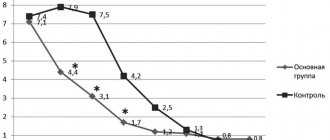
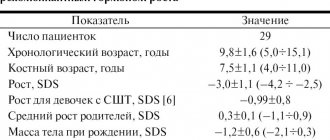
Pharmachologic effect:
The drug Pregnil contains hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). This hormone has biological activities similar to those of LH (luteinizing hormone). LH is indispensable for the normal growth and maturation of female and male gametes and for the formation of sex hormones.
Among women:
- Pregnil is used as a substitute for the mid-cycle surge of endogenous LH to induce the final phase of follicular maturation leading to ovulation. The drug Pregnil is also used as a substitute for endogenous LH during the luteal phase.
For men and boys:
- The drug Pregnil is used to stimulate Leydig cells to accelerate the process of testosterone formation.
Indications for use:
Among women:
- induction of ovulation in case of infertility caused by anovulation or impaired follicle maturation;
- preparation of follicles for puncture in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation programs (for assisted reproduction techniques);
- maintaining the corpus luteum phase.
For boys and men:
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism;
- delayed puberty due to insufficiency of the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland;
- cryptorchidism not due to anatomical obstruction.
Directions for use and dosage:
After adding the solvent to the lyophilisate, the reconstituted Pregnil solution is slowly injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Among women:
- when inducing ovulation in case of infertility caused by anovulation or impaired follicle maturation, one injection of Pregnil is usually given in a dose of 5,000 to 10,000 IU to complete treatment with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH);
- when preparing follicles for puncture in programs of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation;
- to maintain the corpus luteum phase, two to three repeated injections of the drug can be given at a dose of 1000 to 3000 IU each within 9 days after ovulation or embryo transfer (for example, on days 3, 6 and 9 after ovulation induction).
For boys and men:
- for hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: 1000-2000 IU of Pregnil 2-3 times a week. In case of infertility, it is possible to combine the drug Pregnil with an additional drug containing follitropin (FSH) 2-3 times a week. The course of treatment should continue for at least 3 months before any improvement in spermatogenesis can be expected. Testosterone replacement therapy must be suspended during this treatment. When improvement in spermatogenesis is achieved, in some cases, isolated use of hCG is sufficient to maintain it;
- with delayed puberty caused by insufficiency of the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland 1500 IU 2-3 times a week. The course of treatment is at least 6 months;
- for cryptorchidism not caused by anatomical obstruction:
- under the age of 2 years: 250 IU is administered twice a week for 6 weeks;
- under the age of 6 years: 500-1000 IU is administered twice a week for 6 weeks;
- over the age of 6 years: 1500 IU is administered twice a week for 6 weeks.
The course of treatment can be repeated if necessary.
Pregnyl®
Among women
In pregnancies that occur after ovulation induction with gonadotropic drugs, there is an increased risk of multiple pregnancies. Since infertile women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies, and especially in vitro fertilization, often have fallopian tube disorders, the incidence of ectopic pregnancies may increase. Therefore, early ultrasound confirmation that the pregnancy is intrauterine is important.
The incidence of pregnancy loss in women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies is higher than in the general population.
The presence of uncontrolled extragonadal endocrinopathies (for example, diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands or pituitary gland) should be excluded.
The incidence of congenital malformations after assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be slightly higher than as a result of spontaneous conceptions. This slightly increased incidence is thought to be related to parental characteristics (maternal age, sperm characteristics) as well as the high incidence of multiple pregnancies after ART. There is no indication that an increased risk of congenital malformations is associated with the use of gonadotropins during ART.
