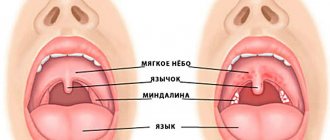
The carbuncle is most often located on the back of the neck, lower back, and hips.
Purulent inflammation is acute and requires immediate treatment. Below in the article you will find the causes of the disease; the doctors who treat him; necessary medical procedures for treatment; as well as general information about the disease, its localization, features of diagnosis of diseases and their treatment. However, we advise you to consult a doctor, because self-medication in 90% of cases is fraught with the disease progressing to the chronic stage with extremely unpleasant complications. Make an appointment and consultation
Causes of carbuncle
The appearance of a carbuncle is preceded by an inflammatory process in the soft tissues, which usually begins with an inflammatory disease of the hair follicle - staphylococcal folliculitis, less often - with streptococcal folliculitis.
The development of inflammation can lead to the formation of a boil, which is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle. When several such boils form in one area of the body, they can merge with each other.
The product of the merger of several boils is a carbuncle. A sharp bursting pain occurs in the area of infiltration. The skin over the infiltrate becomes purple, tense, and swollen. Large amounts of gray-green pus are released from the pustules.
The tissues become necrotic. There are clear signs of general intoxication: tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, severe headache, hyperthermia up to 39-40 ° C, leukocytosis, shift of the blood count to the left, lack of appetite, insomnia. If the carbuncle is localized on the face, the symptoms of intoxication are much more pronounced, even to the point of fainting.
After exfoliation of necrotic tissue and removal of pus, the severity of signs of intoxication weakens significantly.
Risk factors for carbuncle formation:
- the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders;
- exhaustion of the body;
- psychological overload;
- immunodeficiency states;
- recent operations or serious illnesses;
- skin contamination, poor sanitary culture;
- nutritional deficiency;
- obesity;
- prolonged friction of the skin with clothing;
- increased sweating.
Carbuncle mainly affects teenagers and young adults. Men get sick more often than women.
Carbuncle. general information
Carbuncle is an acute purulent inflammation of the skin with subcutaneous fat that occurs around several hair follicles. The disease is most often acute and requires immediate treatment. The lesions are usually located on the back of the neck, lower back, hips - those places where the edges of clothing come into contact with the skin and hair. This creates conditions for infection to penetrate the hair follicle.
When treating Carbuncles, doctors at the BIOSS clinic use both time-tested and the latest developments and proprietary techniques.
The BIOSS MC employs the best doctors in Moscow who have extensive experience in the treatment of carbuncles
Symptoms of carbuncle
Clinical signs of a carbuncle are:
- suppuration and wound formation;
- hyperemia of the skin around the lesion;
- severe pain in the entire affected area.
The appearance and development of a carbuncle is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature, which often reaches 40 degrees;
- major intoxication;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- headache;
- general malaise.
These signs are especially pronounced when the carbuncle appears on the face or neck.
There are 3 stages of carbuncle:
Stage 1: infiltrate (folliculitis)
During this period, nodes form under the skin, which will be represented by inflamed hair follicles. The infiltrate contains adipose tissue, pus, lymph and lymphocytes. Nodules rise above the surface of the skin.
Since the nutrition of the dermis is disrupted, it acquires a bluish color. After a few days (from 9 to 12), the infiltrate reaches impressive sizes. It can be about 10 cm in diameter. The skin is swollen, tense, and hot to the touch. The more swelling there is, the more intense the pain will be.
Stage 2: purulent formation
At the stage of suppuration, the carbuncle reaches maturity. Blisters form on it, which are filled with pus. They open, so the surface of the carbuncle resembles a sieve. Through these small holes, pus leaks out, mixed with blood and dead epithelium.
The suppuration stage lasts about 14-21 days. During this period, the patient’s general health deteriorates.
Stage 3: necrosis and tissue rejection
During this period, pus from the carbuncle stops oozing. At the site of inflammation, ulcers are formed that will have rods. They merge with each other, forming one large defect. Tissue damage is very intense and often involves muscles. The affected area is black.
The wound heals slowly, gradually filling with granulations. A scar remains in its place. The necrosis stage lasts about 21 days.
Complications of carbuncle
The occurrence of a carbuncle is fraught with various complications. This is due to the fact that the causative agent of the disease penetrates the body tissues through the vessels and enters the blood. Complications in the presence of a carbuncle can be observed in people who practically do not receive adequate treatment, and their health is already weakened during the course of the disease.
In soft tissues, under the influence of infection, phlegmon, or abscess, forms. If bones become infected, there is a risk of osteomyelitis. If the infection spreads to the blood vessels, a person may develop thrombophlebitis; patients often experience bleeding. In complex forms of the disease, erysipelas of the skin may develop in parallel.
