Muscles are organs of the human body that are made up of muscle tissue. They allow a person to perform body movements and contract under the influence of nerve impulses. The term "myalgia" is used to describe a symptom that is expressed by muscle pain. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, which will be discussed in this article.
Myalgia occurs when moving or pressing on muscles. It can affect one or several muscles at once. Painful sensations may affect ligaments and tendons located nearby. If you want to know why the muscles in your body hurt and how to relieve muscle pain, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. Our doctors will conduct a diagnosis and find out the reason why you are experiencing discomfort. In accordance with it, treatment will be prescribed, which will definitely be effective.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
Make an appointment
Muscle fatigue
In our technological age, many people are gradually forming a new “bad habit”. Spending most of the day in front of a computer screen or holding mobile gadgets in our hands, we may not even notice that we are sitting in a completely uncomfortable and unnatural position. It especially affects the muscles of the shoulder girdle, neck, back and right arm, which is constantly on the computer mouse of office workers1. Staying in one position for a long time or using stereotyped movements can lead to overstrain of the muscles involved, which we feel as soreness1.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
Patients suffering from muscle pain undergo diagnosis, treatment and restoration of the body without leaving the clinic. The Kuntsevo Medical Center has its own rehabilitation department. The success of its work is based on the availability of modern highly efficient equipment, a staff of experienced specialists, and the application of the principle of an individual approach.
The technical equipment of the clinic meets modern world standards. To restore the body after an illness, manual therapy sessions are often prescribed. Its peculiarity is its effect on tissues to ensure the normal functioning of the systems of the human body. During the procedures, restriction of joint mobility is eliminated, muscles are relaxed, and minor tissue compactions are removed. Properly performed manual therapy is gentle and completely painless.
Exercise stress
“Body aches” after physical activity can occur both in untrained people and in professional athletes8. And the cause of discomfort is the accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products in muscle cells; in particular, painful sensations are caused by an excessive amount of lactic acid (lactate)2. Less commonly, the cause is microtrauma, but this can only occur if the training rules are violated8.
Muscle soreness due to overwork does not occur immediately, but after a few hours or within 1-2 days after training or unusual physical activity and disappears within a week8.
Pathologies
Pathological pain in the muscles, requiring a mandatory visit to a specialist, is expressed in the following:
- constant or chronic pain;
- twitching nature of the disease;
- pain appeared after training, but does not go away after rest;
- redness of soft tissues or swelling is observed;
- accompanying symptoms are observed in the form of fever, shortness of breath, rash, and urinary retention.
Important! If at least one of the above conditions occurs, it is recommended to contact a specialist.
Injuries
Severe pain can occur when muscle fibers and tendons are torn. This usually happens if the load is excessive and the muscles are not prepared for it1. But they can also be damaged by sudden movements3. Unlike “ache” due to muscle overwork, pain due to injury occurs immediately, at the peak of the load3.
It should be remembered that even a small, but untreated injury can cause an even more severe sprain3. Therefore, if you experience pain during physical activity, be sure to consult a doctor to rule out a serious injury.
to come back to the beginning
Lifestyle recommendations
As preventative measures for myalgia of various origins, it is important to avoid heavy physical activity and stress, not to get too cold, to fully treat infectious diseases and to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Aching muscle pain is a fairly common occurrence; sometimes it is harmless and goes away soon, but sometimes it is a consequence of serious diseases that require monitoring and treatment. Highly qualified specialists of the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center are ready to provide timely and high-quality assistance in resolving this issue.
Diseases of the spine and joints
Muscles react to disruption of the joints4 and vertebrae5 associated with them. Therefore, myalgia is one of the symptoms of diseases of the spine5,11 and joints of the limbs4. For example, with osteochondrosis or scoliosis (curvature of the spine), pain in the neck, chest or lower back is associated with overstrain of the paravertebral muscles5,11. And in advanced cases, when the vertebra compresses the nerve root emerging from the spinal cord, the pain can “radiate” to the arm or leg11.
Often myalgia with osteochondrosis is combined with a feeling of numbness or “crawling goosebumps”. At the moment of acute pain, a person freezes, taking a forced position11.
Treatment results
Treatment of muscle pain is carried out in various ways. Patients are prescribed:
- acupuncture and acupressure treatments;
- electro- and physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- manual manipulations.
Special exercises are especially relevant for chronic pain that is a consequence of spinal pathologies, for example, osteochondrosis, disc herniation or spondylosis. For severe muscle tissue injuries, surgical treatment methods are used.
Other reasons
Almost any disease of the internal organs can lead to myalgia11. When an organ is affected, it creates pain impulses that are partially transmitted to the muscles located nearby11.
