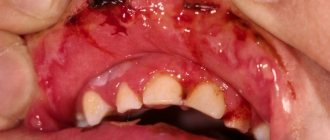
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat
The first cold symptoms appear within 1-2 weeks after infection with the Coxsackie virus. The pathogenic virus enters the body through the fecal-oral or contact route. The disease state begins with a flu-like illness:
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling unwell;
- fever;
- body aches;
- irritability.
Over time, herpetic sore throat acquires more defining symptoms - pain in the pharynx and nasopharynx, acute rhinitis, anterior cervical lymphadenopathy on both sides, profuse salivation.
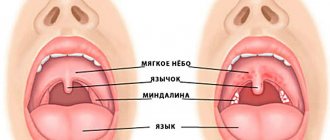
The mucous membranes of the inflamed throat become covered with blisters with a hyperemic halo, inside of which serous contents can be found. Such herpetic rashes are localized on the tonsils, back of the throat, uvula, and soft palate. The rash dries out over time and becomes crusty.
If the disease is aggravated by a bacterial infection, the herpetic blisters suppurate. Signs of intoxication also appear - vomiting, diarrhea, nausea.
We care about your health
Tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases. Infections of a viral or bacterial nature enter the respiratory tract (often one of them is joined by another), causing an inflammatory process. A surge in tonsillitis is most often observed in the spring and winter, when many people have a weakened immune system. Also, this disease can develop against the background of existing foci of infections in the body, for example, with dental caries, periodontal disease, sinusitis and others.
Tonsillitis is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets, pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci, fungi, bacilli.
Tonsillitis can have both acute (called sore throat) and chronic forms. Acute tonsillitis most often occurs as a result of an exacerbation of the chronic form, when a person with reduced immunity could, for example, become hypothermic.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Compared to chronic tonsillitis, acute tonsillitis occurs in a more severe form: the body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, the patient feels a very strong pain in the throat, and it is difficult for him to swallow. The tonsils are swollen and enlarged, with the presence of purulent plugs. Patients feel headache, weakness, and their lymph nodes are enlarged.
Depending on the type of sore throat, which can be lacunar, herpetic, catarrhal, follicular, etc., ulcers, follicles, and a film called plaque form on the palatine tonsils.
With chronic tonsillitis, the temperature can rise to 38. The patient has a light coating on the palatine tonsils, and the tonsils themselves look enlarged and reddened. A person feels weakness, muscle pain, and aching joints.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by stages of remission and exacerbation. During the period of remission, the focus of infection is passive, and the person is not bothered by unpleasant symptoms. But as soon as one becomes hypothermic (especially with reduced immunity), he immediately begins to feel an unpleasant sore throat, pain when swallowing, cough, fatigue, poor general health and lack of appetite. The patient's lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the pharynx and palate. Its simple form has only a local symptom: sore throat. But if the picture is complemented by persistent lymphadenitis of the neck, changes in the functioning of the heart and high temperature, then this is already a toxic-allergic form.
Chronic tonsillitis has several stages: compensated, when the source of infection is not active, and decompensated, when exacerbation occurs due to repeated sore throats, inflammation of the ear and nose.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis) - what inflammation looks like (photo of the disease)
Photograph of the throat with purulent sore throat
Photo - throat with follicular sore throat
Catarrhal sore throat - photo
Photo - lacunar tonsillitis
Possible complications of tonsillitis
Like many other diseases, tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications . These include, first of all, rheumatism. After suffering from a sore throat, a person may feel severe aching in the joints and an increase in temperature.
In second place, as a rule, are cardiovascular diseases. Interruptions in heart function, shortness of breath, tachycardia are sure signs that a sore throat has caused complications.
Another unpleasant symptom after tonsillitis is swelling and tenderness of the lymph nodes, which have become infected from the tonsils. This is lymphadenitis.
The infection can also spread from the tonsils to the surrounding tissues of the upper respiratory tract, leading to pain when swallowing. And this disease is a complication of tonsillitis and is called paratonsillitis.
