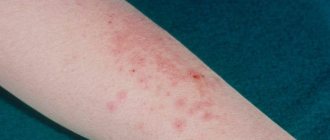
Treatment of dermatitis: ointments and creams
Dermatitis therapy always includes the use of topical products. How do they differ and which release form is better to choose?
- The ointment is made on a fat basis. These can be vegetable and mineral oils or animal fats. Due to this, it has a dense, viscous structure, is absorbed into the skin for a long time and leaves behind a sticky or greasy film. The active components of the ointment penetrate deeply into the skin. Typically, such products are used to treat dry rashes and are not used for application to wet surfaces.
- The cream is produced on a hydrophilic basis, due to which its structure is lighter than that of an ointment. The product is easily and quickly absorbed, leaving no traces on the skin. But at the same time, the depth of its penetration is less than that of the ointment. Such products are suitable for application to moderately weeping rashes.
When treating dermatitis, topical products should solve the following problems:
- Reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process.
- Relieve itching and burning.
- Fight swelling and redness of the skin.
- Disinfect the skin.
- Promote the regeneration processes of damaged skin.
- Nourish and protect the skin.
Depending on the main active ingredients, ointments and creams for dermatitis can have a hormonal and non-hormonal composition.
Dermatitis: prevention
You can prevent dermatitis or its exacerbation if you adhere to the following recommendations of dermatologists: follow a diet and personal hygiene rules, properly care for your skin, harden your body, lead a healthy lifestyle, and treat all diseases in a timely manner. If the patient has previously had dermatitis, then he needs to adhere to the following rules of personal hygiene and skin care:
- wash your face twice a day, using special cosmetics;
- try not to touch your face with your hands during the day;
- do not squeeze out acne and comedones yourself, so as not to spread inflammation across the face;
- swim once every two days for no more than 15 minutes;
- do not use hard washcloths when bathing;
- do not use cosmetics with fragrances and dyes;
- cut your nails short to avoid scratching the skin on your face when itching occurs;
- do not use other people’s hygiene items;
- provide complete hydration and nutrition of the facial skin;
- try to use decorative cosmetics as little as possible, as they clog pores.
Dermatitis can also be prevented if the patient’s diet is normalized, which includes excluding allergenic foods from it, removing toxins from the body, normalizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and providing the body with all the necessary vitamins. First of all, you should avoid foods that contain large amounts of glucose, as it creates favorable conditions for the development of fungus. To prevent the disease, it is worth limiting the diet of baked goods, sweet pastries, and confectionery.
Foods that are not recommended for consumption during skin inflammation also include quickly digestible carbohydrates (potatoes, sweets, pasta), salty, spicy and pickled foods (canned food, sauces, seasonings), fatty and fried foods (sausages, pork, lamb, goose), allergenic foods (eggs, citrus fruits, honey, red fruits and vegetables). You can prevent dermatitis if you include in your diet as many foods as possible rich in vitamins A, E, C, B, since they strengthen the immune system and accelerate the regeneration of the epidermis. Vitamins A and E are found in large quantities in vegetable oils (grape, olive, flaxseed), C - in black currants, spinach, rose hips, and sea buckthorn.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 10865 Date of publication: 08/22/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
Hormonal cream for dermatitis
Hormonal ointments and creams against dermatitis contain glucocorticoid hormones. These drugs are usually prescribed during the acute period of the disease and for extensive skin lesions. The effect of their use becomes noticeable after just a few sessions of use. When acute symptoms of dermatitis gradually decrease, it is recommended to switch to treatment using non-hormonal agents.
Hormonal drugs for dermatitis are divided into 4 groups:
- First (low activity). This group includes drugs for dermatitis, characterized by slow absorption and a slight decrease in the intensity of the symptoms of the disease. Due to the low activity of the main components, such drugs usually require frequent use and a long course of treatment. Corticosteroids included in this group are usually prescribed for minor rashes and inflammatory processes. However, despite their relatively low effectiveness, they are the safest of all hormonal drugs. If there is a need to prescribe glucocorticosteroid drugs to a child, doctors usually give preference to such dermatitis creams for children.
