- Allergic rhinitis - what is it?
- Symptoms
- Types of allergic rhinitis
- Forms of allergic rhinitis
- Causes of allergic rhinitis
- How to Diagnose Allergic Rhinitis
- What to treat: allergy medications
- How to treat allergic rhinitis
- Prevention
- Precautionary measures
- Conclusion
Allergic rhinitis is classified as a non-infectious rhinitis, where the leading component is the vascular component. This type of disease is also called “false runny nose.”
Allergic rhinitis - what is it?
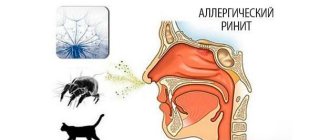
Allergic rhinitis (popularly called “hay fever”) is an inflammation of the nasal mucosa due to various allergens. Determine that it is allergic rhinitis ( runny nose
), quite simply: if a person does not have signs of inflammation, but has symptoms of rhinitis, then most likely it is hay fever. Sometimes it is almost impossible to understand which allergen causes rhinitis, because the patient is sensitive to several groups of allergens at once (polysensitization). In this case, you need to immediately visit a doctor so that he can prescribe the correct treatment, since just removing certain allergens may not be enough.
Symptoms
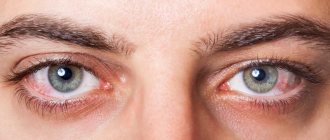
The disease is manifested by several symptoms: itching of the mucous membranes, sneezing, watery nasal discharge (rhinorrhea), and nasal congestion, and sometimes even conjunctivitis. With obstruction (obstruction syndrome of the human respiratory system), headaches often occur. Allergic rhinitis can lead to complications such as sinusitis.
The causes of rhinitis can be pollen, mold spores, wool, fluff and waste products of animals (cats, dogs, rodents), dust mites, cockroaches.
Asthma is a frequent accompaniment of allergic rhinitis, but it is not yet clear whether a false runny nose is the cause of asthma or whether both of these diseases are based on the same cause - the allergic process. With asthma accompanying hay fever, the patient may experience shortness of breath and a severe cough.
Types of allergic rhinitis
There are two types of allergic rhinitis: chronic (year-round) and seasonal. The first appears all year round, since the allergens that cause it are always present in a person’s life. And the second is associated with the seasonal flowering of plants and the appearance of spores of some fungi (Cladosporium, Penicillium, Alternaria).
A characteristic sign of seasonal rhinitis is an increase in symptoms when certain plants appear outside during flowering, using cosmetics and medications containing extracts of plants to which a person is allergic, deterioration in health when coming into contact with rotten grass, and so on.
With persistent rhinitis, sensitivity to allergens of dust mites, animals, birds, insect allergens (from insects), food allergens, mold fungi and chemical elements (platinum salts, chromium compounds, nickel compounds, epoxy resins, etc.) increases.
Predisposing factors
Circumstances that increase the likelihood of developing rhinitis and other acute respiratory viral infections are:
- violation of the body's defenses caused by chronic or acute diseases of the digestive system, vascular disorders, etc.;
- poor nutrition with a deficiency in the diet of nutrients and biologically active substances;
- professional or everyday work involving contact with volatile chemicals (for example, paint and varnish products) and staying in a gassy, dusty room without personal protective equipment;
- hereditary predisposition to respiratory forms of allergies (in the family history there are/were cases when one of the relatives suffered from allergic rhinitis or conjunctivitis);
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- frequent and/or inappropriate use of vasoconstrictor drops or nasal sprays.
Forms of allergic rhinitis
Doctors distinguish mild, moderate and severe forms of rhinitis.
In the first case, the symptoms are mild, quality sleep, daily quality of life and activity are preserved, and the general condition can be called satisfactory.
In the second case, the symptoms already affect all of the above points. A person is more susceptible to exposure to allergens and experiences discomfort.
When the disease is severe, the symptoms become so painful that the human body cannot function normally.
According to the forms of its course, allergic rhinitis can be intermittent (symptoms persist only up to 3 days a week and up to 4 weeks a year) and persistent (symptoms persist more than 4 days a week and more than 4 weeks a year).