It should be noted that more than a hundred diseases are known that arise as a result of complications after acute tonsillitis. These include a variety of kidney, eye, skin and thyroid diseases.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
It begins, of course, with an examination by a doctor, who determines whether the tonsils and adjacent tissues are swollen and red, and whether the ear and cervical lymph nodes are inflamed. The patient is sent for a general blood test.
Before prescribing treatment to the patient, the ENT doctor determines the nature of the inflammatory process: in what form does tonsillitis occur - chronic or acute, the type of inflammation (purulent, catarrhal), is the sore throat primary or secondary, what is the causative agent (this is determined in the laboratory - a culture is done from the throat ).
Treatment of tonsillitis - specifics of therapy
In the treatment of tonsillitis, both conservative methods and surgical intervention can be used. Treatment methods depend on the specifics of the disease.
For chronic tonsillitis, if necessary, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets, and for sore throat they are often administered intramuscularly. Local treatment is also carried out: purulent plaque on the tonsils is removed, the lacunae are washed with antibacterial solutions, physiotherapy and a course of vitamins with immunomodulators are prescribed.
In case of acute tonsillitis, it is recommended to irrigate the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, rinse, treat the tonsils with iodine-containing preparations (if there are no allergic reactions to iodine), inhalations, and resorption of antibacterial tablets are useful. You should also drink a lot (weak teas, fruit drinks, juices, rosehip decoctions, etc.), take antipyretic and painkillers.
Acute tonsillitis is not recommended to be treated with antibiotics, because they reduce local immunity. But if the form of the disease is more severe, then the patient requires mandatory bed rest and antibiotic therapy. However, the prescription of antibiotics should be preceded by an analysis of the results of culture in the pharynx area, which will identify the causative agent of the infection. It is recommended to include in the course of treatment drugs that enhance immunity, as well as general strengthening and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physiotherapy will also be useful.
If a person suffers from tonsillitis more than twice a year, has complications from this disease, and conservative treatment does not bring the expected results, then removal of the tonsils may be recommended. There are many modern methods of performing this operation (infrared laser, ultrasound, biopolar, radiofrequency ablation and others), but many consider the cold plasma coblation method to be the most effective and gentle. However, it should be remembered that the tonsils are the first protective barrier that stops and disarms pathogenic bacteria . But in many cases (especially after frequent colds), the tonsils stop performing their functions and themselves become a source of infection, causing serious complications. In this case, it is better to remove them.
Treatment of tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the Medkvadrat ENT center in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki.
Diagnosis of herpetic sore throat
The doctor can make a diagnosis only when characteristic rashes are already visible. Before this, the disease is easily confused with the flu. Several factors play a role in the diagnosis of herpetic sore throat:
- age;
- seasonality (summer-autumn);
- type of inflammation in the throat;
- localization of bubbles.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes serological or virological examination methods. For serological testing, special sera labeled with fluorescein are used. Material for analysis should be taken during the first few days of illness, and repeated after 1-2 weeks. For virological examination, swabs and swabs are taken from the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
It can be difficult for an inexperienced doctor to recognize herpetic sore throat and distinguish it from diphtheria, scarlet fever, pneumonia or meningitis. In children, the examination should begin with a visual examination of the pharynx and nasopharynx, a general blood test should be prescribed, and a swab from the nasopharynx should be taken.
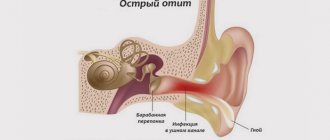
Complications
Unfortunately, this type of tonsillitis has dangerous negative consequences if the disease is started and left to chance. The greatest danger is from complications of the kidneys, brain and heart. Since the sore throat virus spreads through the flow of lymph and blood, inflammation can overtake certain parts of the brain, causing meningitis and encephalitis. Convulsions, persistent headache, increasing temperature are reasons to seek medical help again.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, ENT doctors with extensive experience will carefully examine an adult and a small patient and immediately perform a serological and virological analysis to determine the causative agent. The technical equipment of our medical center allows us to obtain diagnostic results within a couple of hours. Thanks to this, therapeutic therapy is prescribed in a timely manner, with positive dynamics occurring the very next day.
