Articles › RLS - register of medicines and drugs of Rosminzdrav registered in Russia
To control and regulate the use of medicines in Russia, the State Register of Medicines of Rosminzdrav or GRLS . A list of patented drugs acceptable for sale and use in the pharmacy network and the system of medical institutions in the country that have undergone laboratory research and clinical trials.
- Official website of the RF GRLS register
- What is the difference between GRLS and radar
- Limit prices
- Clinical researches
- Certification of drug manufacturers
- Accreditation of medical organizations
- Questions and answers
The creation of a state register of drugs has several goals:
- familiarization of the medical community with medicines approved for use in the country;
- legal basis for wholesale and retail sales or use of drugs in the treatment and prevention of various diseases on the territory of the Russian state;
- confirmation of research, study of the declared properties and qualities of the drug;
- orders, instructions, recommendations for use, identification and specification of the properties of drugs;
- justification for those controlling the use in medical institutions and the sale of drugs in the wholesale and retail network and organizations.
The GRLS of the Ministry of Health contains a list of domestic and foreign drugs with their international names and dates of registration or deregistration in the Russian Federation.
Official website of the RF GRLS register
For wide access to the Unified Russian Federal Register of Medicines, the official website of the Ministry of Health has been created, which reflects a complete database of registered manufacturers of medicines, their authorized persons, and the medicines themselves.
On the pages of the Rosreestr Internet portal you can find lists:
- medicines and their manufacturers;
- medical organizations;
- authorized persons;
- approved clinical trials;
- principal investigators;
- maximum selling prices.
As well as documents, letters, orders related to various operations in the field of production, distribution and use of drugs.
Official website of the register of medicines of the Russian Federation GRLS: grls.rosminzdrav.ru.
On the website you can submit an application for registration or certification of authorized persons. Find information on any drug or product approved for use in the Russian Federation.
Registration is required to enter the site and access the GRLS database.
Technical support telephone numbers (from 9:00 to 18:00 Moscow time), +7 (495) 105-99-77.
Information about the EpiVacCorona vaccine against COVID-19 from an RCT
Help: All screenshots presented in this publication were made from the site grls.rosminzdrav.ru. A full link to the source of information is provided at the end of the publication.
EpiVacCorona-N.
RCT No. 197. The date of creation of this vaccine is April 8 of this year. On the same day, her trials began. The end of testing is September 30 of this year. That is, it is currently undergoing clinical trials (CT). Moreover, this is only phase I-II of the CI.
EpiVacCorona
RCT No. 644. This EpiVacCorona clinical trial was registered on November 18, 2021. It was on this day that her clinical trials began. The end date for clinical trials is August 31, 2021. These are phases III-IV of the CI and at the moment, as we see, the CIs are continuing (!). I would like to note that many Russians who decided to get vaccinated against COVID-19 were vaccinated with this particular vaccine. What happens? Did the people who were vaccinated with EpiVacCorona act as experimental animals? Or am I misperceiving information from RCTs?
RCT No. 639. Their third phase ended on May 15 of this year. Here I am embarrassed to ask: “The third phase of the study has ended in humans?”
RCT No. 376. These are clinical trials of EpiVacCorona at stages I-II, which will end only on December 30, 2021 (!). How so? People have already been vaccinated with EpiVacCorona (!).
For reference: The RCT also contains information about other vaccines against COVID-19, but no matter how hard I tried, I couldn’t find them, but there is information about them there...
What is the difference between GRLS and radar
The State Register of Medicines is the official publication of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. All the products listed in it are registered and recommended for use by the Russian Ministry of Health. GRLS contains orders for medical use, regulatory documents, explanatory letters, registration data on unique numbers, pharmacopoeial articles. GRLS is the basic basis for systematization and control in the field of sales and use of medicines.
The Register of Medicines is a popular scientific online publication of a commercial nature. In addition to the list of existing medications, it contains a lot of educational, explanatory, guiding and recommendatory information. Here you can learn about new products in the field of medicine and pharmacology from around the world. Get acquainted with drugs used in different countries, but not registered in Russia. On the RLS pages you can find instructions and descriptions of drugs, prices for drugs in different regions of the country. Information about government and commercial medical organizations and medical institutions is posted here.
