Mucus is a thick, slippery substance that is produced in various human organs. In the intestines, it is needed to moisturize the mucous membrane and ensure the free passage of feces. Therefore, a small amount of mucus in the stool is not a cause for concern. But an increase in the amount of mucus, especially in combination with other symptoms, may indicate certain diseases of the digestive tract. Sometimes this is how malignant tumors manifest themselves.
- Causes of mucus in stool
- Symptoms to look out for when you have mucus in your stool
- What diseases cause mucus to appear in stool?
- In what cases should you consult a doctor?
- Examination for the appearance of mucus in the stool
What diseases cause mucus to appear in stool?
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional disorder when there are no pathological formations in the intestine, but its functioning is disrupted. The main manifestation is constipation, diarrhea, or alternating between them. The appearance of such a symptom as mucus in the stool is also very typical.
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease that can be severe and lead to the development of malignant tumors. The lesion can spread to all parts of the digestive tract - from the oral cavity to the rectum. At the same time, mucus is often present in feces.
Ulcerative colitis also belongs to the group of inflammatory bowel diseases and leads to the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane. They bleed, secrete pus and mucus - all these impurities are present in the stool. Other characteristic symptoms of the disease: pain and cramps in the abdomen, diarrhea.
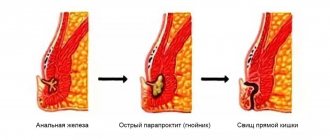
Proctitis is inflammation in the rectum. It develops as a result of various infections (including sexually transmitted infections), injuries, hemorrhoids, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Mucus in the stool is one of the characteristic symptoms.
Pseudomembranous colitis is a severe infectious disease that affects the rectum. It is caused by the microorganism clostridioides difficile, usually after the normal intestinal flora has been destroyed by antibiotics. Pseudomembranous colitis can cause severe, even life-threatening diarrhea, and the stool is foul-smelling and contains a lot of mucus.
Food poisoning usually manifests itself as flu-like symptoms, blood, and large amounts of mucus in the stool. It usually goes away within a few days, but in some cases it can be serious.
Intestinal infections and helminths can also lead to mucus in the feces.
Colon and rectal cancer. The leading symptom of the disease is blood in the feces. But mucus may also appear.
Anal fistulas or rectal ulcers . Ulcers are defects in the mucous membrane, and fistulas are pathological communications between the intestine and the surface of the skin. In both cases, the stool often has an unpleasant odor, and mucus is released in large quantities.
Allergic colitis most often occurs in young children as a reaction to cow's milk.
In this case, feces often contain a lot of mucus.
Mucus secretion
The following intestinal pathologies can lead to such discharge:
:
- haemorrhoids;
- Crohn's disease;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- anal fissures;
- fistula;
- neoplasms;
- proctitis;
- intoxication (usually the discharge is watery);
- herpes in the intestines;
- dysbacteriosis;
- peptic ulcer;
- condylomas, etc.
More often, mucus is released along with feces during bowel movements. However, there are also cases of discharge between trips to the toilet. This may be due to inflammation or low sphincter tone. In a number of pathologies, the mucus may have a pinkish tint, which indicates the presence of bleeding.
Examination for the appearance of mucus in the stool
To understand why mucus appears in the stool, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- General blood analysis.
- Stool analysis is a coprogram.
- Analysis of stool for infections, helminth eggs.
- Fecal occult blood test.
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic procedure during which the mucous membrane of the rectum and colon is examined using an instrument in the form of a thin flexible hose (colonoscope) inserted through the anus.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- Endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Video capsule endoscopy is an alternative to classical endoscopic examinations of the digestive tract. The patient is asked to swallow a small capsule containing miniature video cameras. This capsule will pass through the intestines, “inspect” its mucous membrane and leave the body naturally.
- CT, MRI.
Whatever disease causes mucus to appear in feces, it is better to diagnose it at an early stage. You can check the condition of your digestive organs using the comprehensive GIT program at the Euroonko clinic. This program includes all basic instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods, as well as consultations with our leading medical specialists.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Associated symptoms
Basically, various discharges are accompanied by other symptoms that accompany pathologies.
Among these symptoms
:
- itching and burning in the anus;
- blood in stool;
- pain in the anus or intestines;
- defecation disorders;
- weakness.
