Cri-cat syndrome, also called Lejeune's syndrome, is a fairly rare chromosomal disease characterized by a defect in the structure of the fifth chromosome. With this chromosomal defect, various severe malformations of internal organs and tissues are noted. Children with cry-the-cat syndrome very often suffer from complications that arise from a defect in the fifth chromosome.
According to statistics, cry-the-cat syndrome is not a very common chromosomal pathology. Thus, this disease occurs in 1 child in 30-60 thousand newborns. At the same time, the occurrence of Lejeune syndrome does not depend on the region or climatic conditions. However, it has been noted that female gender is a risk factor.
Compared to most other hereditary pathologies, cry-the-cat syndrome has a relatively favorable prognosis. With this pathology, children can live to adulthood with appropriate medical care and avoiding the development of serious complications. However, people with this disease cannot lead a normal life without physical and mental disabilities.
Interesting information about the syndrome:
- Cri-cat syndrome was originally discovered and described in the mid-twentieth century by geneticist Jerome Lejeune, after whom the syndrome was named.
- This pathological condition has specific symptoms by which it can be diagnosed in newly born children.
- This syndrome is distinguished by a specific cry of a child (high-pitched and very loud), which resembles the meowing of a cat. With this disease, there is a defect in the development of laryngeal cartilages.
- With Lejeune syndrome, patients have a normal amount of chromosomal material, which distinguishes it from other genetic pathologies. There is only a slight deficiency of the fifth chromosome, which is the cause of the disease.
Causes of Cry Cat Syndrome
Lejeune syndrome is a chromosomal disorder. The leading cause of Cry Cat Syndrome is a change in the structure of chromosomes in the child's genetic information. The genome contains all the information about an organism. The genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes. Chromosomal diseases occur due to a violation of the integrity of any of the chromosomes.
Cri-cat syndrome is characterized by the fact that in the genome, every fifth chromosome will have a defect in any cell, regardless of its function. With this pathology, the fifth chromosome does not have a short arm on which a large number of genes are localized. In genetics, this pathological condition is called a deletion (the absence of a certain section of DNA).
There are several variants of mutations that are factors in the development of the syndrome:
- Absolute absence of a short arm on the fifth chromosome. This option is typical for a very severe course of the disease.
- A reduction in the short arm is characterized by the loss of certain gene information. With this form, there is a loss of gene information, which leads to the appearance of this syndrome.
- The mosaic version of Lejeune's syndrome is a relatively mild course of the disease (less pronounced physical and mental abnormalities). In this form of the disease, the genome initially changes its structure during the growth of the embryo. During the division of the fifth chromosome, the short arm was lost, which was the cause of the disease.
Cry-cat syndrome, a mutation of which is located on the fifth chromosome, is observed in all of the above deviations. In this case, specific symptoms are noted that are the result of the division of cells that have a defective gene. The division of such cells is characterized by less intensity, since they lack the necessary chemical components. As a result, children with Cri-Cat Syndrome often have low body weight.
As a rule, a defect in the fifth chromosome is inherited from one of the parents. The main cause of Cry Cat Syndrome is not clear, since the development of this pathology is due to many environmental factors. These factors lead to disruption of the zygote division process at the very beginning of pregnancy or damage to the germ cells of one of the parents.
Factors that provoke the development of pathology of the fifth chromosome:
- The age of the woman who is the mother of the child. The likelihood of hereditary diseases increases with maternal age. For the syndrome, this dependence is quite weak. With this pathology, the risk of developing the disease increases after 45 years in the mother. However, the age of the father does not affect the risk of developing Lejeune syndrome;
- Smoking. Smoking is especially dangerous at a young age, when the reproductive system is actively developing. This is a common cause of chromosomal pathology;
- Alcohol acts in the same way as smoking (there is a disruption of biochemical processes, which significantly increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities); Some medications negatively affect the reproductive organs, including chromosome mutation. This is especially true for taking medications in the first trimester of pregnancy. This contributes to the development of the risk of the mosaic form of Lejeune syndrome. At the same time, narcotic substances are the most teratogenic;
- Cry of the cat syndrome, a mutation in which can be observed in the presence of intrauterine infections;
- Radioactive radiation directed at the genitals often manifests itself as chromosomal mutations;
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. Scientists note that in regions where toxic minerals are mined, the birth of children with chromosomal diseases is often observed.
