pharmachologic effect
Manufacturer: USB Pharma, Belgium
Release form: film-coated tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: hydroxyzine hydrochloride
Synonyms: Hydroxyzine
The drug contains hydroxyzine hydrochloride, which is a derivative of diphenylmethane. The substance reduces excitability, tension, anxiety and fear. The drug exhibits sedative, antihistamine, antiemetic effects. Atarax reduces muscle tension, relaxes the respiratory and digestive muscles, and also reduces itching in allergic diseases.
With long-term use of the drug there is no addiction or withdrawal syndrome.
Characteristics of the drug
Atacrax is available in 2 forms: injection and tablets. The main active ingredient is hydroxyzine. The drug and its analogues, which are sold without prescriptions, improve cognitive function and concentration.
For severe anxiety, which is accompanied by chronic insomnia, the active substance Atarax eliminates the symptoms of the condition, makes sleep sound and long, reducing the number of awakenings to a minimum. Due to the effect of the active component on certain areas of the subcortex of the brain, the drug has the ability to relax smooth muscles and skeletal muscles.
The drug is indicated for use in the following conditions:
- for somatic, neurological, mental pathologies in order to relieve excessive irritability, psychomotor tension and agitation;
- symptomatic treatment of withdrawal syndrome caused by chronic alcohol dependence;
- increased anxiety;
- a period of premedication to provide a sedative effect;
- treatment of itchy skin.
Conditions and pathologies in which Atarax is contraindicated:
- porphyria;
- hypersensitivity and intolerance to the components of the drug;
- hereditary galactose intolerance;
- angle-closure glaucoma.
The drug is not prescribed during pregnancy, breastfeeding or during labor. This is due to the fact that the active substance penetrates the placenta and negatively affects the intrauterine development of the unborn child.
Atarax is also able to relax the smooth muscles of the uterus, preventing it from contracting, which can negatively affect the process of labor. When breastfeeding, the active ingredient enters the baby's body with mother's milk, and the drug is contraindicated in children.
If any of the above pathologies and conditions are present, consultation with a specialist is necessary before use.
Atarax - instructions for use
According to the instructions for use, Atarax is used to treat children from one year old and adults. The dosage of the drug and the regimen are determined individually and depend on the patient’s age, the severity of the disease and accompanying symptoms.
How to take Atarax: before or after meals
Tablets are taken orally regardless of food intake. Take the medication with a small amount of liquid.
The injection solution is used only for intramuscular administration. Subcutaneous, intravenous, and intra-arterial injections are prohibited.
Analogues of Atarax
There is a wide range of Atarax substitutes on the shelves of pharmacies. Medicines differ in composition, mechanism of action, and indications.
Analogs of Atarax, which are available without a doctor's prescription:
- Afobazole;
- Glycine;
- Novo-passit;
- Persen;
- Tryptophan Calm Formula;
- Motherwort extract.
Russian analogues of Atarax are represented by the following medicines:
- Bellataminal;
- Phenazepam;
- Amitriptyline;
- Chlorprothixene;
- Gidazepam;
- Teraligen;
- Paroxetine;
- Mexidol;
- Sibazon;
- Mälarena;
- Escitalopram;
- Picamilon;
- Azafen;
- Alprazolam;
- Hydroxyzine;
- Mebicar;
- Fluoketine.
Imported analogues of Atarks and their prices are presented in the table
| Name | average cost | Manufacturer country |
| Atarax | 310 | Belgium |
| Eglonil | 210-356 | France |
| Adaptol | 715 | Latvia |
| Strezam | 560-910 | France |
| Zoloft | 490-930 | Germany |
| Phenibut | 110 | Republic of Belarus |
| Grandaxin | 370-840 | Hungary |
| Clonazepam | 170 | Poland |
| Trittico | 740 | Italy |
| Elycea | 1150 | Slovenia |
| Sonapax | 280-450 | Poland |
| Donormil | 135-370 | France |
| Fevarin | 860-2300 | France |
| Paxil | 612 | Romania |
| Arcoxia | 520-1300 | Spain |
| Cipralex | 1100 | Denmark |
| Spitomin | 800 | Hungary |
Often patients are faced with the high cost of the drug or its absence in the pharmacy, then the question arises what can replace Atarax. The medication should be replaced by the attending physician.
Glycine
Manufacturer: LLC MNPK BIOTIKI, RF
Release form: sublingual tablets
Active ingredient: microencapsulated glycine
Synonyms: Glycised, Glycine Extra
A drug to improve metabolism in brain cells – Glycine. The medicine is an analogue of Atarax without side effects and exhibits a wide spectrum of action. The metabolite is used in the following cases:
- anxiety, tension, irritation;
- low performance;
- memory and attention disorders;
- sleep problems;
- consequences of brain injuries;
- hangover.
Glycine is approved for use in children from birth, pregnant and lactating women.