Specific symptoms of a particular pathology, combined with complaints about discharge, allow the doctor to make a primary diagnosis and prescribe additional diagnostic tests.
When you urgently need to call an ambulance
An ambulance should be called if intestinal obstruction is suspected. That is, in addition to tenesmus, a person has symptoms such as the inability to empty the intestines for a long time, severe and cramping pain, or slowly increasing pain in the intestines. The symptoms are also dangerous if the patient has vomiting, frequent tenesmus with blood and there is no discharge of gases or feces even after enemas.
Before the ambulance arrives, you should put the person on the bed, apply cold to the stomach and not give any food. In this condition, the patient should not take painkillers and laxatives. You should also not apply a heating pad to your stomach.
Treatment at home
Illnesses that produce false urges to defecate can often be treated at home. However, it should be noted that any use of medicines, including traditional medicine, must be agreed with the attending physician. For example, in addition to the main treatment, the patient is also prescribed auxiliary phytotherapeutic agents at home.
Let's give examples. To achieve temporary relief of the patient's condition, baths with herbal decoctions are sometimes prescribed. Enemas using sea buckthorn and rosehip (for ulcerative colitis) are often used. With dysentery, painful symptoms are eliminated by bed rest, a special diet, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
Answers to some popular questions
Many people are interested in the question of what urinary tenesmus is. Tenesmus is a false urge to defecate or urinate. Therefore, there are intestinal false spasms, and there is also bladder tenesmus. Accordingly, with such spasms, a tonic contraction of the muscles of the rectum or bladder occurs. Spasmodic contraction of the sphincters may also occur simultaneously. In both cases, false spasms do not allow either the intestines or the bladder to empty, that is, they are ineffective. Such phenomena are uncomfortable and may be accompanied by severe pain.
Another popular question from patients is: how to get rid of tenesmus? The success of treatment depends on correct diagnosis. The speed of the patient’s recovery will depend on how quickly and correctly the doctor determines the cause of the pathology. In cases where false urges cause tumors in the rectum, inflammatory, infectious diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, treatment should be started as early as possible. Then the result of therapy will be positive, and the process of recovery from the disease will take less time. Therefore, at the first symptoms of tenesmus, you should not hesitate, but get examined in a professional clinic.
Coprogram, general stool analysis
You can submit a coprogram at the nearest INVITRO medical office.
A list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory research is presented in the “Addresses” section. Interpretation of study results contains information for the attending physician and is not a diagnosis. The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: medical history, results of other examinations, etc.
Diagnostics
A proctologist deals with intestinal diseases. Already at the first appointment, the specialist is able to identify one or another cause of discharge from the anus. However, collecting anamnesis and digital examination is not enough for a comprehensive and accurate diagnosis.
Therefore, the proctologist may additionally prescribe the following types of studies:
:
- instrumental examination;
- stool tests;
- blood tests;
- endoscopic examination of the intestine;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity and intestines;
- Ultrasound.
What is mucus
The human body is very clever. It provokes a constant secretion of mucus in order to protect tissues and organs. Mucus is a jelly-like substance that is whitish, light orange, green or brown, or completely transparent. Formed during the secretion of intestinal glands.
Some of the mucus consists of epithelial cells and leukocytes. This dense secretion has an important role in the body: it protects the intestinal walls from the effects that toxic components of feces can have on it. White mucus is also a way to protect the intestines from mechanical effects caused by coarse dietary fiber. The secret helps prevent constipation, which is explained by difficulties in passing feces.
Causes of mucus from the anus. An adult body produces mucus constantly. It is also considered normal that the viscous contents of the intestines are constantly excreted. This is a guarantee of facilitating the movement of feces to the anus. The answer to the question of why constipation occurs can be simple: a lack of mucus slows down the process.
Constipation
If the process of inflammation begins in the intestines, then the removal of natural lubrication becomes more difficult. Its absence is the cause of anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and bleeding. Pathologies can also develop in case of excessive mucus production.
