Composition and release form
| Capsules | 1 caps. |
| chondroitin sulfate sodium | 0.25 g |
| excipients: lactose (milk sugar); calcium stearate | |
| gelatin capsule composition: titanium dioxide; Azorubine dye; crimson dye (Ponceau 4R); patented blue dye (patent blue V); diamond black dye (diamond black BN); methyl parahydroxybenzoate (methylhydroxybenzoate); propyl parahydroxybenzoate (propylhydroxybenzoate); acetic acid; gelatin |
in a blister pack 10 pcs.; in a cardboard pack of 5 packs or in jars of 20 pcs.; in a cardboard pack 1 jar.
| Ointment 5% | 100 g |
| chondroitin sulfate sodium (calculated on dry matter) | 5 g |
| dimexide (dimethyl sulfoxide) | 10 g |
| excipients (base): anhydrous lanolin; medical Vaseline; purified water |
in aluminum tubes of 30 g; in a cardboard pack 1 tube.
The role of chondroitin in the human body
Chondroitin performs several important functions in the human body:
- stimulates the formation of glycosaminoglycans - the main building material of connective tissue, slowing down the destruction of cartilage and promoting its restoration;
- activates the formation of hyaluronic acid, which retains water in the tissues - this is important for maintaining the elasticity necessary for full shock absorption of the joint;
- interacts with all other components of cartilage, uniting and structuring them, providing the necessary strength;
- forms small water cavities in the cartilage, increasing shock absorption;
- stimulates the production of intra-articular fluid necessary to nourish cartilage tissue and smooth movement of articular surfaces relative to each other;
- makes synovial fluid more fluid, maintaining its natural viscosity;
- reduces pain in joint diseases and increases mobility in them, including by increasing the amount and fluidity of intra-articular fluid;
- prevents the growth of blood vessels into the cartilage;
- suppresses the formation of reactive oxygen species, which accumulate in large quantities during joint aging;
- blocks enzymes that destroy connective tissue;
- suppresses lipid synthesis, thereby preventing the development of atherosclerosis in the walls of blood vessels.
Pharmacodynamics
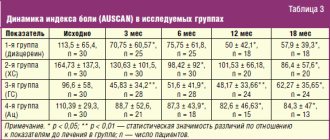
Capsules. Affects metabolic processes in hyaline and fibrous cartilage, reduces degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of joints, stimulates the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans. Slows down bone resorption and reduces calcium loss, accelerates bone tissue restoration processes. When treated with Chondroitin-AKOS, pain decreases and mobility of the affected joints improves. The therapeutic effect persists for a long time after the end of the course of treatment.
Ointment. Chondroitin-AKOS contains chondroitin sulfate, a stimulator for the restoration of cartilage tissue in joints (chondroprotector), obtained from bovine tracheal cartilage, and dimethyl sulfoxide.
Chondroitin sulfate is a high-molecular mucopolysaccharide that inhibits the processes of destruction of cartilage tissue and accelerates the processes of its restoration. Suppresses enzymes that cause damage to cartilage tissue and prevents its degradation; stimulates the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans by chondrocytes; promotes the restoration of the joint capsule and cartilaginous surfaces of the joints, increases the production of intra-articular fluid. Improves phosphorus-calcium metabolism and reduces calcium loss in cartilage tissue, slows down bone resorption, normalizes metabolism in hyaline tissue, accelerates regeneration (recovery) processes and inhibits degeneration (destruction) of cartilage tissue. Structurally close to heparin, it prevents the formation of fibrin blood clots in the synovial and subchondral microvasculature. As a result of the effect, pain decreases and mobility of the affected joints increases.
Dimethyl sulfoxide, which is part of the ointment, has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and fibrinolytic effect, promotes better penetration of chondroitin sulfate through cell membranes deep into tissues.
Chondroitin-AKOS ointment has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, normalizes metabolism and stimulates restoration processes in joint tissues, leads to a reduction or disappearance of pain in the joints, improves joint mobility, and slows down the progression of osteoarthrosis and osteochondrosis.
Chondroitin-Acos ointment 5% 30g
Compound
Active substance: chondroitin sulfate 50 mg.
Excipients: dimethyl sulfoxide (100 mg/g), anhydrous lanolin, medical petroleum jelly, purified water.
Pharmacokinetics
Data on the pharmacokinetics of the drug Chondroitin-AKOS are not provided.
Indications for use
Treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis of peripheral joints and spine.
Contraindications
- Acute inflammatory process in the wound area at the site of intended application of the ointment;
- widespread tissue necrosis;
- excessive granulation, violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of intended application of the ointment;
- hypersensitivity to the drug.