- Second (moderate action). Drugs in this group are more effective, so they are prescribed for moderate and moderate inflammatory processes. The frequency of use is up to 3 times a day.
- Third (high activity). The agents included in this group are characterized by a long-lasting action and a fairly high intensity of absorption of the active components. The frequency of application to the affected areas of the skin is 1-2 times a day.
- Fourth (super strong action). This group includes the most active and aggressive glucocorticosteroids. They are characterized by a prolonged action and a rapid decrease in the intensity of the symptoms of the disease. They are used for severe inflammatory processes, as well as in cases where weaker drugs do not give the desired result. The duration of treatment is no longer than 7 days (under the supervision of a doctor), the frequency of application is 1 time per day.
The main rule to remember when treating dermatitis: never prescribe hormonal drugs to yourself. Their composition is quite aggressive, so you should use such products only as prescribed by a doctor, without exceeding the recommended dose and frequency of application. Otherwise, there is a danger of side effects, including skin atrophy. Withdrawal of corticosteroids should occur gradually. In addition, hormonal products for external use have contraindications: they are not used in cases of liver and kidney dysfunction, in the presence of fungal skin infections and tuberculosis, and skin cancer is also a contraindication.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
The diagnosis is made based on the existing symptoms, the results of an external examination of the patient’s skin and mucous membranes, visual assessment and localization of pathological changes.
An anamnesis of the disease must be studied in order to establish the possible cause of dermatitis and its genetic cause. Laboratory diagnosis of dermatitis includes the following studies:
- General clinical blood test. During an allergic reaction, an increase in the number of eosinophils is observed, and an accelerated ESR indicates inflammation.
- Blood chemistry. Includes determination of the concentration of AST, ALT, total bilirubin, triglycerides, cholesterol, total protein.
- Determination of the level of immunoglobulins in blood serum, antibodies to food, household antigens, antigens of plant, animal and chemical origin.
If necessary, it is possible to conduct a histological examination of the biomaterial obtained through skin biopsy. Genetic blood testing helps determine hereditary predisposition to the development of atopic disease. In the presence of a purulent process or severe inflammation, a microscopic and bacteriological examination of the smear is prescribed in order to clarify the causative agent. Additionally, for dermatitis, tests are carried out for giardiasis and other forms of intestinal parasites, and the organs of the digestive tract are examined.
Non-hormonal cream for dermatitis
Non-hormonal preparations for dermatitis include herbal ingredients, vitamins, zinc, ichthyol, tar and other safe ingredients. They are characterized by the following positive properties:
- Unlike hormonal products, these products can be used for a long time.
- They do not cause addiction or withdrawal symptoms, almost never cause allergies (except in cases of individual intolerance to the active components of the product) and have no side effects.
- If you are looking for a suitable cream for atopic dermatitis in children, non-hormonal drugs are exactly what you need.
- Suitable for use during pregnancy and lactation (but only as prescribed by a doctor).
However, it must be taken into account that non-hormonal drugs have a significant drawback: when using them, the first positive results of treatment are not immediately noticeable. Therefore, non-hormonal drugs are usually prescribed during the period of remission of the disease.
Choosing a cream for dermatitis on the face and body, depending on the type of disease
Dermatitis is divided into the following types:
- Atopic.
- Allergic.
- Seborrheic.
- Contact.
- Diaper.
These types of diseases have different symptoms and causes of occurrence. Therefore, there is no universal remedy for dermatitis that would be equally effective in treating all types of this disease. In each specific case, the dermatologist prescribes the drug to the patient individually.
Dermatitis: general principles
Treatment of all types of dermatitis on the face begins with a consultation with a dermatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist and gastroenterologist. This is due to the fact that dermatitis often appears against the background of other diseases, so first of all you need to exclude this possibility. If it turns out that facial dermatitis has become a complication of another disease, therapy focuses on eliminating it. However, in most cases, dermatitis develops due to exposure of the body to dangerous chemical or physical factors. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to limit the patient as much as possible from the causative agent of the disease. For this purpose, it is recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital.
