"Reamberin" is a solution for a dropper, which is used to treat the consequences of poisoning with food, alcohol, drugs and other substances. Used to relieve acute symptoms of cholecystitis and pancreatitis. The product has a pronounced effect, while it has virtually no side effects. It is placed intravenously, mainly in a hospital setting. In some cases, home use is also allowed.
The drug is used to place IVs. It is produced in the form of a solution. The composition contains the active ingredient - sodium meglumine succinate (15 g per 1 l) and additional components, including:
- sodium chloride;
- magnesium chloride;
- potassium chloride;
- sodium hydroxide;
- water for injections.
The description states that physically “Reamberin” is a colorless solution, has no smell or taste. It is produced in different volumes - 200 ml, 400 ml and 1 l.
"Reamberin" is used as a detoxifying agent to eliminate the effects of poisoning of various natures. The drug protects internal organs (heart muscles, neurons, kidneys, liver) from damage by toxic substances. Acts as an antioxidant and antihypoxic agent (prevents a critical decrease in oxygen concentration in the blood). Stimulates enzymes that destroy dangerous molecules that destroy tissue - free radicals.
Also, the active substance strengthens the membranes of brain neurons, normalizes metabolic processes, and increases the energy potential of the cell. At the same time, Reamberin does not accumulate in cells - it is consumed in full.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The active substance protects the heart muscle, nerve cells, liver and kidneys from toxins . It also has antihypoxic, antioxidant and detoxification activity. By inhibiting the reactions of fat peroxidation , during hypoxia and ischemia antioxidant are stimulated .
The membranes of brain , kidney, liver and heart are stabilized The product also has a diuretic effect.
Sodium N-methylammonium succinate penetrates cell mitochondria and participates in the Krebs Cycle , inhibiting oxidation reactions and increasing intracellular energy potential ( creatine phosphate and adenosine triphosphate ).
Penetrating into the body, the drug does not accumulate, but is completely consumed.
special instructions
Due to the activation of aerobic processes in the body by the drug, a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood and the appearance of an alkaline reaction in urine are possible. In patients with diabetes mellitus and patients with reduced glucose tolerance, periodic monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is required. If the color of the solution changes or there is a precipitate, the use of the drug is unacceptable.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery It is not recommended to drive vehicles or operate machinery during a course of treatment with REAMBERIN®.
Instructions for use of Reamberin (Method and dosage)
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, different rates of administration and daily dosages are prescribed.
Instructions for use of Reamberin for alcohol intoxication : the drug is administered intravenously , the injection rate is 90 drops per minute. The daily dose is 400-800 ml.
For children, an IV is placed based on the principle of 8 ml of the drug per kilogram of the patient’s weight. The maximum amount of Reamberin is 400 ml per day.
The course of treatment is no more than 11 days.
Side effect
According to the World Health Organization, adverse effects are classified according to their frequency as follows:
– very frequent (≥ 1/10); – common (from ≥ 1/100 to – infrequent (from ≥ 1/1000 to – rare (from ≥ 1/10000 to – very rare ( – frequency unknown (cannot be determined based on available data).
If the drug is administered quickly, undesirable effects are possible.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site: very rarely - hyperthermia, chills, sweating, weakness, pain at the injection site, edema, hyperemia, phlebitis. Immune system disorders: very rarely - allergic reactions, angioedema, anaphylactic shock. Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: very rarely - allergic rash, urticaria, itching. Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: very rarely - shortness of breath, dry cough. Cardiac disorders: very rarely - tachycardia, palpitations, shortness of breath, pain in the heart, chest pain. Vascular disorders: very rarely - arterial hypotension/hypertension, short-term reactions in the form of a burning sensation and redness of the upper body. Gastrointestinal disorders: very rarely - nausea, vomiting, metallic taste in the mouth, abdominal pain, diarrhea. Nervous system disorders: very rarely - dizziness, headache, convulsions, tremor, paresthesia, agitation, anxiety. To avoid unwanted effects, it is recommended to adhere to the dosage regimen and rate of administration of the drug. If adverse reactions occur, it is recommended to reduce the rate of drug administration. If any of the undesirable effects indicated in the instructions get worse or you notice any other undesirable effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride
Magnesium sulfate
Sodium chloride
Potassium chloride
Rheosorbilact
Analogues of the product are: xylate, potassium chloride, glyxyl, calcium chloride, lactoxyl, magnesium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium chloride, plerigo .
