N. A. Tsubanova, National Pharmaceutical University
One of the pressing problems of modern medicine and pharmacy remains the treatment of constipation. According to some data, constipation or functional bowel diseases have been considered the most common among gastroenterological patients in the last decade. This is confirmed by data from epidemiological studies cited by Prof. N.B. Gubergrits, where it is noted that constipation is diagnosed in 12% of the adult population of the Earth, 50% of the population of Great Britain, Russia, 30% of the population of Germany, 20% of the population of France. According to T.V. Borodina, N.D. Bunyatyan, this disease reaches 10% only among school-age children. And this is just the tip of the iceberg, considering that people suffering from constipation often do not consult a doctor, but self-medicate. According to foreign authors, about 75% of older people self-medicate for constipation. Given the above, it is not difficult to understand that the true prevalence of constipation is apparently much higher than what appears from epidemiological studies.
Constipation is defined as an increase in the intervals between bowel movements of more than 48 hours, and straining takes up more than 25% of the time of bowel movements. In chronic constipation, this condition occurs for more than three months. Constipation often involves irregular bowel movements, too hard stool consistency, a feeling of incomplete evacuation, or a small amount of stool (less than 35 g; normal 100–150). Constipation is caused by a disruption in the formation and movement of feces through the intestines. There may be several reasons: disorders of motor activity (motility) of the intestinal muscles, weakening of the urge to defecate, changes in the structure of the intestine or organs closest to it, preventing the normal movement of contents, a discrepancy between the capacity of the colon and the volume of intestinal contents. A problem in the pharmacotherapy of constipation is also the polyetiology of the disease (Table 1). First of all, these are endocrine and metabolic diseases, various neurogenic factors (autonomic dysfunction, which is a disorder in the activity of the autonomic part of the nervous system, regulating the functions of internal organs). Factors that cause constipation with the participation of nervous mechanisms also include reflex effects on the intestines from various organs, primarily the stomach and bile ducts. Diseases of the rectoanal zone occupy a significant place in the etiology of constipation.
The most effective drugs for treating constipation.
October 1, 2021
22004
4.1
3
Content
- Why does constipation occur in adults?
- Constipation symptoms
- How to choose the right laxative
- What types of laxatives are there?
- The most effective laxatives
- Mukofalk
- Forlax
- Guttasil
- Exportal
- Senna leaves
- Guttalax Express
- Duphalac
- Magnesium sulfate
- Regulax Picosulfate
Such a delicate problem as constipation has happened to everyone, and this is the most common disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. Constipation is dangerous to your health, especially if it is chronic. We will talk about the causes of this condition and the best laxatives. Read also The most effective probiotics for the intestines: top 5 How to choose a probiotic and for what problems it is prescribed.
Literature:
- Minushkin O.N. Functional constipation: dynamics of ideas, diagnosis, some therapeutic approaches. Medical advice. 2017; 20:92-95
- Turchina M.S. The use of complex laxatives in the treatment of chronic constipation. Medical advice. 2017; 5:77-79
- Minushkin O.N. Chronic constipation (definition, epidemiology, diagnosis): modern drug therapy. Medical advice. 2015; 13: 100-105
- Plotnikova E.Yu., Krasnov K.A. Constipation needs to be treated. Medical advice. 2018; 14:61-66
- Stepanov Yu.M., Vlasova O.N. et al. Negative effects of laxative abuse in medical practice. Gastroenterology. 2018; 52 (3): 168-173
- Luzina E.V. Safety of using laxatives. Russian medical journal. 2014; 5:41-44
- Parfenov A.I. Three options for the pathogenesis and treatment of chronic constipation. Gastroenterology. 2012; 3:7-19
- Plotnikova E.Yu. Modern ideas about constipation. Attending doctor. 08/2015
- Pharmacology of drugs affecting the function of the digestive organs: textbook by A.N. Leventa, L.B. Kuklina, S.G. Alexandrov, N.V. Verlan, L.O. Gutsol, I.Zh. Seminsky, O.V. Shabaturova; GBOU VPO IGMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia - Irkutsk, 2013. -112 pp. 102-103
- Global practical recommendations of the World Gastroenterological Organization. Probiotics and prebiotics. 2021 — 37 p.
- Instructions for use of MICROLAX® microenemas. // Reg. number P N011146/01 // GRLS of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=f052fb31-5426-4bc1-958f-9fce793aa43f&t= (date accessed 05/05/2010).
- Erdes S.I., Matsukatova B.O. and others. Episodic and chronic constipation in children: a step-by-step approach to therapy within the framework of the IV Rome criteria. Pediatrics. Consilium Medicum. 2019; 1:71-76
- Constipation in young children: causes and features of dietary correction O.N. Komarova, A.I. Khavkin (Questions of modern pediatrics. 2014; 13 (1): 114–118
- Clinical recommendations. Constipation in adults (as a manifestation of systemic diseases). Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia (NOGR), Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists (RNSOT) - 2019
- Lactulose: arguments and facts. Yu.O. Shulpekova. EFFECTIVE PHARMACOTHERAPY. Gastroenterology. 5/2011 - pp. 28-71.
- Clinical guidelines: Constipation / Russian Gastroenterological Association. Association of Coloproctologists of Russia - 2021.
- Minushkin O.N. 1, Elizavetina G.A. Forlax in the treatment of chronic constipation: features of therapy for elderly patients / “Breast Cancer” No. 1 - 2006.
Up to contents
Watch in our video which laxative to choose for constipation: tablets, syrup or microenemas
Why does constipation occur in adults?
There are many reasons for constipation (both medical and social). Temporary constipation can occur due to stress, some illness, a certain lifestyle, poor diet, while traveling, or taking certain medications. There are organic and functional causes of constipation.
1. Organic causes of constipation.
Among these reasons are any diseases of the intestines or stomach that prevent normal bowel movements:
- congenital anomalies of intestinal development;
- postoperative period (treatment of the stomach or intestines);
- inflammatory processes in the stomach or intestines;
- tumors of the intestine and surrounding tissues.
