Discharge from the mammary glands (when pressed or spontaneously) causes discomfort and a feeling of anxiety. This phenomenon can be caused by both natural physiological processes and pathology. Discharge from the breast can occur on its own or with pressure, during or after lactation. These factors play an important role and allow the doctor to determine the cause of the problem.
The main thing is to promptly identify dangerous symptoms that require medical intervention.
In any case, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. If you have any suspicions, consult your doctor.
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed
In most cases, discharge is observed due to physical pressure on the chest. During pregnancy and lactation, discharge from the mammary gland when pressed is considered normal if it is not accompanied by acute pain, increased body temperature and blood. Also, do not worry if secretions are released after nipple stimulation. As excitation increases, the gland begins to work more actively. In other cases, you need to contact a specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy. The main causes of unpleasant symptoms are the following diseases:
- Oncology. A malignant tumor in the mammary gland causes discomfort or pain in the breasts, redness of the skin, changes in the shape of the nipples and bloody discharge.
- Intraductal papilloma. It is a benign formation arising from the epithelium of the mammary gland. Among the main symptoms, it is worth noting painful sensations on palpation, as well as clear, white, green or yellow discharge mixed with blood.
- Hormonal disbalance. This disorder occurs due to pregnancy or taking contraceptives. The discharge may be clear or in the form of colostrum.
- Mastitis. It is an acute inflammatory process in the mammary gland, which in most cases is provoked by a staphylococcal infection. From the first days of the disease, the patient feels unwell, fever and pain in the breast area. If left untreated, purulent discharge with a greenish tint may appear.
- Ectasia of the milk ducts. This is an age-related or pathological expansion of the milk ducts, accompanied by an inflammatory process, pain, itching and dark green discharge from the mammary glands when pressed.
These diseases can progress quickly and move into a more severe stage. Effective treatment at the initial stage will avoid serious consequences.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Detection of unusual discharge from the breast is an indication to consult a doctor. Attempts at self-medication can provoke progression of the disease and serious complications. To reduce discomfort in the chest, which interferes with the quality of life, various analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs from the NSAID group are used. Patients during lactation who have serous or purulent discharge are advised to regularly express milk to prevent lactostasis.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the disease that caused the leakage of mammary gland secretions from the nipples; the patient’s age, pregnancy, and extragenital pathology also matter. For treatment, etiotropic and pathogenetic agents are selected. Complex therapy includes medications and physiotherapeutic methods. The most frequently prescribed groups of drugs are:
- Antibiotics
. These medications are used in all cases of bacterial infection of the breast. At the beginning of treatment, the selection of drugs is carried out empirically, the treatment regimen is usually adjusted after receiving the results of bacteriological culture. Most often, antibiotics from the group of beta-lactams and macrolides are used. - NSAIDs
. Anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated as pathogenetic therapy for mastitis and the consequences of chest injuries. The drugs improve general well-being, eliminate pain, and relieve local signs of inflammation well. NSAIDs are prescribed with caution in the presence of concomitant gastrointestinal diseases (ulcers, gastritis). - Hormonal agents
. For the treatment of various forms of mastopathy, antiestrogens are recommended - medications that reduce the effect of sex hormones on breast tissue and prevent the proliferation of fibrous tissue. Oral contraception is prescribed to reduce the concentration of estrogen and normalize hormonal levels. - Cytostatics
. Chemotherapy drugs are used for malignant neoplasms of the mammary glands as an independent method or as a preparation for surgical treatment. Treatment regimens are selected individually, taking into account the results of cytological and molecular diagnostics. Treatment may be supplemented with radiation therapy.
Surgery
In complicated forms of mastitis, opening and drainage are indicated. If the discharge is caused by benign or malignant tumors, surgery is recommended. Based on data on the stage of the disease and the histological characteristics of the tumor, different types of surgical operations are prescribed: excision of a fibrous node or cyst, sectoral resection of the mammary gland, lumpectomy. Diffuse breast changes and the presence of a malignant neoplasm are indications for radical mastectomy followed by mammoplasty.