Register of medicines
The state register of medicines includes both foreign and Russian drugs, preventive and diagnostic drugs, which are registered by the Russian Ministry of Health.
The State Register is issued officially by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Published and maintained strictly in accordance with the Law on Medicines on the website https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru.
The official documents of the Russian Ministry of Health, in accordance with which the Register is compiled, are as follows:
- — registration certificates;
- — regulatory documents for foreign medicines;
- — orders to authorize medical use;
- — pharmacopoeial and temporary pharmacopoeial articles;
- — certificate of registration of a unique number.
How to work with the register of medicines?
Let's try to figure out how to work with the registry and how to find the right medicine if you have never opened this site. We go to the site through the search bar of your browser. We are recruiting: State Register of Medicines. We immediately get to the main page, on which information about the safety of medicines is first displayed.
The safety of medicines is those medicines whose state registration has changed : either cancelled, or renewed, or suspended. If you need to print out detailed information about the state registration of a drug, it is presented in PDF file format. There, when you open the file, you can find out the reason for the changes in registration .
Further on the page, current news and documents open where you can familiarize yourself with orders on the certification of authorized persons of manufacturers of medicinal products for medical use. Also, all orders are readable, transparent and presented in PDF files for printing.
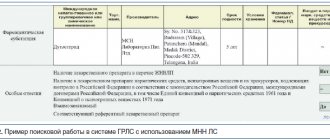
Let's proceed directly to the register of medicines itself. The search is in the upper right corner of the page. Click on the text itself and an advanced search opens. The first line is the registration certificate number.
This search is more useful for pharmacy and medical organizations that work with suppliers and can request the necessary identification.
And citizens who just want to check whether the drug they purchased at the pharmacy is registered will need to search by Trade Name. This is the name that is written in large letters on the box, bottle, tube, etc., depending on the form of release of the purchased drug. We enter the name and the options are displayed immediately below, select the one you need.
Then you can simply click the Find button. But if there are a lot of drugs, then it will take too long to review the found options. Therefore, it is better to introduce the dosage form; this is the easiest thing for a person without knowledge of pharmacy. The dosage form is what the drug is produced in: tablets, solution, powders, aerosol, etc. Then the search options will decrease.
INN grouped (chemical) name is the chemical name of the substance itself. It is written mainly in small print under the trade name, or in the composition. This is the active substance itself, the name of which may coincide with the trade name.
Okay, that's sorted out. Next item in the search: Name of the marketing authorization holder. This point is also for pharmacies and hospitals that work with wholesale suppliers, and these documents are provided to them along with the medications. The following are the items: Manufacturer and Country. You can also read them on the packaging you bought and type them into a line. You can skip it.
When all the information found on the package has been entered into the search columns, you can click the Find button. The number of lines with drugs found is immediately displayed. The more information was entered, the smaller and more accurate the list will be. We are looking for the column: Date of state registration (it is highlighted in pale green) and through the column from it the Date of re-registration of the RU. We look at the dates and look at the Status column. The letter D means the drug has a valid registration certificate and has passed all the necessary tests.
If the drug is not found, then it is not registered in the state registry and this is a reason to think about the advisability of taking it.
All companies that sell pharmacological drugs always rely on the State Register in their work. Therefore, if a product, in accordance with the registration certificate, is classified as a medicinal product or preparation, obtaining a pharmaceutical activity license is mandatory for wholesale trade of these products.
Lists A and B, a list of vital drugs, PKKN lists, lists of preferential and over-the-counter drugs, all are compiled based on the information presented in the Register. Since the Register contains information about trade and INN drugs, their release forms, dosage, packaging, pharmacological groups, it serves to present the drug and to fully describe it. The register is also used when collecting applications from regions for supplies, when assessing production at enterprises, when selling abroad, and when drawing up the state balance of supply and demand for medicines.
Having understood in more detail how to work with the state register of medicines, it is clear that the information in it is accessible, understandable and transparent for any user. Even a person without special education can find useful information about the relevance of the registration certificate of the drug of interest and have no doubt about taking it.
Limit prices
Regulation of price markups for the wholesale and retail pharmacy system occurs in accordance with the adopted law “On Medicines”, the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On State Regulation of Prices for Medicines”, orders and resolutions adopted at the level of local executive authorities.