Carbuncles that appear on the face can lead to serious complications. Such formations, if untreated, can provoke the disease of purulent meningitis if the infection affects the brain. The pathogen enters the blood, sepsis develops in the body, this process often leads to death of the patient.
Methods for diagnosing carbuncle
Carbuncle is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- rupture of an epidermal cyst;
- hidradenitis (if the carbuncle is localized in the perineum or armpit);
- anthrax;
- chronic ulcerative herpes.
Laboratory diagnostics
Microscopy of the smear reveals staphylococci. Bacterial culture allows identification of the pathogen and assessment of sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
2. Reasons
Carbuncle is a typical focal staphylococcal infection. The pathogen is usually Staphylococcus aureus, less often other types of staphylococcus; Even more rarely, streptococcus or a polymicrobial infection is cultured, where staphylococci are again present, and only in isolated cases are other bacterial pathogens found.
Risk factors include hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands, the presence of microtraumas, cracks and abrasions on the skin, prolonged physical activity in polluted areas or in dusty air, as well as the presence of underlying diseases with metabolic disorders and/or a decrease in general resistance and local immunity.
Visit our Dermatology page
Treatment methods for carbuncle
Small carbuncles that occur without noticeable intoxication and deterioration of the patient’s general condition are treated on an outpatient basis.
In cases where
- the patient is severely intoxicated,
- the carbuncle is large and localized on the face,
- the patient suffers from uncompensated diabetes mellitus or other serious diseases,
treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Conservative treatment
If treatment of the carbuncle was started at the stage of its maturation, then conservative methods are used, which in most cases leads to regression of the disease, that is, resorption of the infiltrate.
Antibacterial drugs with a broad spectrum of action are indicated for oral administration to the patient.
At the same time, the carbuncle itself is injected with antibiotics. To reduce pain, analgesics (Novocaine, Lidocaine) are used.
The surface of the carbuncle is treated with ethyl alcohol or other alcohol-containing antiseptics. An aseptic dressing is applied. Syntomycin or streptomycin emulsions are also used.
Surgery
If the carbuncle enters the necrotic stage, then this is an indication for surgery, which is performed while using antibiotic therapy.
The operation consists of dissecting the carbuncle and removing necrotic tissue from it.
Then a tampon with a hypertonic sodium chloride solution and proteolytic enzymes is inserted into the wound.
To clean the postoperative wound and completely remove necrotic tissue, the dressing is changed daily.
Physiotherapy
At the maturation stage, as well as in the postoperative period, UHF therapy and local ultraviolet radiation are prescribed.
To stimulate the body's defenses, intravenous laser and ultraviolet irradiation of blood can also be performed.
More information about the treatment method
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
1.General information
Carbuncle is one of the common types of infectious and inflammatory skin lesions. The name comes from the ancient Greek "carbon" (coal) and is based on an association with a smoldering coal, which can be caused by the appearance of a blackened focus of purulent-necrotic tissue decay in combination with inflammatory hyperemia, and sometimes bleeding.
The carbuncle differs from clinically similar ulcers in the tendency for the inflammatory process to quickly spread to several hair follicles simultaneously, which creates the precondition for further expansion, and under unfavorable conditions (for example, against the background of diabetes mellitus or weakened immunity) it can result in sepsis, meningitis, phlegmon and other life-threatening diseases. states.
Carbuncles occur in all age categories, but there is a statistical predominance of young people (which is explained by the characteristics of hormonal activity and secretory function of the sebaceous glands), and the male gender predominates.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes
The disease usually develops with a combination of external and internal factors and a decrease in the body's defenses.
The reasons for the appearance of a carbuncle include:
- Active reproduction of pathogenic organisms on human skin.
- Violation of the integrity of the epidermis (wounds, scratches, splinters, insect bites, calluses, scratches, bruises, abrasions).
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Disruption of the sebaceous glands.
- Poor facial and body hygiene.
- Endocrine pathologies (disorders of the thyroid or parathyroid glands, adrenal glands) and metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity).
- Immunodeficiencies and hypovitaminosis.
- Frequent infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza, parainfluenza, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis).
- Serious chronic pathologies (arthritis, myocarditis, hepatitis).
- Poor nutrition and inactive lifestyle.
- Stress and psycho-emotional stress.
Diagnostics
Photo: skin.lviv.ua
A carbuncle is a purulent inflammation of the epidermis with one or more lesions on the surface of the skin. The diagnosis of carbuncle must be made by a dermatologist. The disease is diagnosed according to its clinical picture.
