Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
The pharmacy is closed on Sundays and holidays.
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
Papaverine hydrochloride (Papaverini hydrochloridum)
Description. White crystalline powder, odorless, slightly bitter taste.
Solubility. Slowly soluble in 40 parts of water, slightly soluble in 95% alcohol, soluble in chloroform, practically insoluble in ether.
Storage. List B. In a well-closed container, protected from light.
VRD orally 0.2 g; IRR orally 0.6 g.
VRD subcutaneous, intravenous, intravenous 0.1 g; IRR subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous 0.3 g.
Antispasmodic.
Paraffin (Paraffinum)
Description. White semi-translucent dense mass of crystalline structure, odorless and tasteless, slightly greasy to the touch. Solubility. Insoluble in water and alcohol, easily soluble in ether, chloroform, gasoline, essential and fatty oils.
Melting point + 50-57 C. Storage: In a well-closed container
Pepsin (Pepsinum)
Description. White or slightly yellowish powder with a sweet taste and a faint, peculiar odor. Solubility. Soluble in water and 20% alcohol.
Storage. In well-closed jars in a cool place, protected from light.
Enzyme preparation.
110. Perhydrolum or concentrated hydrogen peroxide solution 30% (Perhydrolum seu Solutio Hydrogenii peroxydi concentrata)
Description. Transparent, colorless, odorless liquid or with a weak peculiar odor, slightly acidic reaction. Slowly decomposes when interacting with alkalis and organic substances, releasing oxygen.
Storage. List B. In bottles with ground stoppers in a cool place protected from light.
Pilocarpine hydrochloride (Pilocarpini hydrochloridum)
Description. Colorless crystals or odorless white crystalline powder. Hygroscopic.
Solubility. Very soluble in water, easily soluble in alcohol, practically insoluble in ether and chloroform.
Storage. List A. In a well-closed container, protected from light and moisture.
IRR under the skin 0.01g, IRR under the skin 0.02g.
Cholinomimetic (miotic) agent.
Platyphyllini hydrotartras
Description. White crystalline powder, odorless or with a very weak peculiar odor, bitter taste. Solubility. Easily soluble in water, very slightly soluble in 95% alcohol, slightly soluble in hot alcohol, practically insoluble in chloroform and ether.
Storage. List A. In a well-closed container.
IRR inside and under the skin 0.01 g, IRR inside and under the skin 0.03 g.
Anticholinergic (spasmolytic, mydriatic) agent.
Papaverine
Papaverine
(lat.
papaverine
) - antispasmodic, vasodilator, hypotensive drug. Papaverine is an alkaloid of opium poppy, an isoquinoline derivative. Chemical compound: 1-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-6,7-dimethoxyisoquinoline. The empirical formula is C20H21NO4.
Papaverine is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of the drug. According to the pharmacological index, papaverine belongs to the groups “Vasodilators” and “Myotropic antispasmodics”. According to ATC, papaverine is included in two different groups:
- into the group “A03 Drugs for the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders” and has code A03AD01
- into the group “G04 Drugs for the treatment of urological diseases”, subgroup “G04BE Drugs for the treatment of erectile dysfunction” and has the code G04BE02.
“Papaverine”
, in addition, is the trade name of a number of drugs produced in Russia and other republics of the former USSR. Papaverine, registered in the Russian Federation, is available in the form of tablets, suppositories for rectal use, and solution for injection.
Pharmacological action of papaverine
- relaxation of smooth muscles of blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and genitourinary systems reduces blood pressure
- large doses of papaverine reduce the excitability of the heart muscle and slow down intracardiac conduction
- papaverine has a weak effect on the central nervous system; large doses of papaverine have a sedative effect
Indications for use of papaverine
- spasms of smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, including pylorospasm, spastic colitis
- for cholecystitis, renal colic - as part of complex therapy
- spasms of smooth muscles of the genitourinary system
- bronchospasms
- spasms of cerebral and peripheral vessels (endarteritis)
- as an adjuvant for premedication.
Method of use of papaverine and dose
- Inside. Adults: 3–4 times a day, 40–60 mg. The maximum single dose is 400 mg, daily dose is 600 mg.