Maximum allowable premiums are registered in the list of vital and essential drugs (vital and essential medicines), compiled and approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development. This includes more than 620 names of registered drugs. For all the rest, which is almost 18 thousand items, prices are determined based on the policies of local executive authorities - constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Because of this division, in the process of adjusting maximum markups, there is a significant difference in the cost of drugs in different regions of the country and even between different pharmacies.
Any violation of the procedure for setting prices for drugs established by regulatory documents is regarded as a violation of the law and is punishable by penalties in accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation under the article “Violation of the pricing procedure.”
New generation directories
Readers' questions are answered by the editor-in-chief of the radar reference system, MAI academician G.L. Vyshkovsky
1
1 year ago, medical workers in Russia first became acquainted with the new reference publication “Register of Medicines of Russia” (RLS), which contained information about all medicines registered in Russia. This was a real revolution in the field of pharmaceutical information. After all, many remember that until the early 90s, detailed and objective information about the latest highly effective drugs was practically inaccessible to most doctors. In 1993, thanks to the RLS directory, specialists gained access to detailed, reliable and up-to-date information about medicines.
Years passed. The system of radar reference books grew and developed. The circle of readers expanded. During this period, the RLS publishing house published more than one and a half million copies of reference books, which became guides in the field of pharmaceutical information for doctors and pharmacists.
The editors receive many questions from experts regarding the quality and functionality of reference books. Taking into account the keen interest of doctors and pharmacists in the problems associated with the search for pharmacological information, the RLS publishing house organized a “Direct Line” with readers. Each specialist had the opportunity to call the editorial office by phone, as well as send an email to the editor-in-chief of RLS, Academician of the Moscow Aviation Institute G.L. Vyshkovsky. Below are excerpts from this dialogue.
S. Sharapova (doctor, N. Novgorod):
How does the “Encyclopedia of Medicines” differ from the “Pharmacist” reference book? Which of these books contains more information?
– These directories solve completely different problems. "Encyclopedia of Medicines" is a universal reference book for doctors on pharmacology and pharmacotherapy. It contains detailed descriptions of the latest highly effective medicines announced for supply to the pharmacy chain this year, includes original descriptions of active ingredients, allows for a quick and convenient search for synonyms, analogue drugs (by pharmacological action), etc.
Unlike the Encyclopedia of Medicines, the Pharmacist directory contains the entire range of pharmaceutical products. These include medicines, dietary supplements, medical products, care and hygiene products, medical devices, instruments, reagents, diagnostic tools and other goods sold in pharmacies. In addition, the reference book includes detailed descriptions of more than 1000 active ingredients, as well as a pharmacological index. This year, each Pharmacist reference book includes a free CD containing training programs and a demo version of the Electronic Encyclopedia of Medicines, which can easily be turned into a working one. Thus, “Apothecary” is intended for pharmacists and pharmacists. This is what makes it different.
K. Chernobaev (doctor, Irkutsk):
Why are not all drugs included in the Encyclopedia of Medicines? What should I do if I cannot find information about the drug I am interested in?
Descriptions of some drugs used in medical practice are not included in the reference book due to the fact that the manufacturing companies did not promptly provide information about them to the publishing house this year or are not interested in informing a wide range of doctors about their products. We are talking, in particular, about long-known domestic drugs, the manufacturers of which do not work to promote them, because they are already sold, as well as about drugs from companies aimed at a narrow audience of patients. Some companies are in the process of reorganization, so at the time of preparation of directories they are not able to provide information about themselves. Some drugs are at the stage of re-registration. These drugs are on the market, but information about them is lacking.
If you cannot find the necessary information about a drug in the Encyclopedia of Medicines, we recommend that you refer to the directories “Pharmacist”, “Electronic Encyclopedia of Medicines”, as well as the RLS database located on the website www.rlsnet.ru. Here you will definitely find the answer to your question.
M. Zolotarev (doctor, Chelyabinsk):
The RLS publishing house is not state-owned and is not controlled by the Ministry of Health. In this regard, the question arises about the reliability of the information published in your publications.