The disease itself can be detected both during an exacerbation and during remission.
How to Diagnose Allergic Rhinitis
To identify allergic rhinitis, it is necessary to collect an allergic history:
- quality of living conditions, presence of mold in the apartment (house), presence of pets, house dust collectors;
- does the manifestation of the disease depend on seasonality;
- what is the situation in which the symptoms of the disease occur (in nature, in a damp room, etc.);
- is there a clear temporal relationship between allergen exposure and exacerbation;
- is there any improvement after stopping contact with the suspected allergen.
Currently, there are a number of methods for laboratory diagnosis of the disease that help to create a complete picture and make an accurate diagnosis. Laboratory diagnostics includes the following methods:
- clinical blood test;
- X-ray of the nasal cavity and sinuses;
- skin tests and provocative nasal texts (allergy testing);
- cytological examination of nasal secretions;
- examination of nasal discharge for the presence of microflora;
- anterior rhinoscopy;
- endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity;
- computed tomography of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses;
- anterior rhinomanometry.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults begins with obtaining a detailed medical history. Close attention is paid to the seasonality of exacerbations of allergies, which is associated with the flowering periods of certain plants. Allergic rhinitis is diagnosed by an allergist. He orders the following studies:
- to confirm hay fever: a positive result of a subcutaneous prick test with a respiratory allergen. This is the most sensitive, fastest and cheapest test to confirm the disease. Also, the development of an allergic reaction is indicated by an increase in the concentration of specific immunoglobulins IgE in the blood serum. However, this test is not recommended for screening purposes.
- Sinus endoscopy and anterior rhinoscopy. During the examination, bilateral, often asymmetrical swelling of the mucous membrane with watery discharge (in chronic rhinitis - thick discharge) may be detected.
- Cytological analysis of a smear from the nasal cavity is a nonspecific analysis. Only during an exacerbation is it possible to detect an increased percentage of eosinophils (more than 2%), mast and goblet cells (more than 50%).
- A blood test detects an increased number of eosinophils. The detection of neutrophils indicates the addition of a secondary infection.
- In some cases, a CT scan of the nose and maxillary sinuses is prescribed, which makes it possible to identify concomitant inflammation of the mucous membranes.
With year-round allergic rhinitis, anamnesis is not of great importance. Regular interaction with the allergenic factor leads to the fact that manifestations of rhinitis are constantly observed. In this case, it is almost impossible to accurately determine the allergen.
The year-round form should be differentiated from vasomotor rhinitis. The clinical manifestations of the diseases are very similar, but vasomotor rhinitis is more often provoked by nonspecific irritants. Sometimes allergic rhinitis is “masked” as:
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract of infectious etiology;
- anatomical defects of the nasal septum.
What to treat: allergy medications
During the period of illness, it is first recommended to carry out non-medicinal measures, such as eliminating allergens (removal):
- Group of pollen allergens. It is necessary to keep windows and doors closed indoors and in the car, limit your time outside, use air conditioning indoors, and take a shower or bath after every walk.
- Mold spores. Doctors recommend cleaning rooms frequently, cleaning air humidifiers and hoods, using fungicides, and maintaining indoor humidity at about 50%.
- House ticks and cockroaches. It is important to remove all carpeting, replace them with wooden floors or laminate, choose leather sofas, wash bed linen once a week in hot water (60°C and above), and clean with a special vacuum cleaner with a built-in HEPA filter and a dust container with thick walls. At the same time, it is important to remove the root cause - insects using chemicals and insecticides for baiting insects, as well as carry out preventive treatment of residential premises. At this time, it is better for the allergy sufferer to stay in another room until the chemicals have completely evaporated.
- Allergens from animals. Limit the presence of an animal with allergies, bathe the animal weekly, and use HEPA filters.
- Food allergens. They appear in young children on certain types of food and should be excluded from the diet.
The following medications are used in treatment: nasal corticosteroids (hormonal sprays that help relieve swelling), decongestants, antihistamines, moisturizers, vasoconstrictor drugs. Sometimes for severe rhinitis, a procedure such as desensitization (specific immunotherapy) is performed. Each of these types of treatment has its own characteristics.