The cause of Cri-Cat Syndrome often lies in one of these factors, but there are cases where parents who were not affected by the above factors give birth to children with Cri-Cat Syndrome.
Causes of monosomy
Monosomy can occur at various stages of cell division. For example, with Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome, the process of X chromosome divergence is disrupted. As a result, one woman’s egg gets two X chromosomes, and the second gets none. During the fertilization process, the zygote receives a set of X0 and Y0, - instead of the normal XX or XY.
The causes of monosomy are not related to hereditary factors. Violations occur when exposed to unfavorable factors. Bad habits, radiation, some medications, chemicals, unfavorable environmental conditions, harmful working conditions, etc. can affect reproductive cells.
Appearance of newborns with cry-the-cat syndrome
Scientists have identified a set of symptoms and syndromes that are collectively characteristic of cry-the-cat syndrome. These symptom complexes can be seen immediately after the birth of the child. Typical symptoms of the disease that are observed immediately after the birth of the baby:
- Specific cry of a newborn baby.
- Anomalies in the development of the skull bones.
- A certain shape of the palpebral fissures.
- Atypical shape of ear cartilage.
- Agenesis of the lower jaw.
- Low birth weight.
- Anomalies in the development of the bone apparatus of the hand.
- Clubfoot.
Cry cat syndrome is constantly manifested by the specific crying of a child. A defect of the fifth chromosome is clinically manifested in the first minutes after the birth of a child with a characteristic cry in the form of a cat’s meow. This cry differs in tone from the cry of normal children. The reason for this is:
- Reduction in the size of the epiglottis cartilage;
- Reducing the lumen of the airways in the projection of the epiglottis;
- Abnormal increase in the elasticity of cartilage tissue;
- Formation of folds in the mucous membrane that lines the cartilage of the larynx.
Since these changes occur in the area of the vocal cords, the tone of the voice in children changes.
Anomalies of head development
Children with cry-the-cat syndrome in more than 80% of cases have abnormalities in the development of the shape of the skull. Most often, microcephaly is observed, which is accompanied by a decrease in the size of the skull. Therefore, in newborns, the head has an oblong shape and is proportionally smaller than the size of the body. In order to confirm the diagnosis of microcephaly, it is necessary to do craniometry. Microcephaly is always accompanied by encephalopathy of varying severity.
Specific shape of palpebral fissures
This symptom is characteristic of many chromosomal diseases, including Lejeune syndrome. This anomaly is mainly due to the pathological shape of the skull bones. Children with Cri-Cat Syndrome have eye developmental disorders that can be distinguished by four characteristics:
- The antimongoloid ocular section is distinguished by the fact that the medial corner of the eye is always located above the outer one;
- Strabismus is characterized by an asymmetrical arrangement of the corneas in relation to the eyelids;
- Hypertelorism of the eyes is characterized by a wide setting of the eyeballs;
- The epicanthus is a fold at the inner corner of the eye.
Deformation of the outer ear
Newborns with cry-the-cat syndrome are characterized by changes in the structure and location of the ears. The most common pathology is ptosis of the ears. This is a consequence of underdevelopment of ear cartilage, which is visually represented by a decrease in the size of the ears. Also, peculiar compacted skin nodules may be observed on the skin near the ears.
Agenesis of the lower jaw
Underdevelopment of the lower jaw is manifested by micrognathia or microgenia. During pregnancy, due to chromosomal abnormalities, the bone that forms the lower jaw may not reach the desired size. All this leads to retraction of the chin in relation to the maxillary bone. Frequent forms of micrognathia are bilateral or unilateral. In general, impaired development of the lower jaw in such children leads to difficulty in feeding (the child cannot completely close his lips near the nipple, which leads to a disruption of the sucking reflex).
Pathologically low child weight
Newborn babies with Cri-Cri-Cat Syndrome often have an abnormally low birth weight. This is a consequence of severe developmental disorders of internal organs.
Pathology of bone development of the skeletal apparatus
Cry-cat syndrome often manifests itself as the development of syndactyly. This syndrome is characterized by fusion of a child's fingers and toes. In this case, it is possible to connect the fingers only with a thin membrane of skin, which can be easily corrected with surgical intervention. In case of fusion of fingers with bone tissue, it is much more difficult to correct this pathology.
