Ambrovix syrup with banana flavor 15mg/5ml 150ml bottle No. 1
International nonproprietary name: Ambroxol Dosage form: syrup 15 mg/5 ml pineapple flavor syrup 30 mg/5 ml pineapple flavor syrup 15 mg/5 ml banana flavor syrup 30 mg/5 ml banana flavor
Description of the dosage form Ambrovix, syrup with pineapple flavor: transparent, colorless or yellowish, slightly viscous liquid with a specific pineapple odor; Ambrovix, banana flavored syrup: clear, colorless or yellowish, slightly viscous liquid with a specific banana odor.
Composition: 5 ml of syrup contain as active substance 0.015 g (15 mg) or 0.03 g (30 mg) ambroxol hydrochloride Excipients: methyl parahydroxybenzoate, propyl parahydroxybenzoate, sorbitol non-crystallizing solution, propylene glycol, ethyl alcohol, concentrated hydrochloric acid, flavoring additive Aromatic Pineapple AE 111, flavoring additive Aromatic Banana AE 210, purified water. Pharmacotherapeutic group: mucolytic agent. ATX code: R05CB06.
Indications for use Secretolytic therapy for acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases associated with impaired bronchial secretion and weakened mucus movement.
Method of administration and dosage The drug can be taken regardless of meals. Ambrovix 15 mg/5 ml: adults and children over 12 years of age: 10 ml (2 teaspoons) 3 times a day; children 6-12 years old: 5 ml (1 teaspoon) 2-3 times a day; children aged 2-6 years: 2.5 ml (1/2 teaspoon) 3 times a day. Ambrovix 30 mg/5 ml: adults and children over 12 years of age: 10 ml (2 teaspoons) twice daily. The duration of treatment for acute respiratory diseases and initial treatment of chronic conditions is up to 14 days. You should consult your doctor if symptoms last more than 14 days and/or symptoms worsen despite taking Ambrovix. A high dose dosing regimen should be used during initial treatment, the dose may be halved after 14 days of taking the drug. In case of acute illnesses, you should consult a doctor if symptoms do not disappear and/or intensify despite taking Ambrovix syrup.
Side effects The assessment of undesirable effects is based on the following data on the frequency of occurrence: very often (>1/10), often (>1/100 to <1/10), infrequently (>1/1000 to <1/100), rarely ( >1/10,000 to <1/1000), very rare (<1/10,000), unknown (cannot be estimated from available data). From the immune system, skin and subcutaneous tissue Rarely: rash, urticaria. Not known: angioedema, pruritus, anaphylactic reactions including shock, other hypersensitivity reactions. From the nervous system: often: dysgeusia. From the gastrointestinal tract Often: nausea, numbness of the mouth. Uncommon: vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, dry mouth. Very rare: constipation, drooling. Unknown: dry throat. Respiratory, chest and mediastinal disorders Common: numbness in the throat. Very rare: rhinorrhea. Unknown: shortness of breath (as a symptom of a hypersensitivity reaction). From the kidneys and urinary tract Very rarely: dysuria. Other Uncommon: fever, skin and mucous membrane reactions.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; - children under 2 years old; pregnancy (first trimester); lactation period.
Overdose Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspeptic disorders, drop in blood pressure. Treatment: Artificial vomiting, gastric lavage (in the first 1-2 hours after taking the drug); intake of fat-containing foods. If necessary, carry out symptomatic therapy.
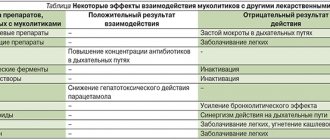
Interactions with other drugs Ambrovix is not prescribed simultaneously with antitussives (for example, those containing codeine), as this makes it difficult to clear liquefied sputum from the bronchi while suppressing the cough reflex. Ambroxol promotes the penetration of antibiotics (amoxicillin, cefuroxime, oxytetracycline, doxycycline, erythromycin) into bronchial secretions.