Discharge during pregnancy
Changes in the breasts begin to occur starting in early pregnancy. In addition to an increase in size and increased sensitivity, discharge may appear. This is a natural process.
The mammary glands are actively preparing for lactation and producing colostrum. This is a yellow-tinged liquid that appears in all women at different stages of pregnancy. If the discharge is bloody or accompanied by painful sensations, you should consult a specialist to rule out possible health problems.
Competent diagnostics
Pathological processes in the mammary gland are the sphere of influence of the mammologist. When contacting him, you will be assigned:
- mammography;
- microscopy and culture of breast discharge;
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT;
- clinical blood test;
- cytological examination;
- tests for the level of various hormones in the body;
- radiography;
- ductography;
- biopsy, etc.
These diagnostic methods allow you to examine the structure of the mammary gland, assess the degree of its functionality, identify the presence of an inflammatory or infectious process, and also eliminate the risk of developing a cancerous tumor.
In addition, the doctor will listen to the patient, analyze her complaints, trace her medical history, and find out about cases of malignant neoplasms in the woman’s family.
He will then conduct a thorough contact examination of the breast. The concentration and appearance of the discharged fluid will be assessed, as well as the presence of blood in it. The specialist will carefully examine the condition of the breast itself. First of all, he will check for compliance with the norm the size, shape, color, type of nipple, its color and the severity of any changes.
If there are nodules, lumps or painful tumors in the patient’s mammary gland, he will conduct a differential diagnosis.
Discharge outside of pregnancy
In the absence of pregnancy, discharge can appear for many reasons. The main ones are hormonal disorders, injuries, benign and malignant formations, as well as inflammatory processes. In any of these cases, qualified treatment is required. To establish a diagnosis, the doctor conducts an examination, prescribes tests and other types of examination. Self-medication can lead to deterioration of well-being and also jeopardize the health and life of the patient.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is also required if intraductal papilloma is found. The affected area should be removed. The removed particles are subjected to histological examination to reliably exclude the malignant nature of the papilloma. For Paget's disease, a mastectomy is prescribed, which involves removing the affected gland. Next, chemotherapy sessions are prescribed.
Dangerous symptoms
Discharge from the chest is always accompanied by certain symptoms and characteristics. This allows you to make a preliminary diagnosis and determine a further diagnostic plan. Among the dangerous symptoms it is worth highlighting:
- Bloody issues. They are a sign of an acute inflammatory process, trauma, as well as malignant and benign formations.
- Increased temperature, enlarged mammary glands and purulent discharge are signs of mastitis.
- Yellow or green discharge may be a consequence of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Nipple discharge during breastfeeding
During pregnancy, a clear or cloudy droplet may come out of the breast when pressed. The mammary glands prepare to feed the baby and begin to produce secretions.
Immediately after childbirth, the discharge from the nipple becomes thick, bright yellow, even orange. This colostrum is the baby's first food. Colostrum is rich in protein, while it contains less fat and carbohydrates, and is easily digestible. A newborn eats a very small amount. In addition, colostrum provides it with beneficial bacteria for proper intestinal function and immune protection for the body.
On the third or fourth day after birth, colostrum is replaced by milk. In the first weeks, while lactation is established, milk may expand in the breast, flow out spontaneously, for example, when a nursing mother leans over, hears her baby crying, or even without any reason. At this time, you need special pads in the bra so that the clothes in the chest area do not get wet. Gradually, everything will return to normal, and milk will be released strictly “on demand” - when the baby starts to suckle or you pump your breasts.
Discharge from the breast may appear when pressure is applied for some time after breastfeeding has ended - from several weeks to several months.
All these discharges are normal.
Natural and non-hazardous discharge
There are a number of situations when discharge from the mammary glands is a natural physiological process that does not pose a threat to health. These include:
- Colostrum during pregnancy. The main function of the mammary glands is to produce milk to feed the baby. During pregnancy, the hormone prolactin is activated, which provokes the appearance of a special secretion in the alveoli - colostrum. It has a thick structure and is yellow in color.