Nasal corticosteroids such as beclomethasone and fluticasone relieve swelling. They are used 1 or 2 times a day (the daily dose is determined by the doctor).
Decongestants include acrivastine, ebastine, cetirizine, promethazine, loratadine, and others. They block the release of inflammatory and allergic mediators, have antiallergic, antipruritic, decongestant and sedative effects.
Antihistamines come in 1st and 2nd generation; 2nd generation medications are used more often because they are more harmless. In addition, these drugs are divided into nasal (azelastine, levocabastine) and those used for the conjunctival sac (azelastine, olopatadine, epinastine, emedastine, ketotifen, olopatadine).
Moisturizers help cleanse the nasal mucosa.
Vasoconstrictor or vasoconstrictor drugs relieve unpleasant symptoms: they cause vasospasm, making them less swollen. As a result, nasal congestion decreases and breathing improves.
If the help of other means is insufficient, it is recommended to resort to desensitization. During this procedure, a gradually increasing dose of the allergen is introduced into the body, due to which sensitivity to it gradually decreases. For this purpose, subcutaneous injections or sublingual drops are used.
What to do if you have nasal congestion due to allergies?
Time-tested recommendations
Nasal antihistamines
Currently, the most widely used drugs are levocabastine1. With a mild form of allergy and timely initiation of treatment, they can prevent the appearance and alleviate the symptoms of the seasonal form of the disease. For year-round rhinitis, they are used as part of complex therapy or as an independent symptomatic remedy 1. An example of such drugs is Tizin® Alergy.
Levocabastine is a second-generation antihistamine that acts on histamine H1 receptors and thereby reduces its effect on the mucosa1.
A high safety profile and effect of levobaxtine were observed during clinical trials1. It can be used not only by adults, but also by children over 6 years old. According to the results, it relieves symptoms of the disease after just 5 minutes and can maintain its effect for 12 hours1.
TIZIN® Alergy is available in the form of a spray, which allows you to evenly irrigate the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
Up to contents
How to treat allergic rhinitis
Three main methods are used to treat the disease:
- non-medicinal (removal of allergens),
- medicinal (using various drugs),
- surgical.
The first two methods are discussed in detail in the previous paragraph, and now we will talk about the third.
Surgical intervention is performed in three cases: when non-drug and drug treatment methods do not help, when correction of structural disorders of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses is needed, when pathologies appear (purulent or polypous sinusitis, etc.). This method is distinguished by its accuracy, the ability to penetrate any part of the nose and sinuses where surgery is necessary, functionality and efficiency. If the operation is performed in a timely manner, recovery and return to a full life occurs quickly and without serious complications.
Important: operations are performed with complete exclusion of contact with the allergen. The procedure is not carried out during flowering or other active exposure to allergens.).
After surgery, scars, osteomyelitis, empty nose syndrome, facial pain, bleeding, and atrophic rhinitis may occur.
In addition to surgical intervention, laser coagulation (cauterization) of the nasal turbinates is also performed (submucosal, targeted, selective ablation of hypertrophied areas).
Among the most effective drugs for the treatment of sinusitis symptoms are
Sialor Rhino based on silver ions. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and prevents the proliferation of bacteria. Thanks to the mild action of the drug, the balance of microflora is maintained and favorable conditions are created for the regeneration of the nasal mucosa.
Treatment at home
Treatment of acute and chronic runny nose at home is an auxiliary form of therapy, the goal of which is to cover all aspects of the disease as fully as possible. So, in addition to medications prescribed by a doctor, the patient can independently carry out some procedures (unless the ENT doctor indicates otherwise):
- steam inhalations using essential oils, decoctions of medicinal herbs;
- rinsing the nasal cavity with prepared solutions;
- warm foot baths;
- plenty of warm drinks.
It should be remembered that at elevated body temperatures, any thermal procedures are contraindicated, and if we are talking about a child, rinsing the nasal passages is carried out only in a treatment room.