anatomy of the liver
To understand how the liver works, you must first understand its structure.
First of all, let's look at how many lobes there are in the organ, and what is the structure of the human liver. The organ consists of two large elements (lobes) – right and left. The right lobe is much larger than the left lobe - almost six times. What is the name of the ligament that divides the organ into lobes? Its name is sickle-shaped or pendulous. It is represented by a double layer of peritoneum, which is directed from the upper hepatic surface to the diaphragm.
Longitudinal and transverse grooves run along the lower surface of the organ. They additionally distinguish the quadrate and caudate lobes, located between the main (right, left) lobes.
The principle of blood supply to an organ is designed in such a way that it receives blood in two ways. Arterial blood flows through the proper hepatic artery, which divides into two branches and supplies the corresponding lobes. In addition, blood enters the gland through the portal vein, which is formed after the fusion of the vessels of the stomach, intestines, as well as the spleen and pancreas.
The organ has hepatic veins that connect to the inferior vena cava. The pattern of lymph outflow is represented by superficial and deep lymph vessels that pass through the gates of the gland and are also directed along the hepatic veins.
Innervation is provided by the nerve branches of the solar plexus, vagus and phrenic nerves.
Blood clotting
The liver synthesizes substances necessary for blood clotting, components of the prothrombin complex (factors II, VII, IX, X), the synthesis of which requires vitamin K. The liver also produces fibranogen (a protein necessary for blood clotting), factors V, XI, XII , XIII. Strange as it may seem at first glance, the liver synthesizes elements of the anticoagulant system - heparin (a substance that prevents blood clotting), antithrombin (a substance that prevents the formation of blood clots), and antiplasmin. In embryos (fetuses), the liver also serves as a hematopoietic organ where red blood cells are formed. With the birth of a person, these functions are taken over by the bone marrow.
The importance of the liver in the human body
Now, knowing the structure of the gland, we can accurately analyze what the liver does. The importance of the liver in human life is quite difficult to overestimate. Each of us is well aware of the role of the liver in digestion. The organ produces bile, which accumulates in the bladder. How much bile is produced per day? Its daily volume fluctuates around 1500 ml.
Bile, entering the ducts, then follows into the intestines, where it accelerates the digestive process. Thanks to bilirubin, cholesterol, phospholipids, as well as bile acids found in bile, the latter performs the following functions:
- emulsification, absorption of fats;
- neutralization of pepsin, which is the main component of gastric juice;
- activates peristalsis;
- stimulates mucus production;
- activates the synthesis of gastrointestinal hormones in the small intestine, which regulate the secretory function of the pancreas;
- prevents the gluing of protein components;
- participates in the formation of feces;
- has an antimicrobial effect.
Thanks to the gland that produces bile, the main process of digestion, begun in the stomach, successfully continues in the intestines, thereby supplying the body with nutrients.
The special importance of the liver is detoxification. The barrier function of the liver lies in its ability to retain many toxic products of protein metabolism that are delivered to the gland through the bloodstream. The organ that functions as a “filter” is responsible for binding ammonia, as well as processing toxic substances (indole, skatole).
Not only endogenous poisons are neutralized, but also toxins that enter the body from the outside. These include medications and various chemical compounds. The human liver is involved in the inactivation of many hormones (estrogens, androgens, as well as pancreatic hormones).
Not everyone knows what function the liver performs during the prenatal period. The importance of the liver for the fetus during pregnancy is the production of red blood elements - red blood cells, which ensure the delivery of oxygen to all tissues of the embryo.
Few of us know what the liver does besides aid in digestion. Thus, the following main functions of the liver are distinguished, which are responsible for the vital functions of the entire organism:
vitamin exchange. The gland is actively involved in the synthesis of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, K, E), deposits and also removes excess vitamins A, C, PP;
During fasting, when the body does not receive enough vitamins from food, they are consumed from the gland reserve.