Precautions In extremely weakened patients, patients with anatomical narrowing of the bronchi and increased mucus secretion, when using ambroxol, difficulties may arise in the evacuation of bronchial secretions. In these cases, measures should be taken to suck out the secretions. The drug should be prescribed with caution for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. For patients with diabetes mellitus, the content of sorbitol solution in the syrup should be 70%. If you miss taking the drug, you should not double the dose. In case of severe renal and liver dysfunction, lower concentrations should be used or the interval between doses of the drug should be increased. Several cases of severe skin damage have been reported, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, associated with expectorants such as ambroxol. This condition can usually be explained by the severity of the concomitant disease or the simultaneous use of other drugs. In addition, in the early stages of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, patients may exhibit nonspecific signs of the onset of a flu-like illness: fever, body pain, rhinitis, cough, and sore throat. The appearance of these signs may lead to unnecessary symptomatic treatment with cold medications. Therefore, if damage to the skin or mucous membranes occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, and treatment with ambroxol should be discontinued as a precaution.
Pregnancy and lactation It is possible to use it in the second and third trimester of pregnancy if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
Effect on the ability to drive a car or other moving mechanisms. There are no known cases of the drug affecting the ability to drive a car or use machinery. No relevant studies have been conducted.
Release form and packaging 100 ml and 150 ml of syrup in bottles, placed together with the package insert in cardboard packs.
Storage conditions Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life: 2 years. The expiration date is indicated on the packaging. This medicine should not be used after the date stated on the package. Shelf life after opening the bottle is 6 months.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies The drug is dispensed without a doctor's prescription.
Ambroxol syrup
Release form
The syrup is colorless or slightly yellowish, transparent, with a characteristic odor.
Compound
Active ingredient : ambroxol hydrochloride (15 mg/5 ml or 30 mg/5 ml).
Excipients : benzoic acid, glycerin, sorbitol, hydroxyethylcellulose, fruit flavoring, purified water.
The composition may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Exact information is provided in the instructions included in the package.
Pharmacological group
Mucolytic and expectorant drug. Secretolytics and stimulants of motor function of the respiratory tract.
Action
Mucolytic agent with expectorant action. Ambroxol increases the secretion of the glands of the respiratory tract, stimulates the activity of the villi of the respiratory tract, and enhances the formation of surfactant in the lungs. Ambroxol is a metabolite of bromhexine.
Ambroxol - description of the substance
The effect occurs 30 minutes after administration and lasts 6-12 hours.
Indications
Acute and chronic diseases of the respiratory tract with the release of viscous sputum: acute and chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma with difficulty in sputum discharge, bronchiectasis.
Contraindications and restrictions
- Hypersensitivity to ambroxol or one of the excipients;
- pregnancy (first trimester); lactation period;
- fructose intolerance, because the drug contains sorbitol.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, and with renal and/or liver failure.
Application and dosage
The syrup should be taken orally after meals. The drug should not be taken immediately before bedtime.
- 1 measuring cup or measuring spoon contains 15 mg or 30 mg of ambroxol;
- 5 ml syrup = 1 measuring cup or 1 measuring spoon;
- 10 ml syrup = 2 measuring cups or 2 measuring spoons;
- 2.5 ml syrup = ½ measuring cup or ½ measuring spoon.
Syrup 15 mg/5 ml
Adults and children over 12 years of age: during the first 2-3 days, take 10 ml of syrup 3 times a day, then the dose should be reduced to 10 ml of syrup 2 times a day.
Children from 6 to 12 years old: 5 ml of syrup 2-3 times a day. Children from 2 to 6 years: 2.5 ml of syrup 3 times a day. Children under 2 years of age: 2.5 ml of syrup 2 times a day.
Syrup 30 mg/5 ml
Adults and children over 12 years of age: during the first 2-3 days, take 5 ml of syrup 3 times a day, then the dose should be reduced to 5 ml of syrup 2 times a day.