The main advantages of the analogue are:
- soft action;
- wide range;
- no adverse reactions;
- over-the-counter;
- affordable price.
The drugs differ in composition, mechanism of action, and indications. Atarax and Glycine can be used as part of complex treatment for a quick recovery.
Analogs
Atarax (non-prescription analogues have identical effects) is prescribed by a specialist who will select the optimal dosage taking into account the course of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Phenibut
The drug has similar indications and actions. Phenibut is a mild nootropic and psychostimulant. It differs in composition. A medicine based on the active component of the same name in the form of tablets stimulates the relationship between different parts of the brain and normalizes metabolic processes in tissues.
Phenibut is used as an independent medication in therapy, and as an adjuvant in the complex treatment of the consequences of stroke, intoxication, brain injuries and various mental and neurotic disorders.
Phenibut
Main indications for use:
- increased anxiety: worry, fear;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- decreased concentration;
- nervous tics and stuttering in children;
- alcohol addiction;
- claustrophobia;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus.
Unlike the original, the substitute is allowed to be used for the treatment of children over 8 years of age.
Taking the drug may cause the following side effects:
- headache;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- heaviness in the stomach, nausea;
- redness or rashes on the skin, itching;
- May be addictive.
If negative reactions occur, it is recommended to additionally consult with a doctor, who will determine whether you should continue taking the drug or whether you should refuse treatment. Like Atarax, Phenibut is not prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Therapy with the drug is not recommended in case of hypersensitivity to the components and the presence of intestinal or stomach ulcers.
Compared to the original, the analogue has fewer contraindications. The drugs have an identical scope of application, but the substitute is more often used in the treatment of anxiety-neurotic and asthenic conditions.
Afobazole
An analogue of therapeutic action based on the active substance fabomotizole. Has an identical release form. The tablets eliminate increased anxiety, improve concentration and memory. The action of the drug is used for mental and neurotic disorders in order to reduce internal tension.
The drug, unlike the original, has wider application.
The analogue is prescribed for the treatment of the following disorders and pathologies:
- problems associated with adaptation;
- arterial hypertension;
- neurasthenia;
- ischemia;
- bronchial asthma;
- arrhythmia.
Afobazole can also be prescribed in complex therapy:
- alcohol addiction;
- sleep disorders;
- consequences of quitting smoking;
- premenstrual syndrome.
The medicine, like Atarax, is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any component. The product contains lactose, therefore, people with intolerance to this substance should not take it. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for the treatment of children, the analogue, like the original, is not prescribed. Compared to Atarax, the substitute has fewer contraindications, so the medicine has wider application.
Selank
The substitute has a similar effect. It differs in the form of release. Nasal drops based on the active substance threonyl-lysyl-prolyl-arginyl-prolyl-glycyl-proline-diacetate reduce or completely eliminate nervous tension, increased anxiety and the effects of stress. Silank effectively combats psycho-emotional stress that provokes stress.
The analogue, like Atarax, has the following effects:
- eliminates symptoms of anxiety, depression, apathy and asthenia;
- has a positive effect on learning processes: memorization, the ability to analyze and reproduce received information;
- increases concentration;
- normalizes psychomotor reactions;
- eliminates emotional overstrain during stress;
- simulates adaptive behavior in order to achieve results.
The drug does not cause drowsiness, withdrawal syndrome or addiction.
The analogue is indicated for use in the presence of the following pathologies and conditions:
- increased anxiety;
- panic attacks
- asthenia;
- neurasthenia;
- adaptation disorders;
- insomnia;
- lack of self-confidence and communication;
- stress disorders.
The substitute has similar contraindications. The drug is not prescribed for intolerance to the components, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for patients under the age of majority.
Tenoten
The substitute in the form of lozenges has identical indications. The drug has a calming, stress-protective, anti-anxiety, anti-amnestic, antidepressant, and anti-asthenic effect. At the same time, it does not provoke a hypnogenic and muscle relaxant effect. Increases resistance to psycho-emotional stress.
The substitute has similar indications for use:
- psychosomatic pathologies, neurotic conditions;
- disorders due to stress, accompanied by excessive irritability, anxiety, nervous tension and autonomic reactions;
- organic lesions of the central nervous system of moderate severity, including dyscirculatory and traumatic nature with emotional instability, autonomic disorders, memory loss and irritability.
Tenoten
The drugs also have similar contraindications. They are not prescribed for individual hypersensitivity to components and for patients under the age of majority.
loophole
Atarax (non-prescription analogues differ in composition) has substitutes according to indications and action. Lazeya in the form of herbal soft capsules based on Silexan lavender oil is one such medicine.
The medication has a similar effect: relaxing, anxiolytic and antidepressant. Lazeya safely and effectively eliminates the symptoms of increased anxiety, unmotivated worry and sleep disturbances provoked by psycho-emotional disorders.