Compound
Active ingredient: sodium meglumine succinate – 15.00 g.
Excipients: sodium chloride – 6.00 g, potassium chloride – 0.30 g, magnesium chloride hexahydrate (in terms of anhydrous) – 0.12 g, sodium hydroxide – 1.788 g, succinic acid – to pH from 6.0 to 7.0, water for injection – up to 1.0 l.
Ionic composition per 1 l:
- sodium 147 mmol - potassium 4.02 mmol - magnesium 1.26 mmol - chlorides 109 mmol - succinates 46.0 mmol - meglumine 44.7 mmol
Theoretical osmolarity 353 mOsm/l
Description: transparent colorless liquid.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: solutions affecting water and electrolyte balance. ATX code: В05ВВ
Reviews of Reamberin
Reviews about Reamberin are good. The drug copes well with the task of freeing the body from toxins and rehabilitation after severe infectious diseases. In itself, while not being a panacea for any specific disease, the medicine significantly speeds up the healing process. Sometimes side effects occur, and therefore the drug is not recommended for use outside the hospital.
Reviews of Reamberin for psoriasis : The use of the drug in the treatment of this disease is a controversial issue, but some experts prescribe the drug in order to free the body of toxins, improve metabolic processes, improve liver function and, as a result, cure a person of psoriasis. With long-term use in courses, under the supervision of an experienced doctor, the medicine gives good results.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance, condition after traumatic brain injury, accompanied by cerebral edema, acute renal failure, chronic kidney disease (stage 5, glomerular filtration rate less than 15 ml/min), pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
With caution
In case of alkalosis, renal failure.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding The use of REAMBERIN® during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated due to the lack of clinical studies in these groups of patients.
Reamberin price, where to buy
The price of Reamberin in 1.5% packages is about 142 rubles per 250 ml.
The cost of 500 ml of the drug with the same dosage is 162 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Reamberin (vial 1.5% 200ml) Polisan NTFF
196 rub. order - Reamberin (vial 1.5% 400ml) Polisan NTFF
RUB 248 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Reamberin 1.5% 200 ml solution for infusion TOV NTFF Polisan, Russian Federation
74 UAH order - Reamberin 1.5% 400 ml TOV NTFF Polisan, Russian Federation
92 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Reamberin infusion Reamberin solution inf. 200ml Russia, Polisan
96 UAH order
- Reamberin infusion Reamberin solution inf. 400ml Russia, Polisan
103 UAH order
show more
| Main page | To help the practitioner | ||
Reamberin is a new agent for infusion therapy in the practice of critical care medicine.
S.V. Obolensky
St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education (SPbMAPO) Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology SPbMAPO
Guidelines on the medical aspects of the use of a new infusion therapy - 1.5% reamberin solution.
Physiological role of succinic acid
Succinic acid is a universal intermediate metabolite formed during the interconversion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in plant and animal cells. Under physiological conditions, succinic acid is dissociated, so the name of its anion, succinate, is often used as a synonym for the term “succinic acid.” It is the product of the fifth and substrate of the sixth reaction in the Krebs cycle. The transformation of succinic acid in the body is associated with the production of energy necessary to support life. When the load on any of the body systems increases, the maintenance of its operation is ensured mainly due to the oxidation of succinic acid. The power of the energy production system using succinic acid is hundreds of times greater than all other energy production systems in the body. This is what provides a wide range of nonspecific therapeutic effects of succinic acid and its salts. In addition, succinic acid also has effects such as actoprotective and antiviral. In experimental studies, the biological activity of exogenous succinate depended on the dose, mode of administration of the drug, its chemical form (acid, salt, ester), as well as on the functional state of the body. When using physiological doses of succinic acid, two leading groups of effects were identified:
— direct effect of succinic acid on cellular metabolism;
— the effect of succinic acid on the transport of free oxygen in tissues.