- Small transparent discharge from the mammary glands when pressed (stimulating the nipples) may be a secretion. Any gland in the human body secretes a secretion, the mammary glands are no exception.
Thus, normal discharge includes colostrum during pregnancy and the appearance of clear liquid when the nipples are stimulated. In other cases, you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the problem and undergo treatment.
Breast self-examination
In order to “catch” the onset of a disease in time, it is useful to conduct periodic breast examinations yourself. It's easy and doesn't take much time.
The examination is carried out in the first half of the monthly cycle after the end of menstruation
- Once naked to the waist, you need to stand in front of the mirror. With your hands down, carefully examine your chest to see if there is any redness, swelling, or changes in the shape of the glands. Raise your hands behind your head and examine your chest in this position.
- Gently squeezing the nipples at the bases, check for any discharge.
- Holding one hand behind your head, use gentle circular movements to examine each gland from the nipples to the armpits. Repeat the examination in the supine position.
Normally, no hardness or swelling should be felt in the chest. Any oddities should alert you - discharge, inverted nipples, bulges, changes in skin color.
You need to examine your breasts yourself once every 3-4 months, this will allow you to notice any changes in a timely manner.
If you detect discharge from the mammary glands, be sure to consult a doctor immediately. There is no need to panic or be afraid. The vast majority of glandular discharges are not cancer. The term “cancerophobia” is even common among doctors, the fear of this disease is so strong among patients. Timely diagnosis and treatment will prevent the development of complications.
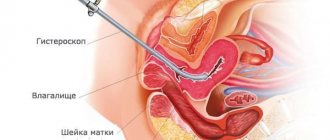
Ductography
Ductography is used to detect papilloma in the mammary duct. To do this, a thin tube (blunt needle) is inserted into the duct (from which discharge is detected), through which a contrast agent is injected into the duct. This drug fills the ducts and “flows around” the papilloma - it becomes noticeable. For small papillomas, the introduction of contrast has a cauterizing effect on them and the discharge may stop. If they appear again, surgery is indicated.
Ductography is a mammography with contrast filling of the breast ducts.
Prevention
To prevent the development of breast diseases it is necessary:
- Maintain optimal body weight and daily physical activity
- Maintain proper diet and sleep
- Avoid blows, bruises, cuts, punctures and other damage to the chest and décolleté area.
- Do not neglect natural feeding
- Give up bad habits, minimize the number of stressful situations
- Limit from excessive use of hormonal drugs
- Be examined by a mammologist twice a year
It is equally important to regularly self-palpate the glands. If there are neoplasms, they can be most clearly felt during menstruation. In everyday life, it is better to use comfortable underwear made of natural fabric. The bra should support the breasts, not compress them.
The listed recommendations have a positive effect on hormonal levels, help strengthen the immune system, and minimize the risk of pathological discharge from the mammary glands.
Cyst in the mammary gland Thyroid cyst: symptoms and treatment Bartholinitis Hypothyroidism Prostate adenoma - what is it? Symptoms and treatment of Pancreatitis
Breast papilloma surgery
Treatment of cystadenopapilloma is surgical. The operation consists of removing all the ducts of the mammary gland (Koenig operation or ductectomy). The patient will not be able to breastfeed after this operation. Such an operation is possible under a compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance policy.
For nulliparous women, or in cases where our patient plans to give birth and breastfeeding in the future, we offer Babcock surgery - this is when we find, isolate and remove only the duct with papilloma . In this way, it is possible to preserve the possibility of lactation in a woman through other (unremoved) ducts of this mammary gland.
Photo of the discharge of a duct with papilloma during Babcock's operation: the duct filled with bloody contents is different from all the others, which remain intact and will allow the girl to breastfeed in the future.
Video of the isolation of a blood-filled duct with papilloma during Babcock's operation: the remaining ducts - the light ones - remain intact, and the girl will be able to breastfeed.