- amino acid synthesis. How much protein is synthesized in the gland? The total number includes albumin, globulins and clotting factors, which are responsible for stopping bleeding. In addition, amino acids are accumulated here in case of protein deficiency from food. The role of the liver in the human body is especially important in cases of exhaustion, massive blood loss and severe poisoning, when there is a lack of proteins. The fact is that the gland releases reserve amino acids, thereby replenishing protein losses. The stock is completely renewed every 20 days. We draw attention to the fact that the organ also produces alpha-fetoprotein, which inhibits immune defense. This protein is detected in the blood during pregnancy, cancer of the gonads and liver;
- lipid metabolism. The gland takes an active part in the synthesis of cholesterol, bile acids, as well as the accumulation of fat. The intensity of use of the latter increases with heavy physical activity. Fatty acids are actively formed during fasting, during the digestion of food and between meals. Fat and carbohydrate metabolism are interconnected. With excess glucose entering the body, lipid synthesis increases. When it is deficient, it is formed from proteins or fats;
- carbohydrate metabolism. Now let’s look at what the liver is responsible for after carbohydrates enter the body. It participates in metabolic processes, transforms carbohydrates into glycogen, and also stores the latter in an improvised depot. When a person spends a lot of energy during intense physical activity, glycogen is converted into glucose, which saturates the cells and provides them with energy;
- pigment exchange. In the gland, free bilirubin is transformed into bound bilirubin, after which it is excreted with bile through the intestine. An increased content of unbound bilirubin in the bloodstream causes endogenous intoxication and icteric syndrome;
- enzymatic functions of the liver in the human body. Thanks to the indicators of ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, GGT in a biochemical blood test, it is possible to assess liver function. An increase in the level of liver enzymes in the bloodstream may indicate damage to hepatocytes, for example, in hepatitis, cirrhosis, as well as necrosis of the heart muscle. In this case, the structure of the liver should be assessed to determine the severity and extent of the pathological process;
- immune, allergic functions of the liver in the body. The gland is involved in immunopoiesis, in other words, in the maturation of cells that work in the immune system. The body's reaction to allergic factors depends on it.
The gland can repair itself, as it has an amazing ability to regenerate. Note that the rapid increase in volume is somewhat deceptive, since it occurs due to an increase in the size of the remaining functional cells - hepatocytes. While the physiological structure of the liver is restored in full much later. In this regard, normalization of human liver function also requires a long period.
There is another way to restore the gland - transplantation. It can only be carried out by a high-level specialist.
An organ transplant is a very expensive operation, so not all people who need a transplant can pay for it. It is carried out when a specialist confirms the inability of hepatocytes to provide the physiological functionality of the organ. Liver failure is diagnosed based on clinical signs, laboratory and instrumental examination results. If a user wants to play with blackjack bonuses, they will likely face strict betting limits of 5%. Triumph Casino gives such a bonus to everyone who tops up their account with at least 2,000 UAH; The wager is X35. Once on the official website of the Pin Up casino, users are immediately offered bonuses on their first deposit. The casino policy may be revised, so the nuances of receiving it need to be clarified periodically. For more than three centuries, roulette has been considered the most popular game in casinos around the world.
Neutralizing function
The liver plays a protective role not only by neutralizing and removing toxic compounds, but even by microbes that get into it, which it destroys. Special liver cells (Kupffer cells), like amoebas, capture foreign bacteria and digest them. In the process of evolution, the liver has become an ideal organ for neutralizing toxic substances. If it cannot turn a toxic substance completely non-toxic, it makes it less toxic. We already know that toxic ammonia is converted into non-toxic urea (urea) in the liver. Most often, the liver neutralizes toxic compounds by forming paired compounds with them with glucuranic and sulfuric acid, glycine, taurine, cysteine, etc. This is how highly toxic phenols are neutralized, steroids and other substances are neutralized. A major role in neutralization is played by oxidative and reduction processes, acetylation, methylation (which is why vitamins containing free methyl radicals-CH3 are so useful for the liver), hydrolysis, etc. For the liver to perform its detoxification function, sufficient energy supply is necessary, and for this, in in turn, it requires a sufficient glycogen content and the presence of a sufficient amount of ATP.
Clinical manifestations of pathologies
Everyone needs to know what the liver is for, how important it is, and how long it takes to suspect liver dysfunction. During the diagnosis, the patient is interviewed, the size, density, surface of the organ is analyzed, and liver function is assessed.
The gland can be affected by:
- Cirrhosis. The structure of the liver is represented by a pathological proliferation of fibrous (connective) tissue, which replaces functional hepatocytes. Liver dysfunction may be caused by:
- chronic alcoholism;
- hepatitis of viral etiology;
- infection of the gland by helminths, Trichomonas.
- Oncological process – cancer. The reasons for its occurrence are not fully known, however, among the predisposing factors it is worth highlighting:
- cirrhosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- alcoholism;
- contact with carcinogenic substances;
- hereditary predisposition.
- Hemangiomas, or abnormalities of vascular development.
- Cysts (parasitic - echinococcosis, as well as non-parasitic).
As soon as it is noticed that the liver hurts, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will examine the body, especially carefully palpate the area of the right hypochondrium, and prescribe the necessary examinations. Palpation can be carried out on the back or side. In addition, you should pay attention to the main symptoms indicating possible organ dysfunction:
- weakness, feeling of constant fatigue;
- weight loss;
- vomiting, nausea, bloating, indigestion;
- yellowing of mucous membranes and skin;
- causeless increase in temperature;
- itchy skin;
- spider veins;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- excessive sweating;
- hypersensitivity to odors;
- change in color of stool and urine.