In vitro experiments showed that the use of succinate led to an increase in oxygen consumption by tissues due to the oxidation of added substrates to the final products - carbon dioxide, water and heat. One molecule of dicarboxylic acid added to tissue ensures the oxidation of many endogenous substrates. In other words, the oxidation of succinate is a necessary condition for the catalytic action of any other carboxylic acid for the uptake of oxygen by tissue (tri- and dicarboxylic acid cycle). The loss of cycle intermediates increases in acute and chronic ammonia poisoning. Replenishment of the Krebs cycle acid pool is disrupted by alcoholism, hypovitaminosis B6, and poisoning with inhibitors of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes. Therefore, replenishment of the pool of Krebs cycle intermediates, including from food sources, is necessary. Succinic acid is a metabolite of the human body and its endogenous level in human blood plasma ranges from 1 to 6 μg/ml. Free succinic acid is common in nature. It is found in significant quantities (0.1-1.0 g/kg, or 0.8-8.0 mmol/kg) in unripe berries, juice of sugar beets, sugar cane, turnips, rhubarb, aloe, hawthorn, strawberries , Kalanchoe, nettle, celandine, wormwood and other plants, as well as in alcoholic fermentation products. An additional source of succinic acid in tissues is lipolysis. To replenish the pool of all organic acids of the Krebs cycle in humans, exogenous administration of only one succinate, which is a stimulator of the synthesis of reducing equivalents in the cell, turned out to be sufficient. The biological significance of this phenomenon lies in the rapid resynthesis of ATP by cells and the increase in their antioxidant resistance. The administration of sodium succinate to laboratory animals or healthy people led to a decrease in the level of organic acids in the blood and the excretion of acidic metabolic products from the body, which indicates the normalization of the aerobic phase of tissue respiration. The advantages of succinate over other substrates of cellular respiration are most pronounced under hypoxic conditions, when the production of endogenous succinate and the rate of its oxidation increase. The therapeutic and preventive effect of succinic acid and its compounds is based on a modifying effect on tissue metabolic processes - cellular respiration, ion transport, protein synthesis. In this case, the amplitude and direction of the modifications depend on the initial functional state of the tissues, and its final result is expressed in the optimization of the parameters of their functioning. Such properties make it possible to classify succinic acid as a new generation of therapeutic and prophylactic drugs - the so-called “smart drugs”. And yet, despite the unique versatility of the manifestations of the biological activity of succinic acid, the scope of its application in medical practice remains narrow.
The role and place of reamberin in infusion therapy in critical care medicine.
Indications for the use of the drug should be determined by its effect on the main links in the pathogenesis of critical conditions, which, despite the polyetiology of their occurrence (blood loss, asphyxia, shock, endotoxemia, etc.), have a single pathophysiological basis, consisting of 3 main processes:
- hypoxia,
- intoxication,
- immunosuppression.
The main role is played by hypoxia and intoxication, which in themselves, i.e. separately, can lead to the development of critical and terminal conditions, accompanied by impaired metabolism and energy exchange in the cells of the body. Considering that hypoxia and intoxication are interconnected and interdependent (the effect of mutual potentiation or aggravation), and are the main factors of thanatogenesis, the study of the antihypoxic and antitoxic effects of reamberin and its effect on the immune system seems relevant.
Antihypoxic effect of reamberin.
Antihypoxants are a new effective group of means for the metabolic correction of critical conditions in the clinic. Sodium succinate (succinic acid) according to the clinical classification belongs to substrate antihypoxants. The final effect of hypoxia is a deficiency of oxygen in tissues, which leads to a decrease in the resynthesis of high-energy compounds. Increased resistance to hypoxia is demonstrated by energy-providing intermediates of the Krebs cycle - fumaric, citric and succinic acids. Involved in energy metabolism as substrates, they direct oxidation processes along the most economical path. Thus, fumaric acid is part of the blood substitute Mafusol, which is successfully used in medical practice for hypovolemic and hypoxic conditions of various etiologies (blood loss, trauma, shock, intoxication). In histotoxic hypoxia caused by sodium fluoride, glycolysis is blocked, but the respiratory chain continues to function. Reamberin, as a Krebs cycle substrate, activates oxidation processes that supply electrons to the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It can be assumed that reamberin extends the lifespan of animals under conditions of histotoxic hypoxia, providing the synthesis of macroergs necessary for cell life. The detected antihypoxic activity of reamberin at the tissue level served as the basis for its study in local myocardial hypoxia-ischemia under experimental conditions. The conducted studies made it possible to conclude that:
— Reamberin exhibits a dose-dependent antihypoxic effect in the model of histotoxic hypoxia caused by the administration of sodium fluoride;
— reamberin in doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg does not affect the size of the necrosis zone under conditions of myocardial ischemia;
— Reamberin at a dose of 250 mg/kg, according to ECG studies, exhibits an anti-ischemic effect in the early phase of myocardial infarction;
— reamberin in doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg eliminates CP deficiency in the heart muscle, thereby improving the energy supply of the myocardium;
— Reamberin at a dose of 250 mg/kg shows a clear tendency for animals to survive under conditions of myocardial ischemia.