2. Functional causes of constipation.
These reasons are not associated with gastrointestinal diseases. Among them:
- emotional disorders (depression, stress, insomnia, conflict situations, phobias and fears, etc.);
- problems with intestinal peristalsis (muscle contraction).
Intestinal motility is disrupted due to insufficient water, poor nutrition, and lack of fiber in the diet. It is plant fiber that increases the volume of feces in the intestines and makes it work properly. Therefore, to prevent constipation, you need to eat vegetables, fruits and grains. Peristalsis is also disrupted if a person leads a sedentary lifestyle - lack of physical activity reduces muscle tone, and intestinal contraction slows down.
- Taking certain medications can also negatively affect intestinal function (reduce its motility). Among the drugs that cause constipation are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen), antispasmodics, antibiotics, drugs for the treatment of fungal infections, etc.
If a person takes laxatives for a long time and then stops, he may also develop constipation due to decreased intestinal tone and the development of dysbiosis.
Chronic constipation negatively affects overall well-being and quality of life in general. Constipation causes abdominal pain, increased gas, loss of appetite and nausea. If you don't go to the toilet for a long time, your risk increases:
- development of dysbacteriosis;
- intoxication (poisoning of the body);
- enterocolitis;
- hemorrhoids;
- problems with the functioning of internal organs;
- the appearance of intestinal polyps and malignant tumors.
Table 1. Main causes of constipation (Zlatkina A. R., 2002)
| Neurogenic factors | VSD |
| Neurological diseases (peripheral level of neuropathology) | Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, sacroleitis, Hirschsprung's disease |
| Diseases of the rectoanal area | Strictures (benign and malignant), proctitis, anism, hypertonicity of the anal sphincter |
| Iatrogenic diseases | Adhesions after surgery, radiation therapy, taking medications |
| Insufficient physical activity | Physical inactivity |
| Nutritional factors | Low fiber content |
Inhibition of intestinal motor function and the appearance of constipation, especially in elderly and old people, is facilitated by insufficient physical activity (physical inactivity). Special attention should be paid to medications that can cause constipation, especially with long-term use. This is inherent in atropine, various narcotic drugs, some anticonvulsants (diphenin), calcium bicarbonate (baking soda). Psychotropic drugs (tranquilizers, antidepressants), some diuretics, iron supplements, aluminum hydroxide (Almagel) can cause constipation. Depending on the etiology of constipation, there are: nutritional; conditioned reflex neurogenic (“habitual” neglect, situational constipation); functional (essential, primary, idiopathic) constipation (causes: irritable bowel syndrome, hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon, chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction); constipation associated with organic intestinal pathology (causes: neoplasms, diverticula, ischemia, stenosis); constipation associated with neuromuscular disorders of the intestines (multiple sclerosis, neuromatosis, systemic scleroderma, amyloidosis); constipation (dyschezia) associated with pathology of the rectal and anal area (fissures, fistulas, enteroceles, rectoceles, abscesses, strictures, viral or syphilitic condylomas); symptomatic constipation; with endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism); for neurological pathology (Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, organic pathology of the central nervous system); constipation associated with inflammation of the urogenital organs; drug-induced constipation (taking psychotropic drugs, clonidine, calcium antagonists, narcotic analgesics, anticholinergics, antidepressants, tranquilizers and antiparkinsonian drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antacids, tricyclic antidepressants, iron supplements, sympathomimetics, bismuth preparations, lithium preparations, barbiturates, phenothiazines, diuretics, barium sulfate). In clinical practice, a classification of constipation according to its course is accepted: acute and chronic. In acute constipation, there is a sudden absence of stool for more than two days. The most common causes of acute constipation are: intestinal obstruction (tumors, inflammation, diverticulitis), pathology of the anorectal region, acute cerebrovascular accident, traumatic brain injury, bed rest and side effects of medications. Sudden onset of constipation requires the exclusion of a neoplasm in the left half of the colon. Constipation, which is based on inflammatory processes, is characterized by the presence of fever, and constipation associated with a neoplasm is characterized by a gradual increase in clinical symptoms and lengthening of the intervals between bowel movements. In patients with chronic constipation, dysbiosis must be excluded. In patients suffering from constipation due to decreased intestinal motor function, as a rule, it is necessary to exclude organic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer). Chronic constipation can cause various complications: secondary colitis, proctosigmoiditis (inflammation of the sigmoid and rectum). With prolonged stagnation of contents in the cecum, it may be thrown back into the small intestine with the development of enteritis (reflux enteritis). Constipation can be complicated by diseases of the biliary tract, hepatitis, and contribute to the appearance of various diseases of the rectum. The most common occurrence is hemorrhoids. With constipation, rectal cracks and inflammation of the peri-rectal tissue (paraproctitis) can also occur. Long-term constipation sometimes causes the colon to expand and lengthen (acquired megacolon), which makes it even more persistent. The most dangerous complication of long-term constipation is cancer of the rectum and colon. Stagnation of contents in the intestines, caused by the consumption of foods poor in dietary fiber, leads to a high concentration of carcinogenic (cancer-promoting) substances formed in the intestines and their long-term effect on the intestinal wall. The basis of treatment for constipation is to eliminate its cause, and the use of laxatives is auxiliary. Prescribing a laxative without identifying the cause of constipation is unacceptable. The choice of therapeutic tactics is also determined by the cause of constipation. Nutritional constipation requires nutritional correction. If constipation occurs on the road or at a time when it is difficult to eat regularly, you should take a laxative for a short time. Constipation, especially if it occurs when moving or on business trips, can also go away when taking eubiotics (Bifikol, Acylact, Bufidumbacterin, etc.). The only type of laxative allowed for self-medication is laxatives that help increase the volume of intestinal contents, such as seaweed, oatmeal, bananas, agar-agar, lactulose. But even their reception should be episodic. Laxatives that help increase the volume of intestinal contents usually begin to act after a time interval of 12 hours to 3 days. For patients suffering from constipation, the dietary fiber content of foods should be taken into account. With a large amount of coarse fiber in food, people with complaints of bloating produce on average 2 times more gases than with a diet with moderate fiber content, and almost 5 times more than with a liquid, chemically homogeneous diet without dietary fiber. Patients with constipation and complaints of bloating should limit or even exclude foods rich in dietary fiber from their diet. Avoid dishes made from beans, cabbage, sorrel, spinach, etc., which cause increased gas formation. Apple and grape juices are not recommended. If there are no special contraindications (heart disease, edema), then a patient suffering from constipation should drink approximately 1.5–2 liters of fluid per day. Taking enough fluid is very useful, since due to the slow evacuation of feces from the intestines, they dry out, which, in turn, makes it difficult for them to move through the colon. It is important to maintain a proper diet. Food must be taken at least 5 times a day. Long breaks between meals are unacceptable. Bran provides a very significant therapeutic effect for constipation. They are resistant to the action of digestive juices, are not a significant source of energy and at the same time stimulate the evacuation function of the intestines to a greater extent. A rather difficult problem in the treatment of constipation is the use of laxatives. They are very effective at first, but with prolonged use, addiction is possible, accompanied by a complete loss of the independent urge to defecate. Laxatives are contraindicated for constipation of nutritional origin. The use of laxatives should be differentiated depending on the etiology and pathogenesis of constipation. The most complete classification of laxatives today can be considered (Y. S. Zimmerman, 1999) [4, 13], given in Table 2.