The drug is used for symptomatic treatment of increased anxiety, irritability, and nervous tension of any severity.
Taking the drug may cause the following side effects:
- disorders of the digestive system (most often in the form of belching);
- allergic reactions on the skin: rashes, itching and redness.
Both drugs are contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components. However, in comparison with the original, the analogue is not recommended for use in cases of liver dysfunction.
Novo-Passit
The natural drug Novo-Passit based on extracts of medicinal plants is similar in action. Like Atarax, the substitute has a sedative effect. Compared to the original, the drug is absolutely safe, therefore it has a wider range of applications.
The drug is prescribed for the treatment and prevention of the following pathologies and conditions:
- neurasthenia and neurotic reactions, accompanied by absent-mindedness, short temper, chronic fatigue, increased anxiety;
- constant psycho-emotional stress;
- mild forms of insomnia;
- headache that occurs due to nervous tension;
- migraine;
- symptomatic treatment of menopausal syndrome and neurocirculatory dystonia;
- functional pathologies of the digestive system;
- dermatoses accompanied by constant severe itching: urticaria, seborrheic and atopic eczema.
The analogue has similar contraindications. In addition to individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug and children under 18 years of age, Novo-Passit is contraindicated if there is a history of epilepsy and myasthenia gravis.
The use of a substitute during pregnancy and lactation is possible only if there is an urgent need and after consultation with a doctor.
Persen
Persen is a herbal medicine that is similar in action and purpose. Used for conditions caused by stress: increased excitability, nervous tension and sleep disorders. The substitute has a calming effect, relieves tension, and eliminates insomnia.
Taking the drug may cause the following side effects:
- nausea, abdominal cramps;
- heartburn.
If other negative reactions occur, you should consult a doctor, who will determine whether it is worth continuing therapy with this drug or whether it is necessary to select an analogue.
Persen has similar contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to any component of the drug;
- the period of bearing a child and breastfeeding.
In addition, the drug is not prescribed for:
- cholelithiasis and inflammation of the biliary tract;
- cholecystitis, cholangitis.
In comparison with the original, the analogue can be used to treat children starting from the age of 12 years.
Like Atarax, the substitute contains lactase, so it is not prescribed to patients with galactose intolerance.
Atarax or Hydroxyzine – which is better, what is the difference
Manufacturer: Pharmproject, Russian Federation
Release form: film-coated tablets
Active ingredient: hydroxyzine hydrochloride
Synonyms: Hydroxyzine Canon, Atarax
Hydroxyzine is a Russian synonym for Atarax. The drugs have the same effect and indications. The substitute is used in children from 3 years of age and adults to eliminate attacks of anxiety, tension, during preparation for operations, and for allergic reactions. Adults are prescribed 50–100 mg at bedtime; for children, the dosage is calculated based on body weight.
Advantages of Atarax compared to its analogue:
- original drug (availability of studies);
- high efficiency;
- use in children from one year of age;
- positive reviews from doctors.
The medications are identical in composition and action. The neurologist decides which remedy to give preference to.
Comparison of safety of Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
At the same time, in Atarax it is quite similar to the Hydroxyzine canon. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others. When assessing metabolism in Atarax, as well as in the Hydroxyzine canon, we look at which organ is the metabolizing organ and how critical the effect on it is.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Atarax does not have any risks when used, just like Canon Hydroxyzine.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon.
Atarax or Teraligen – which is better for anxiety and insomnia
Manufacturer: Valenta Pharmaceuticals, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: alimemazine
Teraligen is a tranquilizer drug. The analogue of Atarax is produced in simple and prolonged-release tablets, ampoules. Teraligen exhibits a mild sedative and anti-anxiety effect. The drug is prescribed as part of complex treatment for the following conditions:
- problems sleeping, insomnia;
- anxiety disorders;
- severe stress and acute reaction to it;
- behavioral disorders, dementia;
- neurasthenia and other neurological manifestations;
- allergies and itching.
The analogue is used in adults 1–2 times a day in the required dosage.
The drugs have a similar effect, but Teraligen has a wider range of indications.
Comparison of side effects of Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Atarax's state of adverse events is almost the same as that of Canon Hydroxyzine. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Atarax are similar to the Hydroxyzine canon: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
Atarax or Phenibut – which is better and more effective for adults
Manufacturer: Belmedpreparaty, Republic of Belarus
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: aminophenylbutyric acid
Synonyms: Noofen, Anvifen
An analogue of the drug Atarax is Phenibut, which belongs to the nootropics. The medication contains aminophenylbutyric acid. The active substance exhibits anti-anxiety, anticonvulsant effects, improves blood supply and the functioning of brain cells.
The analogue is used in adults and children over 8 years of age for neurasthenia, anxiety, stuttering, tics, and sleep problems.
