One of the most effective antioxidants that can significantly improve health is vitamin C. Its other names are also common - ascorbic acid or ascorbate. The human body receives vitamin C through food. It is too unstable to high temperatures, which was one of the reasons for its shortage. The results of the scientists' research made it possible to assess the significance of the compound for all organ systems and became the basis for judging the consequences of its deficiency. Let's figure out how to determine the lack of vitamin C, and how to compensate for the deficiency.
The concept of ascorbic acid
The chemical formula of ascorbic acid is C6H8O6. The powder is no different from other vitamins: it is soluble in water, resistant to fat, has a sour taste, but is odorless. If stored improperly, it disintegrates and resembles a powder in its structure.
At what temperature is vitamin C destroyed? The destructive process begins at 60 degrees, and breaks down into particles at 100 degrees.
Chemists have proven that vitamin molecules are similar in composition to crystalline sugar, but there are still significant differences. Artificially synthesized vitamin C appeared in the food industry, which immediately became a popular food additive under the number E315. It does not have the same beneficial properties as the original, although it is much cheaper.
How many do you need?
The average requirement of an adult for vitamin C is about 90 mg per day. In pregnant and lactating women it is slightly higher - up to 120 mg. And children require less ascorbic acid - from 30 mg, and infants receive their portion through breast milk. A popular theory is that the human body’s need for vitamin C is very high. However, taking large doses of ascorbic acid only speeds up its removal from the body. Suggestions that significant doses of vitamin C help fight colds and cancer have not been confirmed. But an overdose
of ascorbic acid can cause digestive upset and skin reactions.
The maximum permissible daily dose
of vitamin C is 2000 mg.
Functions in the body
The main role of ascorbic acid in the human body is the fight against radicals and antioxidant effect. It is also a powerful antioxidant, as it protects internal organs and tissues from possible damage and the development of cancer.
What is vitamin C for? With its participation, redox processes occur in the body, protein synthesis occurs, and connective tissues are strengthened. Vitamin C accelerates the healing of wounds and scars and has a positive effect on epithelial regeneration.
It is important for athletes to regularly take vitamin and mineral complexes containing ascorbic acid, since it normalizes energy processes and increases endurance. The synthesis of steroid hormones, the metabolism of folic acid, and some metals cannot do without vitamin C. In bodybuilding, the substance is valued for its role in gaining muscle mass, since the level of absorption and processing of protein depends on it.
The importance of ascorbic acid for the body cannot be overestimated. Vitamin C strengthens blood vessels and promotes better permeability of important elements through their walls. If vitamin C is present in the body in the right amount, inflammatory processes occur in a lighter form.
The absorption of iron thanks to vitamin C improves, and the blood is provided with an antianemic factor.
The immune system works at full strength in the presence of three main vitamins: A, C, E. Ascorbic acid is responsible for the functionality of protective cells; if there is enough of it, the immune system resists any foreign agents: viruses, bacteria, parasites.
Oncology is considered the plague of the 21st century; statistics show that the number of cancer cases is steadily growing. Oncologists say that with normal levels of vitamin C in the body, a natural fight against cancer cells occurs. However, if a surplus of ascorbate forms in the body, mutating cancer cells become more resistant, even radiation therapy does not kill them. Cancer patients are advised to maintain vitamin C at the proper level.
Ascorbic acid protects the liver from the effects of toxins, removes copper, radioactive substances, mercury, and lead. To prevent the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, ascorbate has become an indispensable remedy. By controlling the level of the substance in the body, there is a chance to avoid cancer in the colon and bladder.
Acid normalizes the functionality of the nervous system, the body gains resistance to stress, and the strength to resist pathogens appears. In addition, the work of the adrenal glands is balanced and the required amount of hormones responsible for combating stress is produced. This is not all that ascorbic acid is responsible for.
It is impossible to give an objective assessment of the effect of vitamin C. In the twenty-first century, science does not know all the properties that a substance has. Do not underestimate control over the level of ascorbic acid in the body, since its deficiency causes the development of chronic diseases.
Why does a person need vitamin C?
Ascorbic acid or vitamin C is an organic compound that is highly soluble in water, is biologically active and related to glucose. Vitamin C is one of the most effective antioxidants; it prevents the negative effects of free radicals on the cells of living beings. Thanks to ascorbic acid, collagen is biologically synthesized - the basis of the connective tissue of tendons, skin, cartilage, and bones. It also has other functions:
- strengthening the immune system (the body more actively produces antibodies and leukocytes; vitamin C also helps to form interferon compounds that have an antiviral effect and accelerate wound healing);
- antioxidant, that is, prevention of cardiovascular diseases and slowing down the aging process;
- participation in the production of hormones by the adrenal glands;
- processing cholesterol and removing it from the body;
- maintaining the effective functioning of neurotransmitters, on which the general emotional state of a person and the health of his nervous system depend;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increasing blood flow speed by dilating capillaries;
- removal of heavy metal salts from the body.
According to some scientists, vitamin C is one of the important factors in the prevention of cancer. Research is underway on its effect on cancer cells of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system.
