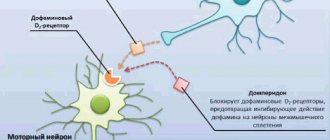
pharmachologic effect
What is Colme? It is a medicine for alcoholism .
The active component inhibits the enzyme acetaldehydrogenase , which is actively involved in the metabolism of ethyl alcohol. Cyanamide increases the level of acetaldehyde , a metabolite of ethyl alcohol, which leads to the development of negative symptoms when alcohol enters the human body.
There is shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, flushes of blood flow to the face, and nausea.
At the level of conditioned reflexes, an aversion to the smell and taste of alcohol-containing drinks is formed.
In comparison with Disulfiram, cyanamide does not have a hypotensive effect.
The sensitizing effect of the active component on ethyl alcohol appears after 45-60 minutes and lasts almost 12 hours.
The advantage of the drug "Kolme"
Most medications for alcoholism in tablet form contain the base component - disulfiram. When combined with ethanol, unpredictable health consequences are possible. In addition, the tablet cannot be easily added to food or drink without being noticed. The drug "Kolme" has a milder effect. Its main component is cyanamide. It provides a faster effect that lasts less than the result of disulfiram, and also does not have a hypotonic effect.
Features of administration:
it is important to know that if the patient was taking disulfiram-based medications, then at least 10 days must pass before switching to Colma!
Also, this medicine should not be combined with drugs of the aldehyde group. If a doctor prescribes long-term treatment, it is necessary to monitor the functioning of the thyroid gland every six months. Within an hour, the maximum concentration of the substance in the blood is reached. Its effect lasts 12 hours. Therefore, you can start taking the drug no earlier than one day after stopping drinking.
The components that make up Colme are eliminated from the body naturally without any problems. At the same time, they do not put a large burden on the kidneys and liver.
Since the drug "Kolme" not only treats alcoholism, but also prevents relapses of drunkenness, it can be used for a one-time breakdown during remission. This will help quickly stop the urge to return to drinking alcohol.
Studies conducted by scientists from Japan have proven the possibility of monitoring a patient during remission, which is almost impossible in world practice. However, this fact requires additional study.
Side effects of Colme
The medicine is well tolerated. The following side effects are rarely reported:
- transient leukocytosis;
- increased drowsiness ;
- feeling tired;
- noise in ears;
- skin rashes.
The medicine is well tolerated if the patient follows the doctor's instructions and does not drink alcoholic beverages. How to neutralize side effects? Avoid alcohol completely. Reaction to ethyl alcohol:
- feeling of pronounced pulsation in the neck and head;
- skin hyperemia;
- nausea;
- chest pain;
- blurred visual perception;
- weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased sweating.
In severe cases, it develops:
- collapsed state;
- drop in blood pressure;
- vomit;
- depression of respiratory function.
The severity of adverse reactions depends on the amount of alcohol. In case of a pronounced clinical picture, it is recommended to prescribe antihistamines and take measures to maintain the functioning of the cardiovascular system and breathing. It is recommended to discontinue Colme's medication.
Contraindications
According to the instructions and experience of practical use, “Kolme” cannot be used to treat alcoholism in people with failure of vital organs at the stage of decompensation (cardiovascular system, lungs, kidneys and liver). A high risk of developing severe complications during use of the product occurs with the following deviations:
- organic lesions of the nervous system
- epilepsy
- hyperthyroidism
- diabetes
Kolme drops are not used in women during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is not used for the treatment of addiction in persons under 18 years of age and those patients in whom individual intolerance to the substances included in its composition is detected. Experts recommend treatment with extreme caution in people over 60 years of age.
Colme, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
Drops for alcoholism can be prescribed only after a thorough examination of the patient. The attending doctor must warn the patient about the development of possible complications and consequences.
Instructions for Colma
According to an individual regimen, the drug is taken daily at 36-75 mg (twice a day, 12-25 drops). Drops are dosed as follows: after opening, the contents of the ampoule are poured into a bottle located in a cardboard package. You must put a special dropper on the bottle. If long-term storage is necessary, close the bottle tightly.
Instructions for use Colme Light
5 ml (teaspoon) three times a day with meals.
How to take the drops? Every day for 1 month.