Main benefits of Phenibut:
- prolonged action;
- effectiveness for insomnia;
- average cost;
- good reviews from pediatricians.
Atarax and the analog have the same effect on the central nervous system and do not cause addiction or withdrawal symptoms. The choice of drug is the prerogative of the doctor.
Basic instructions
Atarax (non-prescription analogues have identical effects) is prescribed for the treatment and elimination of signs of neurotic and mental disorders and diseases. The selection of the drug and its dosage is carried out by the attending physician, taking into account the clinical picture of the pathology, the nature of the course, the severity of symptoms and the individual reaction of the body to the active component of Atarax.
When treating patients with liver or kidney failure, as well as elderly people, it may be necessary to adjust (reduce) the dose.
Due to the fact that Atarax is a drug that acts on the central nervous system, in some cases it is able to suppress paradoxical stimulation or certain functions.
Taking the medication may cause adverse reactions from:
- Heart and blood vessels. In rare cases, a decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate are observed.
- Vision. Accommodation disorder, decreased vision clarity.
- Gastrointestinal tract. Feeling of dryness in the mouth. Rarely, nausea, vomiting, and impaired intestinal motility occur, which leads to chronic constipation.
- Immunity. Hypersensitivity, in rare cases anaphylactic shock may develop.
- Urinary system. Rarely there is a delay in urine output.
- Respiratory organs. Suffocation and bronchospasm are extremely rare.
- Skin. Rashes and itching may occur. Swelling rarely occurs.
- Nervous system. Headache, dizziness, sleep disturbances, rarely – convulsions.
In rare cases, mental disorders in the form of hallucinations, disorientation and agitation may occur. Common disorders include increased fatigue, high temperature and weakness.
During treatment with Atarax, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly contraindicated, since ethyl alcohol enhances the effect of the active component and provokes the development of adverse reactions. This is due to depression of the central nervous system. The state of intoxication intensifies, hypotension develops, and allergic reactions occur. However, there is a high probability of severe intoxication of the body, which can lead to death.
Atarax or Grandaxin - which is better and stronger, what is the difference
Manufacturer: Egis, Hungary
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tofisopam
Grandaxin is a foreign analogue of Atarax. The medication belongs to the group of anxiolytic drugs and is used for neuroses, anxiety, apathy, obsessions, and chronic depression. Numerous reviews from gynecologists confirm the effectiveness of the analogue for premenstrual and menopausal syndromes.
Differences of Grandaxin:
- stronger action;
- effectiveness occurs on day 2;
- Can be used in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Medicines belong to the same pharmaceutical group, have identical effects on the body and are not addictive.
ANTIHISTAMINES: from diphenhydramine to Telfast
Historically, the term “antihistamines” refers to drugs that block H1-histamine receptors, and drugs that act on H2-histamine receptors (cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, etc.) are called H2-histamine blockers. The former are used to treat allergic diseases, the latter are used as antisecretory agents.
Histamine, this most important mediator of various physiological and pathological processes in the body, was chemically synthesized in 1907. Subsequently, it was isolated from animal and human tissues (Windaus A., Vogt W.). Even later, its functions were determined: gastric secretion, neurotransmitter function in the central nervous system, allergic reactions, inflammation, etc. Almost 20 years later, in 1936, the first substances with antihistamine activity were created (Bovet D., Staub A.). And already in the 60s, the heterogeneity of histamine receptors in the body was proven and three of their subtypes were identified: H1, H2 and H3, differing in structure, localization and physiological effects that occur during their activation and blockade. From this time on, an active period of synthesis and clinical testing of various antihistamines began.
Numerous studies have shown that histamine, acting on receptors in the respiratory system, eyes and skin, causes characteristic allergy symptoms, and antihistamines that selectively block H1-type receptors are able to prevent and relieve them.
Most of the antihistamines used have a number of specific pharmacological properties that characterize them as a separate group. These include the following effects: antipruritic, decongestant, antispastic, anticholinergic, antiserotonin, sedative and local anesthetic, as well as prevention of histamine-induced bronchospasm. Some of them are caused not by histamine blockade, but by structural features.
Antihistamines block the effect of histamine on H1 receptors through the mechanism of competitive inhibition, and their affinity for these receptors is much lower than that of histamine. Therefore, these drugs are not able to displace the histamine bound to the receptor; they only block unoccupied or released receptors. Accordingly, H1 blockers are most effective in preventing immediate allergic reactions, and in the event of a developed reaction, they prevent the release of new portions of histamine.