Many vitamins, including the one that this article is devoted to, are not synthesized in the body, which means that a person needs to regularly receive them through drinks or food.
Sources of Vitamin C
The body, due to its characteristics, does not accumulate ascorbic acid, so you should carefully monitor its consumption. The daily diet does not often contain foods rich in vitamin C. The amount of the substance should be replenished in medicinal form or in the form of nutritional supplements. The natural vitamin is water-soluble and easily subject to heat treatment, which destroys its beneficial chemical properties.
Main sources of the substance:
- kiwi;
- rose hip;
- Bell pepper;
- melon;
- black currant;
- onion;
- tomatoes;
- oranges;
- apples;
- peach;
- persimmon;
- Rowan;
- baked potato;
- cabbage;
- leafy herbs.
Previously, oranges and tangerines were considered the main fruits containing the most vitamins. Over time, scientists have proven that this is not so, but it is difficult to compare with rosehip, bell pepper and kiwi in terms of the presence of the substance.
Among animal products, vitamin C is found only in the liver, adrenal glands and kidneys.
Herbs containing ascorbic acid are added to any dishes during cooking:
- mint;
- nettle;
- oats;
- parsley;
- plantain;
- raspberry leaves;
- sorrel.
These plants are easily digestible, as evidenced by more than one table of nutritional value of products. People who adhere to a healthy diet do not have to worry about their vitamin levels, since their diet consists of healthy foods, the caloric content of which will not harm the diet.
There are no recommendations on how vitamin C is absorbed. To absorb as much ascorbic acid as possible, follow these rules:
- Vegetables and fruits are peeled and cut immediately before consumption.
- During cooking, vegetables are placed only in boiling water so that the organic vitamin does not dissolve in the water during heating.
- Cooked vegetables should not be left in the broth, because everything is given up to the liquid, and the fruits become useless.
- Fresh vegetable salads are salted and seasoned with sauces only before serving.
Vitamin C is consumed instantly after it enters the body; take care to consume the vitamin evenly throughout the day.
It is advisable to divide the daily dose into three equal portions, thus maintaining the concentration of the substance in the body constantly. Having found out what contains the most ascorbic acid, try to properly prepare and eat foods with an increased source of the substance.
It is important not to overdo it!
In most cases, a lack of vitamin C will not turn a healthy person into a disabled person, but it will clearly worsen your health. But hypervitaminosis can cause even more harm. For most people, excess ascorbic acid will not harm you. Unless a diet with constant consumption of large amounts of fruit will cause diarrhea or diathesis.
In addition to ascorbic acid, citrus fruits contain B vitamins and phytoncides.
If there is too much vitamin C in the body and you are treated with salicylic acid-based antibiotics, gastritis or stomach ulcers may develop. An excess of ascorbic acid can cause increased blood pressure, headaches, deprive sleep and even cause miscarriage in pregnant women.
The use of loading doses of ascorbic acid is contraindicated for diabetics and people who have rapid blood clotting and a tendency to form blood clots.
Ascorbic acid as a medicine
If there is a lack of vitamin in the body, it is recommended to replenish the supply with medications. Release form:
- dragee;
- pills;
- ampoules;
- powders.
The form of use is determined by the attending physician depending on the nature of the disease. The instructions for use warn of possible side effects if the drug dosage is incorrect.
Ascorbic acid dragees are prescribed to children because they resemble candy and not medicine. Effervescent tablets are popular among professional athletes. One tablet, diluted in a glass of water, replenishes vitamin reserves and invigorates before a grueling workout. The powder is available in sachets.
An injection solution is prepared in ampoules. One ampoule contains 50 mg and 100 mg, which allows you to administer the required dose of the drug at a time.
An overdose negatively affects the mucous membrane of the stomach and digestive tract as a whole. Pregnant women are at risk because the metabolism between the mother and fetus is disrupted. As a result, the child develops allergies, and the mother may develop problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
What prevents it from being absorbed?
The destruction of ascorbic acid provokes the use of nicotine and alcohol. Thus, according to some data, each cigarette smoked
deprives the body of about 25 mg of vitamin C.
Sweet soda
- due to the content of soda that destroys ascorbic acid.
Vitamin C present in products is partially destroyed by prolonged exposure to light, high temperature, as well as during long-term storage and transportation. That is why, in order to obtain its full amount, it is recommended to eat vegetables and fruits fresh or having undergone only minimal heat treatment. And try to choose fruits that grew close to the place where they are sold. The long journey across continents and oceans deprives them of almost the entire dose of ascorbic acid. in frozen vegetables and fruits
than in their fresh travel relatives.
Daily value for humans
Scientists have not reached a consensus regarding the daily requirement of vitamin C for the human body. A common option for the average adult is 60-80 milligrams of the substance per day.
Infants are allowed to consume up to 40 mg of ascorbic acid, for children aged five - 45 mg, at fourteen years of age the daily norm increases to 50 mg.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends using a different calculation method: 2.5 mg of the substance is needed per kilogram of body weight. A 200-pound man should receive 225 mg of vitamin C per day. To replenish ascorbic acid levels for medicinal purposes, doctors increase the recommended dose three times.