Important! In any case, you should always pay attention to the color of stool and its structure. If you suspect any violations, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Necessary measures
What to do with yellow diarrhea should be decided by the doctor after a preliminary examination and a full examination.
| Drink enough liquid. | To prevent dehydration, fluid loss should be regularly replenished. For minor diarrhea, which is not accompanied by signs of dehydration (dry skin and mucous membranes, rare urination, small volume of urine and its dark color, etc.), it is enough to drink a small amount of still water, herbal or weak black or green tea, decoction every 30 minutes dried fruits (50–100 ml:). If the first symptoms of dehydration are observed, rehydrating solutions may be required to replenish the deficiency of fluid and electrolytes in the body. Their use is allowed only with the permission of a doctor. |
| Do not take medications without a doctor's prescription. | Without knowing the cause of diarrhea, you can seriously harm your health with incorrectly selected medications. Therefore, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. |
| Do not place a cold or hot heating pad on the abdominal area. | Heat and cold are relevant “tools” in the treatment of a number of diseases. But they can cause irreparable harm to health if used unnecessarily or with contraindications. |
| Follow a diet. | For the entire period of treatment, it is necessary to give preference to easily digestible simple foods: pureed porridge, baked potatoes, kefir, etc. Sweets, baked goods, fatty and spicy foods, pickles, vegetables and fruits with a high content of coarse fiber, alcohol and carbonated drinks should be excluded. |
Causes of yellow stool
Nutritional Features
Eating large amounts of carrots and sweet potatoes causes stool to change color because these foods contain natural coloring agents. Bright yellow stool appears after eating dishes with turmeric. The symptom is observed when following a dairy diet and a predominance of fermented milk products in the diet. Natural causes only provoke a change in the color of stool; the consistency and frequency of bowel movements remain normal.
Childhood
In newborns, the stool is yellow, which is due to the consumption of breast milk alone. Stools normally have a mushy consistency. After a few months, the color changes to mustard or yellowish-green, which is also a normal variant. In children of the first year of life who are bottle-fed, the stool is light brown or light yellow with a pungent odor.
Intestinal infections
Light-colored stool is detected during infectious processes that affect the small intestine and interfere with normal digestion of food. Escherichiosis is characterized by liquid, golden-yellow stool. The frequency of bowel movements increases to 10-15 times a day. Greenish-yellow stool is produced by the gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis.
Frequent, light yellow stools occur with rotavirus infection. Feces are very liquid, with a specific pungent odor. The disease is usually diagnosed in children of preschool and primary school age who have not yet learned to maintain hygiene. Yellow feces are also provoked by other reasons: enterovirus infection, foodborne toxic infection.
Pancreatic enzyme deficiency
If there is a lack of digestive enzymes in the small intestine, some of the food is not digested, but is excreted from the body in stool, which becomes light or pale yellow in color. In chronic pancreatitis, the symptom is observed periodically: if you follow a special diet, the feces have a normal color; when the gastrointestinal tract is overloaded with fatty foods, it becomes lighter and acquires a mushy consistency.
The yellow coloration of stool is preceded by heaviness and pain in the epigastrium, patients complain of rumbling and flatulence. In acute pancreatitis, the color of stool suddenly changes to light yellow or grayish. At the same time, the person is bothered by severe girdling pain in the upper abdomen and repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief.
Diseases of the hepatobiliary system
The typical brown color of stool is due to bile acids and stercobilin, which enter the intestines with bile. Periodic light yellow stools with a mushy consistency are characteristic of chronic cholecystitis or cholelithiasis in the acute stage, when the secretion of bile is impaired. Similar symptoms are observed in functional disorders of the gallbladder.
Lightening of stool is caused by liver causes: viral or toxic hepatitis of mild to moderate severity, in which the biliary function is partially preserved. The appearance of yellow stool is accompanied by heaviness in the right hypochondrium, constant nausea and loss of appetite. Symptoms worsen after eating fatty foods. With the complete cessation of bile secretion, the yellow color of the stool is replaced by grayish-white.
Giardiasis
Giardia multiplies in the gallbladder, disrupts the flow of bile and helps lighten the stool. The frequency of bowel movements with giardiasis increases to 5-7 times a day, the feces are bright yellow and liquid, with a strong fetid odor. In addition, the person complains of dull pain in the right hypochondrium, flatulence, nausea and vomiting mixed with bile. Normalization of stool color occurs on days 5-7 of the disease.