– As a rule, radar directories include information about drugs agreed upon with drug manufacturers. In addition, RLS specialists carefully check the data for compliance with state registers and information standards, in particular, the State Register of Medicines, the Federal Register of Dietary Supplements, regulations of the Ministry of Health and other official sources. The publishing house works closely with the Institute of Pharmacology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, the Russian Oncological Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. N.N. Blokhin, State Scientific Center for Social and Forensic Psychiatry named after. V.P. Serbsky and other reputable scientific medical centers. The examination of descriptions of drugs and active substances for various nosological and pharmacological groups is carried out by leading Russian clinical scientists who are members of the RLS scientific and editorial board.
A. Anosov (doctor, Nizhny Tagil, Sverdlovsk region):
Why are the Encyclopedia of Medicines and other RLS reference books published annually? What fundamentally new information can a doctor find in the 11th edition of the Encyclopedia of Medicines?
– Information about medicines posted in the “Encyclopedia of Medicines” is updated every year by approximately 40%. This applies not only to the nomenclature of drugs, but also to the pharmaceutical and medical parts of their descriptions. Terminological dictionaries and classifications are also being modified, and information about manufacturers is being clarified.
Every year, descriptions of more than 100 active substances are revised (or new ones are prepared). For example, during the preparation of the 2004 editions, the descriptions of active substances belonging to such pharmacological groups as anxiolytics, hypnotics, sedatives, psychostimulants, nootropics, cerebral circulation correctors, nitrates and nitrate-like drugs, etc. were significantly expanded and updated. newly prepared and revised descriptions of active substances for the 2004 editions (136 descriptions) can be found on our website www.rlsnet.ru. Among them are generic drugs that are widely used in medical practice, for example, nitrates (nitroglycerin, isosorbide di- and mononitrate), benzodiazepines (diazepam, oxazepam, phenazepam), as well as drugs, many of which are original: antipsychotics (including , olanzapine, zuclopenthixol, flupentixol), antidepressants (citalopram, tianeptine). Thus, professionals interested in obtaining up-to-date drug information typically use the latest edition of the Encyclopedia of Drugs.
P. Ostroumov (doctor, Stavropol):
How do the descriptions of active ingredients differ from the descriptions of drugs?
– The presence of detailed descriptions of active ingredients is the most important advantage of the Encyclopedia of Medicines, so I will try to talk in more detail about the methodology for preparing descriptions.
If, when preparing a description of a drug, information provided by the manufacturer is used (instructions approved by the Ministry of Health), then when preparing a description of the active substance, they are guided by additional authoritative sources of information used by specialists from the Ministry of Health and manufacturing companies. This:
– instructions for the drug containing this active substance;
– domestic publications (for example, a reference book edited by Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Professor M.D. Mashkovsky “Medicines”, “Federal Guidelines for the Use of Medicines”);
– foreign publications (“PDR Generics”, “USP Dispensing Information”, “Rote Liste”);
– articles published both in foreign and domestic periodicals, in particular in the journals “Russian Medical Journal”, “Therapeutic Archive”, etc.
Thanks to the use of various sources, the description of the active substance in RLS reference books contains the most complete information about use, contraindications and other properties. In the descriptions of the active substance you can find information that is rarely published in periodicals, including complete information about the side effects observed with the use of this drug, indicating the frequency of occurrence (in%). A number of descriptions provide experimental data on mutagenicity, teratogenicity, and effects on fertility, obtained both in vitro and in vivo experiments on laboratory animals. The descriptions of active substances include information on the results of clinical trials of a drug containing this active substance. Thus, descriptions of active ingredients are the most detailed and objective source of information about drugs.
L. Postnikova (doctor, Voronezh):
Using the reference book "Encyclopedia of Medicines", I regularly refer to the Pharmacological Index. Having compared the 9th and 10th editions, I discovered that certain sections of the index have changed somewhat. What changes have been made to the Pharmacological Index prepared for the 2004 Encyclopedia of Medicines?
– Articles for the Pharmacological Index are supplemented or completely updated annually. The preliminary article to the pharmaceutical group contains an overview of the main properties and areas of application of active substances that are similar in their mechanism of action and/or pharmacological effects. In it you can find information about the mechanisms of action of the drugs combined in this group. It also lists the available classifications (by chemical structure, selectivity of action on receptors), the most important general aspects of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamic effects, main indications and contraindications, etc.