In some categories, it is recommended to increase the standard doses, since the body does not have enough average amount of vitamin C in the body. These categories include:
- Pregnant women – 75 mg. If you have a question about whether pregnant women can take vitamin C, check with the antenatal clinic so as not to worry about the baby’s health. When planning pregnancy, the level of vitamin C in the body is important for both men and women. The daily norm does not exceed 100 mg.
- Nursing mothers – 90 mg.
- Smokers and alcoholics – 120 mg. Alcohol and nicotine accelerate the breakdown of vitamin C, which provokes the formation of a deficiency of the substance in the body.
- Persons in constant stressful situations.
- People living in areas with unfavorable ecology: factory emissions, exhaust gases, untreated drinking water, etc. As soon as harmful substances enter the body, ascorbic acid is used for their disposal. The need for vitamin increases.
- Residents of the Far North and Southern regions. Unusual weather conditions are considered stress for the body, so residents are advised to take 40% more vitamins than other categories.
- Women taking oral contraceptives.
Even if you belong to the group of people suffering from vitamin C deficiency, do not consume large doses of the substance at once. Divide the dose into 3 servings and take them throughout the day.
At what age is the use of ascorbic acid allowed? Vitamins without the presence of pathologies in the baby are introduced into the diet after the end of the breastfeeding period. When breastfeeding, the baby receives all the necessary elements from mother's milk.
The lethal dose for humans is 60-90 tablets in a short period of time. The body does not have time to remove the substance from the body with urine, and an overdose of the vitamin occurs.
Vitamin C. How to understand it?
V. Prozorovsky, professor, doctor of medical sciences
“Science and Life” No. 8, 2007
“What do you have here? - Smoke asked one of those lying... - Smallpox, or what? Instead of answering, the man pointed to his mouth, stretched his swollen lips with effort, and Smoke involuntarily recoiled. “Scurvy,” he said quietly to the Kid, and the patient nodded to confirm his diagnosis. “Is there enough food?” - asked the Kid. “Yeah,” replied the man from the other bed, “you can take it.” There’s plenty of food.”
D. London. Smoke and Baby. 1912
As an independent, widespread and fatal disease, scurvy (scorbut) was described in detail in the Middle Ages. It fell on people like the scourge of God during long sea voyages, protracted wars (Crusades, sieges of cities), in areas suffering from crop failure. Later, she threatened polar expeditions and gold prospectors in the northern lands with death. Now in the spring he visits the northern regions in the form of hypovitaminosis. In addition to general exhaustion, impaired strength of the vascular wall, and with it hemorrhages and bleeding, anemia, ulcerative skin lesions, tooth loss, destruction of cartilage, joint pain and other delights, with scurvy, immunity decreases and fever occurs. Since, moreover, the disease was clearly focal in nature, many considered it contagious. Others associated scurvy with poor quality food and mental depression. With partial fasting, the whole range of scurvy symptoms develops over several months. And in case of infectious diseases, especially influenza, the first signs (hemorrhages) of vitamin deficiency appear within a week.
For the first time, the presence in natural food of some special substances necessary for the life of animals was proven by the Russian pediatrician N.I. Lunin in 1881. His work (dissertation) was a major discovery, since it refuted the accepted as a law opinion of the great chemist J. Liebig (“Organic chemistry in its applications to physiology and pathology,” 1842) that proteins, fats, carbohydrates and mineral salts are quite sufficient. No, it’s not enough, more substances are needed, Lunin said, and thus opened a new era in the problem of nutrition and medicine.
Why vitamin?
In the 19th - early 20th centuries, East Asia with its Polynesian and Japanese islands was the focus of a severe endemic (inherent in a given limited area) beriberi disease (alimentary polyneuritis). It is characterized by damage to peripheral nerves, the cardiovascular system and edema, followed by muscle atrophy. Thus, in 1911 in Java and Sumatra, the mortality rate from beriberi reached 70%. In Japan, it affected mainly sailors - an average of 300 per 1000 people per year. Everyone seemed to live together on the ships, but the officers ate better and got sick less often, so the doctors assumed that the illness was somehow related to diet.
In June 1897, the Dutch doctor H. Eijkman, who served in the colonial administration, drew attention to the fact that chickens bred in the nursery at their institute in Batavia (as Jakarta was previously called) developed a disease reminiscent of beriberi in humans, — they seemed unable to walk and were constantly tumbling. Aikman noted: the disease began from the time when chickens began to be fed husked (polished) rice. He did not find microbes in their corpses, but in the nerves and spinal cord of chickens the same degeneration of nerves was noticed as in humans - the result of polyneuritis. Transferring the chickens to a normal diet led to a rapid recovery. Similar results were described in observations of the health of prisoners in different prisons. And there, transferring patients to feeding regular rice led to the elimination of the disease. For this find, H. Eikman, together with his colleague F.Kh. Hopkins received the Nobel Prize in 1929. All that was found out was that in some Batavia something necessary for health was found in the bran of rice. But they got sick all over the world, especially in the north, where there was no smell of rice, especially polished rice. So what was it?