Constipation symptoms
In European countries, the Thompson scale is used to diagnose constipation .
If during the course of a year a person regularly experiences at least one of the following symptoms, we can talk about constipation:
- every third or fourth act of defecation requires obvious effort;
- with every third or fourth act of defecation - hard stool;
- the volume of feces per day does not exceed 35 g;
- you have to use aids to go to the toilet;
- dry, fragmented stool;
- stool frequency is less than three times a week.
Causes of constipation
Photos from open sources
How to choose the right laxative
Often, to normalize stool, it is enough to establish proper nutrition. It happens that even a one-time intake of vegetables or fruits can improve intestinal motility. If adding plant fiber to your diet does not help, you need to take laxatives. We recommend that you consult with your doctor about medications for constipation, because many of them have contraindications and side effects. When choosing such drugs, you need to consider some points.
- Type of constipation.
If you are constipated due to poisoning, you need to rid your body of toxins as quickly as possible. Saline laxatives are suitable here. If constipation is chronic, irritant drugs (anthraglycosides) are prescribed. - Age.
Many laxatives are contraindicated for children because they contain toxic substances (they are safe for adults). Well, the form of release of the drug matters. Tablets are not suitable for children; it is better to choose syrup or suppositories. - Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Most laxatives are not suitable for pregnant or breastfeeding women because they can have a negative effect on the fetus. In extreme cases, lactulose-based constipation medications are allowed during pregnancy. But it is better to carefully read the instructions for a particular drug.
Almost all laxatives should not be taken for a long time, because the body gets used to them. The natural work of the intestines decreases over time, because it adapts to the fact that the drugs “do the work” for it.
Read also How to treat dehydration: 5 solutions for rehydration What drugs for dehydration are most often prescribed by doctors?
Table 2. Classification of laxatives (Zimmerman Ya. S., 1999)
| I. Drugs that inhibit fluid absorption and stimulate secretion (irritation of the intestinal wall) | Anthraglycosides (senna, buckthorn, rhubarb) Diphenylmethane derivatives (isafenin, bisacodyl) Castor oil Surfactants (sodium and calcium dioctyl succinate) |
| II. Drugs that increase the volume of intestinal contents | Saline laxatives (Glauber's salt, Carlsbad salt, etc.) Macrogels (macrogol) Herbal laxatives (seaweed, bran, agar-agar, flaxseed, psyllium husk) Sugars and their derivatives (sorbitol, lacthiol) Lactulose (duphalac) |
| III. Agents that lubricate the intestinal mucosa | Vaseline oil, almond oil, etc. |
| IV. Combined products | Guttalax (sodium picosulfate + sorbitol) Regulax Laxative teas |
| V. Other means | Rectal (glycerin suppositories, sodium docusate, etc.) Probiotics, prebiotics Prokinetics: cholinergic agonists (betanecol), prostaglandin agonists (misaprostol), 5-HT4 agonists (tegaserod) |
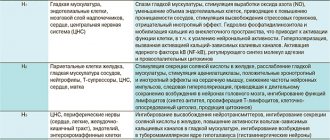
In general terms, the mechanism of action of laxatives is presented in Table 3.
What types of laxatives are there?
There are a lot of laxatives in pharmacies that are used in certain cases. Let's figure out which laxative to choose.
- Laxatives that stretch the intestines and irritate its receptors
(salt laxatives also fall into this category). Such drugs begin to act quickly, but their effect is short-lived. Among the natural remedies for constipation are the same vegetables and fruits rich in fiber, which, when entering the intestines, stretch it. Receptors on the intestinal mucosa sense pressure and contraction occurs. Drugs with this effect are prohibited if the patient has intestinal obstruction, renal failure or an “acute abdomen”. - Stool softeners.
This group of laxatives includes various oils (olive, petroleum jelly). Often, such drugs are prescribed to older people whose intestines contract poorly and their stool becomes hard due to a sedentary lifestyle. Oils soften stool and help it pass out easily, enveloping the intestinal mucosa. Oily laxatives are used in preparation for colonoscopy. - Anthraglycosides.
These include natural laxatives (rhubarb root, marshmallow syrup, senna leaves, etc. These products contain special substances that irritate receptors on the intestinal mucosa, which promotes its contraction. Anthraglycoside laxatives are suitable for cleansing the intestines before diagnostic procedures. - Antispasmodics.