Analyzing the data obtained, it can be assumed that reamberin will have a more favorable effect on the course of early post-ischemic arrhythmias. The infusion method of administering Reamberin during the first hours can enhance the early anti-ischemic effect of the drug.
Antitoxic effect of reamberin.
One of the leading syndromes of intoxication with various xenobiotics is hypoxia, so the study of antihypoxants as a means of pathogenetic therapy for exogenous and endogenous intoxication is relevant. As is known, the liver is the main site of xenobiotic metabolism, so this organ becomes a target for the toxic effects of poisons with primary membrane dysfunction followed by the development of acute multiple organ failure syndrome (OMF). Experimental studies indicate that reamberin in doses of 100 and 250 mg/kg has a hepatoprotective effect comparable to the effects of the well-known hepatoprotector karsil. Reamberin reduces the duration of lipid peroxidation processes, prevents the depletion of hepatocyte glycogen reserves and prevents an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood serum. The antitoxic effect of Reamberin in case of barbamyl poisoning turned out to be more effective than the effect of piracetam and mafusol. Reamberin reduced the duration of hexenal sleep by 2.8 times and prevented the death of animals. Thus, reamberin in doses of 100 and 250 mg/kg had a positive effect on barbamyl intoxication. These data may indicate a protective effect of reamberin on the microsomal enzymatic system that metabolizes xenobiotics. The information accumulated to date on the biological activity of succinic acid allows us to classify it as an adaptogen. The use of Reamberin in addition to traditional therapy is accompanied by an improvement in the clinical picture, a decrease in mortality, and the leveling and acceleration of regression of various laboratory and diagnostic abnormalities.
Mutagenic properties of reamberin
Based on the studies conducted in accordance with the Methodological Guidelines of the Pharmacological State Committee of the Ministry of Health of Russia for testing drugs at the stage of their preclinical toxicological study, it was concluded that reamberin in concentrations of 0.1-1000 μl/cup does not have a mutagenic effect in the Ames test. There were no significant differences in the level of chromosomal oberations in bone marrow cells under the influence of the drug. According to the results of the studies, Reamberin does not have a mutagenic effect, and is also not a carcinogen according to the forecast of carcinogenicity.
Pharmacokinetics of a 1.5% solution of reamberin.
A study of the pharmacokinetics of a 1.5% solution of reamberin showed that when the drug is administered intravenously at a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight, the maximum level of reamberin in the blood is observed within the first minute after administration, followed by a rapid decrease to a level of 9 - 10 mcg/ml and after 40 minutes after administration, the concentration of the drug in the blood returns to values close to background (from 1 to 6 μg/ml) and remains at this level until the end of observation.
Conclusion on the experimental study of reamberin.
The results of a preclinical study conducted in accordance with the protocol for studying the general toxic effect of the drug Reamberin, approved by the Pharmacological Committee of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, allow us to conclude that it belongs to the 5th class of practically non-toxic drugs, is a safe and harmless drug, which allowed its use in clinical practice.
Clinical trial approval and results.
The basis for conducting clinical studies was the decision of the Federal State Committee of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 211-15-1301 on permission to conduct clinical studies as a detoxification agent on healthy volunteers (volunteers). Objectives of the clinical study:
— to study the clinical features of tolerability and safety of the drug when administered parenterally to healthy volunteers;
- identify side effects of the drug;
— study the effect of Reamberin on various aspects of the body’s vital functions.