First, the skin at the site of formation of the future carbuncle turns red and thickens, then nodular formations appear there. Over time, the area becomes more and more inflamed, and the pain intensifies every day until the peak of carbuncle maturation is reached. During the ripening process, the nodules are connected to each other, forming one node. Then it increases in size, and necrosis of the skin may begin, and the area around the lesion first becomes purple, then purple-blue. At the peak of ripening, a purulent focus is observed in the middle of the carbuncle, which causes a burning sensation and tugging pain.
In this case, there may be an increase in body temperature, leading to a fever and chills. In severe cases of the disease, nausea and vomiting and tachycardia are observed. The temperature can rise so high that the person becomes delirious.
After the carbuncle is opened and the pus is cleared out, a deep hole is formed, and the affected tissue takes on a lattice-like appearance. If the diameter of the abscess is large, it is recommended to suture the wound for rapid healing.
During diagnosis, it happens that necrosis continues to spread throughout the muscle tissue even after the abscess is opened. Then it is necessary to take urgent measures to stop this process.
Such carbuncles can be located in one place, or they can cover the entire body. Therefore, during the diagnostic process, it is important to carefully examine the patient for the presence of repeated lesions.
In some cases, differential diagnosis of carbuncle with boil and anthrax is necessary. To exclude anthrax carbuncle, it is necessary to conduct a bacterioscopic examination and take a blood test. The results of the blood test will show an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes in the blood. This is an indirect sign of the presence of the anthrax pathogen in the body. And as a result of a bacterioscopic examination for anthrax, the presence of an aerobic gram-positive anthrax bacillus will be observed. The causative agent of carbuncle is most often Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, upon external examination, a larger area of tissue swelling will be observed, and the contents of the ulcer will be charcoal black. However, while the ulcer is under the skin, this is not always visible, and it is often necessary to open it to determine the color of the contents of the pustule or to conduct an ultrasound of the carbuncle.
The signs of a carbuncle are more pronounced than those of a boil. Also, a boil can be easily identified by the presence of just one initial nodule. An emphysematous carbuncle consists of several nodes that merge together over time. In this case, there may be several places where the integrity of the skin is violated and purulent masses emerge. A boil can have only one such place and its radius is no more than a couple of millimeters. A distinctive feature of a carbuncle in differential diagnosis is the presence of a “honeycomb” in place of burst pustules. Other peptic ulcers are usually characterized by the presence of only one opening.
True carbuncle is a very dangerous disease, so it is important to diagnose it in time and begin to provide assistance to the patient, otherwise extensive tissue necrosis may occur, which will lead to sepsis, the treatment of which is very serious and can cause complications.
Medicines
Photo: obaldela.ru
Outpatients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics in tablets. During hospitalization, drugs are administered intramuscularly. General antibiotic therapy is supplemented by injecting the carbuncle with medications. Pain syndrome is eliminated with the help of analgesics. The choice of painkillers is made taking into account the severity of the symptom; it is possible to use NSAIDs, analgin, ketorol, and in severe cases, short-course narcotic analgesics.
The surface of the unformed carbuncle is treated with an alcohol solution, streptomycin or synthomycin emulsion. After opening the abscess, the above-mentioned proteolytic enzymes are used, then antibiotic ointments are used. To increase the body's defenses and accelerate wound healing, immunomodulators, ascorbic acid, and vitamins A and B are prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, plasma infusions are performed with the addition of anti-staphylococcal antibodies.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Carbunculosis, like other diseases, has general and local symptoms. It is important to notice the signs inherent in this pathology in time and seek medical help.
Manifestations of general symptoms are as follows:
- body temperature quickly rises to 39 – 40°C;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache occurs;
- there is general weakness, increased heart rate;
- If left untreated, sepsis may develop.
How do specific symptoms manifest themselves?
- a small nodule appears on the skin, which grows quickly, becoming quite painful;
- the skin around the infiltrate is inflamed, tense, purple or blue;
- the affected area is covered with small multiple holes from which purulent contents are released;
- swelling of the tissues increases, the areas of the abscesses are hot to the touch, any movement causes an attack of pain, often jerking;
- after opening the carbuncle, pus flows out of it; it looks like a deep ulcer with jagged, blackened edges;
- healing of the affected area occurs slowly, due to tissue necrosis, scars form.
If the pathology becomes malignant, the patient may suffer from neuralgic pain, fever, and fall into a state of prostration and delirium.
Signs of carbunculosis?
An experienced doctor can diagnose a carbuncle simply by examining the patient's skin. However, an additional sample of pus must be taken for laboratory analysis. Indeed, in the early stages of development, the carbuncle is visually similar to an epidermoid cyst. The pus taken for analysis is checked using the Gram stain method. Based on the results of a laboratory test, a specialist will be able to understand whether the bacteria that caused suppuration are a typical staphylococcus or a strain resistant to conventional penicillins.