Celiac disease
Symptoms occur with large consumption of cereals - barley, wheat, rye. Light yellow, pasty stools with a strong unpleasant odor may appear periodically, and then constantly in childhood and adolescence, which is combined with weight loss, stunted growth and physical development. Newly detected yellow stool in an adult indicates a mild form of celiac disease, which can be easily controlled with diet.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Many medications provoke disturbances in the digestion and absorption of food, which is manifested by yellowing of stool and an increase in the frequency of bowel movements. A person notes seething and rumbling in the intestines, pain throughout the abdomen, and lack of appetite. When taking antibiotics, the stool color is greenish-yellow, which is associated with intestinal dysbiosis. The yellow color of stool is caused by the following medicinal reasons:
- Anti-tuberculosis drugs
: isoniazid, ethambutol, streptomycin. - Estrogen derivatives
. - Cytostatics
: methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, adriamycin. - Some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
: aspirin, paracetamol, diclofenac.
Rare causes
- Viral infections
: cytomegalovirus, infectious mononucleosis. - Hormonal changes in women
: premenstrual period, pregnancy, menopause. - Bilirubin conjugation disorders
: Gilbert's syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome. - Psychological reasons
: severe stress, depression.
Intestinal candidiasis. Indications for examination
Indications for examination of the gastrointestinal tract to exclude fungal infection should be the following:
- the presence of 2 risk factors for the possible occurrence of candidiasis,
- double superficial colonization of candida,
- the presence of reasons that can lead to disruption of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract with excessive growth of fungi of the genus Candida.
- febrile conditions of unknown origin, resistant to antibiotic therapy,
- skin and allergic diseases, because Candida is a trigger for allergic diseases and a factor favoring their development.
Algorithm for diagnosing intestinal microflora disorders with overgrowth of Candida flbicans:
- Analysis of medical history, identification of risk factors,
- analysis of clinical data,
- microbiological and gas chromatographic methods for studying disorders of the microflora of the intestinal tract (various biological environments),
- smears - impressions from the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus,
- if systemic candidiasis is suspected, it is necessary to culture blood and biological fluids and tissues for the presence of a fungal infection,
- serological diagnosis and assessment of the effectiveness of treatment based on the levels of antibodies to candida,
- inflammatory markers (lysozyme, a-antitrypsin, elastase),
- secretory immunoglobulin A, which allows assessing the degree of activity of the intestinal-associated immune system,
- immunological status (screening) level 1.
All laboratory data should be assessed and analyzed in conjunction with the patient's current clinical situation.
How is the child examined?
In most cases, diarrhea with mucus does not require any specific examination7. The doctor assesses the child’s condition, examines him and, based on this, makes recommendations for treatment. To distinguish infectious causes of mucous diarrhea from non-infectious ones, the pediatrician prescribes laboratory tests and instrumental research methods4,7.
For a correct diagnosis, you should inform the doctor about the child’s eating habits, recently taken medications, and a tendency to allergies2.
Up to contents
Intestinal candidiasis. Prolonged treatment
The duration of treatment is at least 6 weeks, and then prolonged pulse therapy in short courses with individual selection of drugs for 6 months, but observing the principles of prolonged treatment of gastrointestinal dysbiosis with overgrowth of Candida fungi.
- Rational nutrition continues mainly with the limitation of sugar-containing foods and dishes.
- Repeated courses of citrosept.
- Lactose-containing probiotics 10 days each month.
- Immunomodulatory drugs (repeated courses after 3 months)
- Hepatoprotectors – 2 courses over 6 months.
Assessment of the treatment effect according to the clinical and laboratory data discussed above, during treatment and after 6 months.
Preventive measures
Getting rid of a problem and consolidating the result is far from a reason to relax and let health-related matters take their course. Prevention, which should take a strong place in the life of every person, will help prevent recurrence.
Read also: Diagnosis of chronic appendicitis, symptoms in women and men, treatment and prevention of the disease
The main preventive measures are as follows:
- quality control of food entering the body,
- following the principles of healthy eating,
- maintaining personal hygiene rules,
Personal hygiene
- control of stool regularity,
- prevention of worms,
- avoiding severe overheating and hypothermia of the body,
- eliminating problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
It will help to maintain intestinal health and systematically undergo a medical examination at the clinic at your place of residence. It is not difficult to understand the reasons for the release of mucus from the anus in men and women, but the main thing is not to panic and stick to a clear plan of action, where the first priority is contacting a therapist.