According to their chemical structure, most of them belong to fat-soluble amines, which have a similar structure. The core (R1) is represented by an aromatic and/or heterocyclic group and is linked via a nitrogen, oxygen or carbon molecule (X) to the amino group. The core determines the severity of antihistamine activity and some of the properties of the substance. Knowing its composition can predict the strength of the drug and its effects, such as its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
There are several classifications of antihistamines, although none of them is generally accepted. According to one of the most popular classifications, antihistamines, based on the time of creation, are divided into first and second generation drugs. First generation drugs are also commonly called sedatives (based on the dominant side effect) in contrast to non-sedating second generation drugs. Currently, it is customary to distinguish the third generation: it includes fundamentally new drugs - active metabolites, which, in addition to the highest antihistamine activity, exhibit the absence of a sedative effect and the cardiotoxic effect characteristic of second-generation drugs (see table).
In addition, according to their chemical structure (depending on the X-bond), antihistamines are divided into several groups (ethanolamines, ethylenediamines, alkylamines, derivatives of alphacarboline, quinuclidine, phenothiazine, piperazine and piperidine).
First generation antihistamines (sedatives). All of them are highly soluble in fats and, in addition to H1-histamine, also block cholinergic, muscarinic and serotonin receptors. As competitive blockers, they reversibly bind to H1 receptors, which necessitates the use of fairly high doses. The following pharmacological properties are most characteristic of them.
- The sedative effect is determined by the fact that most first-generation antihistamines, easily soluble in lipids, penetrate well through the blood-brain barrier and bind to H1 receptors in the brain. Perhaps their sedative effect consists of blocking central serotonin and acetylcholine receptors. The degree of manifestation of the first generation sedative effect varies between drugs and in different patients from moderate to severe and increases when combined with alcohol and psychotropic drugs. Some of them are used as sleeping pills (doxylamine). Rarely, instead of sedation, psychomotor agitation occurs (more often in moderate therapeutic doses in children and in high toxic doses in adults). Because of the sedative effect, most medications should not be used while performing tasks that require alertness. All first-generation drugs potentiate the effect of sedatives and hypnotics, narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics, monoamine oxidase inhibitors and alcohol.
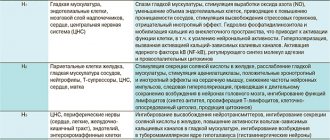
- The anxiolytic effect characteristic of hydroxyzine may be due to suppression of activity in certain areas of the subcortical region of the central nervous system.
- Atropine-like reactions associated with the anticholinergic properties of drugs are most typical for ethanolamines and ethylenediamines. Manifested by dry mouth and nasopharynx, urinary retention, constipation, tachycardia and visual impairment. These properties ensure the effectiveness of the drugs under discussion for non-allergic rhinitis. At the same time, they can increase obstruction in bronchial asthma (due to an increase in sputum viscosity), cause exacerbation of glaucoma and lead to bladder outlet obstruction in prostate adenoma, etc.
- The antiemetic and anti-motion sickness effect is also likely associated with the central anticholinergic effect of the drugs. Some antihistamines (diphenhydramine, promethazine, cyclizine, meclizine) reduce the stimulation of vestibular receptors and inhibit the function of the labyrinth, and therefore can be used for movement disorders.
- A number of H1-histamine blockers reduce the symptoms of parkinsonism, which is due to the central inhibition of the effects of acetylcholine.
- The antitussive effect is most characteristic of diphenhydramine; it is realized through a direct effect on the cough center in the medulla oblongata.
- The antiserotonin effect, primarily characteristic of cyproheptadine, determines its use for migraine.
- The α1-blocking effect with peripheral vasodilation, especially associated with phenothiazine antihistamines, may lead to a transient decrease in blood pressure in sensitive individuals.
- A local anesthetic (cocaine-like) effect is characteristic of most antihistamines (occurs due to a decrease in membrane permeability to sodium ions). Diphenhydramine and promethazine are stronger local anesthetics than novocaine. At the same time, they have systemic quinidine-like effects, manifested by prolongation of the refractory phase and the development of ventricular tachycardia.
- Tachyphylaxis: a decrease in antihistamine activity with long-term use, confirming the need to alternate medications every 2-3 weeks.
- It should be noted that first-generation antihistamines differ from the second generation in their short duration of action with a relatively rapid onset of clinical effect. Many of them are available in parenteral forms. All of the above, as well as low cost, determine the widespread use of antihistamines today.
Moreover, many of the qualities discussed allowed the “old” antihistamines to occupy their niche in the treatment of certain pathologies (migraine, sleep disorders, extrapyramidal disorders, anxiety, motion sickness, etc.) not related to allergies. Many first-generation antihistamines are included in combination medications used for colds, as sedatives, hypnotics and other components.
The most commonly used are chloropyramine, diphenhydramine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, promethazine, fenkarol and hydroxyzine.