Directions for use and doses
The ointment is applied 2-3 times a day to the skin over the lesion and rubbed in for 2-3 minutes until completely absorbed. Usually the course of treatment ranges from 2-3 weeks to 2 months. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated.
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, protected from light at a temperature of 2° to 20°C.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the package.
special instructions
If allergic reactions develop, the drug should be discontinued.
Avoid getting the ointment on mucous membranes and open wounds.
Description
A drug that stimulates the process of regeneration of cartilage tissue, with an anti-inflammatory effect.
Pharmacodynamics
Stimulator of cartilage tissue regeneration in joints (chondroprotector). Chondroitin sulfate is a high molecular weight mucopolysaccharide that is obtained from bovine tracheal cartilage. Affects metabolic processes in hyaline and fibrous cartilage, reduces degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of joints, stimulates the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans in chondrocytes. Suppresses the activity of enzymes that cause damage to cartilage tissue, promotes the regeneration of the joint capsule and cartilaginous surfaces of the joints, and increases the production of intra-articular fluid. Improves phosphorus-calcium metabolism and reduces calcium loss in cartilage tissue, slows down bone resorption, normalizes metabolism in hyaline tissue, and accelerates regeneration processes. Structurally close to heparin, it prevents the formation of fibrin blood clots in the synovial and subchondral microvasculature. As a result of the effect, pain decreases and mobility of the affected joints increases.
Dimethyl sulfoxide, which is part of the ointment, has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and fibrinolytic effect, promotes better penetration of chondroitin sulfate through cell membranes deep into tissues.
Chondroitin-AKOS ointment has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, normalizes metabolism and stimulates restoration processes in joint tissues, leads to a reduction and disappearance of joint pain, increased joint mobility and slows down the progression of osteoarthritis and osteochondrosis.
Side effects
Rarely: allergic reactions.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The need to use the drug during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding) is determined by the doctor individually.
Interaction
There have been no cases of negative drug interactions when prescribing the ointment during therapy with other drugs included in generally accepted treatment regimens for degenerative diseases of the joints and spine.
Overdose
There were no cases of negative drug interactions when prescribing Chondroitin-AKOS ointment during therapy with other drugs included in generally accepted treatment regimens for degenerative diseases of the joints and spine.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Chondroitin-AKOS ointment does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and engage in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentrated attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
For both dosage forms: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
For capsules additionally: children under 15 years of age (due to lack of accurate data).
With caution: bleeding and tendency to bleeding, thrombophlebitis.
For ointment additionally: acute inflammatory processes in the wound area; widespread tissue necrosis; excessive granulation; violation of the integrity of the skin at the sites of intended application.
With caution: do not use Chondroitin-AKOS ointment without consulting a doctor during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as in childhood.
Choosing a remedy for osteoarthritis: which components are especially important?
When osteoarthritis and the symptoms that accompany it appear or worsen, a logical question arises - which remedy should be preferred in order to slow down the destruction of joints, reduce discomfort and pain. What is the difference between the products presented on pharmacy shelves and what exactly should you look for in their composition?
Osteoarthritis and its treatment
According to ICD-10, the disease is called osteoarthritis. This affects mainly large joints - most often the hip and knee. But this does not exclude the involvement of smaller joints, for example, in the hand area.
A group of drugs used to combat changes in joints due to osteoarthritis are called chondroprotectors. These are components that are used as a building material to renew and improve the structure of cartilage tissue. Cartilage covers the surfaces of the bones that form the joint, cushioning it during movements and ensuring full gliding of moving parts. Damage to cartilage in osteoarthritis leads to disruption of the structure and function of the joints and the appearance of symptoms characteristic of the disease. Taking chondroprotectors helps slow down the development of osteoarthritis, influencing not only the symptoms, but also the trigger mechanisms.
Chondroprotectors come in different forms:
o Solution for intramuscular injection is a prescription drug prescribed by a doctor;
o Tablets or capsules;
o Gels or ointments for external use.
The composition can contain either one active substance or a combination: two or three active components.
Today there are three most studied chondroprotectors:
· NEM® complex – a new generation chondroprotector;
chondroitin sulfate;
glucosamine
Let's take a closer look at these substances.
®
complex for joints
The abbreviation NEM ® comes from the English name – Natural Eggshell Membrane, which means “natural eggshell shell”. The complex was the result of innovative scientific development by ESM Technologies LLC (USA). The components are obtained using a specific patented technology of partial hydrolysis with gentle fermentation of the substance.
The NEM® complex is a natural source of substances essential for joints - glycosaminoglycans. They make up the matrix of cartilage tissue. The complex contains chondroitin sulfate, elastin, hyaluronic acid, collagen. These substances ensure the formation of a supporting frame. In addition, the complex contains minerals – magnesium, calcium [8,9].