A study of the tolerability of Reamberin was carried out in a group of practically healthy individuals aged 18-33 years, including 20 men and 10 women. The examination included a medical examination and observation before, during the infusion and after the administration of Reamberin.
Characteristics of the drug.
Reamberin -1.5% solution for infusion is a well-balanced polyionic solution with the addition of succinic acid containing:
Sodium chloride - 6.00 g Potassium chloride - 0.3 g Magnesium chloride - 0.12 g N-(1-deoxy-D-glucitol-1 yl)-`N-methylammonium sodium succinate - 15.0 g Water for injection - up to 1 l
Ionic composition of the solution:
Sodium 142.4 mmol Potassium 4.0 mmol Magnesium 1.2 mmol Chloride 109.0 mmol Succinate 44.7 mmol `N-methylglucammonium 44.7 mmol
Osmolarity and pH of a 1.5% Reamberin solution.
Normal human plasma osmolarity ranges from 275 to 310 mOsm/kg, with an average of 290 mOsm/kg. Reamberin in the form of a 1.5% solution is a balanced drug with an osmolarity close to the normal osmolarity of human blood plasma, i.e. isotonic and slightly alkaline solution, within normal pH values for blood. Biochemical blood parameters did not change significantly after the administration of Reamberin. The indicators of the main electrolytes in the blood also did not change significantly, however, a tendency towards an increase in plasma osmolarity was noted in 9 (30%) people. At the same time, plasma osmolarity values never went beyond the upper limits of normal fluctuations. The administration of Reamberin was accompanied by a significant increase in pH and buffer capacity of the blood (changes in BE, BEecf, BB). This was accompanied by alkalinization of urine (increased urine pH). It should be noted that while the concentrating ability of the kidneys was preserved, a significant decrease in sodium excretion in the urine was observed during the administration of Reamberin. The drug Reamberin in the form of a sterile solution for intravenous administration only was initially used in a volume of 400 ml dropwise at a dose of 3-4 ml/min for an average of 2 hours.
Main results of clinical studies.
1. Temperature reaction - body temperature was studied in the dynamics of observation: before the administration of the drug; during the administration of the drug, at the end of the drug administration and 1 hour after the drug administration. There was no pyrogenic effect.
2. Cardiovascular system: a moderate decrease in blood pressure, but not lower than normal values, was noted in 4 (12%) subjects during the first hour of administration: a moderate increase in blood pressure to borderline values - in 5 (15%) subjects 2 hours after the start administration of the drug. Moderate bradycardia occurred in 1 (3.3%) subject 2 hours after the start of administration. No pathological changes were noted during ECG examination of healthy volunteers under the influence of Reamberin. ECG values did not change in relation to background values and in comparison with the control group receiving placebo (saline solution 0.85%).
3. Nervous system - no complications noted.
4. Gastrointestinal tract - no complications noted.
5. Respiratory system - no complications noted. The respiratory rate remained within normal limits.
6. Skin reactions - hyperemia of the face, neck, upper half of the body, arms as a vascular reaction, which goes away independently when the rate of drug administration is reduced to 1 ml/min in 7 (23%) subjects.
7. Local reactions in the injection area - not noted.
8. Allergic reactions - nasal congestion, which disappeared on its own when the rate of drug administration was reduced in 1 (3.3%) subject.
The drug Reamberin 1.5% for infusion has been found to have antioxidant and antihypoxic properties.
There were no severe reactions or complications that required discontinuation of the drug.