During the work on the 2004 “Encyclopedia of Medicines”, new articles were prepared on such pharmacological groups as “Anxiolytics”, “Sedatives”, “Psychostimulants”, “Nootropics”, “Cerebral circulation correctors”, “Nitrates and nitrate-like drugs”, “General tonics, restoratives and adaptogens.” In addition, the article “Macro- and microelements” has been updated (in the section regarding magnesium preparations).
However, in addition to the content of the articles, this year we have also improved the structure of the Pharmacological Index. For convenience and accuracy of information search, we have introduced a more detailed classification. Adjustments were made in the following groups: “Hormones and their antagonists”, “Neurotropic agents”, “Diagnostic agents”. Let me give you one example. The subgroup “X-ray contrast agents” (group “Diagnostic agents”) is divided into 3 subgroups: “X-ray contrast agents”, “Magnetic resonance contrast agents”, “Ultrasonic contrast agents”.
N. Novikova (doctor, Novosibirsk):
Just recently, having visited the website www.rlsnet.ru, I learned about the new edition of RLS - “Encyclopedia of Psychiatry”. Please tell us what is the fundamental novelty of this book compared to other publications in the field of psychiatry?
– The main goal of the reference book “Encyclopedia of Psychiatry” is to provide specialists with complete, relevant and reliable information about the latest methods of diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders, as well as about medications used in psychiatry.
The editorial team of the publication for the first time systematized the experience of many years of scientific work and clinical practice of all major schools in the field of psychiatry. The preparation of the encyclopedic publication was carried out by leading specialists of the State Scientific Center for Social and Forensic Psychiatry named after. V.P. Serbsky, Department of Psychiatry, Moscow State Medical University, Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, Russian State Medical University, St. Petersburg Psychoneurological Research Institute named after. V.M. Bekhterev and the Register of Medicines of Russia. The editor-in-chief of the Encyclopedia of Psychiatry is Professor Yu.A. Alexandrovsky.
The publication systematizes information about all psychiatric diseases in accordance with the headings of ICD-10, including schizophrenia, mental retardation, neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders, mental disorders and behavioral disorders associated with the use of psychoactive substances.
The guide includes detailed information about medications used in psychiatry (eg, antidepressants, anxiolytics, and antipsychotics). In addition, information on the interaction of psychotropic drugs is posted, as well as information materials on the practice of using psychopharmacological drugs, prepared on the basis of multicenter studies under special programs.
Particular attention is paid to issues that require close interaction between neurologists and psychiatrists, in particular, modern methods of treating patients with epilepsy. A large section is devoted to the problems of child psychiatry, which contains information about emotional disorders and behavioral disorders that begin in childhood and adolescence. In addition, the levels of used doses of psychotropic drugs in children and adolescents are given. When presenting the material, the principles of evidence-based medicine are observed.
V. Kryuchkov (doctor, Samara):
I, like many of my colleagues, am used to looking for information in printed publications of the radar station and medical journals. However, every year I feel more and more that this is not enough. Sometimes I have to look for the latest data on the Internet. Please tell us what advantages electronic radar reference books have and how a doctor can use them in everyday work.
– Currently, such important factors as the speed of obtaining information and the speed of updating it often come first. In this case, electronic directories are beyond competition. A striking example is the “Electronic Encyclopedia of Medicines” (on CD). Its search capabilities are much wider than in printed publications of the radar. In addition to the pharmacological and nosological indexes, the search can be carried out by pharmacological action, dosage form, anatomical-therapeutic-chemical classification and many other parameters. In addition, direct contextual search is possible in description texts that contain a given set of words (at the user’s request, the system will select all texts that contain key search words). To search for a drug by name, just type a few initial letters.
The cumulative procedure for creating a database included in the “Electronic Encyclopedia of Medicines” and the website www.rlsnet.ru on the Internet significantly expands the possibilities of finding the necessary information. Over the ten years of existence of the directory system, the RLS publishing house has accumulated a huge amount of data that cannot be contained in any printed publication. Therefore, more than 4,500 specialists access the radar database via the Internet every day. Every month, with its help, specialists receive answers to more than 500,000 queries.
The use of a unified nomenclature of medicines in the radar, built on the basis of the state information standard, made it possible to create and use a common language of communication for all users. Therefore, it has become possible to comprehensively solve all the user’s problems - from obtaining information about the drug and its active substance to purchasing it through an online pharmacy or a regular pharmacy within the framework of one information resource - www.rlsnet.ru. The radar database on the site is updated 2 times a month, so users have the opportunity to regularly receive the most up-to-date information.
