SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Discharge of different colors, from white to yellow and brown, is one of the common reasons why girls and young girls come to see a gynecologist and is an equally popular topic for discussion on medical websites and women’s forums. Lack of knowledge about the causes of white discharge on panties leads to the fact that we begin to intensively use intimate hygiene products, self-medicate at home, after reading “helpful tips” on the Internet or listening to friends. As a result, the number of used panty liners gradually increases, discharge continues and does not decrease, or even increases...
It is at least naive to hope to solve the problem in this way. I would like to point out that discharge and odor do not necessarily mean a problem in the intimate area and are a sign of a serious illness. First, you need to understand which of them are the norm, and which may indicate problems with the genital organs.
Why does the girl have discharge? Is it good or bad? The fact is that their education during childbearing age is the norm. They are a normal physiological phenomenon for the body. The amount and nature of discharge and their traces on a girl’s panties and, accordingly, their colors and smells depend on the composition of the vaginal microflora, which is largely determined and regulated by hormonal levels. Therefore, different girls have different discharge and smell differently.
general characteristics
Normally, women may have slight, odorless vaginal discharge.
Sticky mucous vaginal discharge, similar to egg white, is observed during ovulation. With pathological leucorrhoea, the patient notices an increase in the amount of secretion and an atypical color of the discharge. Yellowish or brown spots remain on the underwear. With a large volume of discharge, the secretion accumulates between the labia majora and minora, in the perineal area. The discharge may have a sour, fishy, rotten odor. Leucorrhoea is often combined with intense itching in the perineum and vestibule of the vagina; irritation and rashes occur on the skin around the genitals. Sometimes I have pain in the lower abdomen. With profuse vaginal discharge, a woman is forced to use sanitary pads for her menstrual periods. Patients note psychological discomfort due to the sharply foul odor of the discharge. A change in the color and consistency of vaginal discharge indicates pathologies of the genital area or extragenital diseases, so in such cases you should consult a doctor.
The importance of maintaining intimate hygiene when there is heavy mucous discharge
Normal discharge is not dangerous. But if a woman does not adhere to basic rules of intimate hygiene, the mucus accumulated on the genitals can become an ideal place for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Therefore, it is necessary to devote time to hygiene procedures every day.
Intimate hygiene with heavy mucous discharge is very important
Washing gels "Ginocomfort" for daily hygiene of the intimate area effectively cleanse the female genital organs of mucous secretions without disturbing the vaginal microflora. The line of products for daily intimate hygiene includes several gel options, so you can choose the product that best suits you based on the action of its active ingredients.
The gels contain ingredients such as panthenol, bisabolol, sodium lactate, tea tree oil, lactic acid, chamomile extract, etc.
The use of Ginocomfort washing gels ensures the maintenance of normal vaginal microflora, helps fight the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and has anti-inflammatory and tonic effects.
If a woman experiences a reduction in vaginal mucous discharge caused by stress or menopause, using a cleansing gel helps to further moisturize the vagina. All products in the line were created by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and have the necessary documents. Sources:
- Hormonal status and vaginal microbiocenosis. Dobrokhotova Yu. E., Zatikyan N. G. // Obstetrics, gynecology, reproduction. - 2008. - 2 (2): pp. 7-9.
- Innate immunity of the female reproductive tract and its hormonal regulation (mini-review). Lebedeva O. P., Kalutsky P. V., Pakhomov S. P., Churnusov M. I., Karpov P. A. // Scientific bulletins of Belgorod State University. Medicine, pharmacy. - 2009. 12 (67). -WITH. 25-31.
- Normal microflora of the female genitourinary tract and drugs for its correction. Kocherovets V.I., Bunyatyan N.D. // M.: Publishing house "AKTEON". - 2011. - P. 72.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mikroekologiya-vlagalischa-zhenschin-s-nespetsificheskimi-vospalit…
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-predstavleniya-o-mehanizmah-razvitiya-disbioza-vlagali…
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vaginalnye-vydeleniya-prichiny-algoritm-vedeniya-patsientok-i-sovr…
Classification
Vaginal discharge is divided into physiological, associated with the reaction of the epithelium of the reproductive organs to natural changes in hormonal levels, and pathological, caused by various diseases. In terms of thickness and consistency, vaginal discharge can be watery, thick and viscous, dense, cheesy, and sometimes foamy leucorrhoea is observed. To make a diagnosis and choose a medical tactic, it is important to classify discharge by color, according to which the following types of leucorrhoea are distinguished:
- Transparent.
