Terbinafine Canon (125mg, 250mg)
Terbinafine is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild or moderate and transient. The following are adverse events that were observed during clinical trials or post-registration.
ration period. The frequency of side effects was assessed as follows: very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000, including isolated cases), frequency unknown (the incidence of side effects cannot be estimated based on available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
infrequently - anemia;
very rarely - neutropenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia. If qualitative or quantitative changes in blood cells develop, the cause of the disturbances should be established and consideration should be given to reducing the dose of the drug or, if necessary, stopping therapy with terbinafine.
Immune system disorders
very rarely - anaphylactoid reactions (including angioedema), cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus (or their exacerbation).
Mental disorders
often - depression;
infrequently - anxiety.
Nervous system disorders
very often - headache;
often - dizziness, disturbances in taste, even loss (usually recovery occurs within a few weeks after stopping treatment. There are isolated reports of cases of long-term disturbances in taste). In some cases, while taking the drug, exhaustion was noted;
infrequently - paresthesia, hypoesthesia.
Visual disorders
infrequently - visual impairment.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
infrequently - tinnitus.
Gastrointestinal disorders
very often - bloating, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, mild abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
rarely - hepatobiliary dysfunction (mainly cholestatic in nature), including liver failure,
including very rare cases of severe liver failure (some fatal or requiring liver transplantation; in most cases where liver failure developed, the patients had serious underlying systemic diseases and the causal relationship of the liver failure to the drug was questionable); hepatitis, jaundice, cholestasis, increased activity of “liver” transaminases.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
very often - rash, urticaria; uncommon - photosensitivity reactions; very rarely - Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, toxic skin rash, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, psoriasis-like skin rashes or exacerbations of psoriasis, alopecia.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
very often - arthralgia, myalgia.
General disorders
often - feeling tired;
infrequently - increased body temperature.
Laboratory and instrumental data:
infrequently - weight loss (secondary to a violation of the sense of taste).
Based on spontaneous reports received during the post-registration period and literature data, the following adverse events were identified, the frequency of which, due to the inaccurate number of patients, cannot be established:
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions, serum sickness-like syndrome.
Visual disorders
Blurred vision, decreased visual acuity.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (rash, swelling, fever, and swollen lymph nodes).
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
Hearing loss, hearing impairment.
Vascular disorders
Vasculitis.
Nervous system disorders
Loss of smell, including for a long period of time, decreased sense of smell.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Pancreatitis.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Rhabdomyolysis.
General disorders
Flu-like syndrome.
Laboratory and instrumental data
Increased serum creatine phosphokinase activity.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Terbinafine Canon, 10 pcs., 250 mg, tablets
Terbinafine is generally well tolerated. Side effects are usually mild or moderate and transient. The following are adverse events that were observed during clinical trials or during the post-marketing period. The frequency of side effects was assessed as follows: very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000, including isolated cases), frequency unknown (the incidence of side effects cannot be estimated based on available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Uncommon: anemia;
Very rarely - neutropenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Immune system disorders
Very rarely - anaphylactoid reactions (including angioedema), cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus (or their exacerbation).
Mental disorders
Often - depression;
Uncommon: anxiety.
Nervous system disorders
Very often - headache;
Often - dizziness, disturbances in taste sensations, up to their loss (usually recovery occurs within a few weeks after stopping treatment. There are isolated reports of cases of long-term disturbances in taste sensations). In some cases, while taking the drug, exhaustion was noted;
Uncommon: paresthesia, hypoesthesia.
Visual disorders
Uncommon: visual impairment.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
Uncommon: tinnitus.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very often - bloating, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, mild abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
Rare: hepatobiliary dysfunction (mainly cholestatic in nature), including liver failure, including very rare cases of severe liver failure (some fatal or requiring liver transplantation; in most cases where liver failure developed, patients had serious concomitant systemic diseases and the cause-and-effect relationship of liver failure with taking the drug was questionable); hepatitis, jaundice, cholestasis, increased activity of “liver” transaminases.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very often - rash, urticaria;
Uncommon: photosensitivity reactions;
Very rarely - Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, toxic skin rash, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, psoriasis-like rashes or exacerbation of psoriasis, alopecia.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Very often - arthralgia, myalgia.
