Side effects
When using the drug, the following side effects are rarely possible:
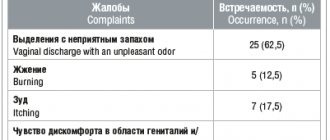
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, discomfort or pain in the epigastrium, laxative effect, the occurrence of erosive and ulcerative lesions, bleeding.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, psychomotor agitation, insomnia.
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
From the urinary system: impaired renal function, cystitis.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, angioedema, anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm, fever, erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome).
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, increased blood pressure.
Buy Ibuprofen-Altpharm rectal suppositories 60 mg No. 10 in pharmacies
Instructions for use Ibuprofen Buy Ibuprofen supp. rect. 60 mg No. 10 Dosage forms suppositories 60 mg, suppositories 60 mg Manufacturers Rofarma (Russia) Group Anti-inflammatory drugs - propionic acid derivatives Composition Active substance: Ibuprofen. International nonproprietary name Ibuprofen Indications for use:
For rectal use (children from 3 months to 2 years): as an antipyretic - acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, other infectious and inflammatory diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature; post-vaccination reactions. As an analgesic - pain of mild or moderate intensity (including headache and toothache, migraine, neuralgia, pain in the ears and throat, pain with sprains). ** Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity. For oral use: erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the acute phase (including peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer), "aspirin" bronchial asthma, urticaria, rhinitis, provoked by taking salicylates or other NSAIDs; bleeding disorders (including hemophilia, hypocoagulation, hemorrhagic diathesis), optic nerve diseases, scotoma, amblyopia, color vision impairment, asthma, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhagic diathesis, confirmed hyperkalemia, severe liver failure or active liver disease, severe renal failure (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min), progressive kidney disease, severe heart failure, children up to 12 years of age (tablets, capsules, granules for solution), up to 6 years (effervescent tablets), up to 3 months (suspension for administration orally for children, rectal suppositories for children). For IV use: life-threatening infection, clinically significant bleeding (especially intracranial or gastrointestinal), thrombocytopenia or coagulation disorder, significant renal impairment, congenital heart disease in which a patent ductus arteriosus is a prerequisite for satisfactory pulmonary or systemic blood flow (eg pulmonary atresia, severe tetralogy of Fallot, severe coarctation of the aorta); diagnosed or suspected necrotizing enterocolitis. For external use: weeping dermatoses, eczema, violation of the integrity of the skin (including infected abrasions and wounds).
Directions for use and doses
Rectally. The dosage for children depends on the age and body weight of the child.
Post-immunization fever: children under 1 year - 1 supp., over 1 year, if necessary, 1 more supp. in 6 hours
Fever and pain
Single dose - 5-10 mg/kg body weight 3-4 times a day. The maximum daily dose is no more than 30 mg/kg/day.
Children aged 3–9 months (5.5–8.0 kg) - 1 supp. (60 mg) 3 times within 24 hours every 6–8 hours, not more than 180 mg/day; from 9 months to 2 years (8.0–12.5 kg) - 1 sup. (60 mg) 4 times within 24 hours every 6 hours, but not more than 240 mg/day.
Duration of treatment: as an antipyretic - no more than 3 days; as a pain reliever - no more than 5 days.
If fever persists, you should consult your doctor.
Ibuprofen supp rect det 60 mg x10
Ibuprofen supp rect det 60 mg x10, ATX code: M01AE01 (Ibuprofen) Active substance: ibuprofen (ibuprofen) Rec.INN registered by WHO
Dosage form
IBUPROFEN
Suppositories rect. (for children) 60 mg: 10 pcs.reg. No.: LP-000778 dated 09/29/11 - Valid
Release form, packaging and composition Ibuprofen
Rectal suppositories for children are white or almost white, smooth, torpedo-shaped.
1 sup.
ibuprofen 60 mg
Excipients: solid fat 516 mg.
Clinical-pharmacological group: NSAIDs Pharmaco-therapeutic group: NSAIDs
pharmachologic effect
NSAIDs. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
The mechanism of action of ibuprofen is due to inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins - mediators of pain and inflammation. The effect of the drug lasts up to 8 hours.
Indications for Ibuprofen
Used in children from 3 months to 2 years of age as:
an antipyretic for acute respiratory diseases, influenza, childhood infections, post-vaccination reactions and other infectious and inflammatory diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature, an anesthetic for pain of mild or moderate intensity, incl. headaches and toothaches, neuralgia, pain in the ears and throat, pain due to ligament damage and other types of pain. ICD-10 codes
Dosage regimen
Ibuprofen is a suppository specially designed for children. The drug is administered rectally.
Fever (fever) and pain: Dosage for children depends on the age and weight of the child. A single dose is 5-10 mg/kg of the child’s body weight 3-4 times/day. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 30 mg per kg of body weight of the child per day.
Children aged 3-9 months (5.5 kg-8.0 kg): 1 suppository (60 mg) 3 times within 24 hours every 6-8 hours, not more than 180 mg/day.