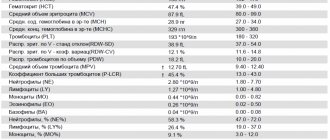
Immediately after stopping the administration of Reamberin, all subjects showed a moderate diuretic effect - at least 400 ml of urine was obtained. A study of peripheral blood parameters showed that after the administration of Reamberin there was an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood without changing the blood formula and a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood. Changes in the absolute values of cellular elements of peripheral blood were unreliable; the indicators fell within the confidence limits of the norm. The data obtained indicate that the drug Reamberin, in the form of a 1.5% solution for intravenous infusion, applied according to the indicated method (dropwise at a dose of 3-4 ml/min, on average for 2 hours, in a volume of 400 ml) , is satisfactorily tolerated by patients and does not lead to the development of complications and side effects with its prolonged use. At the same time, there was no toxic effect of Reamberin on the main vital systems of the body: cardiovascular, respiratory, excretory, as well as on homeostasis indicators. The drug Reamberin 1.5% for infusion showed a high clinical effect as a detoxification agent in patients with severe forms of endogenous intoxication (patients with obstructive jaundice). The drug improved the functional activity of the liver, which was confirmed by the dynamics of intracellular liver enzymes - alkaline phosphatase, AST and ALT . The drug can be recommended as an etiotropic agent in the treatment of endogenous intoxication in patients with obstructive jaundice. The drug improves the detoxification function of the liver, promoting the processes of reparative regeneration of hepatocytes. Reamberin activates the antioxidant system of the enzymatic link, reducing the processes of lipid peroxidation, having a membrane stabilizing effect. The range of use of the drug in clinical practice is quite wide. Along with its use in hepatological practice in complex therapy of various clinical forms of viral hepatitis, it is also possible to use it for detoxification purposes and for the purpose of correcting hypoxic conditions of various origins. Reamberin improves microcirculation and rheological properties of blood: by increasing the osmotic pressure of the blood, an outflow of fluid and toxins from tissues into the blood is observed; At the same time, there is an increase in metabolism, stimulation of diuresis, and removal of toxins from the body. The drug has a membrane-stabilizing effect on liver cells. Evaluation of the clinical and laboratory effectiveness of the drug Reamberin was assessed based on the results of complex therapy of patients with various clinical forms of viral hepatitis with a blood-contact transmission mechanism (OGS, CHC, OGV, CHB and mixed hepatitis). During treatment with Reamberin, there was an improvement in the general well-being of patients, intoxication manifestations decreased, and in 80% of patients, by 5-6 days from the start of treatment, their mood improved, their quality of life increased, and dyspeptic disorders disappeared. In patients with viral hepatitis C who received Reamberin intravenously, jaundice practically disappeared by 8-10 days from the start of treatment (the total bilirubin values were 52.2 ± 1.2 μm/l compared to the initial values of 231.0 ± 1.4 μm / l), and there was also a positive trend in the normalization of liver size (in 87.6% versus 60%). The disturbance of pigment metabolism was restored faster with the administration of Reamberin (p <0.01) in comparison with the group of patients undergoing sympathomatic therapy. When studying the effect of Reamberin on biochemical parameters during therapy in patients with viral hepatitis C, attention is drawn to the rather pronounced positive dynamics of the parameters ALT, bilirubin, as well as SH-, SS-groups. As a result of the study, the effectiveness of the drug as a detoxification and antioxidant agent was established; absence| side effects and allergic reactions make the use of the drug for viral liver lesions promising. In patients in the experimental group, significantly more often than in the control group, positive dynamics of reduction in liver size and relief of jaundice were observed. By the time the patient was discharged from the hospital, normalization of liver size occurred in 45% of those examined. All patients who received basic therapy were discharged with symptoms of hepatomegaly. Among the biochemical parameters, the most significant positive dynamics was noted under the influence of treatment with Reamberin in relation to the level of total bilirubin, ALT and SH-groups in the blood serum, the indicators of which decreased more pronouncedly compared to the control. Based on the results of studying the drug Reamberin, we can come to the conclusion that this drug is advisable to recommend for use for therapeutic purposes in:
— acute viral hepatitis B and C, occurring against the background of toxic liver damage;
— chronic viral hepatitis B and C;
- combined forms of NV and NS viral infection;
- against the background of concomitant pathology of the kidneys and cardiovascular system. The recommended daily dose of Reamberin is 200-400 ml for 2-10 days, depending on the form of the disease.
Reamberin can be used as a detoxification agent before prescribing specific antiviral therapy to patients with various clinical forms of viral hepatitis, including mixed forms. The use of Reamberin for intensive therapy of various forms of severe hepatitis allowed us to draw the following conclusions:
1. Infusions of a 1.5% reamberin solution were well tolerated by patients with various forms of viral hepatitis B and C (there were no allergic reactions). Reamberin has been noted to be highly therapeutically effective in the complex therapy of severely ill patients with CH: the drug has pronounced detoxification, antioxidant, hepato- and nephroprotective properties. A reduction in hospitalization time and a decrease in the number of cases of hormone use in treated patients was revealed compared to the clinical control group.
