Thrush in men is not as well known and does not receive as much attention, articles, or advertising as female thrush or vulvovaginal candidiasis.
This disease can also occur in men, and it occurs quite often, affecting the glans penis, skin of the foreskin, urethra, scrotum, inguinal fold, intergluteal fold, interdigital spaces, mucous membrane of the corners of the mouth, tongue, cheeks and pharynx. In severe cases, candidiasis spreads to the entire gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract.
Therefore, this problem, that is, thrush in men, the symptoms and treatment of this disease remain relevant for doctors and patients. Moreover, there is very little reliable information in the public domain.
Patients often come to me with redness on the penis, ulcers, rashes in the groin and oropharynx. Many of them had unprotected sexual contact with an unfamiliar woman, some with a man. Consequently, they are afraid of contracting a sexually transmitted disease and associate these symptoms with it. Some men cannot even understand where these rashes and itching come from. It seemed like he didn’t even walk to the left, but the whole penis was red, swollen and itchy. So, after examination and diagnosis, they learn about the presence of a disease such as thrush in men, and sometimes about the presence of diabetes mellitus. But more on that below...
Thrush in men is caused by a yeast-like fungus such as Candida of various strains:
- Candida albikans is the most common type of this fungus in our country. But it is already beginning to be gradually replaced by other types of candida brought from abroad, such as:
- Candida krusei
- Candida tropicalis
- Candida parapsilosis
- Candida glabrata and some other rare fungi.
Determining the type of fungus is quite important for planning therapy. Of course, ideally you need to know not only it, but also Candida’s sensitivity to drugs. True, this does not always work out, because cultures, unfortunately, do not provide reliable information every time, but it is much easier to determine the type using PCR. This allows us to predict the effectiveness of fluconazole treatment for diseases caused by various types of candida.
Causes of thrush in men
The causes of candidiasis in men are different, but all one way or another lead to the proliferation of the Candida fungus:
- weak immunity;
- lack of hygiene;
- as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse;
- long-term use of medications/antibiotics;
- sudden change in climatic conditions;
- presence of depression, stress;
The cause may also be a dysfunction of the intestine, as well as its microflora due to damage to the mucous membrane and the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Rules to follow during treatment
During the therapy period, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse so as not to provoke the development of the disease. If possible, you should stop smoking and not drink alcoholic beverages. Avoid hypothermia and stress.
To reduce symptoms, it is recommended to choose loose underwear and clothing, and ensure that the groin area remains dry.
Nutrition:
- Eliminate sugar, fast carbohydrates, yeast and other fermentation products: they contribute to the development of fungal forms.
- Add fermented milk products with live cultures, whole grains, fresh and thermally processed vegetables and fruits to your diet.
Compliance with the diet will strengthen the body's protective functions and shorten the period of the disease, and the formation of healthy eating habits will eliminate the risk of relapse.
What type of thrush does it have in men?
Candidiasis in men most often appears on the head of the penis, causing irritation, pathological discharge and redness. Thrush often occurs in men with uncircumcised foreskin. In this case, the fungus receives more favorable conditions for life and reproduction. When candidiasis occurs, characteristic signs are observed - unpleasant itching and the appearance of a white coating on the mucous membrane. You can determine the disease yourself; you just need to know what it looks like on your underwear. Thrush leaves a thick white or yellow coating on panties.
Complications
Lack of timely treatment can lead to disruption of the structure of the urethral mucosa, which will complicate the process of urination. The long course of the disease reduces the sensitivity of nerve endings, which leads to loss of pleasure from sexual intercourse. It is much more difficult for a man to achieve orgasm, against the background of which libido disappears and sexual dysfunction may develop.
To avoid consequences, you should consult a doctor immediately after detecting symptoms of candidiasis and follow the treatment recommendations prescribed by a specialist.
Important: traditional methods are extremely ineffective in treating fungal infections. Neglecting the methods of official medicine aggravates the course of the disease and leads to the development of complications.
Manifestation of thrush in men
The appearance of characteristic signs of the disease in men is determined by the location of the lesion. If candidiasis appears on the skin, blisters and redness form, and on the mucous membranes - a type of infectious lesion.
The main symptoms of thrush in men are:
- unpleasant sensation of burning and itching;
- swelling of the penis appears;
- pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor appears;
- pathological secretion during urination, similar in appearance to seminal fluid;
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
The disease has an incubation period, and diagnosis and treatment depend on its duration. Most often this period lasts 2-3 weeks. During this time, symptoms may not appear, but the fungi are already multiplying in the body.
Diagnosis and treatment
Thrush can be identified by the main symptoms of the disease, but a similar clinical picture is observed in other diseases, so only a doctor can make a final diagnosis.
Important: thrush does not go away on its own; the disease must be treated.