Back in 1911, the Polish biochemist K. Funk, working in London, isolated a special dry substance from rice bran, 20 mg of which cured patients from beriberi. This substance, along with carbon and hydrogen, contained 8% nitrogen. It is for this reason that Funk proposed calling it the amine of life (vita in Latin) - a vitamin (without any letters yet). Subsequently, he isolated the same substance from yeast, milk, cow brain and lemon juice. The scientist wrote: “...to the well-known list of food elements—proteins, fats, carbohydrates, purines and mineral salts—a new group must be added, namely, “vitamins.” He called diseases caused by their absence, in particular scurvy and rickets (there was no trace of C and D yet), vitamin deficiencies. For me, it was Funk who made the real discovery of vitamins, but... the ways of the Nobel Committee are inscrutable.
Where does "S" come from?
For C to appear, A and B are first needed. In 1909, the German scientist W. Stepp reported that when mice are fed bread made with milk, the animals develop well. However, if fat is extracted from this bread using an organic solvent, the mice wither and die. If you add the extracted substance to low-fat milk bread, then they live, cheerful and vigorous. Adding vegetable oil did not have this effect, therefore, you need something fatty, but not just any fat.
Later, in 1914, the Englishmen E. McCall and M. Davis established that the necessary fat was found in butter and egg yolk. In 1919, the authors proposed to call this substance “fat-soluble factor “A”. Subsequently, it was found that the absence of factor “A” in food leads to dryness and ulceration of the cornea (xerophthalmia), and substance “A” began to be called “axerophthalmine”. A year later, it began to be used to treat retinal diseases (retina in Latin) and was already called vitamin A - retinol. That's his name now.
A year later, the same E. McCall and M. Davis discovered a “vitamin-like water-soluble substance” necessary for the growth of rats, which, alas, turned out to be identical to the vitamin used to combat beriberi. At the suggestion of the same Funk, this antipolyneuritis vitamin was designated the letter B. Less than a dozen years have passed since the number of B vitamins has increased. The first (the same one) naturally became B1, and then came B2, B3, etc. All B vitamins are united by water solubility and thermolability (sensitivity to temperature). This is how they differ from fat-soluble and heat-stable vitamin A.
A. Szent-Györgyi, who discovered vitamin C. He received the Nobel Prize in 1937 for his work on oxidation, including the discovery of ascorbic acid (image: Science and Life)
In reality, scurvy was reproduced in animals, namely guinea pigs, only in 1910 by A. Holst and J. Fröhlich. It all started with feeding experimental animals exclusively oatmeal, and then it turned out that any grain mono-diet is scurvy. Then they clarified that although the antiscorbutic factor is absent in cereal grains, it appears in green sprouts. It is present in juicy vegetables, fruits and plants in general, although in different quantities. It is also found in milk, but only in fresh milk, and is destroyed during sterilization. This is why pasteurization was invented: after it, the anti-scorbutic effect of milk decreases, but does not disappear. In 1920, I. Drummond proposed calling the antiscorbutic substance vitamin C. A very curious circumstance soon became clear - it turns out that only guinea pigs, apes and, naturally, their closest relative, humans, suffer from scurvy. In 1922, researcher N.A. Bessonov was the first to isolate an active antiscorbutic drug from white cabbage juice. Although it was not sufficiently purified, the experimental scurcutus healed in insignificant doses. (By the way, Bessonov is not even mentioned in the Great Medical Encyclopedia.) After its publication, a large series of works by many authors followed with the results of gradual purification of the drug and clarification of its properties, and only in 1933 the German biochemist F. Michel and the Hungarian scientist A. Szent -Györgyi established a formula for an antiscorbutic vitamin isolated from lemons. Szent-Györgyi later gave it the name "ascorbic acid" (he received the Nobel Prize in 1937).
The main concern of ascorbic acid
It seems natural that the main property of ascorbic acid is to prevent and heal scurvy. But only humans and others like him need it, and in all other animals (except the guinea pig), ascorbic acid is synthesized in the liver from sugars. Why? There are many reasons, but, first of all, in order to prevent a living organism from flashing a blue light, to help the necessary oxidation and to resist dangerous oxidation. We are always balancing on a razor's edge: slow oxidation is life, fast oxidation is death!
Crystals of ascorbic acid under a microscope. Photo by M. Davidson. Florida State University, USA (image: Science and Life)
All types of our activities require energy and all of it - chemical, mechanical, electrical, nervous and even mental - is born from the oxidation that oxygen carries. Not everyone can hold their breath for more than a minute. 5 minutes after oxygen supply to the brain stops, it dies. The difficulty is not only that oxygen is needed, but that it is needed only for those processes that are included in the energy metabolism chain. And these processes occur exclusively intracellularly with the participation of a number of enzymes, and the process of biological oxidation occurs not due to the direct interaction of oxygen with combustible material, but by the transfer of electrons from the oxidized substance - carbohydrates and fats - to the oxidizing agent - oxygen through a chain of enzymes. What does ascorbic acid have to do with it?