2. Reamberin contributed to the rapid normalization of basic biochemical parameters in patients with CH. The antioxidant potential of blood serum significantly increased, and the body's nonspecific resistance increased.
3. The use of Reamberin in the complex therapy of severely ill patients with CH drug addicts was accompanied by a clear detoxification effect with a favorable outcome of extremely severe conditions (hepatic coma).
4. Reamberin is recommended to be included as a mandatory pathogenetic agent in the complex therapy of seriously ill patients with various forms of HBV and HCV, as well as patients with signs of multiple organ damage due to exo- and endogenous toxicosis.
Thus, the inclusion of reamberin in the complex therapy of post-hypoxic disorders in patients who have suffered a critical condition undoubtedly helps to increase resistance to hypoxia and reduce the expression of clinical manifestations of multiple organ failure syndrome, in particular encephalopathy. The main pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the ability to enhance the compensatory activity of aerobic glycolysis, reduce the degree of inhibition of oxidative processes in the Krebs cycle under hypoxic conditions with increased ATP and creatine phosphate content. Reamberin activates the antioxidant enzyme system and inhibits the processes of lipid peroxidation in ischemic organs, providing a membrane-stabilizing effect. Positive dynamics according to spectrogram data during EEG monitoring in patients with severe encephalopathies, activation of the state of consciousness in some patients, an increase in life expectancy in patients with severe brain damage, and a decrease in mortality in patients of these groups allow us to recommend the use of the drug Reamberin in clinical intensive care and neurocritical care practice as an infusion neurometabolic corrector. The drug Reamberin 1.5% for infusion can also be used in the treatment of patients with diffuse peritonitis when patients in this group develop multiple organ failure syndrome. The use of this drug can be used both for preoperative preparation of patients with generalized peritonitis, and for intensive therapy in the postoperative period. The drug can be used as a corrector for energy metabolism disorders characteristic of patients with peritonitis and with the development of MODS syndrome, helping to reduce the severity of endotoxemia both in terms of clinical, laboratory and encephalographic parameters. The use of the drug makes it possible to increase the life span of patients and reduce the mortality rate of patients with peritonitis, even with the development of multiple organ failure syndrome. Reamberin 1.5% for infusion can also be recommended for the treatment of patients with vascular lesions of the brain with the development of multiple organ failure syndrome. The use of Reamberin is indicated both for preoperative preparation of patients with vascular lesions of the brain (with hemorrhagic stroke, when surgical intervention is planned), and for intensive care in the postoperative period. The drug can be used as a corrector for patients with ischemic and secondary ischemic lesions of the brain with the development of multiple organ failure syndrome, energy metabolism disorders, which helps reduce the severity of endotoxicosis, post-ischemic lesions both in clinical and laboratory and encephalographic parameters. The use of the drug makes it possible to increase the life span of patients and reduce the mortality rate of patients with vascular lesions of the brain, even with the development of multiple organ failure syndrome. Reamberin can be used as a complex energy metabolite and corrector of infusion disorders in patients with vascular lesions of the brain, both ischemic and hemorrhagic, as a drug of choice for undifferentiated pathogenetically determined therapy. Reamberin is a drug that has detoxification, antihypoxic, antioxidant, hepato-, nephro- and cardioprotective effects. The main pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the ability to enhance compensatory activation of aerobic glycolysis, reduce the degree of inhibition of oxidative processes in the Krebs cycle in the respiratory chain of cell mitochondria with an increase in the intracellular fund of macro-energy compounds adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine phosphate (CP) and stabilization of hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes and other cells body. In the post-infarction period, the drug stimulates repair processes in the myocardium. Reamberin activates the antioxidant enzyme system and inhibits the processes of lipid peroxidation in ischemic organs, having a membrane-stabilizing effect on the cells of the brain, myocardium, liver and kidneys. The drug promotes the processes of reparative regeneration of hepatocytes, which is manifested by a decrease in the blood level of marker enzymes for liver tissue damage. Thus, Reamberin has an antihypoxic and antioxidant effect, having a positive effect on aerobic processes in the cell, reducing the production of free radicals and restoring the energy potential of cells. The drug activates the enzymatic processes of the Krebs cycle and promotes the utilization of fatty acids and glucose by cells, normalizes the acid-base balance and gas composition of the blood. Has a moderate diuretic effect.