Herpetic sore throat in children and its features
Herpetic sore throat in children has its own characteristics. Thus, children under 3 years of age are more susceptible to various viruses and infections than infants, who receive a full range of vitamins and minerals from breast milk. After the baby is weaned, the immune system begins to weaken slightly. In kindergartens, outbreaks of this disease sometimes occur, since the main route of transmission of the virus is through contact.
By the age of three, the baby has formed its own immune system, which protects it from various diseases. Up to 10 years of age, herpetic sore throat is rare in children.
The risk group includes schoolchildren, allergy sufferers, and malnutrition sufferers. The provoking factors are frequent colds, hypothermia, chronic stomatitis, tonsillitis, and reduced immunity.
Diagnosis of acute tonsillopharyngitis
If there are signs of streptococcal infection, the diagnosis is confirmed by a positive microbiological test (rapid test for the detection of GABHS antigen or a throat swab for GABHS). A test or smear should be performed before starting antibiotic therapy, as even a single dose of antibiotics can lead to a negative result.
Rapid tests for GABHS have a specificity of more than 95% and a sensitivity that varies between 70 and 90%. Given the high specificity and limited sensitivity of the available tests, a positive test for GABHS is sufficient to establish the diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, but a negative test, in turn, does not exclude GABHS infection. Therefore, in a child or adolescent, in case of a negative result of the rapid test, it is necessary to perform a throat smear for GABHS. If the rapid test is positive, then subsequent bacteriological examination is not required.
In adults, with a negative rapid test in a standard situation, subsequent microbiological testing is not required.
A test for GABHS is indicated in the following cases:
- there are signs of acute tonsillopharyngitis (erythema, swelling and/or exudate in the tonsils) or a scarlet rash, but there are no symptoms of a viral infection;
- there was contact with a sick person whose diagnosis of streptococcal infection was confirmed (at home, at school);
- suspicion of acute rheumatic fever or post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
GABHS testing is not indicated for children and adolescents with manifestations of a viral infection. From 5 to 21% of children aged 3-15 years are carriers of GABHS, which can be mistakenly perceived as streptococcal rather than viral pharyngitis.
Timely treatment of GABHS in children and adolescents is primarily necessary for:
- prevention of purulent complications and acute rheumatic fever;
- preventing transmission of the disease to others, especially if the patient is in contact with a person who has had a history of an episode of acute rheumatic fever;
- reducing the duration and severity of symptoms of the disease.
Herpetic sore throat in adults and its features
The peculiarity of herpangina in adults is that the disease is diagnosed much less frequently than in childhood, and its course is easier. An adult can catch the virus from a child who became infected in kindergarten, summer camp, or school.
In addition, after suffering the disease once, a stable immunity is formed, which prevents the pathogen from becoming active again. Re-infection can be caused by a severe cold or weakened immune system.
Sources
- Corsino CB, Ali R, Linklater DR. Herpangina. 2021 Jun 23. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 29939569. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507792/
- Ter-Baghdasaryan L.V., Ratnikova L.I., Stenko E.A. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of enterovirus infection // Infectious diseases: news, opinions, training. 2021. Vol. 9, No. 1. pp. 88-93. doi: 10.33029/2305-3496-2020-9-1-88-93 https://infect-dis-journal.ru/ru/jarticles_infection/672.html?SSr=2601343bdb01ffffffff27c__07e4040b011a36-9772
- Alacheva Z. A., Rybalka O. B., Kulichenko T. V. Should everyone escape from Coxsackie?! Or fear has big eyes. Issues of modern pediatrics. 2017; 16 (4): 286–290. doi: 10.15690/vsp.v16i4.1774) https://vsp.spr-journal.ru/jour/article/viewFile/1787/713
- Herpangina Brenda L. Tesini. University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry // MSD Handbook - 2019 https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/infectious-diseases/enteroviruses/herpangina
- Kozlovskaya O.V., Katanakhova L.L., Kamka N.N., Evseeva A.N. Epidemiological, clinical and diagnostic features of enterovirus infection in children and adults. Bulletin of Surgu State University. Medicine. 2018;(2):56-60. https://surgumed.elpub.ru/jour/article/view/140/141
- Kuo KC, Yeh YC, Huang YH, Chen IL, Lee CH. Understanding physician antibiotic prescribing behavior for children with enterovirus infection. PLoS One. 2021 Sep 7;13(9):e0202316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202316. PMID: 30192893; PMCID: PMC6128467. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30192893/
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® AEROSOL:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA:
Up to contents
Treatment of herpetic sore throat
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for herpetic sore throat. It consists of symptomatic therapy. Antibiotics can be prescribed only in case of concomitant bacterial infection - Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Penicillin. Rioflora, Imudon, Immunal and other analogues successfully cope with strengthening the immune system and fighting viruses.