In the animal body, the chain of enzymes and substrates through which electrons are transferred, and with them oxidation energy, is long and diverse. But such a chain necessarily includes adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP), which is the main and unique chemical battery, capable of, under the influence of enzymes and as a result of various transformations, directly transferring the energy accumulated in ATP to chemical, electrical, and mechanical processes. Carbohydrates and fats are also energy accumulators - 4.1 and 9.3 kcal/g, respectively, but without biological slow oxidation they can only burn, giving heat and light, but cannot be directly converted even into mechanical energy, not to mention mental .
However, in biological objects everything does not always proceed as it should. Oxygen can acquire not two, but one electron, which leads to oxygen instability and increased reactivity. The presence of an extra electron in an atom is conventionally indicated by a dot at the top of the element symbol.
For a number of reasons, most often external (excess ultraviolet radiation, poisoning, radiation damage, some diseases), first single activated atoms—radicals—can appear, and then their chains.
Vitamin C molecule model. Black
- carbon,
red
- oxygen,
white
- hydrogen (image: Science and Life)
And then there is a branching of the chain, which gives rise to more and more new radicals that activate individual atoms, and then large molecules. This process not only ramifies, but also accelerates. The theory of the phenomenon, both in general and in particular, including ignition and explosions, was developed by our compatriot and almost contemporary Nikolai Nikolaevich Semenov (Nobel Prize 1959).
Fortunately, in living organisms it does not come to combustion. But there are burns. A fair-haired blonde will lie down for a couple of hours under the southern sun and get a burn, sometimes to the point of blisters. For other reasons, easily oxidized fats and fat-like substances - lipids of internal organs - suffer from the rapid accumulation of atoms and molecules of active oxidants - prooxidants. Occurring in tissues, prooxidants interact primarily with the fatty membranes of the cells lining the blood vessels—endothelial cells. They oxidize and seem to foam. This is not enough; there are fat-like substances in the blood - low-density lipoproteins, which oxidize more easily than others. When oxidized, they cause destruction of endothelial cell membranes more strongly than other pro-oxidants. Cells are destroyed, and non-destructible cholesterol accumulates in the intercellular spaces. Following this comes atherosclerosis. This is not the only, but the main theory of its origin today.
By the way, polycyclic chlorinated hydrocarbons, including simple polyvinyl chloride PVC, but even simple carbon tetrachloride, as well as carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide and other delights of vehicle exhaust gases, can serve as initiators of the formation of active radicals.
Formula of ascorbic acid C6H8O6 - c-vitaminum
(image: Science and Life)
Skin burns under ultraviolet radiation, lungs burn when ozone is inhaled, and hydrogen peroxide generally kills all living things. Salvation from such a scourge is ascorbic acid synthesized by living organisms. That is, for all normal organisms - ascorbic acid, synthesized by themselves, and for the human body - vitamin C. This is our main defense - an antioxidant that protects the entire body and, first of all, all fat-like substances - lipids - from peroxidation. Lipid peroxidation as a biochemical concept is now so widespread that in medical literature it sometimes appears even without decoding - LEX.
Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant because it is an active reducing agent that has the ability to easily oxidize and thereby eliminate reactive oxygen species - “extinguish matches.” This reaction is not simple. Regular ascorbic acid is its reduced form. By reacting with the active oxygen and hydrogen atom, ascorbic acid itself becomes a radical, but... inactive. If the simple radical is R, the oxidized active radical is RO•2, then:
RO•2 + AK-OH = ROOH + AK-O•.
The peculiarity of the resulting AK-O radical is its low activity, which prevents its further transformations and interrupts the reaction chain, and especially its branching. Quenches the reaction. But how so? It seems like a radical is a radical. Where does the low activity of ascorbic acid come from? All acids also seem to have the same hydrogen ion. But you can eat ascorbic acid with a spoon, but it’s better to deal with nitric acid with gloves, and even under traction. Oxidized AK-O can again be converted into a reduced form, or it can be oxidized further, transforming into dehydroascorbic acid, which is then converted in complex ways into oxalic acid or partially reduced.
We should not forget that the ascorbic acid molecule is complex, and it is not just a carrier of a radical, but an enzyme. Its activity as a flame arrester is amazing - in 1 second it eliminates 1010 molecules of active hydroxyl or 107 molecules of superoxide anion radical oxygen. Alas, with food we receive mainly ascorbic acid in an already oxidized form (the longer the food is stored, the more it is oxidized). The content of ascorbic acid in main products is given in table. 1.
Table 1.
Vitamin C content in the most vitamin-rich foods (image: Science and Life)
The most delicious and healthy vitamin C preparation is holosas. These are not only rose hips, but also a choleretic agent that has never harmed anyone. And the benefits!
More than just an antioxidant
Ascorbic acid is an obligatory component (this is called a cofactor) of the activity of enzymes involved in the synthesis of nerve impulse transmitters in the brain, dopamine, adrenaline and norepinephrine, therefore, with vitamin deficiency - a lack of vitamin C - mental activity decreases and even depression develops (early spring depression).