For constipation caused by spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed, which relax the intestinal muscles and help stool pass more easily. The spasm is usually caused by stress or poor diet. With such a spasm, a person feels pain, and feces do not move well through the intestines. No-Spa helps well with spastic constipation.
Treatment of constipation requires mandatory adherence to a diet. It is very important to change your diet to include foods that stimulate intestinal contractions. If you fight constipation only with the help of laxatives, the body will get used to them and “forget how” to work on its own. Therefore, nutrition should be a parallel treatment!
Read also How to treat gastritis: 8 best drugs The best drugs for gastritis: reducing acidity, eliminating excess acid and fighting Helicobacter pylori.
Table 3. Classification of laxatives by mechanism of action
| Group name | Mechanism of action | Efficiency | Drugs |
| Group 1 - chemical laxatives (surfactants) | They cause a laxative effect by chemical irritation of the receptor apparatus of the colon and, thus, stimulate its peristalsis. | The drugs act at the level of the colon and, as a rule, cause a single bowel movement 6–10 hours after administration | Anthraquinone derivatives (senna, buckthorn, rhubarb preparations), diphenylmethane (bisacodyl*), castor oil. |
| Group 2 - osmotic laxatives | When taken orally, these drugs are not absorbed. They retain a large amount of water in the intestinal lumen, increasing the volume of its contents, which leads to mechanical stimulation of intestinal function, increased motor activity and accelerated evacuation. | Drugs in this group act in both the small and large intestines and cause watery diarrhea 3–6 hours after administration. | Sodium and magnesium sulfate, citrate, magnesium hydroxide, Carlsbad salt, non-adsorbable polysaccharide lactulose** (Duphalac). |
| Group 3 - bulk laxatives or bulking agents | Helps increase intestinal volume | The onset of the laxative effect is 8–10 hours. | Bran, agar-agar, methylcellulose, seaweed, etc. |
| 4th group - laxative oils (detergents) | Helps soften hard feces and make them easier to slide | They act at the level of the small intestine, so the laxative effect after taking them occurs within 4–5 hours. | Vaseline, almond, fennel oil, liquid paraffin. |
* Bisacodyl has a laxative effect several hours after ingestion and within an hour when used as rectal suppositories. Dragees contain 0.005 g of active substance, suppositories - 0.01 g. Prescribe 1-3 pills or a suppository per day. In addition to the secretory effect, bisacodyl also affects colon motility. When used in suppositories, it significantly increases the propulsive contractile activity of the colon. ** Lactulose is not broken down in the small intestine and enters the large intestine unchanged. In contrast, in the colon, lactulose is broken down by intestinal flora. The breakdown products of lactulose have a stimulating effect on colon peristalsis, stool softens, and in addition, its volume increases. Currently, more than 200 dosage forms of laxatives are registered on the Ukrainian pharmaceutical market. The top five includes various drugs based on bisacodyl - 44 items; glycerol - 25; Vaseline - 23; drugs based on sennosides - 19; castor oil - 18; they are followed by drugs based on buckthorn, lactulose, etc. It is impossible to talk about a significant variety of laxative drugs on the pharmaceutical market. Basically, as you can see, the same medicinal substances from different manufacturing companies are presented. Let's look at these drugs in more detail. Motor regulators include antispasmodics and prokinetics. Traditionally prescribed myotropic antispasmodics such as papaverine, drotaverine, mebeverine, pinaverium bromide do not eliminate constipation [6]. In recent years, 5-HT4 serotonin receptor agonists have been introduced into practice. Serotonin, released by enterochromophin cells of the intestine, stimulates vagal and enteric afferent nerve fibers, increases the release of acetylcholine, enhances smooth muscle contraction and, thus, normalizes passage. Drugs in this group include tegaserod and cisapride, the latter was withdrawn from the market due to serious side effects (heart rhythm disturbances, extrapyramidal disorders). Prokinetics should not be taken without a doctor's prescription. The effect of taking them begins from the second week of treatment and, what is especially important, can persist for several months after completion of the course of treatment. For spastic dyskinesia, myotropic antispasmodics or M-anticholinergic blockers are included in the treatment complex. New drugs have shown high effectiveness in this condition, as well as in irritable bowel syndrome: pinaverium bromide (Dicetel) and otilonium bromide (Smazmomen). The use of drugs with a high content of bile acids (allochol, lyobil, henofalk) is justified in cases where hypofunction of the gallbladder is diagnosed. Recently, the most physiological corrector of bile formation processes seems to be odeston (1-2 tablets 3 times a day). Constipation caused by acute inflammatory bowel diseases, anorectal fissures and hemorrhoids can be eliminated by treating these diseases, as they cause sphincter spasm. In these cases, the prescription of laxatives is ineffective. For constipation during pregnancy, the drugs of choice are representatives of the group of osmotic laxatives: the synthetic disaccharide lactulose and the stool regulator macrogol. Laxatives that stimulate intestinal motility are contraindicated, as they can cause miscarriage and premature birth. Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide that, after ingestion, is not destroyed by disaccharidase in the small intestine, is not absorbed in the small intestine, and reaches the colon, where, during bacterial decomposition, it breaks down into short-chain fatty acids (lactic, acetic, propionic and butyric). This lowers the pH of the colon contents and stimulates peristalsis. Due to an increase in the volume of feces (fluid influx), a reflex contraction of the intestine occurs - the act of defecation occurs physiologically. Lactulose helps reduce the growth of ammonium-producing bacteria and thereby reduces the flow of ammonia into the blood. Acidification of the colon leads to the death of pathogenic microflora and the proliferation of beneficial ones. Lactulose is often indispensable in the treatment of constipation refractory to other laxatives. Lactulose is effective in the treatment of chronic constipation, hepatitis, liver failure, hepatic coma, hepatic encephalopathy, liver cirrhosis, hyperazotemia, salmonellosis, dysbacteriosis. The drug has been proven to be highly effective in elderly people, after