General disorders
Often - feeling tired;
Uncommon: increased body temperature.
Laboratory and instrumental data:
Uncommon: weight loss (secondary to taste disturbances).
Based on spontaneous reports received during the post-registration period and literature data, the following adverse events were identified, the frequency of which, due to the inaccurate number of patients, cannot be established:
Immune system disorders
Anaphylactic reactions, serum sickness-like syndrome.
Visual disorders
Blurred vision, decreased visual acuity.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (rash, swelling, fever, and swollen lymph nodes).
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
Hearing loss, hearing impairment.
Vascular disorders
Vasculitis.
Nervous system disorders
Loss of smell, including for a long period of time, decreased sense of smell.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Pancreatitis.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Rhabdomyolysis.
General disorders
Flu-like syndrome.
Laboratory and instrumental data
Increased serum creatine phosphokinase activity.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Terbinafine Canon tablets 250 mg bl N7x2 Canonpharma
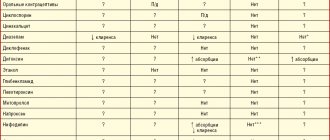
Effect of other drugs on terbinafine. Plasma clearance of terbinafine can be accelerated by drugs that are metabolic inducers, and suppressed by cytochrome P450 inhibitors. If it is necessary to use the above drugs and terbinafine simultaneously, an appropriate adjustment of the dosage regimen of the latter may be required. Cimetidine may enhance the effect of terbinafine or increase its plasma concentration. Cimetidine reduces the clearance of terbinafine by 33%. Fluconazole increases the Cmax and AUC of terbinafine by 52% and 69%, respectively, due to inhibition of the CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes. A similar increase in terbinafine exposure may occur with the use of other drugs that inhibit CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes, such as ketoconazole and amiodarone. Rifampicin may weaken the effect of terbinafine or reduce its plasma concentration. Rifampin increases the clearance of terbinafine by 100%. Effect of terbinafine on other drugs. Terbinafine inhibits metabolism mediated by isoenzyme 2D6 (CYP2D6). These data may be clinically significant for those drugs that are predominantly metabolized by this enzyme: tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, antiarrhythmic drugs (class 1A, 1B and 1C) and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors, in the event that if the drug used simultaneously has a small therapeutic concentration range. Terbinafine reduces the clearance of desipramine by 82%. In studies in healthy volunteers with extensive metabolism of dextrofetorphan (an antitussive and CYP2D6 substrate), terbinafine increased the urinary dextromethorphan/dextrorphan metabolic ratio by 16-97-fold. Thus, terbinafine in individuals with high activity of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme may reduce the activity of the latter. Terbinafine reduces the clearance of caffeine when administered intravenously by 19%. Drug interactions that have no or negligible effect. Terbinafine has little potential to inhibit or enhance the clearance of most drugs metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system (e.g., terfenadine, triazolam, tolbutamide, or oral contraceptives), except those metabolized by CYP2D6. Terbinafine does not affect the clearance of phenazone or digoxin. Terbinafine does not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole. There were no clinically significant interactions between terbinafine and the components of cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole), zidovudine or theophylline. When terbinafine is taken concomitantly with oral contraceptives, menstrual irregularities are possible, although the frequency of these disorders does not exceed the average frequency of such disorders in patients taking only oral contraceptives. Terbinafine may reduce the serum concentrations or clinical effects of the following drugs Terbinafine increases the clearance of cyclosporine by 15%. Interaction with food and drinks. Food has a slight effect on the bioavailability of terbinafine (increase in AUC <20%), which does not require changing the dose of the drug.