Clindactyly may also be observed, which is characterized by a violation of the shape of the fingers in the joints of the hand and foot.
Clubfoot
This symptom manifests itself in the presence of anomalies in the development of the bone apparatus of the lower limb. Clubfoot is a violation of the position of the foot in relation to the axis of the leg. In the future, such children may have problems with walking. The combination of these symptoms can be diagnosed at the prenatal stage.
Treatment in Italy
Russian Medical Server / Treatment in Italy / Center for the treatment of rare diseases in Milan / Cri du chat syndrome - treatment in Italy
Cri du chat syndrome (English cri du chat syndrome, French maladie du cri du chat; also cry cat disease, Lejeune syndrome - named after the French scientist who described it in 1963) is a rare genetic disorder caused by the absence of a fragment of the 5th chromosome.
In this case, a characteristic cry of the child is observed, reminiscent of a cat's meow, the cause of which is a change in the larynx (narrowing, softness of cartilage, reduction of the epiglottis, unusual folding of the mucous membrane) or underdevelopment of the larynx. The sign disappears by the end of the first year of life.
As already noted, the syndrome got its name because of the characteristic crying of children (it is similar to the meow of a kitten, the cry of a cat) suffering from this disease. This cry occurs due to problems with the larynx and nervous system. About 1/3 of children lose this special characteristic by age 2. Other symptoms that indicate Cri Cat Syndrome include:
- feeding problems due to difficulty swallowing and sucking;
- low birth weight of the child and low rates of development (primarily physical);
- significant delay in the development of cognitive, speech and movement functions;
- behavioral problems such as hyperactivity, aggression, tantrums and monotonous movements are constantly repeated;
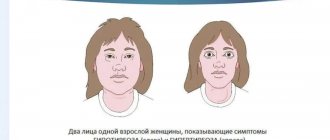
- atypical facial features that may disappear or intensify over time;
- excessive, uncontrollable salivation;
- constipation
Additional typical signs of the disease include: hypotonia, microcephaly, delayed physical development, round face with full cheeks, hypertelorism, epicanthus, drooping palpebral fissures, strabismus, flat bridge of the nose, drooping corners of the mouth, micrognathia, low-set ears, short fingers, 4 -x digital palmar fold and heart defect (for example, ventricular septal defect (ventriculoseptal defect), atrial septal defect (atrioseptal defect), patent ductus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot). People with Cri de Cat Syndrome usually do not have problems with the reproductive system or reproduction (having children).
Less common symptoms include cleft lip and palate, anterior auricular fistula, thymic dysplasia, intestinal obstruction, megacolon, inguinal hernia, hip dislocation, cryptorchidism, hypospadias, rare renal malformations (eg, horseshoe kidneys, ectopic or agenesis, hydronephrosis) , clinodactyly of the fifth finger, clubfoot, flat feet, syndactyly (fusion) of the second and third fingers and toes, oligosyndactyly and increased joint flexibility. The syndrome may also include various dermatoglyphic features, including transverse flexion folds, one palmar fold, etc.
In late childhood and adolescence, physician findings include significant mental retardation, microcephaly, coarsening of facial features, brow ridges, deep-set eyes, hypoplastic nasal septum, severe malocclusion, and scoliosis. Sick girls reach puberty, develop secondary sexual characteristics, and usually have menstruation on time. The structure of the genital organs and tracts in females is usually normal, with the exception of a bicornuate uterus, which is sometimes found in this group of patients. In men, the testicles are often small, but spermatogenesis is mostly slightly impaired.
Cri-cat syndrome is associated with a partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5, also called “5p monosomy.” Approximately 90% of cases of this genetic disease are the result of sporadic or random mutations, meaning new cases. The remaining 10-15% arises from unequal division of parental genetic material with a violation of balanced translocation, where 5p monosomy is often accompanied by a corresponding trisomy of this part of the genome. These individuals may have more severe disease manifestations than those who present with isolated cases of monosomy 5p (due to deletion).
In most cases, the disease is accompanied by a complete loss of distal genetic information, amounting to 10-20% of the genetic material on the short arm of the fifth chromosome. Less than 10% of cases have other rare cytogenetic aberrations (eg, interstitial deletion, mosaicism, rings, and new translocations). Deletion of chromosome 5, of parental origin, occurs anew in approximately 80% of cases.