Unwanted ovarian hyperstimulation
In patients receiving combination therapy with FSH/hCG for infertility caused by anovulation or impaired follicular maturation, the use of an FSH-containing drug may lead to unwanted ovarian hyperstimulation. Therefore, before starting FSH treatment and at regular intervals during FSH treatment, ultrasound examinations should be performed to assess follicular development and estradiol levels should be measured. Estradiol levels can rise very quickly, for example more than a daily doubling over two or three consecutive days, and can reach extremely high levels. The diagnosis of unwanted ovarian hyperstimulation can be confirmed by ultrasound. In the event of unwanted ovarian hyperstimulation (i.e. not as part of treatment aimed at preparing for in vitro fertilization with embryo transfer (IVF/ET), intratubal gamete transfer (GIFT) or intraplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)), administration of FSH-containing the drug must be stopped immediately. In this case, it is necessary to avoid pregnancy and not administer Pregnil®, since the administration of LH-active gonadotropin at this stage can cause, in addition to multiple ovulation, OHSS. This warning is especially important for patients with polycystic ovaries.
Clinical symptoms of moderate OHSS include gastrointestinal disturbances (pain, nausea, diarrhea), breast tenderness, and mild to moderate ovarian enlargement and ovarian cysts. Transient abnormalities in liver function tests indicative of hepatic dysfunction, which may be accompanied by morphological changes on liver biopsy, have been reported to be associated with OHSS.
In rare cases, severe OHSS occurs, which can be life-threatening. It is characterized by large ovarian cysts (prone to rupture), ascites, mass gain, often hydrothorax, and in some cases thromboembolism.
Pregnil® should not be used for weight loss. HCG has no effect on fat metabolism, fat distribution, or appetite.
Contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to human gonadotropins or to any component of the drug;
- established or suspected tumors dependent on sex hormones (ovarian cancer, breast cancer and uterine cancer in women and prostate cancer, breast cancer in men).
For boys (optional):
- premature puberty;
For women (additionally):
- abnormal formation of the genital organs, incompatible with pregnancy;
- fibrous tumor of the uterus, incompatible with pregnancy.
Use during pregnancy and lactation:
The drug Pregnil can be used to maintain the function of the corpus luteum of the ovary, but cannot be used during pregnancy. Pregnil should not be used during lactation.
Pregnyl (Choragon) 1500IU 1ml 3pcs - Instructions
Compound
The functional substance is human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone also known as hCG, in a concentration of 1500 in one ampoule or vial.
Other Ingredients: Mannitol (E421), disodium phosphate, disodium phosphate and carmellose sodium.
The solvent contains sodium chloride (9 mg) and water for injection (1 ml), sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH).
Release form
Pregnil powder for the preparation of solution for injection is a white dry powder or cake supplied in a glass ampoule or glass vial made of transparent colorless glass type I, closed with a bromobutyl rubber stopper and an aluminum cap with a brown polypropylene cap.
The powder should be reconstituted with a clear and colorless solvent contained in a second container, which is a glass ampoule or glass vial of clear type I flint glass, sealed with a chlorobutyl rubber stopper and an aluminum cap with a blue cap.
pharmachologic effect
Placental gonadotropin is a hormone that is obtained from the urine of pregnant women or using recombinant DNA technology. This hormone binds to the LH/CG receptor located on the ovarian follicle cells and testicular Leydig cells. This receptor is the common binding site for placental gonadotropin and luteinizing hormone (LH), so the binding of placental gonadotropin mimics the action of LH. During the normal course of the menstrual cycle (approximately in the middle of its duration), the Graaffian follicle ruptures and the egg is released (ovulation) under the influence of LH. The egg moves towards the fallopian tube and is ready for fertilization, while the remains of the follicle turn into the so-called corpus luteum. If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum becomes the corpus luteum, which stimulates the release of progesterone and other hormones responsible for the proper development of pregnancy. In women with LH deficiency, administration of placental gonadotropin promotes ovulation and the subsequent cascade of events. In men, placental gonadotropin stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone and other sex hormones.
The mechanism of action of placental gonadotropin in neoplasms has not been fully studied. This drug probably suppresses the processes that lead to the death of cancer cells. Additionally, it shows structural similarity to growth factors, which in turn increases the number of cancer cells. It is possible that during the formation of tumor cells, gonadotropin may promote the development of tolerance to tumor antigens and stimulate the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis).
Pharmacokinetics
The bioavailability of the drug is approximately 40%. The maximum concentration of the hormone in the blood plasma in men is achieved 6 hours after intramuscular administration and 16 hours after subcutaneous administration, while in women this time is about 20 hours.