gynecological operations, and for constipation due to adhesions and radiation damage to the intestines. Lactulose is one of the most effective prebiotics, as it selectively stimulates the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Therefore, lactulose is successfully used for intestinal dysbiosis, especially in combination with probiotics containing live strains of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Lactulose preparations can be prescribed to infants, as well as pregnant and lactating women. Lactulose does not reduce the absorption of vitamins and is not addictive. Macrogol acts throughout the intestine. It causes an increase in the volume of intestinal contents and its softening due to the formation of additional hydrogen bonds with water molecules, its retention and accumulation in the intestinal lumen, increasing intracellular osmatic pressure. Due to its high molecular weight, macrogol is not absorbed, is not metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract and does not affect the normal intestinal microflora, does not remove vitamins and salts from the body and does not irritate the intestinal mucosa. In foreign literature, this drug is classified as a new group of laxatives - stool regulators. Macrogol is not intended for a single dose to achieve defecation, but for the systematic and gradual restoration of normal bowel function and regular bowel movements. Macrogol causes painless bowel movements at the patient’s usual time. Macrogol is recommended for constipation, especially in older people, patients with diabetes, hypertension, renal and liver failure, and cardiovascular diseases. Stool softeners: petroleum jelly (liquid paraffin), almond and castor oil, sodium docusate. Oil-based laxatives not only soften feces, but also speed up the passage of small intestinal contents and reduce fluid absorption. Castor oil stimulates peristalsis most strongly. The effect of taking it occurs within 2–3 hours. Currently, the use of this group of laxatives is limited, as they cause nausea, can be involuntarily released from the anus (vaseline oil) and significantly increase the risk of developing malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract; may be partially absorbed; reduce fluid absorption and accelerate its passage. Stimulators of intestinal motility. Saline laxatives (inorganic salts: phosphates, magnesia, Glauber's salt). Saline laxatives act throughout the intestines, which allows them to be used in the treatment of food poisoning to remove toxins. The general properties of saline laxatives are insignificant absorption from the intestine and the need for their use in the form of a hypertonic solution. Stimulants and saline laxatives should be taken in the morning. Their disadvantages: cause nausea; are absorbed into the systemic circulation, which can lead to systemic side effects; the laxative effect is uncontrollable and unpredictable, and therefore there is a high risk of dehydration; contraindicated in children and chronic renal failure. Drugs that increase the volume of intestinal contents: herbal laxatives (bran, seaweed), indigestible fibers (methylcellulose, agar). Mechanism of action: due to the hydrophilic or osmotic properties of drugs in this group, fluid is retained in the intestinal lumen, an increase in volume and softening of the chyme, which leads to an improvement in its passage in the intestine against the background of enhanced peristalsis. Containing anthranoids: preparations of buckthorn, senna, rhubarb, pursenide, tisasen, regulax. Mechanism of action: irritate the colon mucosa or directly stimulate the submucosal (mesenteric) nerve plexuses and smooth muscles. To realize their action, sufficient activity of bacterial sulfatase is necessary, ensuring the transition of anthranoids into anthrones. Strengthen intestinal motility and increase the volume of fluid in the intestines. Anthraquinones are the most common laxatives, as they are found in buckthorn, rhubarb, senna and are part of many combined herbal remedies. Drugs in this group act at the level of the colon and stimulate smooth muscles, accelerate the transport of water into the intestinal lumen and inhibit the thickening of feces (antiabsorption and hydrogonal effects, respectively). With long-term (many months) use, anthraquinones can cause the development of intestinal pseudomelanosis. It is currently believed that laxatives in this group are used unreasonably widely and for an unreasonably long time. The use of laxatives containing herbal components is associated with certain difficulties, since the content of their main active principle - anthraglycosides - is subject to fluctuations, which leads to fluctuations in their activity. Senna preparations may turn urine red or brown. To herbal laxatives, addiction develops most quickly. Disadvantages of intestinal motility stimulants containing anthranoids: antiabsorption and hydrogonal action; mutagenic effect; ability to cause intestinal melanosis; development of post-laxative intestine; addiction; the occurrence of cracks and lacunae in the intestinal mucosa; perianal thrombosis; with long-term use, they increase the risk of developing colon tumors; absorbed into the bloodstream and excreted through the kidneys. Preparations that do not contain anthranoids: diphenylmethane derivatives (bisacodyl, laxodil, laxabene, stadalax), sodium picosulfate. The main indication for the use of bisacodyl is the presence of atonic constipation. Its advantage is the presence of two dosage forms (dragées and suppositories). It can be used in the postoperative period and after childbirth. The advantages of the drug include the rapid (within 1 hour) onset of a laxative effect. The advantage of sodium picosulfate is the ability to select a more precise individual dosage, since it is available in drops. The laxative effect of sodium picosulfate in children is less reliable, since in them the activity of sulfatase-producing bacteria necessary for the action of the drug is significantly lower than in adults. Bisacodyl and sodium picosulfate are most effective for hypotonic constipation and constipation associated with inflammatory pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as in people on bed rest. Disadvantages of intestinal motility stimulants that do not contain anthranoids: cause colic; reduce the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins; Contraindicated for children under 6 years of age, pregnant women, the elderly and patients on bed rest. Summarizing the data on the side effects of laxatives, it should be mentioned that their use is accompanied by increased loss of protein and potassium through the intestines, decreased tone of the intestinal muscles, addiction of the receptor apparatus, requiring