Interaction with other drugs
In vitro studies of hepatic microsomal fractions (a model of drug metabolism by the cytochrome P450 enzymatic system) determined that tamsulosin does not interact pharmacokinetically with finasteride during metabolism in the liver. Additional interactions of tamsulosin with other drugs and other types of interactions No interaction was found with the simultaneous use of tamsulosin and atenolol, enalapril, nifedipine or theophylline. Concomitant use with cimetidine may cause an increase in the plasma concentration of tamsulosin, while furosemide causes a decrease. However, there is no need to change the dose of the drug, because tamsulosin concentration remains within normal limits. In vitro, diazepam, propranolol, trichlormethiazide, chlormadinone, amitriptyline, diclofenac, glibenclamide, simvastatin and warfarin do not change the content of the free fraction of tamsulosin in human plasma. Tamsulosin also does not change the content of the free fraction of diazepam, propranolol, trichlormethiazide and chlormadinone. In in vitro studies of hepatic microsomal fractions (a model of drug metabolism by the cytochrome P450 enzymatic system), no interaction with amitriptyline, salbutamol, glibenclamide and finasteride was observed at the level of hepatic metabolism. However, diclofenac and warfarin may increase the elimination rate of tamsulosin. Theoretically, there is a possibility that co-administration with tamsulosin may enhance the hypotensive effect of other drugs, such as general anesthetics or other α1-blockers. Additional interaction of finasteride with other drugs and other types of interactions No clinically significant interaction has been identified when finasteride is used together with the following drugs: warfarin, ACE inhibitors, α1-blockers, theophylline, acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, beta-blockers, diuretics, nitrates, slow blockers calcium channels, anticonvulsants, NSAIDs, benzodiazepines, quinolones, histamine H2 receptor blockers, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA) inhibitors.
Overdose
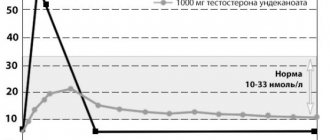
There are no cases of simultaneous overdose with Soniride Duo described. There is no clinical evidence of tamsulosin overdose. Theoretically, acute overdose of tamsulosin may cause hypotension, which may lead to cardiovascular events. To restore blood pressure and heart rate, the patient must be laid down, and, if necessary, plasma replacement drugs and, depending on the patient’s condition, vasopressor drugs should be used. It is recommended to monitor renal function. Dialysis is not indicated due to the significant binding of tamsulosin to plasma proteins. To reduce the absorption of the drug, it is advisable to induce vomiting. Gastric lavage after taking a large amount of the drug should be carried out together with the administration of activated charcoal and an osmotic laxative (for example, sodium sulfate). Overdose of finasteride: the use of a single dose of finasteride 400 mg and repeated doses of up to 80 mg/day for 3 months did not reveal any adverse reactions. In case of overdose, no specific treatment is required.=
Mode of application
Soniride Duo contains tamsulosin 400 mcg in modified-release capsules and finasteride 5 mg in film-coated tablets. The drugs are intended for daily use. The daily dose of Soniride Duo includes 1 modified-release capsule of tamsulosin 400 mcg and 1 film-coated tablet of finasteride 5 mg. Tamsulosin 400 mcg, modified-release capsules, must be taken at the same time of day, after meals. Capsules should be swallowed whole, not broken or chewed, as this may interfere with the sustained release of the active substance. For the full therapeutic effect, long-term use of the drug Soniride Duo is necessary. If adverse reactions occur, the patient can be switched to finasteride monotherapy; however, it is recommended to return to the combination regimen if BPH symptoms increase.
Side effects
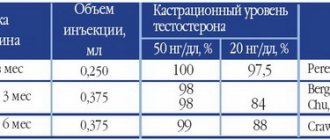
Side effects are defined as: frequent (>1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (>1/1000 to <1/100); rare (>1/10,000 to <1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000). Adverse reactions of tamsulosin monotherapy From the nervous system: frequent - dizziness; infrequently - headache; rare - fainting. From the cardiovascular system: uncommon - postural hypotension, tachycardia. From the respiratory system: infrequently - rhinitis. From the digestive system: infrequent - constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. From the skin and subcutaneous fat: uncommon - rash, itching, urticaria; rare - angioedema. From the reproductive system: infrequent - retrograde ejaculation; rare - priapism. Adverse reactions of finasteride monotherapy From the immune system: uncommon - hypersensitivity. From the side of the organ of vision: infrequent - clouding of the lens. From the digestive system: frequent - abdominal pain. From the skin and subcutaneous fat: infrequently - rash. From the reproductive system and mammary glands: frequent - erectile dysfunction, impaired ejaculation, decreased ejaculate volume, decreased libido; Uncommon: breast tenderness, breast enlargement, testicular pain. During post-marketing surveillance, the following additional adverse reactions were described (no data on the frequency of adverse reactions): hypersensitivity reactions, including itching, urticaria, swelling of the lips and face. Adverse reactions of combination treatment In patients receiving combination treatment (finasteride and an α1-blocker), the same adverse reactions are described, occurring with the same frequency as with monotherapy with finasteride and an α1-blocker.
However, the following exceptions were identified: erectile dysfunction and ejaculatory dysfunction were more common with combination treatment, while disease progression (including worsening BPH symptoms or the need for surgery) was more common with monotherapy.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of the drug Sonirid Duo are: a history of postural hypotension; severe liver failure; impaired renal function (plasma creatinine concentration >2 mg/dL); galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption; women and children; hypersensitivity to active or auxiliary substances. With caution: if there is a risk of developing obstructive uropathy; for liver diseases; when planning surgical treatment of cataracts.
Compound
1 capsule of Sonirid Duo contains: tamsulosin hydrochloride 400 mcg.
Excipients: calcium stearate - 0.8 mg, triethyl citrate - 1.1 mg, talc - 2.5 mg, copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate (1:1) - 43.8 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 281.4 mg. Capsule body composition: titanium dioxide (C.I.77891, E171) 3%, iron oxide dye black (CI77499, E172) 0.01%, iron oxide dye red (CI77491, E172) 0.01%, iron oxide dye yellow (CI77492, E172 ) 0.1714%, gelatin up to 100%. Composition of the capsule cap: yellow iron oxide dye (CI77492, E172) 0.2%, titanium dioxide (С.I.77891, E171) 0.3333%, black iron oxide dye (CI77499, E172) 0.53%, red iron oxide dye (CI77491, E172 ) 0.93%, gelatin up to 100%. 1 tablet of Sonirid Duo contains: finasteride 5 mg. Excipients: magnesium stearate - 0.75 mg, talc - 4.5 mg, sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A) - 7.5 mg, pregelatinized starch - 15 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 15 mg, lactose monohydrate - 102.25 mg. Shell composition: titanium dioxide (CI77891, E171) - 0.1881 mg, lactose monohydrate - 0.3809 mg, macrogol 6000 - 0.6214 mg, hyprolose - 1.9048 mg, hypromellose - 1.9048 mg. 10 pieces. (5 capsules + 5 tablets) - blisters (6) - cardboard packs.