The listed symptoms are the basis for contacting a gastroenterologist, who, through a full examination, will identify abnormalities in the functioning of the gland and prescribe effective therapy. Only a specialist will be able to figure out what is the cause of liver dysfunction, so you should not self-medicate.
Age-related changes
The functional capabilities of the human liver are highest in early childhood and decrease very slowly with age. The liver weight of a newborn child averages 130-135 g. The liver weight reaches its maximum between the ages of 30-40 years, and then gradually decreases, especially between 70-80 years, and in men the liver weight drops more than in women. The regenerative abilities of the liver decrease somewhat in old age. At a young age, after removal of the liver by 70% (wounds, injuries, etc.), the liver restores the lost tissue by 113% (in excess) after a few weeks. Such a high ability to regenerate is not inherent in any other organ and is even used to treat severe chronic liver diseases. So, for example, in some patients with liver cirrhosis, it is partially removed and it grows back, but new, healthy tissue grows. With age, the liver no longer recovers completely. In old people, it grows only 91% (which, in principle, is also a lot). The synthesis of albumins and globulins decreases in old age. Albumin synthesis mainly decreases. However, this does not lead to any disturbances in tissue nutrition or a drop in oncotic blood pressure, because With old age, the intensity of breakdown and consumption of proteins in plasma by other tissues decreases. Thus, even in old age, the liver meets the body’s needs for the synthesis of plasma proteins. The ability of the liver to store glycogen also varies at different age periods. Glycogen capacity reaches its maximum by three months of age, remains for life and only slightly decreases in old age. Fat metabolism in the liver reaches its normal level also at a very early age and decreases only slightly in old age. At different stages of the body’s development, the liver produces different amounts of bile, but always covers the body’s needs. The composition of bile changes somewhat throughout life. So, if a newborn child’s liver bile contains bile acids of about 11 mEq/L, then by the age of four this amount decreases almost 3 times, and by the age of 12 it increases again and reaches approximately 8 mEq/L. The rate of emptying of the gallbladder, according to some data, is the lowest in young people, and in children and the elderly it is much higher. In general, according to all its indicators, the liver is a low-aging organ. It serves a person well throughout his life.
Author: Bulanov Yu.B.
Folk remedies
All folk recipes that restore liver function and support the normal functioning of the organ are based on proven medicinal plants. There are many such recipes and it is best to consult a doctor before using them, because they are prescribed in combination with medications.
- The most famous medicinal plant is milk thistle. It is used to treat various diseases, and this list includes viral and alcoholic hepatitis, poisoning and cirrhosis. You need to drink 900 mg 2 times a day with meals.
- Apple cider vinegar is great for liver detoxification. If taken before meals, it facilitates the metabolism of fat cells. To do this, you need to dilute 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar. l. in 1 glass of water and add 1 tsp. honey, drink 3 times a day.
- You can also drink a decoction of dandelion root, it improves liver function and relieves inflammation. Should be taken 2 times a day, 1 glass.
With the help of folk remedies, you can not only treat liver diseases, but also use them for prevention. If you have pain in the right side, you should not immediately think about the liver; it is best to have it checked by a specialist who will prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment methods
To relieve pain, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed. But it must be prescribed by a specialist, because treatment requires a special approach.
Hepatoprotectors deserve special attention in treatment; their properties are aimed at cell regeneration and restoration. You should take the medicine for a long time. If there is a concomitant pathology, for example, cholecystitis, then the doctor will also prescribe antispasmodics.
Combination drugs that not only relieve pain, but are also aimed at relieving inflammation and restoring liver function have proven to be excellent. The following means can be noted:
- Gepabene;
- Creon;
- Essentiale Forte;
- Karsil;
- Silymarin;
- Ovesol;
- Hepatamine;
- Rezalut Pro.
In addition, these drugs can be used for serious liver damage, for example, chronic hepatitis and even cirrhosis. For cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Liobil;
- Allohol;
- Ursofalk.
No-shpa and Drotaverine will help eliminate spasms. For hepatic colic, Duspatalin, Buscopan, Trimedat are prescribed. Domperidone and Cerucal will help remove bile duct dyspenia.
I would like to say that for pain in the right side, it is best to go on a diet. If the functions of the organ are impaired, then you should not abuse the following products:
- fresh pastries, bakery products;
- canned goods, smoked products, sausages, cheese;
- fatty meats, fish and rich broths;
- citrus fruits, hot seasonings and other spices, garlic;
- alcohol, strong tea and coffee;
- eggs and legumes.