- Inside. Children: 2 times a day. Single dose: 5 mg for children from 6 months to 2 years, 5-10 mg - from 3 to 4 years, 10 mg - from 5 to 6 years, 10-15 mg - from 7 to 9 years, 15-20 mg - from 10 to 14 years.
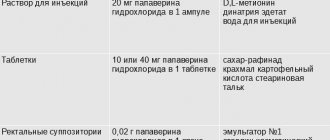
- Injections. Subcutaneously and intramuscularly: 1–2 ml (40–60 mg) of a 2% solution 2–4 times a day. Intravenously: slowly 20 mg with a 0.9% sodium hydrochloride solution previously diluted in 10–20 ml.
- Rectally. For adults. 2-3 times a day, 20m40 mg.
Papaverine in comparison with other antispasmodics
Papaverine was isolated from opium by Merck in 1848. It has been produced in industrial quantities since 1930 by Hinoin, Hungary. In 1961, a hydrogenated derivative of papaverine, drotaverine, was created, which received the trade name no-shpa. No-spa is close in chemical structure and mechanism of action to papaverine. Both are phosphodiesterase (PDE) type IV inhibitors and calmodulin antagonists. At the same time, the selectivity of the action of no-shpa in relation to PDE is noticeably greater and the selectivity of its effect on smooth muscles is 5 times higher than that of papaverine. No-shpa is a more effective drug than papaverine, but in Russia papaverine remains a popular medicine, both due to established tradition and low price.
In the treatment of pain of mild and moderate intensity in the abdomen and pelvis, papaverine, along with other antispasmodics (drotaverine, mebeverine, otilonium bromide and others) is a first-stage drug, which, in the absence of a positive effect with monotherapy with antispasmodics and for prolonged and intensifying pain in the abdomen are replaced with second-stage drugs.
Papaverine, although it has a less pronounced antispasmodic effect than no-spa, usually quite effectively relieves acute spasms of various origins. However, in chronic pathologies such as irritable bowel syndrome or biliary tract disorders, oral administration of such drugs in therapeutic doses is often not enough and there is a need to increase their dose or parenteral administration. Although papaverine is usually well tolerated, in large doses or when used intravenously it can cause dizziness, decreased myocardial excitability, impaired intraventricular conduction, and even the development of atrioventricular block. In such a situation, papaverine should be replaced by mebeverine, which has selectivity against the smooth muscles of the digestive tract, mainly the colon, and does not affect the smooth muscle walls of blood vessels.
There are a number of publications in which prominent Russian gastroenterologists express the opinion that in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, mebeverine is more effective and has fewer side effects than papaverine and no-spa.
Also, leading Russian gastroenterologists warn that papaverine, like other myogenic antispasmodics, due to their relaxing effect on the lower esophageal sphincter, are not recommended for gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Professional medical articles regarding the use of papaverine in the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract
- Belousova E.A. Antispasmodics in gastroenterology: comparative characteristics and indications for use // Pharmateka. – 2002. – No. 9. – p. 40–46.
- Baranskaya E.K. Abdominal pain: clinical approach to the patient and treatment algorithm. The place of antispasmodic therapy in the treatment of abdominal pain // Farmateka. – 2005. – No. 14 (109).
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Anspasmolytics”, containing publications for healthcare professionals that address the use of antispasmodics in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications to the use of papaverine
- hypersensitivity to papaverine
- AV block
- glaucoma
- severe liver failure
- elderly age
- children up to 6 months
Cautions when using papaverine
- Papaverine should be administered intravenously slowly and under mandatory medical supervision.
- During treatment with papaverine, it is forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages
- The visodilating effect of papaverine decreases with smoking
- papaverine is prescribed with caution and in small doses after a traumatic brain injury, with chronic renal failure, with hypothyroidism, with adrenal insufficiency, with benign prostatic hyperplasia, with supraventricular tachycardia, with shock.
Due to the lack of necessary clinical data during pregnancy and breastfeeding,
the use of papaverine is possible only with a careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio. The FDA fetal risk category is N (that is, the drug is not classified by the FDA).