During the 15-year period of studying the effectiveness of the NEM® complex, 16 experimental and clinical studies were published. They were published in different countries - Italy, USA, Germany, Canada, Turkey [10]. According to scientific works, it has been determined that NEM® has anti-inflammatory [11], immunomodulatory [12] effects, and helps slow down destruction processes [13].
Main effects of the NEM complex®:
· reduction in the level of compounds that provoke the inflammatory process [8];
Reducing the severity of pain in the joints caused by physical activity;
· reduction in the intensity of pain, as well as stiffness due to osteoarthritis [14];
· improvement of flexibility, mobility [15];
· inhibition, reduction in the severity of age-related changes in cartilage tissue in osteoarthritis [16];
During the study of the NEM® complex, its high safety profile was proven [17].
Chondroitin sulfate for joints
The substance that makes up the cartilage matrix, its frame. This is one of the most thoroughly studied chondroprotectors. Its use is included in clinical recommendations for the treatment of osteoarthritis, developed by domestic and European professional associations [1-4]. The body uses chondroitin as a building material necessary to renew cartilage and repair its damage. Due to a sufficient supply of chondroitin, it is possible to maintain the necessary viscosity of the intra-articular fluid and inhibit the activity of enzymes - hyaluronidase, elastase, which destroy the structure of cartilage. Plus, chondroitin has analgesic properties, suppressing the concentration of compounds that provoke inflammation and pain [5,6].
Due to its complex action, taking chondroitin helps [5,6]:
· reduce the intensity of pain and reduce the need for painkillers;
· improve mobility;
· slow down destruction.
In joint products, chondroitin sulfate can be either the sole component or combined with other compounds.
Glucosamine for joints
A natural compound necessary for the production of synovial fluid, especially its components such as proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. The effectiveness of this substance has been confirmed through numerous studies.
Glucosamine helps [7]:
· reduce the intensity of pain;
· inhibits the activity of destruction processes in cartilage;
· stimulates the synthesis of polysaccharides that are present in the joint fluid under normal conditions.
Often, several components are combined in the complexes: glucosamine, chondroitin and other chondroprotectors, which mutually enhances their effect.
MUCOSAT capsules®*
All three described components are included in the composition of MUCOSAT® capsules. This drug is classified as a new generation of chondroprotectors. The composition of the capsules is supplemented with harpagophytum root extract (also called fragrant martinia) and manganese.
Harpagophytum root extract is a natural anti-inflammatory substance studied by specialists. Its use helps reduce pain and improve mobility [18,19].
Manganese for joints helps protect and renew cartilage, and our body also uses this mineral to produce collagen [20].
MUKOSAT® capsules can be used as an addition to a complex regimen for osteoarthritis and osteochondrosis [21].
The components of the capsules contribute [21]:
· reducing pain and inflammation;
· increased mobility;
· protection of cartilage tissue of joints and spine.
Detailed information, including the regimen and mode of administration, can be found in the instructions for use of MUKOSAT® capsules.
All about MUKOSAT® capsules on mukosat.ru
* BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE SUPPLEMENT. NOT A MEDICINE.
Sources:
*Contains NEM® complex exclusively in Mucosat® capsules
1. Clinical recommendations “Osteochondrosis of the spine”, All-Russian public organization Association of Traumatologists and Orthopedists of Russia, 2021.
2. Kloppenburg M, Kroon FP, Blanco FJ, et al2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of hand osteoarthritis Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019;78:16-24.
3. Olivier Bruyère et al. An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO), Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, Volume 49, Issue 3, 2021, Pages 337-350.
4. Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Association of Rheumatologists of Russia. 2016
5. Mezenova T.V. Boosted therapy for osteoarthritis: expanding the boundaries of what is possible. Surgery. Journal named after N.I. Pirogov. 2018;(5): 91-95
6 Fedotova A. V., Mironova O. P. Chondroprotector mucosat in an integrated approach to the treatment of patients with nonspecific back pain. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakov. 2018;118(9):133-137.
7. Lopes Junior, Osmar Valadao, & Inacio, Andre Manoel. (2013). Use of glucosamine and chondroitin to treat osteoarthritis: a review of the literature. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia, 48(4), 300-306.
8. Naumov A.V., Khovasova N.O., Tkacheva O.N. Chondropenia at the forefront of the osteoarthritis epidemic: from aging joints to the clinical manifestation of the disease // Attending physician, 2021. No. 12. P. 69-69.
9. Ruff KJ, DeVore DP, Leu MD and Robinson MA. (2009) Eggshell Membrane: A Possible New Natural Therapeutic For Joint & Connective Tissue Disorders. Results From Two Open-label Human Clinical Studies. Clinical Interventions in Aging 4:235–240.