Vitamin C activates the synthesis of collagen, the main protein of connective tissue. And if there is not enough of it, decay and collapse begins: the teeth no longer stay in their sockets, the articular cartilage softens, the sternum moves away from the ribs, the vessels do not hold blood well, hemorrhages occur in the joints, which leads to their stiffness and pain, bones break, and fractures do not occur. grow together.
Relatively recently, it was established that ascorbic acid is a participant in the synthesis of carnitine, which is a substance necessary to ensure the oxidation of fats, as they say in everyday life - combustion. But fats are a source of energy. Their deficiency causes weakness and then exhaustion. Weakness is partly associated with the development of anemia. The fact is that ascorbic acid, by taking on electrons, facilitates the absorption of iron, and therefore accelerates the formation of hemoglobin. There is no ascorbic acid - there is little iron in the blood - there is iron deficiency anemia (in the past it was called the offensive term “pale sickness”).
Previously, nitric oxide - NO - was considered only a poisonous gas, but recently it has been recognized as a participant in numerous beneficial reactions, including a substance that promotes vasodilation. R. Furchgott received the Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1998 (see “Science and Life” No. 2, 1999, No. 7, 2001). Thanks to him, the famous Viagra was created. So, ascorbic acid both promotes the synthesis and protects NO from inactivation (loss of biological activity). Thus, if not a mini-Viagra, then it is a protector against hypertension - that’s for sure. Considering that ascorbic acid also has an anti-sclerotic effect, it is clear that old people need it more than young people.
Common diseases in which hyperoxidation plays a role, in addition to atherosclerosis, include cataracts, some forms of anemia and even cancer. If not in the treatment of these diseases, then there is no doubt about the effectiveness of the preventive action of ascorbic acid.
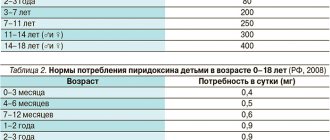
Table 2.
Prophylactic doses of ascorbic acid (image: Science and Life)
Observations of the life activity of thousands of people indicate that regular intake of multivitamins, including ascorbic acid, from mid-winter to autumn is necessary: this protects against vitamin deficiency and improves health. But you need to take vitamins only in preventive doses (see Table 2).
How to take ascorbic acid
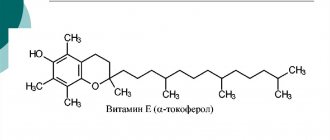
If the need for ascorbic acid is increased, if only because of age, then it is oxidized in larger quantities than usual, and when oxidized, it itself becomes an oxidizing agent, albeit not very active, but still with an extra electron in the outer orbit, that is dangerous. In this case, ascorbic acid must be restored, for which there are other mechanisms inherent to humans. In such situations, it is necessary to take another vitamin, which itself works and restores ascorbic acid. This is vitamin E - tocopherol (translated from Greek as “bearing childbirth”). It is named so because if it is deficient in a woman’s body, miscarriages occur. It is better to buy tocopherol in an oil solution and take 1 drop per day. Regularity is not necessary as it is deposited and used gradually.
The most “ascorbine-containing” products (image: Science and Life)
It is very significant that soon after the isolation and synthesis of ascorbic acid, the effectiveness of the powder began to be compared with lemon. And... for scurvy in pigs, lemon turned out to be much more effective. Naturally, they decided that C alone was not enough. And they also found vitamin P in lemon (from English permeability
- permeability). Permeability vitamin C and P should be taken together. Such tablets are called “askorutin”: “asko” comes from the name of the acid, and “rutin” comes from the word “ruta” - buckwheat. Vitamin P as a substance is called “quercetin”, but it has many other names (that which is obtained from lemon is called “citrine”). And all because many plant substances - flavonoids - have P-vitamin properties, but most of them are found in citrus fruits. Recently, “craftsmen” have obtained another derivative of quercetin, which is 10 times weaker than quercetin, and is sold under the name “capilar” (that’s right) for 10 times more expensive. For capillary toxicosis (inflammation of the capillary walls), the drug venorutin in ampoules is used.
Is ascorbic acid always safe?
As for the recommended (and even slightly larger) doses, they are not only useful, but sometimes necessary, since the need for ascorbic acid increases under any stress, physical and mental stress, and almost any disease.
But in addition to vitamin deficiency, there is also hypervitaminosis (excess vitamin). For some, such as vitamins A, D, K, it is a disease; for most, including vitamin C, it is a nuisance. Excess ascorbic acid can lead to its accumulation in an oxidized form, when it itself becomes an oxidant. At the same time, the absorption of glucose is impaired - pseudodiabetes occurs. A seemingly necessary reduction in blood clotting can lead to bleeding; an increased content of ascorbic acid in the blood violates the results of studies of some of its biochemical parameters, in particular glucose, bilirubin, activity of transferases (enzymes), etc.
There may be other kinds of troubles. Most of the ascorbic acid is reduced after oxidation, but a smaller part is excreted in the urine in the form of oxalic acid. Even if grams are withdrawn, but only 3-4 days - one conversation. But if the excess is constantly removed every day, and even with oxalic acid diathesis, then not only the kidneys, but also the bladder can be clogged with stones.