Chloropyramine (suprastin) is one of the most widely used sedative antihistamines. It has significant antihistamine activity, peripheral anticholinergic and moderate antispasmodic effects. Effective in most cases for the treatment of seasonal and year-round allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, Quincke's edema, urticaria, atopic dermatitis, eczema, itching of various etiologies; in parenteral form - for the treatment of acute allergic conditions requiring emergency care. Provides a wide range of therapeutic doses used. It does not accumulate in the blood serum, therefore it does not cause an overdose with long-term use. Suprastin is characterized by a rapid onset of effect and short duration (including side effects). In this case, chloropyramine can be combined with non-sedating H1-blockers in order to increase the duration of the antiallergic effect. Suprastin is currently one of the best-selling antihistamines in Russia. This is objectively due to the proven high efficiency, controllability of its clinical effect, the availability of various dosage forms, including injectable ones, and low cost.
Diphenhydramine , best known in our country as diphenhydramine, is one of the first synthesized H1 blockers. It has fairly high antihistamine activity and reduces the severity of allergic and pseudo-allergic reactions. Due to its significant anticholinergic effect, it has an antitussive, antiemetic effect and at the same time causes dryness of the mucous membranes and urinary retention. Due to its lipophilicity, diphenhydramine produces pronounced sedation and can be used as a hypnotic. It has a significant local anesthetic effect, as a result of which it is sometimes used as an alternative in cases of intolerance to novocaine and lidocaine. Diphenhydramine is available in various dosage forms, including for parenteral use, which has determined its widespread use in emergency therapy. However, a significant range of side effects, unpredictability of consequences and effects on the central nervous system require increased attention when using it and, if possible, the use of alternative means.
Clemastine (tavegil) is a highly effective antihistamine, similar in action to diphenhydramine. It has high anticholinergic activity, but penetrates the blood-brain barrier to a lesser extent. It also exists in injection form, which can be used as an additional remedy for anaphylactic shock and angioedema, for the prevention and treatment of allergic and pseudoallergic reactions. However, hypersensitivity to clemastine and other antihistamines with a similar chemical structure is known.
Cyproheptadine (peritol), along with an antihistamine, has a significant antiserotonin effect. In this regard, it is mainly used for some forms of migraine, dumping syndrome, as an appetite enhancer, and for anorexia of various origins. It is the drug of choice for cold urticaria.
Promethazine (pipolfen) - a pronounced effect on the central nervous system determined its use in Meniere's syndrome, chorea, encephalitis, sea and air sickness, as an antiemetic. In anesthesiology, promethazine is used as a component of lytic mixtures to potentiate anesthesia.
Quifenadine (fenkarol) has less antihistamine activity than diphenhydramine, but is also characterized by less penetration through the blood-brain barrier, which determines the lower severity of its sedative properties. In addition, fenkarol not only blocks histamine H1 receptors, but also reduces the content of histamine in tissues. May be used in cases of developing tolerance to other sedating antihistamines.
Hydroxyzine (atarax) - despite the existing antihistamine activity, it is not used as an antiallergic agent. It is used as an anxiolytic, sedative, muscle relaxant and antipruritic agent.
Thus, first-generation antihistamines, which affect both H1 and other receptors (serotonin, central and peripheral cholinergic receptors, α-adrenergic receptors), have different effects, which has determined their use in a variety of conditions. But the severity of side effects does not allow them to be considered as the first choice drugs in the treatment of allergic diseases. The experience gained from their use made it possible to develop unidirectional drugs - the second generation of antihistamines.
Second generation antihistamines (non-sedating). Unlike the previous generation, they have almost no sedative and anticholinergic effects, but are distinguished by their selectivity of action on H1 receptors. However, they exhibit a cardiotoxic effect to varying degrees.
The most common properties for them are the following.
- High specificity and high affinity for H1 receptors with no effect on choline and serotonin receptors.
- Rapid onset of clinical effect and duration of action. Prolongation can be achieved due to high protein binding, accumulation of the drug and its metabolites in the body and slow elimination.
- Minimal sedative effect when using drugs in therapeutic doses. It is explained by weak passage of the blood-brain barrier due to the structural features of these drugs. Some particularly sensitive individuals may experience moderate drowsiness, which is rarely a reason to discontinue the drug.
- Absence of tachyphylaxis with long-term use.
- The ability to block potassium channels in the heart muscle, which is associated with prolongation of the QT interval and cardiac arrhythmias. The risk of this side effect increases when antihistamines are combined with antifungals (ketoconazole and intraconazole), macrolides (erythromycin and clarithromycin), antidepressants (fluoxetine, sertraline and paroxetine), when drinking grapefruit juice, as well as in patients with severe liver dysfunction.
- There are no parenteral forms, but some of them (azelastine, levocabastine, bamipin) are available in forms for topical use.
Below are second generation antihistamines with their most characteristic properties.
Terfenadine is the first antihistamine without an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system. Its creation in 1977 was the result of a study of both the types of histamine receptors and the features of the structure and action of existing H1 blockers, and marked the beginning of the development of a new generation of antihistamines. Currently, terfenadine is used less and less, which is associated with an increased ability to cause fatal arrhythmias associated with prolongation of the QT interval (torsade de pointes).