To make a diagnosis, laboratory – bacteriological and microscopic – studies are carried out. After deciphering the test results, the doctor prescribes a course of antifungal therapy.
The basis for diagnosis is the presence of fungal elements in the collected biomaterial. Bacteriological culture analysis allows you to determine the type and genus of fungi. This is necessary in order to correctly select antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
Typically, topical medications are prescribed for treatment - creams and ointments that suppress pathogenic microorganisms. If such therapy is ineffective, the doctor prescribes general medications.
Treatment of thrush in men
Treatment of candidiasis is always completely individual. The course of therapy is prescribed only by a urologist or dermatovenerologist. He assesses the patient’s medical history, age and lifestyle, and then prescribes the necessary treatment. It is strictly prohibited to treat candidiasis at home without going to the doctor. This can lead to complications.
To make a final diagnosis, the patient must take a smear to examine the bacterial flora. In addition to this, several more tests may be prescribed:
- donating blood and genital swabs;
- determination of blood glucose levels;
- blood for HIV;
- general blood and urine analysis.
In case of candidiasis due to other reasons, the necessary treatment is required from highly specialized specialists. If no other pathologies are found, a course of therapy is prescribed and the patient is sent home for treatment.
Men get sick 4 times less often than women, so the choice of drugs for the stronger half of humanity is much smaller. For local treatment, antifungal ointments are used, and tablets that kill the fungus are taken orally. Among the ointments one can highlight pimafucin, clotrimazole, nystatin and others.
What drugs are used to treat the disease?
To overcome this disease, the patient is prescribed antifungal drugs. They can be in the form of ointments or tablets, the ingestion or external use of which can regulate the number of pathogenic microorganisms.
The most commonly used drugs are based on the following substances:
- Miconazole. It comes in the form of a spray or cream. When applied, it disrupts the integrity of various pathogenic microorganisms.
- Ketoconazole. Presented in the form of creams, sprays, tablets. A decrease in the fungal population occurs due to a destructive effect on the biosynthesis of some components of the fungal cell membrane.
- Econazole It comes in the form of creams. It affects the lipid structure of the fungal membrane, having a bactericidal and fungicidal effect.
- Clotrimazole. Presented in the form of creams, ointments and solutions. It has a positive effect on yeast and mold fungi, kills gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, dermatophytes.
Advantages of taking tests at JSC "SZDCM"
- Own laboratory with the latest diagnostic equipment.
- Convenient location of terminals within transport accessibility from anywhere in the city.
- Qualified laboratory technicians and friendly staff.
- Fast analysis and several options for obtaining results. Choose the one that is most convenient for you.
Medical centers and laboratory terminals of the North-Western Center for Evidence-Based Medicine are located in St. Petersburg, Leningrad region, Veliky Novgorod, Okulovka, Kaliningrad and Pskov.
Analyzes
- Bacteriological study for opportunistic pathogenic flora (OPF)
- NC yeasts of the genus Candida: C.albicans, C.krusei, C.glabrata
- Study of the biocenosis of the urogenital tract in women (“Femoflor 13 - screening”)
- Candida albicans
- Mycoses: identification of clinically significant fungi with determination of sensitivity to antimycotic drugs (only for fungi of the genus Candida and Cryptococcus neoformans)
- Specific immunoglobulin E - Candida albicans
go to analyzes
Diagnosis of urogenital candidiasis
Urogenital candidiasis be detected using physical and chemical research methods.
Laboratory analysis methods used include:
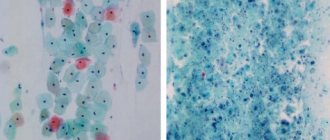
- Microscopy method. The procedure involves the use of uncolored substances, products colored with methylene blue, as well as using the Romanovsky and Gram method. The purpose of the examination is to identify the cellular structures of the fungus: pseudohyphae, pseudomycelium, blastoconidia, and individual budding particles.
- Method of sowing biological material. Prescribed for suspected chronic re-exacerbation of the disease, for the purpose of recognizing yeast-like fungi (most typical for detecting species that do not belong to the genus Candida albicans), to assess the effect of antimycotic drugs on the body, as well as in the case of an atypical course of the disease, when infection with other possible pathogens are excluded.
- PCR diagnostic methods allow you to detect DNA of a specific type of yeast-like fungal infection (in particular, C. albicans).
Classification of the disease
Based on the depth of damage, candidiasis is divided into superficial and systemic forms. The first appear on visible parts of the body: mucous membranes, skin and its appendages. The second, systemic, are combined forms of the disease affecting internal organs. Without proper treatment, systemic (visceral) candidiasis can lead to the development of candidal sepsis. Most often, the fungus affects:
- gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, intestines);
- urinary organs (bladder, urinary tract, kidneys);
- lower respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, lungs).