Myalgia can also be caused by:
- endocrine diseases, such as thyroid hormone deficiency16,7;
- vascular pathologies that disrupt the nutrition of the muscles of the limbs15,16;
- chronic fatigue syndrome7;
- imbalance of microelements in the body16;
- taking medications that lower blood cholesterol levels12.
to come back to the beginning
Vein diseases
Leg pain is accompanied by:
- Varicose veins;
- phlebitis and thrombophlebitis;
- postthrombophlebitic syndrome.
Varicose veins
This disease is widespread and is a very pressing problem in medicine and cosmetology.
Find out more about the promotion >>>
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
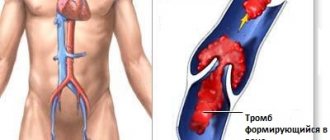
Phlebitis is inflammation of a vein. Thrombophlebitis is a complication of phlebitis or varicose veins of the lower extremities. With thrombophlebitis, a blood clot forms in the inflamed vein. Pain is a concern and swelling of the legs is possible.
Deep vein thrombosis is fraught with complications, the most dangerous of which are venous gangrene of the limb (with high blockage and blockage of all outflow pathways of venous blood) and pulmonary embolism. The risk of thromboembolism is highest in the presence of an unfixed - floating thrombus. The larger the detached fragment of the blood clot, the greater the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome, including death.
A common complication of deep vein thrombophlebitis is postthrombophlebitis syndrome.
Features of myalgia
Pain emanating from the muscles is usually deep6. Acute myalgia is protective in nature because it causes reactions aimed at eliminating the damaging factor11. Such reactions include, for example, muscle spasms4. But despite its protective nature, there is almost always a risk that the pain will become chronic11. There are 2 main causes of chronicity:
- Increased sensitivity. In response to irritation, the muscle releases substances that support inflammation. They further irritate pain receptors in the muscles. In response to frequent signals, the central nervous system lowers the pain threshold, so we can feel soreness in the muscle even when it is not strongly irritated11.
- Spasm. If pain and spasm persist, a “vicious circle” is formed: pain causes spasm, and spasm maintains pain1,5, 11.
Treatment for muscle pain
The CELT Pain Clinic uses modern methods for treating muscle pain, which allows you to effectively cope with the existing problem. First of all, it is aimed at eliminating its original source. Systemic therapy allows you to minimize (or even completely eliminate) pain. It involves the use of painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opiates. Systemic therapy is combined with other treatment methods:
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- electromyostimulation;
- physiological and manual therapy.
CELT specialists recommend the prevention of muscle pain, which consists of maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, ergonomics of the workplace and eliminating bad habits.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Diagnosis of muscle pain
Determining why myalgia occurs is not always easy. Only a doctor can understand the causes and select treatment that helps get rid of disturbing symptoms or alleviate them. To find out the cause of myalgia, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination, including a neurological one, prescribes laboratory tests, ultrasound, computed tomography and other research methods3.
Various specialists treat myalgia. Depending on its cause, a traumatologist, rheumatologist, neurologist or endocrinologist can help you.
Classification
In clinical practice, several classifications of muscle myositis are used, which are based on the etiology, characteristics of symptoms and the course of the disease.
Depending on the origin, all myositis is divided into the following forms¹:
- Infectious purulent. Variants of myositis caused by pathogenic bacteria, in which the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of purulent-necrotic masses.
- Infectious non-purulent. Inflammation of striated muscles of infectious origin (most often viral), in which purulent masses do not form. They occur more easily than purulent forms.
- Parasitic. Muscle myositis, which is the result of toxic-allergic reactions and characteristic changes caused by infection with protozoa.
- Myositis ossificans. A characteristic difference is the deposition of calcium salts in the connective tissue. The shoulders, hips and buttocks are most often affected.
- Polymyositis. A variant of autoimmune myositis, in which a large number of muscles become inflamed at once. In children, such myositis can be combined with damage to the lungs, heart, blood vessels and skin, and in adults it is often associated with malignant tumors of internal organs.
- Dermatomyositis or Wagner's disease. An independent autoimmune pathology, in which, in addition to inflammation of the striated muscles, the skin, smooth muscles and internal organs are also affected.
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, the following are distinguished:
- Local myositis. More often they are of traumatic and infectious origin. Accompanied by inflammation of one or more adjacent muscles.
- Diffuse or generalized. Inflammation of skeletal muscles in different parts of the body differs. In most cases, they are associated with autoimmune pathologies.
Based on the activity and nature of inflammation, myositis is divided into the following options:
- Spicy. They are characterized by a debut with pronounced symptoms.
- Subacute. They often appear gradually, but progress relatively quickly.
- Chronic. They can be the result of acute myositis or develop independently, accompanied by moderate persistent symptoms.