Astemizole is one of the longest-acting drugs in the group (the half-life of its active metabolite is up to 20 days). It is characterized by irreversible binding to H1 receptors. It has virtually no sedative effect and does not interact with alcohol. Since astemizole has a delayed effect on the course of the disease, its use in acute processes is inappropriate, but may be justified in chronic allergic diseases. Since the drug tends to accumulate in the body, the risk of developing serious heart rhythm disturbances, sometimes fatal, increases. Due to these dangerous side effects, the sale of astemizole in the United States and some other countries has been suspended.
Akrivastine (Semprex) is a drug with high antihistamine activity with minimally expressed sedative and anticholinergic effects. A feature of its pharmacokinetics is its low level of metabolism and lack of accumulation. Acrivastine is preferable in cases where there is no need for constant antiallergic treatment due to the rapid achievement of effect and short-term action, which allows the use of a flexible dosing regimen.
Dimethenden (fenistil) is closest to first-generation antihistamines, but differs from them in having a significantly less pronounced sedative and muscarinic effect, higher antiallergic activity and duration of action.
Loratadine (Claritin) is one of the most widely purchased second-generation drugs, which is understandable and logical. Its antihistamine activity is higher than that of astemizole and terfenadine, due to greater binding strength to peripheral H1 receptors. The drug has no sedative effect and does not potentiate the effect of alcohol. In addition, loratadine practically does not interact with other drugs and does not have a cardiotoxic effect.
The following antihistamines are topical drugs and are intended to relieve local manifestations of allergies.
Levocabastine (Histimet) is used as eye drops to treat histamine-dependent allergic conjunctivitis or as a spray for allergic rhinitis. When applied topically, it enters the systemic bloodstream in small quantities and does not have undesirable effects on the central nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Azelastine (allergodil) is a highly effective treatment for allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis. Used as a nasal spray and eye drops, azelastine has virtually no systemic effect.
Another topical antihistamine, bamipin (Soventol) in the form of a gel, is intended for use in allergic skin lesions accompanied by itching, insect bites, jellyfish burns, frostbite, sunburn, and mild thermal burns.
Third generation antihistamines (metabolites). Their fundamental difference is that they are active metabolites of previous generation antihistamines. Their main feature is their inability to influence the QT interval. Currently there are two drugs available: cetirizine and fexofenadine.
Cetirizine (Zyrtec) is a highly selective peripheral H1 receptor antagonist. It is an active metabolite of hydroxyzine, which has a much less pronounced sedative effect. Cetirizine is almost not metabolized in the body, and the rate of its elimination depends on renal function. Its characteristic feature is its high ability to penetrate the skin and, accordingly, its effectiveness in treating skin manifestations of allergies. Cetirizine, neither experimentally nor in the clinic, showed any arrhythmogenic effect on the heart, which predetermined the field of practical use of metabolite drugs and determined the creation of a new drug - fexofenadine.
Fexofenadine (Telfast) is the active metabolite of terfenadine. Fexofenadine does not undergo transformations in the body and its kinetics does not change with impaired liver and kidney function. It does not enter into any drug interactions, does not have a sedative effect and does not affect psychomotor activity. In this regard, the drug is approved for use by persons whose activities require increased attention. A study of the effect of fexofenadine on the QT value showed, both experimentally and in the clinic, a complete absence of cardiotropic effects when using high doses and long-term use. Along with maximum safety, this drug demonstrates the ability to relieve symptoms in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria. Thus, the pharmacokinetic features, safety profile and high clinical efficacy make fexofenadine the most promising of the antihistamines at present.
So, in the doctor’s arsenal there is a sufficient number of antihistamines with various properties.
It must be remembered that they provide only symptomatic relief for allergies. In addition, depending on the specific situation, you can use both different drugs and their varied forms. It is also important for the doctor to remember the safety of antihistamines. Three generations of antihistamines (trade names in parentheses)
| I generation | II generation | III generation |
|
|
|
Return
Atarax or Phenazepam – which is better for anxiety?
Manufacturer: Biosynthesis, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets, injection solution
Active ingredient: bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine
Synonyms: Elzepam
Phenazepam is a prescription analogue. The medicine has a complex effect on the human body. The substitute exhibits a hypnotic, sedative, anticonvulsant effect, and eliminates muscle tone. Phenazepam is effective for the following disorders:
- irritability, tension, anxiety;
- insomnia;
- obsessions, panic attacks, schizophrenia;
- alcohol addiction.
In addition, the analogue is used as a sedative before operations and other medical procedures.
Phenazepam has a stronger effect on the body and can be addictive. Which medicine is preferred depends on the severity of the disease, accompanying symptoms and the age of the patient.
Atarax or Afobazol – which is better?