Depending on the condition of the patient’s skin (the area of the lesion on the face, oiliness, elasticity, moisture), the dermatologist prescribes diet therapy, systemic and local medications, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment should begin with gentler and weaker drugs, gradually moving to stronger ones. The doctor also adheres to the rule - the more acute the dermatitis, the milder its treatment should be. In general, eczema therapy is aimed largely not at normalizing the functioning of the sebaceous glands, but at reducing the manifestations of the disease on the face.
Usually, for the treatment of all types of dermatitis, the patient is prescribed a course of medications to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. To do this, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination by a gastroenterologist. Based on the results of the consultation, the doctor prescribes choleretic drugs (hepabene, berberine, odeston, artichoke extract), digestive enzymes (biozyme, mezim, pancreatin, penzital), sorbents (polysorb, polyphepan, enterosgel). Enzymes and choleretic medications normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and sorbents cleanse the intestines and remove pathogenic microorganisms, allergens, and toxins from it.
Atopic dermatitis: ointments and creams for children and adults
Atopic dermatitis occurs mainly in childhood, so doctors try to prescribe predominantly non-hormonal drugs to treat it. However, if the rash affects large areas of the body and is accompanied by severe skin itching and pain, a dermatologist may recommend a hormonal cream for atopic dermatitis for children. These may be drugs based on hydrocortisone 17-n-butyrate, alklometasone, methylprednisolone aceponate. In addition to glucocorticosteroids, during the acute phase of the disease, antimicrobial and antifungal agents are prescribed for external use: they prevent the development of pathogenic flora that can get into areas of scratching. It is also important to use local preparations that promote the resorption of infiltrate and are made on the basis of naphthalan, birch tar, sulfur and ichthyol.
When remission of the disease occurs, prophylactic use of products with polyunsaturated fatty acids, plant extracts (oak bark, string, chamomile), vitamins E and A is recommended.
Causes and types of dermatitis
The disease occurs when the protective function of the skin is weakened due to prolonged exposure to aggressive substances or decreased immunity. The cause of the pathology can be the following factors:
- mechanical irritation, friction, compression of the skin;
- thermal burn or frostbite, ionizing, UV and other radiation, electric current;
- contact with chemicals contained in skin care products, household chemicals, decorative cosmetics, as well as salts of heavy metals, acids or alkalis, medications for external use;
- allergic reaction to plant pollen, animal hair, food, medications;
- infection with viruses, bacteria or fungi;
- taking antibiotics, sulfonamides, novocaine-containing drugs;
- systemic diseases, hormonal disorders, hypovitaminosis, pathology of the digestive organs, liver, disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism, helminthic infestation, influenza and ARVI.
According to etiological factors, there are:
- Perioral dermatitis. It occurs due to the abuse of cosmetics, improper local use of hormonal drugs, the use of medicated fluoride-containing toothpastes, hypovitaminosis A and E. In childhood, it appears with increased salivation and during teething.
- Atopic dermatitis. Occurs mainly in children prone to allergic reactions and has a hereditary predisposition. Irritants may include foods, allergens of plant or animal origin, dust mites, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, and mold fungi. Rashes in a child of the first years of life are localized mainly on the face and extensor surfaces of the limbs, and at an older age and in adults, dermatitis appears on the elbows and popliteal folds.
- Contact allergic dermatitis. Appears when the skin comes into contact with substances to which the immune system is sensitized. May develop at lightning speed and be accompanied by anaphylactic shock.
- Actinic dermatitis. An allergic reaction to ultraviolet radiation, also known as sun allergy.
- Drug dermatitis. Occurs as a reaction to the use of medications (iodine, brilliant green).
- Seborrheic dermatitis. The cause of the disease is fungi of the genus Malassezia. Exacerbation occurs in hot and humid weather, with stress, hormonal, immune and neuroendocrine disorders, when the activity of the sebaceous glands increases. In places where they accumulate, the symptoms are more pronounced. Most often, seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp, face, and upper third of the body.
- Infectious dermatitis. It develops when the skin is damaged by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Dry dermatitis. Occurs in people with sensitive skin during the cold season.