increasingly large doses of laxatives, often constipation is replaced by diarrhea due to the resulting drug colitis If you have chronic constipation, you should avoid long-term daily use of laxatives. Different drugs have different ranges of side effects. Very often, the patient is faced with a situation where, against the background of an initial beneficial effect, when the dose is increased, addiction occurs, which subsequently leads to the abuse of laxatives with all the negative consequences. In many cases, it is necessary to carry out painstaking work aimed at weaning patients off the use of laxatives, especially when complaints associated with stool retention are accompanied by complaints characteristic of irritable bowel syndrome (pulling, sometimes cramping abdominal pain, flatulence, etc.). Bisacodyl, senna, buckthorn have a laxative effect, irritating the intestinal mucosa. It is not recommended to take them for a long period of time to treat constipation, as they gradually impair intestinal functions. This leads to increased constipation and the development of colonic atony, in which the intestines lose the ability to move the bolus of food without chemical stimulation. The most serious problem is the occurrence of dependence when taking laxatives, which develops in 13-15% - aloe, 10% - senna preparations, 8-10% - bisacodyl and saline laxatives. Contraindications for prescribing laxatives: intestinal obstruction, acute surgical pathology, severe dehydration, acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the colon, Crohn's disease. Also, the use of laxatives should be avoided in persons taking broad-spectrum oral antibiotics. Signs of an overdose of laxatives are: diarrhea, symptoms of hypovolemia, symptoms of hypokalemia (decreased reflexes, weakness, rhythm disturbances). Laxatives refer to medications that really sick people or supposedly sick people take in large quantities. They are widely purchased and taken even without a doctor’s prescription, without taking into account contraindications, which can aggravate the course of the disease and cause side effects. Considering the above, it should be noted that laxatives should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the etiopathogenetic factors of each patient. Literature Baranskaya E. K. Constipation // Concilium Provisorum.— 2001.— Volume 1, No. 4. Borodina T. V., Bunyatyan N. D. Pharmacological analysis of modern laxatives // Pharmacist.— 1997.— No. 18.— pp. 54–55. Grigorieva P. A., Yakovenko E. P. Constipation: from symptom to diagnosis and adequate treatment // Therapeutic. archive.— 1996.— T. 8.— No. 2.— P. 27–30. Gubergrits N. B. The problem of constipation in therapeutic practice // Health of Ukraine. - 2004. - No. 3. - P. 28. Ducrot F. Constipation: diagnosis and tactics of patient management // Clinical perspectives of gastroenterology, hepatology. - 2002. — No. 9.— P. 35–37. Zlatkina A. R. Problems of choosing laxatives in the treatment of chronic constipation // Farmateka. - 2002. - No. 9. - P. 53–56. Maev I.V. Chronic constipation // Attending physician. - 2001. - No. 7. - P. 53–59. Mumladze R.B., Seltsovsky A.P., Bilyk A.V. et al. Current issues in the prevention and treatment of disorders of intestinal motor-evacuation function in the early postoperative period // Mosk. honey. magazine.— 1998.— No. 1.— P. 18–21. Nikitin I.G., Storozhakov G.I., Fedorov I.G. et al. Duphalac (lactulose) in the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis // Clinical perspectives of gastroenterology, hepatology. - 2002. - No. 1. - P. 24 –29. Sekacheva M.I. Carbohydrate malabsorption syndrome in clinical practice // Clinical perspectives of gastroenterology, hepatology. - 2002. - No. 1. - P. 29–35. Tolochko V. M. Development of the market of herbal medicines for the treatment of diseases of the scolio-intestinal tract // Bulletin of Pharmacy. - 2001. - No. 1. - P. 39–42. Fadeenko G. D. Functional diseases of organs and etching // Suchasna gastroenterology. - 2001. - No. 2. - P. 7–10. Zimmerman Ya. S. Chronic constipation. Diarrhea / Perm: PGMA. - 1999. - 120 p. Brethange JE, Vidon N. Increased all lass in the human jejunum indicated by Laxative/ Gut.— 1981.— No. 22.— P. 246–249. Fusgen I., Schumann C. Clinical aspects and treatment of constipation / Hanover. Curt R. Vincentz Verlag, 2001. 56 p. Hallmann F. Toxicity of commonly used Laxative/ Med Sci monit.— 2000.— No. 6.— P. 618–628.
Mukofalk
A German herbal laxative (psyllium husk) is sold in powder form from which a suspension is prepared. This is convenient for those who have problems swallowing. Plantain seeds absorb a lot of water, which has a positive effect on constipation. In addition to plantain seeds, “Mukofalk” contains a lot of plant mucus, which ensures easy passage of feces. This laxative is prescribed to children from 12 years of age, and is also used in the complex treatment of high cholesterol. Among the advantages of the drug are a pleasant orange taste, excellent tolerability, long-lasting effect and the possibility of use during pregnancy. There are some side effects that you should definitely read in the instructions.
Mukofalk
Dr. Falk Pharma, Germany
- constipation (including during pregnancy);
- anal fissures; - haemorrhoids; - postoperative period during interventions in the anorectal area (in order to create a softer stool consistency); - functional diarrhea; - irritable bowel syndrome. from 421
1075
- Like
- Write a review
Forlax
A synthetic laxative whose active ingredient is macrogol. Forlax is prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of constipation in adults and children over 8 years of age. Doctors consider this laxative to be as safe as possible, but it is better to familiarize yourself with the list of contraindications. Among them: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, gastrointestinal perforation, intestinal obstruction (or suspicion of it), abdominal pain for unknown reasons, hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary substances. The laxative effect after taking Forlax occurs within 24-48 hours. The drug is not suitable for emergency relief from constipation. Forlax is considered one of the best laxatives. The active ingredient of the drug retains water in the intestines, which causes its walls to stretch and the urge to evacuate. This is a very mild drug that does not stimulate frequent urge to go to the toilet, so you do not need to be at home during treatment. “Forlax” for constipation is approved for pregnant women, there is a dosage for children from 6 months, addiction does not develop when taking it, the body does not lose electrolytes, and there are no side effects.
Forlax
IPSEN (Bofur Ipsen), Ukraine
Forlax powder helps restore normal intestinal motility in young children.