Side effects when using papaverine
Possible side effects:
nausea, constipation, increased transaminase levels in the blood, AV block, ventricular extrasystole, low blood pressure, drowsiness, increased levels of eosinophils in the blood, allergic reactions, sweating, jaundice of the skin and sclera, with intravenous administration - thrombosis (rarely) .
Overdose.
- Symptoms:
double vision, weakness, drowsiness, hypotension. - Treatment:
gastric lavage (milk, activated carbon), maintaining blood pressure. Completely curable with hemodialysis.
Interaction of papaverine with other drugs
- Barbiturates - enhanced antispasmodic effect
- Tricyclic antidepressants, reserpine, quinidine and procainomide - the hypotensive effect of papaverine may be enhanced
- Levopoda - decreased antiparkinsonian effect
- Methylpoda - decreased hypotensive effect
Papaverine and erectile dysfunction
In 1983, the erectogenic effect of papaverine
hydrochloride was discovered when administered intracavernosally into the penis.
The effectiveness of papaverine is up to 40-70%, however, due to the high risk of developing priapism
(prolonged, most often painful erection not associated with sexual arousal), and with long-term use also due to possible progressive sclerosis of the cavernous bodies, modern sexologists do not recommend give injections of papaverine to achieve an erection. At the same time, papaverine, when used as part of complex preparations (alprostadil + papaverine, alprostadil + papaverine + phentolamine) does not produce as many side effects and, in addition, combined preparations increase the effectiveness of action. Before the advent of Viagra (the active substance sildenafil is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase (PDE) type V), intracavernosal therapy was widely used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, despite its disadvantages: pain at the injection site, fear of an injection into the penis, the possibility of developing ecchymosis (subcutaneous hemorrhages).
Pharmacokinetics of papaverine
- absorption
of papaverine is good, depends on the dosage form - bioavailability
on average 54% - binding to
plasma proteins about 90% - penetration
through histohematic barriers is good - half-life
is approximately 0.5 - 2 hours, but sometimes increases to a day - metabolized
- mainly by the kidneys
Papaverine is an over-the-counter medicine.
Trade names of drugs with the active ingredient “papaverine”
- " Papaverine
", tablets 0.04 g, manufacturers: Irbitsky chemical farm, Moscow pharmaceutical factory, Pharmstandard-Tomskkhimpharm OJSC (Russia), Borisovsky ZMP (Belarus) - " Papaverine
", rectal suppositories, JSC "Biokhimik" (Russia) - " Papaverine
", solution for injection, ampoules of 2 ml, papaverine content 20 mg/ml, JSC "Biosintez", JSC "Biokhimik", JSC Novosibkhimpharm (Russia), Borisovsky ZMP (Belarus) - " Papaverine hydrochloride
", rectal suppositories, JSC "Biosintez", JSC Dalkhimfarm (Russia) - " Papaverine hydrochloride
", solution for injection, ampoules of 2 ml, papaverine content 20 mg/ml, manufacturers: Federal State Unitary Enterprise Armavir Biological Factory, JSC Dalkhimfarm, NPO Microgen, JSC Moskhimfarmpreparaty named after N.A. Semashko (Russia) - " Papaverine MS
", tablets 0.04 g, manufactured by Medisorb CJSC (Russia) - " Papaverine Bufus
", solution for injection, ampoules of 2 ml, papaverine content 20 mg/ml, JSC Update PFK (Russia) - " Papaverine hydrochloride tablets for children 0.01 g
" Borisovsky ZMP (Belarus)
Papaverine as part of drugs with a combined active ingredient
- platiphylline + papaverine, trade names of the drug: platiphylline and papaverine-MEZ tablets
,
platiphylline with papaverine - belladonna leaf extract + papaverine, trade name papaverine hydrochloride 0.02 g, belladonna extract 0.015 g tablets
- bendazole + metamizole sodium + phenobarbital + papaverine, trade name andipal
- bendazole + papaverine + theobromine, trade name theodibaverine
- bromisal + calcium gluconate + caffeine + papaverine + phenobarbital, trade name pagluferal
- nicotinic acid + papaverine, trade name nicoverine
- bendazole + papaverine, trade names papazole, papazole-UFB
Back to section