For the purpose of successful and effective treatment, the patient needs to follow some rules:
- The patient must be isolated. It is necessary to provide him with separate hygiene products and dishes to prevent infection of other family members.
- Bed rest - it will take some time to regain strength.
- Special diet - it is necessary to exclude foods that can irritate the already inflamed mucous membranes of the throat. The patient will have to abstain from confectionery, spices, hot and cold foods, and hard fruits. The diet should consist of cottage cheese, liquid cereals, and soups.
- Lots of liquids - drink plenty and warm. It is recommended to drink warm tea, fruit juice, and neutral juices.
During colds, including during herpetic sore throat, the herpes virus can be activated. In this case, the doctor prescribes the following drugs:
- Cycloferon;
- Cytovir;
- Viferon.
To relieve a sore throat, you can take Strepsils, Septolete and other cough lozenges and lozenges. Antiseptic sprays are also effective - Ingalipt, Hexoral, Yox, Kameton.
To reduce the temperature, the doctor prescribes Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Panadol, as well as antihistamines in case of a possible allergic reaction - Zyrtec, Loratadine, Claritin, Diazolin.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the appointment, the ENT doctor will examine the patient and conduct an examination. Based on the diagnostic results, drug therapy is prescribed, including:
- Taking antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Taking antiviral drugs prescribed after identifying the exact pathogen.
- Taking antihistamines. The active substance helps relieve swelling and ease breathing.
- Resorption of lozenges, lozenges, use of local sprays. Their antiseptic and bactericidal properties reduce sore throat.
- Local use of antiviral ointments based on interferon.
- Taking immunostimulants to activate the body's defenses to fight the pathogen.
It must be emphasized that antibiotics are powerless for this type of tonsillitis, because they do not affect the reproduction of viruses.
Important to remember! Do not apply heat compresses to the throat. Heating promotes the further spread of viruses throughout the body.
In addition to taking medications, the patient must be isolated from others and observe strict quarantine. The infectious period lasts two weeks. You need to follow a diet and eat pureed liquid food, drink more liquid. Water not only prevents dehydration, but also relieves symptoms of intoxication. If you are sick, you should not smoke, drink boiling water or water from the refrigerator.
Since the throat is constantly injured, healing occurs within 10-14 days. Crusts and sores are washed off with saliva without any residue.
It is important to know! Do not touch the bubbles with your hands or try to squeeze them out.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating herpetic sore throat can also be supplemented with folk remedies. But you should agree on the chosen prescription with your doctor. The most effective traditional medicine recipes are:
- Propolis. 2 grams of propolis should be chewed in the mouth for 15 minutes. The procedure must be repeated three times a day.
- Honeycomb can also be consumed as chewing gum three times a day.
- 1 teaspoon of aloe juice twice a day.
- Kalanchoe leaf will help cope with pain in the nasopharynx - you need to chew it until the juice stops secreting. Kalanchoe can be chewed three times a day.
- Propolis in the form of an alcohol tincture for gargling - dilute 1 teaspoon of solution in one glass of water.
Before using this or that folk remedy, you should make sure that the patient does not have allergies. Honey and propolis are fairly common allergens.