The drug distributes in the extracellular space. The half-life is approximately 4.5 hours.
Placental gonadotropin is metabolized mainly in the kidneys (approximately 80%).
The half-life is 29-36 hours. About 10-20% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Indications for use
Pregnil is used to induce ovulation in women with infertility caused by complete anovulation or impaired maturation of the Graaffian follicle (before the use of assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization). It is also used by women who rarely ovulate and to prevent corpus luteum failure.
In men, the medication is prescribed to treat insufficient testosterone production by the testes (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism). It is used in men with delayed puberty and cryptorchidism for non-anatomical reasons.
Pregnil is also used in diagnostics to distinguish between cryptorchidism and congenital absence of testicles in children, as well as to determine the degree of testicular dysfunction before starting stimulating therapy.
Contraindications
Contraindications include placental hypersensitivity to gonadotropin, genital malformations that prevent pregnancy, unknown cause of vaginal bleeding, existing thromboembolic disorders, hypothalamic and pituitary tumors, sex hormone-dependent tumors (eg, ovarian, nipple, uterine, prostate cancer), enlarged ovaries and the presence of cysts caused by causes other than polycystic ovary syndrome.
Contraindications also include uterine fibroids, ectopic pregnancy in the last 3 months, ovarian hyperstimulation, postmenopausal period and organic cryptorchidism.
Side effects
In general, the medication is well tolerated and has virtually no unwanted effects. However, local reactions at the injection site, such as bruising, pain, redness, swelling or itching, are possible. Allergic reactions at the injection site (most commonly pain and/or rash) have been reported rarely, and a general rash or fever may occur even more rarely.
Drug interactions
When using Pregnil to improve spermatogenesis, additional testosterone therapy should not be used in parallel.
The use of the drug may lead to a false-positive pregnancy test result based on the immunological method for determining hCG in serum or urine within 10 days.
The medication promotes positive results in anti-doping tests.
It is possible that treatment with Pregnil leads to slight stimulation of the thyroid gland.
Application and dosage
Pregnil is used subcutaneously and intramuscularly.
The dose used in treatment depends on the disease, age, gender, concomitant diseases, etc.
The maximum dose for women is 10,000 IU, administered once or divided into two/three injections on the appropriate days of the menstrual cycle (depending on the indications).
The maximum weekly dose for adult men is 6000 IU.
The maximum weekly dose for boys under 2 years old is 500 IU, for boys from 2 to 6 years old - 2000 IU, for boys over 6 years old - 3000 IU.
For diagnostic purposes, men can be given 5000 IU at a time.
Overdose
Data on cases of intoxication are limited. After an overdose, there is a possibility of severe symptoms of ovarian hyperstimulation.
Therapy is carried out in accordance with the symptoms that arise.
special instructions
The decision to treat infertility with Pregnil requires a preliminary interview with the couple to determine the cause of infertility and contraindications to pregnancy. Particular attention should be paid to concomitant diseases in women, such as pituitary or hypothalamic cancer, adrenal hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia.
As a result of the use of the drug, women may experience excessive stimulation of the ovaries, which can lead to the formation of cysts with a tendency to rupture and further complications. The first symptoms to note of ovarian hyperstimulation are gastrointestinal distress, chest pain, and abnormal liver function tests. Regular monitoring of estradiol levels and assessment of ovarian response using ultrasound are necessary.
As a result of ovulation stimulation, the likelihood of multiple pregnancies (most often twins) increases.
There is an increased risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy in patients receiving treatment for fertility problems.
It is possible that use of the drug may increase the risk of congenital malformations.
The benefit/risk ratio of the drug should be weighed in patients with a predisposition to thromboembolic disorders.
In men, attention should be paid to concomitant renal / cardiac dysfunction, arterial hypertension, migraine, epilepsy, since increased production of androgens can cause exacerbation or relapse of the disease.
In younger boys, the drug should be used with caution so as not to lead to premature puberty, and the skeletal system should be checked regularly.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The medication is contraindicated.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
No special precautions are required.
Terms of sale
As prescribed by a doctor.
Storage conditions
At room temperature, in a place out of reach of children.