Children aged 9 months-2 years (8.0 kg-12.5 kg): 1 suppository (60 mg) 4 times within 24 hours after 6 hours, not more than 240 mg/day.
Post-immunization fever: 1 suppository for children under 1 year of age, after 1 year, if necessary, another suppository after 6 hours.
Duration of treatment:
no more than 3 days as an antipyretic, no more than 5 days as an analgesic.
If fever persists, consult your doctor. Do not exceed the indicated dose.
Side effect
When using the drug, side effects are rare, but the following side effects may occur:
From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, feeling of discomfort or pain in the epigastrium, laxative effect, possible occurrence of erosive and ulcerative lesions, bleeding.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, urticaria, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, angioedema, anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm, fever, erythema multiforme exudative (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome).
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, psychomotor agitation, insomnia.
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, increased blood pressure.
From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
From the urinary system: impaired renal function, cystitis.
If these or other side effects occur, stop using the drug and consult a doctor.
Contraindications for use
bronchial asthma, urticaria, rhinitis, provoked by taking acetylsalicylic acid (salicylates) or other NSAIDs, the presence of gastrointestinal ulcers in a child, active gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel diseases, confirmed hypokalemia, blood diseases: hypocoagulation, leukopenia, hemophilia, renal and/or or liver failure, hearing loss, hypersensitivity to ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs, as well as to other components of the drug.
Carefully:
You should consult your doctor before using the drug if your child:
takes other painkillers, has a history of peptic ulcers, gastritis, ulcerative colitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, suffers from liver or kidney diseases, takes indirect anticoagulants (drugs for oral administration that reduce blood clotting), drugs to lower blood pressure, glucocorticosteroids, antiplatelet agents, diuretics (drugs to increase urination), lithium drugs, methotrexate, suffers from bronchial asthma, urticaria.
Use for liver dysfunction Use with caution in liver diseases. Contraindicated in liver failure.
Use for impaired renal function Use with caution in case of kidney disease. Contraindicated in renal failure.
Use in children Used in children from 3 months to 2 years of age
Overdose
Problems with overdose occur very rarely, but if you accidentally exceed the recommended dose, consult a doctor immediately.
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, rapid eye movements (nystagmus), difficulty breathing, cyanosis of the lips and tip of the nose, bradycardia, tachycardia.
Drug interactions
The simultaneous use of Ibuprofen with anticoagulants can lead to an increase in their effect.
Ibuprofen increases the concentration of digoxin, phenytoin, methotrexate, lithium in the blood plasma when used simultaneously with these drugs.
Using ibuprofen with diuretics and antihypertensive drugs reduces their effectiveness.
Increases the side effects of mineralocorticosteroids and glucocorticosteroids.
Storage conditions Ibuprofen
The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life Ibuprofen Shelf life - 2 years.
Terms of sale Without a prescription.
Ibuprofen for children
Ibuprofen for children is an NSAID that has anti-inflammatory, analgesic (relieves pain) and antipyretic (antipyretic, antifever) effects. The action of the drug is based on its ability to inactivate the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which, in turn, controls the process of biochemical transformation of arachidonic acid into eicosanoids. COX is represented by two types of isoenzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. With the development of an inflammatory reaction under the influence of interleukin 1β, interleukin 6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, COX-2 is formed, which stimulates the metabolism of arachidonic acid and activates the synthesis of inflammatory mediators. Inactivation of COX-2 in the central nervous system determines anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. COX-2, in turn, ensures the synthesis of prostaglandins-cytoprotectors that act on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Ibuprofen has moderate selectivity (selectivity of action) against COX-2. When choosing a drug for use in pediatrics, preference is given to drugs with the least toxicity and the likelihood of unwanted side reactions. Of all NSAIDs, paracetamol and ibuprofen have the most favorable safety profile with a high level of effectiveness, which predetermines their widespread use in pediatrics to reduce fever and eliminate pain (headaches, muscles) accompanying colds.
According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization, ibuprofen, along with paracetamol, is the standard for the symptomatic treatment of febrile conditions and moderate pain in children starting from three months of age. Other NSAIDs cannot be used in pediatric practice due to the lack of reliable information about their effectiveness and safety in patients of this age group. The analgesic effect of ibuprofen is more pronounced than that of paracetamol, which allows the drug to be used effectively for mild to moderate pain. Ibuprofen has been successfully used in pediatric practice for several decades. The low toxicity of the drug has been confirmed in large clinical studies. One of them, in particular, involved more than 84 thousand children. As an analgesic, it can be used for pain of various etiologies, including pain after surgical removal of the tonsils. Ibuprofen is characterized by a rapid development of its antipyretic effect: in most cases, a clinically significant decrease in body temperature can be achieved within 15 minutes. In this case, the duration of the antipyretic effect is up to 8 hours. The drug has a low risk of developing side effects typical of NSAIDs, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, liver and kidney dysfunction. In relation to the digestive tract, ibuprofen is the safest drug of all NSAIDs. Cases of overdose with this drug are extremely rare.