The discharge is mucous, thick or very thin, watery. Such odorless leucorrhoea appears when there are disturbances in the absorption of excess fluid into the vagina, which is caused by changes in the normal microflora and fluctuations in the level of sex hormones. - White.
Thick, curdled or viscous discharge is observed with an increase in the secretion of the glands of the cervix and the vestibule of the vagina, which occurs against the background of genital pathology. Pathogenic microorganisms contribute to the formation of white discharge. - Bloody.
Vaginal leucorrhoea can be ichorous, the color of “meat slop”, often with a smell. Sometimes scarlet or dark red blood may be discharged. Bleeding is associated with endometrial dysfunction, damage to the vaginal or cervical epithelium. - Gray.
Such leucorrhoea is the result of a disturbance in the vaginal microflora, which is accompanied by a decrease in the number of beneficial Doderlein bacilli and the colonization of the vagina by pathogenic bacteria. The discharge is thick, foul-smelling, or has a fishy odor. - Yellow.
Such discharge is typical for infectious lesions of the reproductive system. The symptom develops as a result of an intense inflammatory reaction in the vagina, disruption of the exocrine glands. Leucorrhoea can be either thick or watery and foamy. - Purulent (yellow-green
). Thick, often creamy vaginal discharge indicates a bacterial infection. The characteristic color is due to dead leukocytes. Abundant leucorrhoea with a specific purulent odor occurs when the uterus, its appendages are damaged, abscesses and cysts are opened.
Vaginal discharge is also classified by smell - in a number of patients, leucorrhoea has a sour, putrid, fetid aroma. Quite often there is a discharge with the smell of fish, sometimes the stench of rotten meat is felt. Taking into account the localization of the pathological process that caused leucorrhoea, they are divided into vestibular, vaginal, and cervical (cervical). With discharge that forms in the uterus and appendages, they speak of corporal and tubal leucorrhoea.
Why does the color of menstrual discharge change?
The color changes because the discharge is a combination of menstrual blood, vaginal secretions, and loose uterine lining (these are the same clots you may have noticed when changing hygiene products). On different days of menstruation, their composition and consistency are not the same. As you already know, in the very first and last days the color of normal menstruation is dark, the rest of the time it is red or brownish. The cause of changes in the color of menstrual discharge can be hormonal fluctuations, taking oral contraceptives, stress, hypothermia, pregnancy, and various diseases.
Causes of vaginal discharge
Causes of clear vaginal discharge
A scanty, watery or mucous (“snot-like”) secretion without aroma periodically forms in healthy women. Copious discharge with a sour odor indicates the presence of a disease. Transparent vaginal discharge causes such reasons as:
- Physiological factors
: exposure to estrogen in the first half of the menstrual cycle, puberty in girls. - Allergic vulvitis and vaginitis
. - Helminthiasis:
enterobiasis, ascariasis, schistosomiasis, etc.
Causes of white vaginal discharge
Thick, cheesy discharge is characteristic of vaginal and cervical localization of pathological changes. The combination of leucorrhoea with intense perineal itching and pain during sexual intercourse indicates an infectious process. White vaginal discharge provokes:
- Physiological changes
: second half of the menstrual cycle, sexual intercourse, pregnancy. - Vaginal candidiasis
. - Genital tuberculosis.
- Rare reasons
: use of intrauterine devices, contraceptive creams.
Causes of vaginal bleeding
Bleeding from the vaginal lumen, not associated with recent injuries to the groin area, usually indicates a serious organic disease. The main pathologies that cause bleeding from the vagina are:
- Endometriosis
. - Damage to the cervix
: erosions, polyps, malignant neoplasms. - Tumors of the reproductive organs
: fibroids, adenocarcinomas, vaginal cancer. - Injuries to the genital tract
: during rough sexual intercourse, due to exposure to foreign objects, with bruises in the pubic and perineal area. - Taking oral contraceptives
. - Postpartum uterine involution
.