Buy Colma drops orally 60 mg/ml 15 ml No. 4 in pharmacies
Instructions for use Colme Dosage forms drops 60 mg/ml 15 ml Group Drugs for the treatment of alcoholism International nonproprietary name No INN. Composition Active substance: cyanamide 0.9 g (1 drop 3 mg). Manufacturers Laboratory Vitoria S.A. (Portugal) Pharmacological action The action of cyanamide is based on the blockade of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, which is involved in the metabolism of ethyl alcohol. This leads to an increase in the concentration of ethyl alcohol metabolite - acetaldehyde, which causes negative sensations (flushing, nausea, tachycardia, shortness of breath, etc.), which make drinking alcohol extremely unpleasant after taking the drug. This leads to a conditioned reflex aversion to the taste and smell of alcoholic beverages. The sensitizing effect of cyanamide on alcohol appears earlier (after about 45-60 minutes) and lasts shorter (about 12 hours) than the effect of disulfiram. Also, unlike disulfiram, cyanamide does not have a hypotonic effect. Side effects The drug is usually well tolerated if alcohol is not consumed. Sometimes fatigue, drowsiness, skin rashes, tinnitus, and transient leukocytosis are possible. Indications for use : Used to treat patients with chronic alcoholism and prevent relapse. Contraindications Severe heart disease, respiratory tract and kidney diseases with decreased function, severe liver disease, pregnancy, breastfeeding, increased individual sensitivity to the drug. Method of administration and dosage Treatment is prescribed after a thorough examination of the patient and warning about the consequences and complications. The drug is taken orally at 36-75 mg (12-25 drops 2 times a day with an interval of twelve hours) according to an individual regimen. To dose, break the ampoule containing the drug solution, pour the contents into the bottle included in the package, and place a dropper on the bottle. The bottle must be tightly closed. Overdose Symptoms are not described, increased side effects are possible. If too large doses of the drug are taken, it is recommended to lavage the stomach and prescribe symptomatic treatment aimed at maintaining the functions of the liver, breathing and cardiovascular system; monitoring the hematocrit and, if necessary, blood transfusions are also necessary. Reaction to alcohol. When taken simultaneously with alcohol, the following symptoms appear: severe hyperemia of the skin, “pulsation” in the head and neck, nausea, tachycardia, difficulty breathing, weakness, blurred vision, profuse sweating, chest pain. In the most severe cases - vomiting, decreased blood pressure, respiratory depression, collapsing state. The nature and severity of symptoms depend on the amount of alcohol and drug taken. In severe cases, it is necessary to carry out symptomatic therapy aimed at maintaining the functions of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and intravenous infusion of antihypertensive drugs. Interaction Avoid prescribing the drug together with metronidazole, isoniazid, phenotoin and other aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors, which may increase the reaction with alcohol. After taking disulfiram, before prescribing the drug, there should be a break of at least 10 days. The drug Kolme is not compatible with drugs of the aldehyde group (paraldehyde and chloral products). Special instructions The drug should be used only under the supervision of a physician and with the knowledge of the patient. You may have a reaction to alcohol contained in some medications and foods. Treatment can begin only after 12 hours have passed since the last drink. The drug should be used with caution in cases where a reaction to simultaneous use with alcohol may entail a risk to the patient’s health: hyperthyroidism, diabetes, epilepsy, cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases. With long-term use, it is recommended to monitor thyroid function at least once every six months. Storage conditions List B. Store in a place protected from light, out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 C. Dispensing procedure Sold by prescription Attention! The information presented in the directory is not
Interaction
The anti-alcohol drug Colme is incompatible with medications of the aldehyde group ( chloral and paraldehyde ).
The mandatory time interval between the use of Colme and Disulfiram is 10 days.
Medicines that can worsen your reaction to alcohol:
- Phenytoin;
- Isoniazid;
- Metronidazole.
Content:
- What is Colme
- How to use
- The advantage of the drug "Kolme"
- Contraindications for use
- The effectiveness of treatment with the drug "Kolme"
The drug "Kolme" is used to treat alcoholism. It is also suitable as a prophylactic agent for patients who have recovered from addiction, but are at risk of relapse. In this article we will talk in more detail about its properties, the possibility of prescribing it for different groups of patients, contraindications, action and effectiveness.
Colma's analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Antaxon
Metadoxyl
Antabuse
Vivitrol
Naltrexone
Medichronal
Disulfiram
Teturam
Proprothene-100
Lidevin
Esperal
Drug substitutes based on pharmacological effect:
- Lidevin;
- ProProTen-100.
Structural analogues have not been developed.
Literature:
- Sreznevsky, Vyacheslav Vyacheslavovich (1880-) On the issue of outpatient treatment of alcoholism / [Oc.] Dr. V.V. Sreznevsky. — St. Petersburg: type. MM. Stasyulevich, [1907]. — 10 s
- Entin, Gennady Mikhailovich. Treatment of alcoholism / G. M. Entin. - M.: Medicine, 1990. - 413, [2] p.
- Zakharov, Yuri Alexandrovich. Treatment of alcoholism / Yuri Zakharov. - M.: Shk. Press, 1999. - 160 p.
- Granik, Vladimir Grigorievich (1939-2011). Neurodegenerative diseases: chemical and medical-biological aspects / V. G. Granik. - Moscow; St. Petersburg: Nestor-History, 2014. - 467 p.
Reviews about Colma (opinion of doctors and patients)
The medicine is widely used in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Reviews of Colme drops are mostly positive. Relatives of patients write that they gave drops for alcoholism without warning their addicted relatives about it. And after some time, they noted a complete refusal to take alcohol-containing drinks against the background of a significant deterioration in well-being after taking even small doses of ethyl alcohol.
Treatment of alcoholism is complex, and in most cases it is possible if the patient is motivated and really wants to get rid of the bad habit.
Reviews about Colma Light are positive. Reviews from doctors about the drug Colme Light confirm the effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of alcohol dependence.