Children from 6 to 12 years old: 2.5 ml of syrup 2-3 times a day. Children from 2 to 6 years: 1.25 ml of syrup 3 times a day. Children under 2 years of age: 1.25 ml of syrup 2 times a day.
Maximum daily dose
- for adults 120 mg ambroxol;
- for children from 6 to 12 years old – 45 mg ambroxol;
- for children from 2 to 6 years – 22.5 mg of ambroxol;
- for children under 2 years of age – 15 mg ambroxol.
During treatment, it is necessary to consume enough liquid (juices, tea, water) to enhance the mucolytic effect of the drug.
The duration of treatment is selected individually depending on the course of the disease. It is not recommended to take ambroxol for more than 4-5 days without a doctor's prescription.
Side effect
The drug is well tolerated by patients.
- Digestive tract : dyspepsia, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea/constipation, hypersalivation, dry mouth, hypersthesia of the oral mucosa and/or pharynx.
- Respiratory system : rhinorrhea, dryness of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, shortness of breath (as a symptom of a hypersensitivity reaction).
- Urinary system : dysuria.
- Nervous system : dysgeusia (disorder of taste).
- Immune system, skin and subcutaneous tissues : itching, rash, urticaria, anaphylactic reactions (including angioedema, anaphylactic shock), fever, chills, other allergic reactions.
- severe skin lesions may occur , such as erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
- Other : reactions from the mucous membranes, weakness, headache.
Storage
Store out of reach of children, protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Shelf life: 3 years.
Production
- Ozon LLC;
- Atoll LLC;
- JSC "VERTEX";
- JSC "Tatkhimfarmpreparaty";
- JSC "EKOlab";
- VIAL LLC;
- PJSC "NPC Borshchagovsky Chemical and Pharmaceutical Plant" (Ukraine);
- Hemofarm A.D. (Serbia);
- Sopharma JSC (Bulgaria);
- Pharmtechnology LLC (Republic of Belarus).
Package
100, 150 or 200 ml in polymer bottles and glass jars, 1 bottle or 1 jar together with a dosing spoon or measuring cup in a cardboard box.
Recipe
Available without a prescription.
Instructions for use Ambrovix solution (tablets): description, composition, FTG, INN
There is no information about cases of overdose in humans. In case of accidental overdose, symptoms may be similar to undesirable effects when used in recommended doses. In this case, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Interaction with other drugs or food products
Ambrovix solution is not prescribed simultaneously with antitussives (for example, those containing codeine), as this makes it difficult to clear liquefied sputum from the bronchi while suppressing the cough reflex.
The use of ambroxol hydrochloride increases the concentration of the antibiotics amoxicillin, cefuroxime, erythromycin and doxycyline in sputum and bronchial secretions. The clinical significance of this has not yet been established.
Precautionary measures
In extremely weakened patients, patients with anatomical narrowing of the bronchi and in the case of increased mucus secretion, when using ambroxol, difficulties may arise in the evacuation of bronchial secretions. In these cases, measures should be taken to suck out the secretions.
The drug should be prescribed with caution for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
In children aged 2 to 6 years, the risk-benefit ratio should be assessed before using the drug.
The drug contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride. When inhaled, it may cause bronchospasm in sensitive patients with airway hyperresponsiveness.
Since inhalation poses a risk of bronchospastic reactions, patients with airway hyperresponsiveness or a history of atopic diseases should not use Ambrovix inhalation solution.
Cases of severe skin lesions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, that occurred while taking expectorant drugs, including ambroxol hydrochloride, have been described. As a rule, such symptoms were explained by the severity of the underlying disease or the simultaneous use of other medications. In addition, in the early stages of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, nonspecific flu-like symptoms may occur, such as fever, joint pain, runny nose, cough, and sore throat. The occurrence of such symptoms can be misinterpreted, which leads to symptomatic therapy with cold and antitussive medications. If new lesions appear on the skin and mucous membranes, you should immediately stop using ambroxol hydrochloride and consult a doctor.