Causes of gray vaginal discharge
Abundant grayish discharge from the genital slit is associated with disturbances of the vaginal microflora as a result of genital infections or damage to other organs. Gray vaginal discharge is characteristic of conditions such as:
- Bacterial vaginosis
. - Inflammatory processes
: colpitis, endocervicitis, atrophic vaginitis. - Sexually transmitted infections
: trichomoniasis and chlamydia at the initial stage. - Rare causes
: pathologies of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, chronic adrenal insufficiency), tuberculosis.
Causes of yellow vaginal discharge
A thick, scanty light yellow secretion is sometimes found in women a few days before the onset of menstruation. Foamy yellow vaginal discharge, which has an unpleasant odor, is typical of the following diseases of the genital organs:
- Infectious diseases
: aerobic vaginitis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia. - Inflammatory process
: colpitis, salpingitis, adnexitis. - Vesicouterine fistulas
.
Causes of purulent vaginal discharge
During various inflammatory processes, from a few drops to several milliliters of thick, foul-smelling pus can be released from the vagina, which is accompanied by sharp pain in the lower abdomen and fever. With purulent vaginal discharge occurs:
- Complicated genital infections:
gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis. - Pathologies of the external genitalia
: bartholinitis, boils of the skin of the perineum. - Diseases of the uterus and appendages
: pyometra, pyosalpinx, postpartum endometritis.
Periods of brown discharge in women and their causes
Before and after menstruation
Usually the bleeding at the beginning and at the end of menstruation is light. During these periods, the blood has a brown or even black tint because it is oxidized. Such discharge these days (before and after menstruation) is absolutely normal.
In the middle of the cycle
Some women experience spotting during ovulation. However, the volume of such secretions is small, and they can be either brown or pinkish in color. In the middle of the cycle, light spotting most often occurs in women who take oral contraceptives and who are already approaching menopause in age. In these cases, it is necessary to visit a doctor to rule out the presence of pathologies.
Instead of menstruation
If your cycle is a little off (a difference of up to 7 days is absolutely normal). But if your period does not come, you should consult a gynecologist.
During pregnancy
Brown discharge may be a sign of pregnancy. Light bleeding may occur 10-14 days after fertilization, when the egg attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Pay attention to other signs of pregnancy. These may include tender and painful breasts, nausea, frequent urination, fatigue, and vomiting.
Take a home test if you think you might be pregnant but your period is brown or late. Visit your gynecologist if the test is positive to confirm the result and plan next steps.
When taking oral contraceptives (OC)
Taking OCs affects the level of sex hormones, so brown discharge in women is most often normal in this case, especially in the first months of taking it. If such discharge is not accompanied by pain and has no odor, but continues longer than 3 months after starting to take OCs, a consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
Diagnostics
If there is vaginal discharge with or without any unpleasant odor, a consultation with a gynecologist is indicated, during which the external and internal genital organs are examined in detail using physical and instrumental methods. To clarify the cause of leucorrhoea, various clinical and microbiological studies are performed, of which the greatest diagnostic value is:
- Vaginal examination.
Examination of the vagina and cervix in speculum is the main diagnostic method, during which the amount and nature of pathological discharge is assessed, inflammatory or atrophic changes in the epithelium are identified. The condition of the excretory ducts of the Bartholin glands and the urethral orifice must be studied. - Colposcopy
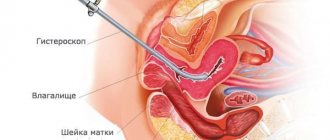
. Visualization of the mucous membrane of the vaginal part of the cervix is necessary to exclude erosions, genital precancerous conditions and malignant neoplasms. During colposcopy, a test with acetic acid and a Schiller test are performed. If necessary, the method is supplemented by cervicoscopy, and if uterine leucorrhoea is suspected, by hysteroscopy. - Ultrasonography
. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is recommended if the discharge is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen and intermenstrual bleeding. Sonography allows you to identify the causes of leucorrhoea: neoplasms, cysts, inflammatory changes in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. To clarify the diagnosis, hysterography is sometimes prescribed. - Bacteriological analysis of secretions
. Discharge with a foul odor often occurs with genital infections, therefore, to detect them, a vaginal smear is taken for microflora, and a cultural examination of the leucorrhoea is carried out. To quickly detect the most common pathogens, ELISA reactions and direct RIF, PCR diagnostics are used.