10. URL: stratumnutrition Access date 04/07/2021
11. Wedekind KJ, Ruff KJ, Atwell CA, Evans JL and Bendele AM. (2016) Beneficial Effects of Natural Eggshell Membrane (NEM) on Multiple Indices of Arthritis in Collagen-Induced Arthritic Rats. Modern Rheumatology, 27(5):838-848.
12. Ruff KJ. Eggshell membrane hydrolyzates activate NF-κB in vitro: possible implications for in vivo efficacy. J Inflamm Res. 2015.
13. Sim BY, Bak JW, Lee HJ, Jun JA, Choi HJ, Kwon CJ, Kim HY, Ruff KJ, Brandt K and Kim DH. (2015) Effects of natural eggshell membrane (NEM) on monosodium iodoacetate-induced arthritis in rats. Journal of Nutrition and Health, 48(4):310-318.
14. Ruff KJ, Winkler A, Jackson RW, DeVore DP and Ritz BW. (2009) Eggshell Membrane in the Treatment of Pain and Stiffness from Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized, Multicenter, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Clinical Study. Clinical Rheumatology 28:907–914.
15. Brunello E and Masini A. (2016) NEM® Brand Eggshell Membrane Effective in the Treatment of Pain and Stiffness Associated with Osteoarthritis of the Knee in an Italian Study Population. International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7:169-175
16. Eskiyurt et al. (2019) Efficacy and Safety of Natural Eggshell Membrane (NEM®) in Patients with Grade 2/3 Knee Osteoarthritis: A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Single-crossover Clinical Study. Journal of Arthritis, 8(4):1000285
17. Ruff KJ, Endres JR, Clewell AE, Szabo JR and Schauss AG. (2012) Safety evaluation of a natural eggshell membrane-derived product. Food and Chemical Toxicology 50:604–611.
18. Ribbat JM, Schakau D. Tratamiento de los dolores crónicos activos en el sistema de locomoción // Natura Med. - 2001. - V. 16, No. 3. - P. 23-30.
19. Chrubasik JE, Roufogalis BD, Chrubasik S. Evidence of the effectiveness of herbal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of painful osteoarthritis and chronic low back pain // Phytother. Res. - 2007. - V. 21. - P. 675-683.
20. Delmas PD Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Lancet. 2002;359(9322):2018–2026. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08827-x
21. Biologically active food additive Mucosat® capsules. Certificate of state registration No.RU. 77.99.88.003.E.001059.03.18 dated 03/15/2018
**ADVERTISING
Directions for use and doses
Orally, during or after meals, with at least 1/2 glass of water.
Adults and adolescents over 15 years of age are prescribed 1 g/day (2 capsules 2 times a day).
The recommended duration of the initial course of treatment is 6 months, the period of action of the drug after its discontinuation is 3–5 months, depending on the location and stage of the disease, the duration of repeated courses of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Externally. Chondroitin-AKOS ointment is applied 2-3 times a day to the skin over the lesion and rubbed in for 2-3 minutes until completely absorbed. Typically, the course of treatment ranges from 2–3 weeks to 2 months. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated.
What is chondroitin for?
Chondroitin is a substance that is part of cartilage tissue, ligaments and bones, an important component of the joint, on which its condition and normal functioning depend. This is not just a building material: chondroitin retains moisture, participates in metabolic processes, and stimulates the production of synovial fluid. Chondroitin affects the functions of cartilage tissue cells - chondrocytes. While the body is young, chondrocytes produce a sufficient amount of collagen and other structural elements of cartilage, but with age, cell activity decreases. Chondroitin deficiency primarily affects the condition of the cartilage: destruction processes begin in it, strength and elasticity decrease, it loses moisture and becomes thinner.
The amount of synovial fluid, which allows the articular surfaces to slide relative to each other, decreases—as a result, the range of motion in the joint is limited. The consequence of these processes is usually inflammation - arthrosis and arthritis develop, accompanied by pain. For people in this situation, it is possible to compensate for chondroitin deficiency only with the help of external sources - food and medications.
How does taking chondroitin affect joints?
Once in the body, chondroitin is absorbed in the intestines and enters the connective tissue through the bloodstream, where it is used in the same way as its natural counterpart. Due to the similar structure of the substance, the body does not see the difference between internal and external chondroitin, so it actively uses chondroitin taken orally. In joints, chondroitin is “embedded” in cartilage tissue, where it stimulates metabolic processes and the formation of synovial fluid. First, it slows down and stops the destruction of cartilage, then gradually reverses the process, starting restoration. But this is only possible with a continuous and long-term intake of chondroitin into the body, therefore drugs containing it (chondroprotectors) are prescribed in long courses.