- Lichen planus. It is characterized by the appearance of red or pink plaques and intense itching. May affect nail plates.
- Toxidermy. A disease of an allergic nature, in which an irritant enters the body through the blood, respiratory system or oral cavity. There are medicinal, food and professional forms.
Seborrheic dermatitis cream
Seborrheic dermatitis usually affects areas of the body that have a large number of sebaceous glands. One of the most unpleasant signs of this type of disease is that it is often localized in exposed areas of the body. This causes a person not only physical, but also psychological discomfort. Therefore, it is very important to pay special attention to choosing a suitable cream for seborrheic dermatitis on the face (especially in the nasolabial triangle), scalp, neck and other affected areas.
The cause of seborrheic dermatitis is infection of the skin by yeast-like fungi Malassezia, so external antimycotics (antifungal drugs) are prescribed to combat the disease. For treatment, external agents based on ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clotrimazole are used. Another task, in addition to normalizing the skin microflora, is to ensure rapid exfoliation of scales and normalization of sebum (sebum) production.
Allergic dermatitis cream
This form of the disease occurs as a result of human contact with an allergen - chemical, food, drug, etc. The disease is characterized by dry and itchy skin, the appearance of flaky, reddened areas, and the formation of papules and blisters. Most often, the rashes are localized on the hands and face.
Treatment involves stopping contact with the allergen and using antihistamines. As for the choice of cream for dermatitis on the hands and face, it depends on the intensity of the symptoms, age and general health of the patient. For mild forms of the disease, remedies based on string, chamomile, violet, menthol, and ichthyol are prescribed. The use of calcineurin inhibitors may also be recommended. If we are talking about a severe form of allergic dermatitis, the use of methylprednisolone aceponate, hydrocortisone acetate, betamethasone dipropionate may be required.
Symptoms of dermatitis
The main manifestations of the disease are redness and increased pigmentation of the skin, the formation of focal rashes, thickening, swelling, itching of varying intensity in the affected areas, burning, pain and other symptoms of tissue irritation. In acute form, the inflammation process occurs in stages:
- In the erythematous stage, redness, itching and burning are moderate, and there is slight swelling.
- The bullous stage is more severe. Blistering rashes appear on the affected areas, and the itching becomes intense. When scratching, first weeping wounds are formed, which are subsequently covered with a dense crust.
- The last necrotic stage is characterized by the formation of scabs and ulcers at the site of scratching. The rash covers increasingly larger areas. Old injuries gradually heal without consequences or with the formation of scars.
With chronic dermatitis, the symptoms are less pronounced, the disease remains in the first stage for a long time.
As a result of prolonged inflammation, the skin becomes rough, dense scales and a white coating resembling a dry callus appear on it. In severe cases, the affected areas atrophy and turn pale. The clinical picture depends on the form of the disease. In the case of its allergic nature, the itching and burning are more intense, the redness is more pronounced than with contact dermatitis. Affected skin areas can spread throughout the body, regardless of where the irritant is applied.
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by intense itching. As it progresses, blisters filled with cloudy liquid form in hyperemic areas of the body. In the last stages of the disease, severe dryness and pallor of the skin predominate.
In the oral form of dermatitis, the first rashes are localized on the face - in the area of the cheeks, bridge of the nose, chin, and near the mouth. This is characterized by the presence of a rim of healthy skin around the red border of the lips. Itching, flaking, dryness and a feeling of tightness are noted.
Contact dermatitis is characterized by local redness of the skin in places of contact with the irritant, swelling, a rash in the form of blisters, the appearance of cracks, dryness and weeping. There is itching of varying severity, burning and pain in the inflamed areas.
Eczema is manifested by a variety of rashes, severe itching, dryness and flaking of the skin, cracks, redness, swelling or weeping.
Toxidermia is characterized by urticaria, the appearance of red and pigmented spots on the skin, oozing, swelling of the face and limbs, peeling of large scales, and acne.
The generalized form can occur as lichen planus, allergic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus.