It has been shown that long-term (three months) intake of ascorbic acid 500 mg per day reduces the content in cells of one of the most dangerous endogenous mutagens - 8-hydroxyguanine. This is good! But taking ascorbic acid in the same dose for six months increases the content of the active mutagen 8-hydronsiadenine. But this is already bad. Although it is believed that the positive influence outweighs the negative, it is not worth the risk.
An interesting story about ascorbic acid is connected with the name of Nobel laureate L. Pauling. In the 70s of the last century, it was reported that ascorbic acid in large doses, 1–3 grams per day, taken at the first signs of acute respiratory infections, including influenza, could interrupt or at least weaken the course of the disease. Pauling, who was not only an extraordinary man, but also a passionate one, was inspired by this idea. He decided to use his own example to convince humanity that ascorbic acid prolongs life, for which he took it in large doses every day. Yes, Pauling lived to be 93 years old. But this means absolutely nothing. If this were proof enough, then my grandmother, who lived 94 years without even knowing about the existence of vitamin C, proved that it is not needed at all.
Obviously, the truth in Pauling's argument with my grandmother lies somewhere between them, but closer to my grandmother.
Literature:
1.
Davis M. et al.
Vitamin C. Chemistry and biochemistry.
- M., 1999. 2. Mussky S. A.
100 great Nobel laureates.
- M.: Veche, 2004. 475 p. 3. Heller Retal.
Vitamin C: poison, prophylactic or panacea? // TIBS. 1999. Vol. 13. P. 1007-024.
Vitamin C deficiency and its signs
Let us remember that since ancient times, citrus fruits were considered the only salvation from scurvy. 10 mg of ascorbic acid, which is equal to two fresh apples or a bunch of grapes, will help prevent the development of the disease. However, this is not enough to maintain the productive functioning of the body in conditions where the world is filled with negative factors: factories, exhaust fumes, dirty water, chronic stress.
Hypovitaminosis is manifested by a decrease in the functioning of the immune system, the body's vulnerability to respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases. Studies have proven that with a deficiency of ascorbic acid in schoolchildren, the body’s ability to resist pathogens is halved. Acid deficiency causes the development of serious diseases. Signs of vitamin C deficiency:
- sensitivity and bleeding gums;
- loss of teeth;
- decreased visual acuity;
- varicose veins;
- the appearance of bruises;
- prolonged wound healing;
- fatigue;
- hair loss;
- obesity;
- the appearance of wrinkles;
- irritability;
- inattention;
- joint pain;
- insomnia;
- depression;
- apathy.
With insufficient intake of ascorbic acid for two to three months, vitamin deficiency develops.
Before taking vitamins, find out their amount in the body in order to avoid unwanted consequences from an overdose. An excess of vitamin C is indicated by its presence in the urine.
You need to replenish vitamin C reserves in the body with the right foods, which were already mentioned above. Try to heat-treat fruits and vegetables as little as possible, since beneficial substances are destroyed extremely quickly.
Symptoms and consequences of deficiency
Vitamin C deficiency can be suspected by external signs and changes in health status. A deficiency is indicated by bruises appearing on the body for no reason, the appearance of chronic fatigue and depressive mood. The lack of this substance provokes the appearance of muscle and joint pain, as well as bone aches. Vitamin C deficiency is reflected in dry skin, swelling and excess weight. A long-term lack of the active compound provokes a decrease in the body's defenses. A person begins to get colds often. Deficiency leads to decreased concentration. Children suffering from a lack of vitamin C are at high risk of abnormal skeletal development.
Excess ascorbic acid in the human body
Ascorbic acid is extremely beneficial for humans, but in large quantities it can cause irreparable harm. The body functions normally only when it receives the required amount of vitamins and minerals, not exceeding the permissible norm. Excess and deficiency become impetus for undesirable processes that affect the overall health.
Consequences of excess ascorbic acid:
- Diarrhea.
- Destruction of blood cells.
- The simultaneous consumption of vitamin C and aspirin leads to irritation of the gastric mucosa and even the formation of erosion and ulcers. Aspirin causes increased consumption of ascorbic acid, which is excreted in the urine through the kidneys. Such a loss becomes the first sign of a serious vitamin deficiency.
- A high dose of vitamin C interferes with the absorption of vitamin B12, which is used as a dietary supplement. B12 deficiency has an extremely negative effect on the body, so its level should be regularly monitored by a doctor.
- Candies and chewing gums with a high content of vitamin C damage tooth enamel, so after eating them, be sure to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
- Excessive doses of ascorbic acid slow down the functioning of the pancreas, which is dangerous for patients with diabetes and people with anemia, thrombophlebitis, and thrombosis. Vitamin C influences the formation of a separate group of hormones that affect the functioning of the kidneys and blood vessels.
Ascorbic acid is freely available in stores and pharmacies, and can be purchased without a doctor's prescription.
Excess vitamin C has negative consequences that are as serious as deficiency.