The disease is also classified based on the rate of spread of infection and the presence of relapses. Candidiasis of the liver and spleen often takes a chronic form. The acute, generalized form is asymptomatic candidemia, candida septicemia, candida thrombophlebitis, myositis, arthritis, cerebral candidiasis and other forms.
Classification of candida lesions according to ICD-10
- Candidiasis.
- Candidal stomatitis.
- Pulmonary candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the skin and nails.
- Candidiasis of the vulva and vagina.
- Candidiasis of other urogenital locations.
- Candidal meningitis.
- Candidal endocarditis.
- Candidal septicemia.
- Candidiasis of other locations.
- Candidiasis, unspecified.
Officially, the diagnosis is made in accordance with ICD-10. In practical healthcare, such a classification is not entirely convenient, so they use the classification of deep candidiasis, which is a deeper list. When making a diagnosis, first indicate the name and form of the infection with a description of all localization points.
Skin treatment is carried out by a pediatrician in children and by a dermatologist in adults. Therapy is also carried out by doctors of other specializations, depending on the affected organ. For example, this could be a dentist, neurologist, gynecologist, pulmonologist.
Symptoms of urogenital candidiasis
Among the subjective signs of the disease it is worth highlighting:
- burning, itching of the skin and genital mucosa;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- the presence of thick, dull yellow, white, creamy, cheesy discharge from the vagina;
- difficult painful urination.
Objective signs of infection may be:
- swelling of the genitals at the entrance to the vagina, vulva;
- dryness of the genitals;
- scanty white discharge;
- vaginal atrophy;
- the presence of cracks and microdamages of the skin and mucous membrane of the perianal area, vulva, and posterior commissure.
In complicated forms of chronic urogenital candidiasis, inflammation of the genitourinary system, vaginal pathologies, and urethrocystitis are observed.
Factors that contribute to the disease
The most common causes of urogenital candidiasis are:
- weakened immune system;
- existing endocrine disorders (sharp weight gain, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, etc.);
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- use of spermicidal, intrauterine contraceptives;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- use of hygienic douches;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, in particular intravaginal ones (in the form of capsules, creams, suppositories);
- prolonged use of sanitary pads that have little or no air permeability;
- long-term treatment with corticosteroid hormones, immunosuppressants, cytostatics.
Sometimes a woman does not have any factors conducive to infection, but against the background of stress and hormonal imbalance, she is diagnosed with persistent recurrent thrush. In such a situation, individual congenital pathologies are analyzed that affect changes in the vaginal epithelium, causing a failure of the mechanisms of the local immune response.
Reasons for the development of candidiasis
What causes thrush? This disease occurs from infection by candida fungi. By their origin, they are relatives of the well-known yeast. These parasites are usually controlled by the human immune system and pose no threat to the body.
Infection can occur due to the following factors:
- Dysbacteriosis is one of the most important causes of the clinical manifestation of candidiasis.;
- the occurrence of endocrine disorders in the human body;
- stressful situations in a man’s life;
- emotional turmoil;
- immunodeficiency - both acquired and congenital;
- drug overdose;
- work related to changing climate and time zones;
- injuries of various types;
- diabetes;
- penetration of viral pathogens of infectious diseases into the body;
- violation or failure to comply with the rules of hygiene of the oral cavity, genitals and other parts of the male body.
In such cases, the fungus activates and thrush occurs. This manifests itself during sexual intercourse - single-celled organisms transfer to the man’s body
Risk factors for development
The likelihood of infection increases with casual sexual intercourse, uncontrolled use of antibiotics and drugs that disrupt the natural microflora. Foods with large amounts of sugar and carbohydrates create a favorable environment for fungal growth. Excessive sweating also leads to an exacerbation of candidiasis, so it is necessary to wear cotton underwear that allows the skin to breathe and moisture to evaporate.
At the same time, excessive cleanliness can also cause harm. We are talking about douching. It should not be used as a method of contraception, since it is not effective, and also as a means of hygiene, because it leads to the leaching of the protective flora. If you experience discomfort, you should first consult a doctor.
Interpretation of results
If there are clear signs of candidiasis (thrush), and during a laboratory test blastospores and pseudomycelia of the fungus were identified, the study ends here. A diagnosis is made and treatment begins.
If a microscopic examination gives a negative result, this does not indicate the absence of infection. The disease can occur in a latent chronic form. It is necessary to carry out a number of other tests, for example, microscopic examination of scrapings, determination of Candida DNA in scrapings, urine, and prostate secretions. Also prescribed:
- Clinical blood test.
- Test for HIV infection.
- Determination of trace element reserves in the body.
- Test for glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
These laboratory tests can help identify conditions that may be causing the fungus to grow.