Loss of a small area in area 5p15.2 (the critical region for this disease) correlates with all clinical signs of the syndrome except for the cry of the cat, which occurs when there is an abnormality in area 5p15.3 (the critical region for cats). The results suggest that two non-contiguous critical regions contain genes involved in the etiology of this disease. Two genes in these regions, semaphorin F (SEMA5A) and delta catenin (CTNND2), are potentially involved in brain development. Deletion of the reverse telomerase transcriptase (hTERT) gene located at 5p15.33 may contribute to the phenotypic change in patients with cry-the-cat syndrome.
If there have already been cases of chromosomal diseases in the family, even at the stage of pregnancy planning, future parents are recommended to visit a geneticist and undergo genetic testing. During pregnancy, the presence of “cry the cat” syndrome in the fetus can be suspected based on the results of prenatal ultrasound screening. In this case, to definitively confirm the chromosomal abnormality, invasive prenatal diagnosis (amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling or cordocentesis) and direct analysis of the fetal genetic material are recommended.
After birth, a preliminary diagnosis of “cry of the cat” syndrome is established by a neonatologist based on typical diagnostic signs (characteristic crying, phenotypic features, multiple stigmas of dysembryogenesis). To confirm chromosomal pathology, a cytogenetic study is performed.
Considering the presence of multiple developmental anomalies in children with “cry the cat” syndrome, it is necessary that in the first days of life newborns are examined by a pediatric cardiologist, a pediatric ophthalmologist, a pediatric urologist, a pediatric orthopedist and other specialists.
To stimulate psychomotor development, courses of drug therapy, massage, physiotherapy, and exercise therapy are conducted under the supervision of a pediatric neurologist. Children with “cry of the cat” syndrome need help from psychologists, defectologists, and speech therapists.
Congenital heart defects in “cry the cat” syndrome often require surgical correction, so children need consultation with a cardiac surgeon, echocardiography and other necessary studies. Children with pathologies of the urinary system should be under the supervision of a pediatric nephrologist and periodically undergo a set of necessary examinations (ultrasound of the kidneys, general urinalysis, biochemical testing of blood and urine, etc.).
! Despite the fact that many of the diseases described in this section are considered incurable, the Center for the Treatment of Rare Diseases in Milan is constantly looking for new methods. Thanks to gene therapy, it has been possible to achieve outstanding results and completely cure some rare syndromes.
Contact a consultant on the website or leave a request - this way you can find out what methods Italian doctors offer. Perhaps this disease has already been treated in Milan.
Features of children with cry-the-cat syndrome
The survival rate of children with this syndrome is quite high, so many of them reach adolescence. Children with cry-the-cat syndrome have the following phenotypic features of appearance:
- Mental retardation;
- Decreased muscle tone;
- Reduced coordination of movements;
- Constipation;
- Moon-shaped face;
- Shortened neck;
- Labile nervous system;
- Deterioration of vision.
Mental retardation
Often this symptom becomes noticeable in the first years of a child’s life and is one of the important diagnostic signs of this disease against the background of complete health.
Decreased muscle tone
This symptom develops with pathology of the nervous system or defective development of certain muscles. Clinically, this is noticeable in the form of increased fatigue in children while walking.
Reduced coordination of movements
This manifestation of cry the cat syndrome develops with underdevelopment of the cerebellum, since such children have microcephaly.
Constipation
This symptom is observed due to a pathologically narrowed gastrointestinal tract, as well as due to a violation of the neurohumoral regulation of the intestine.
Moon shaped face
This symptom occurs as a result of impaired development of the skull bones and dolichocephaly. In this case, the bones of the facial part of the skull are larger than the brain.
Shortened neck
With this symptom, it is difficult for children to turn their heads in different directions. This occurs as a result of underdevelopment of the cervical vertebrae and the cartilage between them.
Lability of the nervous system
Such children often change their mood without any justifiable reason. This is a consequence of underdevelopment of the nervous system. Often such children show increased aggressiveness and activity in children's groups.
Deterioration of vision
This symptomatology occurs due to impaired development of the organ of vision.
Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome
It is a consequence of monosomy on chromosome X. Affected children are often born premature or have reduced body weight. One of the classic signs of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome, which can be noticed immediately after birth, is a pronounced skin fold on the neck. Other clinical manifestations include:
- heart defects;
- swelling of the upper and lower extremities;
- impaired lymph circulation;
- delayed speech and physical development.