Cream for diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis is a common problem occurring in infancy. It appears as a result of non-compliance with hygiene rules, insufficient removal of excrement residues from the skin in the anogenital area of the baby, irrational use and rare changes of diapers, and excessive sweating of the baby. This type of disease can affect not only children, but also adults who are forced to wear diapers - the elderly and bedridden patients.
To reduce the symptoms of this type of disease, non-hormonal children's remedies for dermatitis are usually prescribed - for example, with zinc, panthenol, and plant extracts. To prevent the appearance of diaper dermatitis, you can use La-Cri diaper cream. It contains zinc oxide, panthenol, shea and jojoba butters, beeswax and licorice extract.
If an infection joins the rash and inflammation begins, antimycotics and antibiotics are prescribed.
Facial dermatitis:
To get rid of dermatitis on the face you will need a comprehensive approach. To eliminate the symptoms of a disease, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence.
First of all, diagnosis is important. A dermatologist will identify the type of dermatitis, prescribe tests to find the allergen and prescribe treatment.
- A lifestyle adjustment will be required: a minimum of stress, regular sleep, sports and walks in the fresh air will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the body in general and the health of the skin in particular.
In advanced cases of chronic facial dermatitis, patients sometimes require a change in climate, place of work and place of residence. Don't let the disease get worse so you don't have to take extreme measures!
- Therapy includes a hypoallergenic diet. First of all, it is important to exclude the identified allergen product. Adjust your diet in favor of vegetables and fruits (except citrus fruits), boiled meat, fish and cereals. It is better to give up spicy, salty, sweet, smoked, and canned foods.
- Proper skin care is important. A cosmetologist-dermatologist will help you choose hypoallergenic cleansers and cosmetics individually for you.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face: ointments
- When treating allergic dermatitis, individuals are prescribed anti-inflammatory (hormonal and non-hormonal) topical agents (ointment, cream), which reduce all symptoms, and antihistamines.
- Treatment of contact dermatitis on the face begins with excluding any contact with the allergen and prescribing anti-inflammatory and healing ointments. If there has been prolonged contact with the allergen, and the disease is very advanced, it is possible to prescribe a steroid cream or ointment containing hormones. Only they can cope with serious ulcers on the face.
- For atopic dermatitis of the facial skin, anti-inflammatory drugs (hormonal and non-hormonal) are often used to relieve redness and itching.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by a fungus, so it is treated with antifungal agents.
- When treating perioral facial dermatitis, the main symptoms are eliminated with antihistamine ointments; Hormonal creams are prescribed in special cases, if the cause of the disease is accurately diagnosed.
Cream “La-Cri” is an effective remedy for facial skin dermatitis
Experts recommend soothing the manifestations of dermatitis on the face with the help of La-Cri cleansing gel, enriched with life-giving extracts of licorice, violet, string and walnut, with the addition of avocado and olive oil. It gently cleanses irritated skin and helps reduce inflammation.
In addition, treatment of dermatitis involves the use of La-Cri emulsion and cream for sensitive skin, which help restore and disinfect the skin. The cream has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, and the emulsion stimulates metabolism and restores the water balance of the epidermis, moisturizing and softening the skin.
Skin dermatitis on the face: folk ways to combat the disease
“Grandma’s recipes” are effective mainly for relieving symptoms of the disease. We urge you to take your health seriously and undergo treatment under the supervision of a doctor. Use natural remedies exclusively as auxiliaries and only after the doctor’s permission.
Homemade ointments
Tar: Add 6 g of tar to a regular tube of shaving cream. Heat to 600C. Use the cream 2-3 times a day.
Potato: mix 100 g of grated potatoes with 7 ml of liquid honey (if you are not allergic to it). Apply the ointment to your face and leave it overnight.
Herbal decoctions
It is recommended to store decoctions in a cool place for no more than 3 days. Use in courses: wipe the skin 2-3 times a day, course – 1 month.
Walnut: chop 6-7 walnut leaves, add 1 glass of water, boil over low heat for 5-6 minutes. Leave for 2 hours.
Hops: 10 g of hops and 10 g of string, pour 150 ml of boiling water. Leave for 40 minutes.