The duration of the intestinal “training” effect ranges from 1 to 6 months and depends on the duration of taking the drug. from 137
731
- Like
- Write a review
Constipation suppositories for children
According to statistics, every second child develops constipation. The reasons are related to the imperfection of the digestive system, to irregularities in the mother’s diet if she is breastfeeding, to improper introduction of complementary foods, and more.
When choosing a drug for constipation, you need to focus on safety. Although most often suppositories do not have a systemic effect on the body, they should be approved for use by children. Suppositories that are used to treat adults are not suitable for children.
If your baby often suffers from constipation, you need to contact a specialist and undergo treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of stool retention. Suppositories help eliminate constipation, but nothing more.
Microlax
Price: 200 rubles
Microlax suppositories act gently, the effect develops within 5-15 minutes after administration of the drug into the rectum. It has a high safety profile, so it can be used to treat children from birth. I have already written about them above.
Glycelax
Price: 120 rubles
The active ingredient is glycerin. The drug has an irritating effect on the intestinal mucosa, increasing its peristalsis. At the same time, the stool softens, making it easier for them to move toward the exit. The drug can be used for constipation, regardless of the reason that caused it. Use in children is permissible from 3 months [7].
Pros:
- Can be used from an early age.
- The list of side effects is minimal.
- The price is affordable.
Minuses:
- Increases blood glucose levels.
- Allergic reactions are possible.
- Do not use for longer than 7 days due to the progression of disturbances in the physiological process of defecation.
Sea buckthorn candles
Price: 160 rubles
The active component of the drug is sea buckthorn fruit oil. The main indication for the use of suppositories is the treatment of hemorrhoids, but they are often used as a means to combat constipation. They have a softening effect, promoting the act of defecation. Suppositories can be used from birth [8].
Pros:
- A safe drug based on herbal ingredients.
- Can be used from birth.
- The drug has an antioxidant and healing effect.
- Minimum list of side effects and contraindications.
Minuses:
- Allergic reactions are possible.
- Diarrhea may develop.
- The indications for use do not include constipation.
Guttasil
Guttasil tablets have a mild laxative effect, do not cause intestinal spasms, and are prescribed to adults and children over 10 years of age. The active substance of the drug stimulates the nerve endings of the intestine, as a result of which its peristalsis improves. Doctors often prescribe Guttasil for irritable bowel syndrome. Among the advantages of the drug: it helps to get rid of constipation due to errors in diet, softens stool well, and is suitable for constipation caused by taking medications and problems with the gallbladder. But if you exceed the dosage of Guttasil, severe abdominal pain is possible.
Guttasil
PAK "Farmak", Ukraine
Constipation caused by hypotension and sluggish peristalsis of the colon.
Regulation of stool for hemorrhoids, proctitis, anal fissures. Preparation for surgical operations, instrumental and x-ray examinations. from 131
708
- Like
- Write a review
Exportal
Lactitol is a hydrocarbon alcohol that is obtained from lactose (milk sugar). This alcohol destroys putrefactive bacteria in the intestines and stimulates the growth of acidophilic (beneficial) bacteria. It is this alcohol that is contained in the drug “Exportal”, which is prescribed not only for constipation, but also for preparation for intestinal examinations, operations, intestinal dysbiosis, hepatic encephalopathy, increased levels of ammonia in the blood, etc. Among the contraindications: galactosemia, obstruction intestines, organic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain of unknown origin, intolerance to the active substance of the drug. After taking Exportal, the laxative effect usually occurs within a day. If the drug is used for the first time, the effect may occur later - after two to three days. Doctors warn that sometimes flatulence and abdominal discomfort are possible during treatment with this laxative. But this quickly passes as soon as the body gets used to the drug.
Exportal
Ellara LLC, Russia
- constipation;
- the need to regulate stool for medical purposes (cleansing the intestines in preparation for endoscopic and x-ray examinations, surgical interventions on the rectum, anal sphincter and the area adjacent to it); — intestinal dysbiosis; - hepatic encephalopathy, hepatic coma and precoma, hyperammonemia. from 210
5.0 5 reviews
1554
- Like
- Write a review
Instructions for use
Rectal suppositories must be inserted correctly. If you take a suppository and immediately insert it into the rectum, it will simply fall into its lower ampullary section, which is why the desired effect will not be achieved. This is why it is so important to administer rectal suppositories correctly.
Instructions:
- Release the suppository from the packaging.
- Lie on your left side with your knees bent. They should be brought to the stomach.
- Relax and with your right hand carefully insert the candle into the anus, but not entirely. It needs to be held in this position for about 30 seconds so that it melts a little under the influence of body temperature.
- Push the suppository completely into the rectum.
When performing the procedure, it is recommended to use gloves or a fingertip. If the candle was inserted with bare hands, they should be washed with soap.
Senna leaves
Perhaps this is the most natural laxative on this list. Senna leaves are the most harmless laxative that irritates the intestinal mucosa. Senna leaves, in addition to stimulating contractions of the intestinal muscles, also improve its normal functioning. Laxatives serve as an excellent prevention of constipation in the future. Senna leaves are prescribed for adults and children over 12 years of age as a remedy for constipation. By the way, this particular medicine is often used for weight loss, but it is harmful to the body. Among the advantages of senna are the absence of an addictive effect, a mild effect on the intestines, an affordable price, a neutral taste, and the ability to combine the drug with other drugs. But overdose must be avoided.
Senna leaves
Lek S+, Russia; OJSC Krasnogorskleksredstva, Russia
Senna leaves are a herbal laxative.
Sena leaves contain flavonoids, anthraglycosides (senosidine A and B, rhein, aloe-emodin), organic acids, and resinous substances. This complex of biologically active substances has a mild laxative effect. The laxative effect of a decoction of Sena leaves appears 6-10 hours after administration and is due to anthraglycosides, which enhance the motor function of the large intestine. from 12
5.0 1 review
699
- Like
- Write a review
Candles during pregnancy
Suppositories for constipation for pregnant women are selected individually in each trimester, together with a specialist.