However, doctors use not only the radar database, which contains descriptions of drugs and active ingredients, but also other sections of the site. Experts regularly refer to reference books, textbooks and articles posted in the “Library of Scientific Works” section. For example, for 6 months of 2003 to the monograph ed. Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Professor V.T. Ivashkin “Diseases of the liver and biliary tract”, posted on the website, doctors contacted 8776 times.
A. Belkina (doctor, Perm):
Several months ago I became familiar with your reference book “Patient 2003”. This is a useful book for a doctor. But I got the impression that the authors of the book are promoting self-medication. The title of the book “Patient” - does this book mean for the patient? Did I understand correctly?
– All reference books of the “Register of Medicines of Russia” system are intended for professionals. However, the “Patient” reference book occupies a special place, because is a physician's manual that focuses on patient education. We are not saying that this is a book for the patient. It will still be quite difficult for him. But if he is being treated by a doctor and the doctor recommends that he read some section of the book, then with the help of a specialist he will gain knowledge for himself that will help make the treatment more effective. After all, many diseases shape a person’s lifestyle.
In conclusion, I would like to thank the doctors who called the RLS publishing house and asked meaningful questions, as well as the editors of the Russian Medical Journal for the opportunity to post answers to questions from specialists on the pages of their publication.
Dear readers!
To receive a new edition of the reference books in the “Register of Medicines of Russia” series, you must fill out an application posted on the website https://www.rlsnet.ru
, and send it to the RLS publishing house:
123007, Moscow, PO Box 28. Telephone (095) 258–97–06, fax (095) 258–97–07, e-mail
Clinical researches
To confirm the declared qualities of drugs, describe the pharmacological properties, study contraindications, confirm recommendations for use, and determine the correspondence in actions, clinical studies are conducted.
Before testing, each drug must undergo a series of laboratory tests. The results confirm its composition, determine its form and describe its pharmacotherapeutic group.
The next stage of clinical trials involves volunteers taking the drug under the supervision of medical personnel. All actions are carried out under the supervision of physicians, are recorded, changes in the clinical picture of the disease as a result of use are described, side effects are clarified and confirmed, and the interaction of the drug with other drugs is studied.
Based on the results of this work, a conclusion is written that confirms, partially confirms or refutes the declared qualities of the drug. Based on these studies, the drug may be recommended for use, the description of some properties may be changed and recommended for use, or the use of this medicine may not be recommended.
Certification of drug manufacturers
In the Russian pharmaceutical industry, each enterprise engaged in the production of drugs, in addition to the mandatory license for their manufacture, must have a guarantor of compliance of the drugs produced with the requirements of state registration and production that meets the rules of the adopted technology. Such a guarantor is an authorized person. This is a pan-European practice of a quality control system according to GMP rules.
An authorized person may be an individual with higher education in one of the areas of training:
- pharmacy,
- chemistry, chemical technology, chemical protection,
- biology, biotechnology,
- clinical or basic medicine,
- radiation, biological protection,
- veterinary medicine
The specialist must have more than 5 years of practical work in the field of manufacturing or in the drug quality control system. He must go through a registration procedure in several stages with the Russian Ministry of Health. The name of the authorized person must certainly be reflected in the licensing documents of the enterprise.
Quality control of drugs at the stages of production, storage, and sales is entrusted to the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare and is regulated by regulations.
Accreditation of medical organizations
Each medical organization undergoes accreditation to obtain or confirm a certificate to work in a certain field of medicine. State-owned organizations are accredited once every 5 years, non-state owned organizations are accredited once every three years. In special cases, this procedure may be carried out ahead of schedule. The regulations for its implementation are based on the resolution “On approval of the regulations on licensing of medical activities.”
Accreditation is carried out by a specially convened commission. Includes: representatives of healthcare management structures, professionals from medical and insurance associations at the republican, territorial or city level.
At the time of the conduct, the following documents must be available: a charter, an agreement confirming joint activities with a government body, documents on the availability of premises, current types of declared medical services, qualification characteristics and certificates of employees, a list of equipment used, financial reports for the previous reporting period.
The resulting certificate confirms the degree of compliance of the types of medical care and services provided with the statutory documents of the organization.