Potential danger
The danger of herpangina, like many other diseases, lies in potential complications. Thus, among the main problems that can occur as a result of the development of herpangina is inflammation of the soft palate.
“Hence, paratonsillitis is a situation where the tissue is tense, swollen, red, swollen. Then a purulent cavity may form here; this is a peritonsillar abscess - an acute purulent inflammation that must be opened. Moreover, the risks of developing such abscesses with herpangina are high,” the otolaryngologist emphasizes.
It should be understood that therapy for herpetic sore throat should be started as quickly as possible, because the progression of pathological processes can occur faster than with ordinary sore throat.
There are contraindications, you should consult your doctor.
Recommendations
At the first signs of discomfort, you should consult a doctor. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, serious complications may develop:
- meningitis with inflammation of the meninges;
- encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue);
- hemorrhagic conjunctivitis - an infection of the eyes;
- rheumatism – connective tissues become inflamed;
- myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart muscle.
By following all the doctor’s recommendations and adhering to the course of treatment, you can avoid the development of these complications and significantly speed up the recovery process.
Prevention
As mentioned above, herpetic sore throat is transmitted from person to person by contact or airborne droplets, then the main method of prevention is the introduction of quarantine, that is, isolation of a sick family member or team, limiting contacts with him.
Preventive measures also include:
- systematic strengthening and maintenance of immunity.
- Maintaining a routine means getting enough sleep.
- Proper nutrition.
- Getting rid of bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the house, regular ventilation and wet cleaning.
- Reducing stress levels.
- Timely treatment of colds.
If a child shows signs of a cold, he should not be taken to kindergarten or school. It is better to take the baby to the doctor and let him rest at home. Such measures will allow the child’s body to regain strength. In addition, the likelihood of infecting other children will be reduced.
Symptoms
To accurately diagnose herpetic sore throat, it is necessary to conduct clinical studies over a long period of time. It is important to start timely treatment, so you should pay attention to the characteristic symptoms of the disease in children:
- heat;
- prostration;
- sore throat;
- the appearance of vesicles and ulcers in the oral cavity and on the back of the pharynx;
- poor appetite;
- nasal discharge;
- swelling of the cervical lymph nodes;
- rashes on the skin (except for the face).
The patient must be isolated from others during the recovery period. When treated at home, he is given separate tableware and personal hygiene items.
Question answer
Can you have herpetic sore throat without fever?
During herpetic sore throat, the temperature always rises. In the initial stages, the temperature rises slightly, as with a cold, but when a rash has already appeared on the mucous membranes, the temperature can rise to 40. Hyperthermia lasts from 3 to 6 days.
Is it possible to wash with herpetic sore throat?
You can wash with this disease. The rash appears only on the tonsils and in the nasopharynx; there are no signs of vesicles or papules on the skin, so there are no contraindications to showering. But with hyperthermia, all measures should be taken to avoid hypothermia.
Is it possible to get herpangina again?
After experiencing the disease once, immunity is formed. But sometimes a re-exacerbation of herpetic sore throat occurs. A recurrent disease can be diagnosed many years after the first case, and only with reduced immunity and a weakened body.
Is it possible to go to the pool with herpetic sore throat?
You will have to refuse to visit the pool during a herpetic sore throat. Swimming in the pool is physical activity that should be limited. And the water in the pool is quite cool, which can lead to hypothermia. The pool is considered a public place - you should not become a source of infection for many people.
Incubation period
From the moment the virus enters the body until the first symptoms of the disease develop, some time passes when the presence of the disease cannot be judged by external signs. In medicine, this is referred to as the incubation period. For different diseases, it amounts to different time periods, which can vary from several hours to several years and even decades.
In the case of herpetic sore throat, caused in most cases by the Korsaki virus, it ranges from 6 to 20 days. This depends on the concentration of the virus in the blood, the state of immunity, the patient and other individual characteristics.
Important! A child becomes a transmitter of infection long before the first symptoms appear - 3-4 days after infection.