As the child grows, characteristic features of the body structure appear. Height usually does not exceed 150 cm, wing-shaped folds on the neck are preserved, the ears may be deformed, the upper jaw is underdeveloped, and the chest is wide. Monosomy on chromosome X affects the development of reproductive organs. In women, there is a lack of follicles in the ovaries, menstrual irregularities, and underdevelopment of the mammary glands. In men, testosterone levels decrease and one or both testicles may be absent or underdeveloped.
The prognosis for Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome is relatively favorable. In the absence of severe developmental defects and regular monitoring by a specialist, life expectancy is not reduced.
Diagnosis of Cry Cat Syndrome
Diagnosis of any chromosomal abnormality is carried out in two stages. The first stage is to identify women who have an increased risk of developing children with chromosomal abnormalities. The second stage is carried out to confirm a specific disease. Thus, all pregnant women need prenatal diagnosis, which is a set of diagnostic studies at the prenatal stage. Thanks to these measures, genetic abnormalities are identified at an early stage, among which is Cry the Cat Syndrome.
Cry-cat syndrome includes the following diagnostic methods:
- Anamnestic data;
- Karyotyping of both parents;
- Ultrasonography;
- Blood test to identify plasma markers;
- Invasive research methods;
- Study at the postpartum stage.
Detailed history taking
A detailed survey of parents by a pediatrician or geneticist.
Karyotyping of parents
If there is an increased risk of developing a chromosomal abnormality, the doctor prescribes this study, which allows you to fully study the structure of the cell and its nucleus.
How is Cree-du-chat syndrome diagnosed?
Cri de feline disease is a genetic disorder caused by an abnormality in the patient's chromosomes. Therefore, to confirm this syndrome in a child, it is necessary to conduct a molecular karyotype test, which allows one to analyze all chromosomes with a resolution unattainable by other methods (the so-called microarray method - aCGH).
Molecular Karyotype Test
Modern medicine also makes it possible to identify this type of defect at the stage of intrauterine development. After the 10th week of pregnancy, free fetal DNA appears in the mother's blood, based on which, with a probability of >99%, the risk of developing chromosomal defects, such as cry-the-cat syndrome, can be assessed. The prenatal tests that make this possible are completely safe and non-invasive. These include:
- Sanco test;
- Sanco Plus test;
- Nifty Pro test.
Fetal karyotype tests detect trisomies (eg, Down, Edwards, Patau) and also evaluate the occurrence of rare genetic defects called microdeletion and microduplication syndromes. Each of these tests also determines the sex of the fetus and defects resulting from sex chromosome aneuploidy (Turner, Klinefelter, XXX, XXYY, XYY syndromes).
Prenatal tests such as Sanco or Nifty Pro are also recommended in case of incorrect results from initial pregnancy tests such as ultrasound or dual test. They are also a good alternative to invasive tests such as amniocentesis, fetoscopy in situations where there are contraindications for their performance, for example, an increased risk of miscarriage or viral infection (eg, HIV, HBV).
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
[contact-form-7 id=”296″ title=”Untitled”]
Abortion and contraception clinic in St. Petersburg - department of the medical gynecological association "Diana"
Make an appointment, tests or ultrasound via the contact form or by calling +8 (812) 62-962-77. We work seven days a week from 09:00 to 21:00.
We are located in the Krasnogvardeisky district, next to the Novocherkasskaya, Ploshchad Alexander Nevsky and Ladozhskaya metro stations.
The cost of a medical abortion in our clinic is 3,300 rubles. The price includes all pills, an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound to determine the timing of pregnancy.
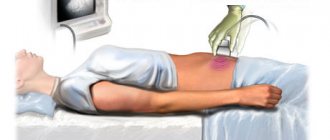
Ultrasound
Frequent nonspecific signs of cry-the-cat syndrome on ultrasound:
- Increased collar space;
- Increased or decreased amount of amniotic fluid;
- Anomalies of heart development;
- Brachycephaly or dolichocephaly;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Short tubular bones.
A blood test for plasma markers includes the following studies:
- Determination of hCG;
- Detection of protein A level;
- Determination of estriol concentration;
- Determination of alpha-fetoprotein.