The main condition is a gentle effect on the intestines, since while the fetus is in the uterus, stress on the abdominal wall is excluded. The use of oral laxatives that stimulate intestinal filling with fluid is not recommended. Preference should be given to suppositories.
Suppositories that can be used to treat constipation during pregnancy: [9]
- Microlax.
- Sea buckthorn candles.
- RectActive.
- Dulcolax.
- Guttalax express.
- Glycerin suppositories.
- Bisacodyl.
Guttalax Express
This laxative produced in France has the fastest effect. The active substance of rectal suppositories is bisacodyl. Guttalax Express begins to act within 20 minutes after administration, so the drug is considered ideal for the emergency treatment of constipation in bedridden patients and those after surgery. This laxative can also be used in children over 10 years of age. Among the advantages: does not affect digestion, can be used during breastfeeding, excellent prevention of hemorrhoids, very fast action. Disadvantages: if used for a long time, addiction may develop; Guttalax Express suppositories must be stored in the refrigerator.
Guttalax Express
Institute de Angeli, Italy
Guttalax Express is a local laxative from the group of diphenylmethane derivatives with a slight antiresorptive effect.
As a laxative in the following cases: - constipation caused by atony and hypotension of the colon (including in old age, in bedridden patients, after operations, after childbirth and during lactation); - constipation caused by taking medications; - to regulate stool in case of hemorrhoids, proctitis, anal fissures (to soften the consistency of stool); - gallbladder diseases, irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of constipation; - constipation caused by intestinal dysbiosis and diet disorders. from 185
5.0 1 review
675
- Like
- Write a review
How long does it take for constipation suppositories to work?
The effect of using suppositories for constipation develops at different times. This depends on the effect the active component has on the body, as well as on the composition of the suppository:
- After 5-10 minutes, Glycerin suppositories, RectActiv, Microlax begin to act. They should be used in a place where immediate defecation is possible.
- After 30 minutes, the effect of using Guttalax Express and Dulcolax suppositories develops.
- After 15-60 minutes, Bisacodyl suppositories begin to work.
Duphalac
This combined laxative is based on lactulose. Duphalac not only relieves constipation, but also removes toxins from the body and reduces the number of pathogenic organisms in the intestines. Duphalac can be taken when there is an “overdose” of protein foods in the diet (to avoid the processes of putrefaction in the intestines). Among the advantages of this drug are the possibility of taking it from birth, it is not prohibited for inflammatory processes in the intestines, there are a minimum of contraindications, it is indicated for dysbacteriosis, diabetes, pregnancy, and is suitable for people with severe liver diseases.
Duphalac
Solvay Pharma, Germany
Constipation: regulation of the physiological rhythm of colon emptying;
softening of stool for medical purposes (for hemorrhoids, conditions after surgery on the colon and in the anal area); hepatic encephalopathy in adults: treatment and prevention of hepatic coma or precoma. from 221
1.0 1 review
2637
- Like
- Write a review
The connection between intestinal microflora and constipation
The consequences of chronic constipation may be disturbances in the balance of intestinal microflora, but there is also an inverse relationship: dysbiosis leads to the development of prolonged constipation. In both cases, the intestinal microbiome should be restored and, at the same time, stool retention should be corrected.
For this purpose, both prebiotics and combination preparations containing them can be used. This is especially true for cases when dysbiosis develops against the background of antibacterial therapy.
Magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate is a strong saline laxative that promotes the accumulation of water in the intestines, causing muscles to reflexively contract. Magnesium sulfate also has a choleretic effect, which stimulates digestion and prevents constipation due to dietary errors. The advantages of this laxative: the effect after taking lasts all day, blood pressure decreases slightly, swelling decreases, and sleep improves. Among the obvious disadvantages is an unpleasant taste.
Magnesium sulfate
YuzhPharm, Russia
Constipation, bowel cleansing before diagnostic procedures.
Poisoning with salts of heavy metals (mercury, arsenic, tetraethyl lead, barium). from 12
1009
- Like
- Write a review
Regulax Picosulfate
A popular German laxative in drops, which also helps with complicated constipation: hemorrhoids, rectal fissures, fistulas - all cases where constipation only worsens the patient’s condition. Regulax Picosulfate is prescribed to older people and in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (but only once). Among the advantages of the drug: mild action, low price, acceptable taste, many positive reviews from patients.
Regulax Picosulfate
Meuselbach-Pharma, Germany
- atonic constipation;
- regulation of stool (hemorrhoids, proctitis, anal fissures); — preparation for surgical operations, instrumental and x-ray examinations. from 190
414
- Like
- Write a review
The most inexpensive candles
If you have one-time problems with bowel movements, there is no need to spend enormous sums on suppositories for constipation. In such a situation, you can get by with inexpensive drugs that promote quick and painless bowel movements.
Bisacodyl
Price: 45 rubles
The active ingredient is bisacodyl. The drug affects the intestinal mucosa, irritating its receptors. Strengthening peristalsis and increasing the volume of mucus produced helps to gently cleanse the organ. Suppositories are used for hypotonic and atonic constipation, including in older people. The drug can be used to facilitate defecation after surgery, as well as for women who have given birth [6].
Pros:
- You don’t have to wait long for the effect; it develops within an hour.
- The drug is budget-friendly and affordable for every patient.
- Bisacodyl does not affect concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Minuses:
- Contraindications include intestinal obstruction, spastic constipation, peritonitis, abdominal pain, the cause of which is unknown, acute hemorrhoids and cystitis.
- The drug should not be prescribed to children under 8 years of age.
- Side effects include: burning sensation and pain in the rectum, intestinal colic, diarrhea, allergic reactions.
- The drug should not be used for more than 7 days.