Manufacturer: Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: fabomotizol
An over-the-counter analogue with a long-lasting effect is Afobazol. The medication exhibits an anti-anxiety effect and restores damaged nerve cell receptors. The substitute eliminates stress, tension, and insomnia. Afobazole is used as part of complex therapy for PMS, alcoholism, and smoking cessation. The medicine is prescribed for adults, 1 tablet three times a day.
If we compare the analogue and Atarax, the first drug has a gentler effect on the body, has no adverse reactions and can be used while driving.
Atarax or Adaptol – which is better?
Manufacturer: Olainfarm, Latvia
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tetramethyltetraazabicyclooctanedione
Adaptol is an analogue of Atarax, which requires a prescription. The drug eliminates anxiety, stress, fear and anxiety. Adaptol does not cause a feeling of euphoria, does not impair coordination of movements and mental performance. The medication enhances the effect of sleeping pills. The drug can be used during the working day, before an exam or an important event.
Adaptol and Atarax have a similar effect on the body, but they differ in composition, indications and contraindications. Which medicine is best depends on the condition and accompanying manifestations.
Price of funds
Atarax (analogues without prescriptions can be purchased at any pharmacy) should be used only after consultation with a specialist who will select the optimal dosage taking into account the general condition of the patient.
| Name of the drug | Cost, rub.) |
| Atarax | 280 – 380 |
| Phenibut | 150 – 750 |
| Afobazole | 300 – 650 |
| Selank | 520 – 600 |
| Tenoten | 250 – 300 |
| loophole | 1000 – 1100 |
| Novo-passit | 210 – 400 |
| Persen | 240 — 460 |
You can purchase Atarax only with a prescription from your doctor. The analogues presented above are sold without prescriptions. Despite this, it is recommended to consult a specialist before using any medication.
Atarax or Stresam - which is better?
Manufacturer: Biocodex, France
Release form: capsules
Active ingredient: etifoxine hydrochloride
Stresam is an imported analogue of Atarax 25 mg. The drug is a tranquilizer, has a selective effect on the body with a mild sedative effect. Stresam is used for increased tension, excessive irritability, and anxiety.
Medicine occupies a special place in gynecology. The analogue is used in the complex treatment of menopause, menopausal syndrome, and PMS. Strezam is taken 50 mg 3 times a day. Duration of treatment is 4–6 weeks. A noticeable effect occurs after 10–14 days.
Atarax or Amitriptyline – which is better?
Manufacturer: OZONE, RF
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: amitriptyline hydrochloride
An analogue of Atarax that is cheaper than other drugs is Amitriptyline. The medicine is an antidepressant. The medicine has a wide spectrum of action. Amitriptyline eliminates anxiety disorders and has a sedative and analgesic effect. The substitute is used for the following pathologies:
- depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- psychosis, schizophrenia;
- bed-wetting;
- pain syndrome in chronic diseases.
Amitriptyline is prescribed as part of complex therapy for problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
The attending physician decides which medication to choose.
Atarax or Mebicar – which is better?
Manufacturer: Tatkhimpharmpreparaty, Russian Federation
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: tetramethyltetraazabicyclooctanedione
Synonyms: Adaptol
The anxiolytic drug Mebicar has a nootropic effect and improves the supply of nutrients to the body. The analogue eliminates tension, excitement, anxiety, but does not cause euphoria. Indications for taking Mebicar:
- neurotic disorders;
- psycho-emotional disorders;
- alcoholism, nicotine addiction.
The analogue is used as part of complex treatment of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.
The daily dosage of the substitute is 3–10 grams.
Atarax and Mebikar differ in composition, action, indications and limitations. Which drug is best depends on the severity of the disease and symptoms.
Comparison of the effectiveness of Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon
The effectiveness of Atarax is quite similar to the Hydroxyzine canon - this means that the ability of the medicinal substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Atarax is more pronounced, then using Hydroxyzine canon, even in large doses, will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy is an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action; Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon are approximately the same. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Atarax or Fluoxetine – which is better?
Manufacturer: Biocom, Russian Federation
Release form: capsules
Active ingredient: fluoxetine
Synonyms: Fluoxetine Canon
Fluoxetine and Atarax belong to different pharmaceutical groups and differ in action. The analogue is a receptor antagonist, reduces feelings of fear, anxiety, irritation, and improves mood. Fluoxetine is prescribed for depression of various natures, bulimia, and psycho-emotional disorders. The medication is taken 1 capsule per day, which must be swallowed whole.
The drugs differ in their active substance, principle of action and indications. A neurologist or psychiatrist decides which medication to give preference to.
Comparison of addiction in Atarax and Hydroxyzine canon
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “o syndrome” in Atarax is quite similar to the similar values in the Hydroxyzine canon. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, in Atarax the meaning of the “syndrome” is quite small, however, just like in the Hydroxyzine canon.