If, even after successful treatment, the patient’s carbuncles grow again and again, the specialist will prescribe additional tests:
- urine;
- blood;
- skin scrapings.
Additionally, the rate of sebum production is assessed.
Differences between carbunculosis and furunculosis?
The most important external difference of a purulent neoplasm: size. Unlike a single boil, a carbuncle can grow in width and reach the size of a soccer ball.
Other signs of carbunculosis:
- severe itching, felt even before the appearance of a subcutaneous lump;
- nagging pain;
- unexplained fatigue;
- fever and chills;
- increased skin sensitivity.
You need to understand that a carbuncle is much more dangerous than a boil. Therefore, if the above symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of a boil
- The disease begins with a slight tingling sensation, changes in sensitivity (numbness) of a certain area of the skin, chills and a slight increase in body temperature.
- Pain, swelling and redness of the skin appear with the formation of a dense nodule with a diameter of up to 2 cm.
- Then, in the center of this nodule, corresponding to the exit of the hair, a so-called rod (a section of dead tissue) appears, which is gradually torn away, after which the wounded defect is cleared of pus and heals with the formation of a scar.
- With a boil in the area of the upper lip, nose, nasolabial folds and bridge of the nose, there is a high risk of infection spreading with the development of purulent meningitis and sepsis. Over the course of 1–2 days, an inflammatory infiltrate forms. A facial boil is accompanied by severe swelling, although the pain may be minor.
Carbunculosis - what is it?
A carbuncle is an acute purulent inflammation that occurs around the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. It develops in the epidermis and penetrates the subcutaneous tissue.
Carbuncles have the property of rapid growth; formations can reach up to 10 cm in diameter. They are most often multiple and represent a cluster of adjacent abscesses.
The affected area is susceptible to tissue necrosis. The rapid development of a purulent necrotic process is a reason to seek help from a dermatologist.
In the old days, carbuncle was called charcoal for its dark color - translated, the word “carbuncle” means “coal”.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, each disease has its own ICD-10 code. Carbuncle, along with skin abscess and boil, is designated as L02.
The carbuncle of the face has the code L02.0, the neck - L02.1, the torso - L02.2, and so on.
How is it different from a boil?
The main difference between a carbuncle and a furuncle is that a boil affects only one hair follicle or sebaceous duct, while a carbuncle affects several follicles.
What else is the difference between these pathologies:
- carbuncles are accompanied by penetration of the inflammatory process deep into the skin - into the dermis and hypodermis. With furunculosis such lesions are not observed;
- An area of necrotic skin with carbunculosis may acquire a black color, but this is not typical for boils;
- The localization of boils is more extensive - any part of the body except the soles and palms. The places where boils occur are limited - pathology selects special areas, most often the face, the occipital region, and ulcers also form on the butt, in the perineum, on the back;
- the inflammatory reaction with furunculosis is weaker than with carbunculosis. Accordingly, the general condition varies: in the first case, the state of health is relatively normal, but carbuncles are accompanied by a severe clinical picture;
- a purulent-necrotic core with a carbuncle takes longer to form than with a boil - in 2-3 weeks;
- pus from the area affected by the carbuncle comes out through multiple holes, and in case of furunculosis - through one;
- A carbuncle is fraught with the formation of a noticeable scar; after a boil, no such traces remain.
Carbunculosis is more severe, intoxication is stronger, and the disease requires more serious treatment, often in a hospital.
Disease prevention
It is easier to prevent the formation of carbuncles than to treat abscesses for a long time and persistently.
Preventive measures mainly come down to strengthening the immune system and maintaining personal hygiene:
- consuming sufficient amounts of vitamins, microelements, fresh vegetables and fruits;
- avoiding overwork, excessive stress, stress, and nervous feelings;
- regular water procedures - shower (even without gel or soap), wiping the skin with a damp towel, baths with decoctions of chamomile, string, oak bark, sage, calendula;
- treating the skin with antiseptic solutions for bites, abrasions, scratches, cuts;
- using only personal hygiene items - washcloths, razors, towels;
- choosing clothes made from natural breathable fabrics, excluding synthetic tight items;
- timely treatment of colds and other diseases;
- alternating loads and proper rest;
- giving up bad habits.
Carbuncles cause a lot of inconvenience - they are painful, unpleasant from an aesthetic point of view, and, most importantly, they are dangerous for the development of severe complications.
You should not experiment on yourself by self-medicating. Leave the choice of appropriate methods to combat the disease to specialists.