Indications for use
Hypoxic conditions of various origins: critical conditions, early postoperative period, massive blood loss, acute heart failure, various types of acute and chronic respiratory failure, circulatory disorders of organs and tissues.
Intoxication of various etiologies: poisoning with xenobiotics or endogenous intoxication.
Against the background of medicinal, toxic and cholestatic hepatitis, icteric, protracted forms of viral hepatitis.
Directions for use and doses
Reamberin is used only intravenously by drip: for children from 1 year of age at a daily dose of 10 ml/kg, for adults 400 - 800 ml of solution per day. The rate of administration and dosage of the drug is determined in accordance with the patient’s condition, no more than 90 drops per minute (4 - 4.5 ml/min). Depending on the severity of the disease, the course of drug administration is up to 11 days.
Side effect
With rapid administration of the drug, short-term reactions are possible in the form of a feeling of heat and redness of the upper body.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance, a condition after a traumatic brain injury, accompanied by cerebral edema.
special instructions
Due to the activation of aerobic processes in the body by the drug, alkalization of the blood and urine is possible.
Release form
Solution in bottles of 200 and 400 ml.
Marking
The label indicates: the manufacturer and its trademark, the name of the drug in Latin and Russian, the volume of the drug, composition, “isotonic solution”, storage conditions, registration number, barcode, batch number, expiration date.
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light, under normal conditions. Freezing during transportation is allowed. If the color of the solution changes or there is a precipitate, the use of the drug is unacceptable. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life: Shelf life 3 years.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies: By doctor's prescription.
197022, Russia, St. Petersburg, PO Box 156, tel/fax E-mail https://www.polysan.spb.ru
| Main page | To help the practitioner | ||
In what cases is an anti-hangover drip needed?
Hangover syndrome is a consequence of general intoxication with acetaldehyde and other compounds formed during the breakdown of ethyl alcohol, and disruption of the production of basic neurotransmitters. At the initial stage of alcoholism, withdrawal is relatively easy to bear, and by and large you can cope with its symptoms on your own. Helps:
- cold and hot shower;
- drink plenty of fluids (rehydration solutions and still mineral water are ideal)
- sound sleep (but in no case should you take sleeping pills or sedatives without a doctor’s prescription);
- moderate physical activity, walks in the fresh air;
- a gentle diet, limiting caffeine-containing drinks.
But as addiction progresses, the intensity of withdrawal symptoms increases. In addition to increased cravings for alcohol, the following symptoms are typical:
- tremor of the fingers, lower jaw, tongue, eyelids (in later stages, the trembling spreads to the whole body);
- irritability, emotional lability, aggressiveness towards family members that prevent continued drinking;
- nausea;
- sleep disorders: difficulty falling asleep, nightmares, waking up with a feeling of severe anxiety and restlessness;
- tachycardia with a feeling of heartbeat in the temples, ears, chest, hypertension;
- excessive sweating;
- diarrhea;
- increase in temperature, etc.
To get rid of these symptoms, you definitely need a hangover drip. Otherwise, against the background of progressive insomnia and realistic nightmares, there is a high probability of developing alcoholic psychosis. It is manifested by affective disorders, disturbances of consciousness, hallucinosis, persecution mania, at the peak of which a person can harm both himself and others. And in such a situation, a dropper against a hangover is no longer enough; serious intensive therapy with potent antipsychotics is necessary.
Literature:
- Problems of addiction. Ed. A. M. Rapoport / Mosgorzdravotd. Neuropsychiatric. Institute named after P. B. Ganushkina and Neuropsychiatric. hospital for acute alcoholism. - Moscow / Leningrad: Medgiz, 1934 ([M.]: 16th type of the Polygraph Book trust). — Region, 116 s
- Alcoholism / Donald W. Goodwin; [Transl. from English B. Pinsker]. - M.: Olimp-business, 2002. - XII, 224 p.
- A manual on narcology for doctors and paramedics of primary medical care / A. A. Churkin, T. V. Klimenko. / Moscow ; Khanty-Mansiysk: Health and Society, 2006 (Cheboksary: IPK Chuvashia). — 173 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7