To exclude syphilis, the Wasserman reaction is performed, and tests aimed at diagnosing tuberculosis are performed according to indications. Clinical and biochemical blood tests help to establish the causes of the inflammatory process; in case of space-occupying formations, the level of the main tumor markers is determined. For clarification, CT or MRI of the pelvic organs is used; in difficult cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is used. If you have persistent, scanty, odorless discharge, you may need to consult an endocrinologist.
A vaginal smear test will help determine the cause of leucorrhoea.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce itching and other uncomfortable sensations, it is recommended to regularly carry out hygiene procedures and use pads. Local baths with antiseptic solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs are effective, which are aimed at stopping the inflammatory process and reducing the number of pathogenic bacteria. For severe pain, take analgesics from the NSAID group and antispasmodics. If you experience foul-smelling leucorrhoea, discharge with a sour odor, or bloody vaginal discharge, you should urgently visit a doctor to determine the cause of the disorder.
Conservative therapy
The treatment regimen is selected individually after determining the cause of leucorrhoea and assessing the condition of the patient’s reproductive system. The main one is etiopathogenetic therapy, supplemented by symptomatic agents. Drug treatment is combined with local and physiotherapeutic methods. If discharge with a noticeably unpleasant odor is caused by genital infections, simultaneous treatment of both sexual partners is advisable. The following groups of drugs are used in clinical practice:
- Antibacterial agents
. For sexually transmitted diseases and other purulent genital pathologies, properly selected antibiotics ensure the eradication of pathogenic microorganisms. Depending on the cause of the discharge, antiprotozoal and anthelmintic medications are sometimes prescribed. - Antihistamines
. Eliminate itching and discomfort in the perineum, quickly reduce the amount of inflammatory mediators in the affected area. To enhance the effect, medications are usually combined with anti-inflammatory drugs, which have an analgesic effect. - Local medications
. Vaginal suppositories with lactobacilli acidophilus are intended to restore normal microflora in the vagina. To eliminate the cause of discharge, odor, and other unpleasant symptoms, suspensions with tetracyclines and intravaginal suppositories with other antibiotics and antimycotics are used.
Surgery
Accumulation of pus in the uterine cavity or fallopian tubes, suppuration of cysts, abscesses of the Bartholin glands are indications for sanitation and drainage of pathological foci. When fistulas form, they are excised and repaired to preserve the anatomical structure of the genital tract. In the case of benign neoplasms, it is necessary to remove the tumor within healthy tissue; in the case of a malignant process, oophorectomy and amputation of the uterus are usually recommended. To treat endometriosis, altered areas of tissue are removed, followed by cauterization.
Treatment of diseases accompanied by bleeding
You should not self-medicate; you should go to a clinic for medical help. Only a doctor will be able to study the symptoms in detail and determine the cause of the discharge.
Brown discharge, which is accompanied by a delay in menstruation or natural aging of uterine tissue, requires correction in diet and abandonment of bad habits.
It can be recommended to drink more water, since the problem may arise due to a decrease in water balance in a woman’s body.
If dark discharge appears as a result of diseases (cancer, erosion, infection), hormonal medications, antibiotics, chemotherapy, and dietary supplements are prescribed.
Surgery is possible in severe cases.
For additional treatment, you can douche with soda or chamomile, which will help relieve inflammation and speed up the healing process of the vaginal mucosa.
The entire course of therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
After antibiotic therapy, measures are taken to restore the natural microflora of the vagina - lactobacilli and physiotherapy are prescribed.
The doctor must order follow-up tests at the end of the course of treatment to check how effective the treatment was.
If necessary, re-treatment is carried out.
Important! Self-treatment can lead to complications.