Figure 1. Exercises for the neck: maximum turns of the head to the right and left (5 times), slow tilts of the head to the shoulders to the right and left (5 times in each direction). Dynamic resistance of the neck and palms to head tilts in different directions. Image: cteconsulting/Depositphotos
Nutrition for myositis
The diet should consist of nutritious but easily digestible dishes. Foods high in vitamins A, B, C, D, E, PP help fight inflammation. The daily menu should include:
- fresh vegetables and herbs;
- sweet and sour fruits - oranges, apples, plums, kiwi;
- foods rich in salicylates - honey, vegetable oils, legumes, nuts, black and green tea, peppers;
- boiled and stewed beets, carrots, potatoes;
- decoctions of beneficial herbs;
- sea fish.
In addition to clean water, it is recommended to consume more vitamin drinks: juices, fruit drinks, homemade compotes. The total volume of liquid should reach 2 liters.
For spasmodic pain, it is recommended to include foods rich in calcium, magnesium, and zinc in the diet. These elements are found in cereals, dairy products, green crops, liver, pumpkin, and chicken eggs.
Types of myositis and causes
The appearance of muscle pain with compaction in the affected area, a feeling of spasms, swelling, general malaise, and increasing pain with movement indicate the development of myositis. The disease is classified according to its cause.
- Traumatic myositis. The occurrence is provoked by trauma. Muscle fibers are affected by excessive physical activity or injury. As a result, internal tissue ruptures, hemorrhage occurs, and local inflammation progresses. Pathology is indicated by redness, swelling, local pain, and muscle weakness.
- Parasitic. This form is caused by parasitic larvae. The disease is easily confused with other types of degenerative and inflammatory diseases. Muscles in any part of the body can be affected: diaphragm, tongue, eye muscles, buttocks, calves.
- Infectious. The impetus for development is a previous infection. The disease can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, and other viral diseases. The pain affects one muscle group or several.
- Rheumatic. A disease of an infectious-allergic nature that develops against the background of infectious intoxication in the presence of immune disorders. The cause is often streptococcus.
- Ossifying. It means the gradual ossification of muscle tissue. This is a rare genetic disease.
- Dermatomyositis. A progressive disease of a systemic nature with an unknown etiology. Affects smooth, skeletal muscles and connective tissues. Causes damage to the skin. Accompanied by impaired motor functions.
- Polymyositis. Refers to a chronic type of muscle inflammation. The reasons lie in autoimmune disorders. May occur as a result of a viral infection.
The disease is also classified according to the nature of its course. The chronic form means that after treatment the disease subsides, but the problem is not completely eliminated. There is a sluggish manifestation of symptoms. As a result of an unfavorable combination of circumstances, for example, severe hypothermia, the disease worsens again. Traumatic and infectious myositis occurs in acute form. It is characterized by the sudden onset of pain, which is most often local in nature.
The main causes of myositis include:
- infectious diseases;
- soft tissue injuries;
- physical stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- muscle infection by parasites;
- regularly performing work in an awkward position.
Features of therapy in pregnant women
Myositis develops during pregnancy for two reasons: against the background of an infectious disease and due to increased load on the back muscles as a result of weight gain.
The difficulty of treatment is the fact that a limited list of medications can be used during pregnancy. Most analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs have a wide range of side effects and contraindications. The active substances from their composition can penetrate the placenta to the fetus and cause harm and have a negative impact on development. The doctor must take into account the duration of pregnancy, the peculiarities of its course in the patient, and correlate the risks of taking medications with the effect of treatment.
To relieve inflammation and reduce fever, medications containing paracetamol are mainly prescribed. Creams and ointments based on herbal ingredients are suitable for local anesthesia and relief of muscle spasms. It is prohibited to use ointments containing animal and insect poisons.
To relieve pain, dry heat and light massage procedures are suitable. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to avoid sudden weight gain, use a bandage in the third trimester, and perform special exercises for pregnant women.
Prevention of myositis
You can exclude recurrent manifestations of myositis if you pay attention to prevention:
- harden the body, often walk in the fresh air, regularly ventilate the room, conduct contrasting douches with cool and warm water;
- sunbathing, swimming in natural reservoirs in the warm season;
- avoid drafts, protect the body from hypothermia, dress according to the weather;
- exercise in moderation, avoid unnecessary stress on the muscles, start with warm-up exercises;
- when working in an uncomfortable position, take short breaks, perform warm-up exercises for stiff and tired muscles;
- Regularly use the services of a massage room, do a general preventive massage for all muscle groups, massage the back or collar area.
The myositis treatment program includes drug treatment, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and dietary nutrition. Following the doctor’s recommendations and giving up bad habits speeds up recovery and serves as a preventive measure against relapses.