What products contain
The leader in vitamin C content can rightfully be called rose hips. In second place you can put currants, Brussels sprouts and sea buckthorn. There is also a lot of ascorbic acid in the following foods:
- bell pepper;
- kiwi;
- radish;
- tomatoes;
- sorrel;
- cabbage;
- horseradish;
- gooseberry;
- cauliflower;
- green pea;
- wild garlic;
- porcini mushrooms and chanterelles;
- citrus.
In spring, the best source of vitamin will be young nettle. It is added to pies, casseroles, omelettes, and a traditional dish made from nettles is green borscht.
Vitamin C in medicine
The beneficial properties of ascorbic acid have become the reason for its popularity in medicine. Vitamin C-based preparations are prescribed for a wide range of diseases:
- scurvy;
- avitaminosis;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- helminthiasis;
- ulcer;
- fracture;
- bleeding;
- diathesis;
- infectious diseases;
- dystrophy.
Doctors, after studying the patient's medical history, may increase the dosage of vitamin C to 1.5 g per day. Intramuscular medications are administered in case of acute vitamin deficiency; in other cases, the diet is regulated and pills are prescribed.
The famous doctor Linus Pauling became an ardent supporter of the use of vitamin C for medicinal purposes. The scientist advocated the use of the substance in the treatment of serious diseases and minor ailments, but this trend was not confirmed by research by physiologists. Some patients, after exceeding the daily norm, developed serious problems caused by hypervitaminosis.
During pregnancy, additional examinations and tests are carried out, since both the woman and the child can be affected. It is not for nothing that there are restrictions on the use of vitamin C for pregnant women, since in the early stages its excess provokes miscarriage.
Ascorbic acid is prescribed for delayed menstruation and irregular cycles. Vitamin C is involved in the production of estrogen, an essential hormonal component necessary for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. When there is a sufficient amount of this hormone, the muscle layer of the uterus contracts, provoking menstruation. Thus, the substance helps regulate the flow of menstruation and improves women’s health.
Why is it needed?
The main function of vitamin C is to increase the body's resistance to infections and protect the walls of blood vessels from damage. Ascorbic acid is involved in the synthesis of collagen
, the main building material of connective tissue.
In addition, ascorbic acid helps in the absorption
of other important vitamins, minerals and nutrients: folic acid, vitamin E, iron, proteins and carbohydrates.
Vitamin C is involved in the functioning of the hormonal system. It is necessary, for example, for the synthesis of adrenal hormones - corticosteroids
.
It also helps the immune system work - it stimulates the synthesis of interferons
- proteins that fight viruses in the body. It is also considered a strong antioxidant that protects the body from free radicals. – “molecular fragments” that destroy cells.
Application in cosmetology
Ascorbic acid, as an antioxidant, is included in anti-aging cosmetics for women. Products based on vitamin C prevent the effects of free radicals on the skin of the face, which is why it is used in the manufacture of anti-aging creams.
The presence of a vitamin in the list of cosmetic ingredients does not guarantee quality, since the amount of the element used is not always enough to produce an effect. The optimal dose in cosmetology ranges from 0.3% to 10%. Professional preparations on the labels contain information about the amount of active substance and the percentage of components.
Due to the sensitivity of the vitamin to light and air, cosmetics based on it are produced in sealed, tinted packaging with a dispenser.
Vitamin C-based facial cosmetics perform the following functions:
- protect the skin from exposure to infrared rays;
- synthesize collagen;
- restore collagen fibers;
- slow down the aging process;
- increase skin tone;
- prevent the appearance of age spots;
- relieve inflammation;
- refresh and improve complexion;
- strengthen vascular walls.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
In winter, to replenish vitamin C reserves, it is necessary to take vitamin and mineral complexes for the skin.
Ascorbic acid is useful for hair; it gives hair shine and silkiness. Liquid vitamin C in ampoules is added to ordinary shampoo or hair conditioner. Nutrition along the entire length is provided during each wash.
Vitamin C intake rate
There is no universal answer to the question of how much vitamin C a person needs. When calculating the daily allowance, many factors need to be taken into account:
- climate and season;
- state of ecology;
- bad habits (nicotine addiction, passive smoking, alcohol intake);
- gender and age of the person;
- chronic diseases.
Doctors have calculated that the average adult should consume from 60 to 100 mg of vitamin C daily. If the doctor has prescribed complex treatment for any disease, it is recommended to increase the dosage to 500 mg or more (but not more than 1500 mg per day).
Increasing the amount of vitamin C entering the body is necessary for those who take contraceptives or antibiotics. People who smoke usually suffer from a lack of ascorbic acid. The combustion products of tobacco interfere with its absorption, which means that those with nicotine addiction should increase the daily dose of vitamin C intake by 20-35 percent.
Fans of kebabs, fried pork, beef stewed with vegetables and other meat dishes, including smoked meats, sausages and sausages, should also consume an increased amount of vitamin C. The fact is that an excess of nitrogenous compounds has a negative effect on the human body. In addition, when making sausages, manufacturers use saltpeter as a preservative, a nitrate compound that, when mixed with gastric juice, can provoke the growth of cancer cells.