Oils
Oils can be used undiluted or added as an ingredient to various recipes. Oil formulations should be applied pointwise to areas affected by dermatitis 2-3 times a day.
Cypress and myrrh: add 2 drops of these essential oils to 10 g of baby hypoallergenic cream.
Geranium, cedar, mint: pour 5 drops of oil into 16 ml of milk (do not use inside!)
Essential oils of black currant, geranium, cedar, ylang-ylang, lavender, jojoba, almond, sea buckthorn, and chamomile help well in treatment.
Cream for dermatitis during pregnancy
Dermatitis in pregnant women is quite common. Even if a woman has never suffered from this disease before, it may first appear during pregnancy. One of the reasons for its appearance during this period is a change in the hormonal background of the expectant mother and a decrease in the defenses of her body.
In most cases, the disease goes away on its own after the birth of the child. But this does not mean that you just need to wait for the body to heal itself, because during pregnancy the disease can cause serious physical and emotional discomfort to a woman and make her irritable. In addition, if an infection gets into the scratching area, there is a real danger of inflammation and suppuration of the skin.
Choosing a remedy for the treatment of dermatitis in pregnant women is a serious task, which only a qualified doctor can cope with. Therefore, under no circumstances use drugs that you are not sure of, and do not follow unverified advice and recommendations from neighbors and friends. Trust a professional in this matter, because an incorrectly selected product can cause harm not only to you, but also to the child.
Hormonal creams for dermatitis are prescribed to pregnant women extremely rarely - only in cases where the benefits of their use outweigh the potential harm. If there is no other option, then the doctor must assess the possible risks and prescribe a glucocorticosteroid drug with a minimum dose of hormones.
If possible, instead of corticosteroid medications during pregnancy, it is recommended to use moisturizing and nourishing products containing natural ingredients - vitamins, zinc, plant extracts and oils.
Preparations for internal use
Thus, tableted antihistamines are prescribed to inhibit inflammatory processes and reduce the harmful effects of allergens. Depending on the degree of damage, drugs are prescribed for a period of 2 weeks to several months. To treat dermatitis on the hands, products of various generations are used.
First generation antihistamines (diphenhydramine, mebhydrolin, chloropyramine, clemastine, cyprohepadine, promethazine, quifenadine) have a powerful antipruritic and decongestant effect, and also reduce muscle tone and cause drowsiness. They are recommended for therapy in the acute period.
Second-generation drugs have virtually no effect on the nervous system and do not reduce physical activity, but can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, so they should not be taken by people with cardiac diseases and elderly patients. Second generation antiallergic drugs include terfenadine, astemizole, acrivastine, dimethendene, loratadine.
If it is impossible to provide the patient with bed (home) treatment, third generation . They do not affect the functioning of the brain and heart muscle, which means they can be taken by people whose work involves mental activity. Third generation antihistamines on the pharmaceutical market include cetirizine, fexofenadine, desoloratadine, and hifenadine.
To quickly remove allergens from the body, medications are prescribed that stabilize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Sorbents absorb and remove toxins accumulated in the liver and intestines from the body. These include activated carbon, enterosgel.
La-Cri is your assistant in the prevention of dermatitis
La-Cri's non-hormonal products, made from natural, safe ingredients, are excellent for accelerating recovery and preventing this disease. For example, there are many positive reviews about the use of La Cree cream for dermatitis. The active components included in the La-Cri cream for dry skin provide delicate care for damaged skin:
- Natural hypoallergenic oils (wheat germ, jojoba and shea) provide skin nutrition, combat dryness and normalize water-lipid balance.
- Plant extracts (licorice and string) help cope with itching, redness and flaking.
- Beeswax perfectly softens and nourishes the skin.
Clinical researches
La-Cri creams for sensitive skin and La-Cri cream for dry skin are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Sources:
- Tulchinskaya, V.D. Nursing assistance to children / V.D. Tulchinskaya. — Moscow: Russian State University for the Humanities, 2021.
- Andropova T. V., Gudina M. V., Odintsova I. N., Hygiene of children and adolescents, Siberian State Medical University Publishing House, 2021.
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2021.