Abrovix solution should be used with extreme caution in cases of impaired bronchial motility and an increased amount of bronchial secretion (for example, in the rare case of malignant ciliary syndrome), since there is a risk of secretion stagnation in the respiratory tract.
In case of renal failure or severe liver dysfunction, Ambrovix solution should be used only after consultation with a doctor. As with other drugs metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys, in severe renal failure there may be an accumulation of ambroxol hydrochloride metabolites formed in the liver in the body.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Ambroxol hydrochloride penetrates the placental barrier. There is no data indicating direct or indirect negative effects on pregnancy and fetal development. However, general precautions for the use of medications during pregnancy must be followed.
The use of ambroxol hydrochloride in the first trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated.
It can be used in the second and third trimester of pregnancy if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
It is not recommended to use Ambrovix solution during breastfeeding, as ambroxol hydrochloride is excreted in breast milk.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no information about the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. No relevant studies have been conducted.
Package
Bottles of 25 and 50 ml with a dropper stopper and a screw cap. The bottle with the leaflet is placed in a cardboard package.
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 30°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years. The expiration date is indicated on the packaging.
The shelf life of the bottle after opening is 6 months.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Without a doctor's prescription.
Manufacturer information
Pharmtechnology LLC, 220024 Minsk, st. Korzhenevsky, 22.
Phone fax;
E - mail :
.
AMBROVIX (Ambroxol) tab 30 mg N20
Dosage form and its description:
round biconvex tablets of white or almost white color with a score on one side.
Composition Each tablet contains 30 mg of ambroxol hydrochloride as an active substance. Excipients: corn starch, sodium starch glycolate (type A), magnesium stearate, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: expectorant, mucolytic agent.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Studies have shown that ambroxol has a secretomotor, secretolytic and expectorant effect, stimulates the serous cells of the glands of the bronchial mucosa, increases the content of mucous secretion and the release of surfactant in the alveoli and bronchi. Normalizes the disturbed ratio of serous and mucous components of sputum. By activating hydrolyzing enzymes and enhancing the release of lysosomes from Clara cells, it reduces the viscosity of sputum. Increases the motor activity of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, increases the mucociliary transport of sputum. It has an anesthetic effect, which is explained by the property of ambroxol to block sodium channels. This process is reversible and depends on concentration. An in vitro study also found that the release of cytokines from tissue mononuclear and polymorphonuclear blood cells was significantly reduced. The effect of ambroxol begins after 30 minutes and lasts 6-12 hours. The maximum therapeutic effect appears on the 3rd day of treatment.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction and distribution:
Ambroxol is characterized by rapid and almost complete absorption with a linear dose dependence in the therapeutic concentration range. Cmax in plasma is reached after 0.5-3 hours. In the therapeutic concentration range, binding to plasma proteins is approximately 90%. The transition of ambroxol from the blood to tissues when administered orally occurs quickly. The highest concentrations of the active component of the drug are observed in the lungs. Penetrates through the blood-brain and placental barriers and is excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion:
Approximately 30% of the dose taken undergoes a first-pass effect through the liver. Studies on human liver microsomes have shown that CYP3A4 is the predominant isoform responsible for the metabolism of ambroxol. The remainder of ambroxol is metabolized in the liver, mainly by conjugation to form pharmacologically inactive metabolites (dibromanthranilic acid and glucuronic conjugates).
T1/2 of ambroxol is 10 hours and may increase with severe renal failure, but does not change with impaired liver function. It is excreted primarily by the kidneys (90%) and the gastrointestinal tract in the form of metabolites, 5% unchanged. The total clearance is within 660 ml/min, renal clearance accounts for approximately 8% of the total clearance.
No clinically significant effect of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics of ambroxol was found, so there is no basis for selecting the dosage based on these characteristics.
Indications for use
Acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases, accompanied by the release of viscous sputum: - acute and chronic bronchitis; - pneumonia; — chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; - bronchial asthma with difficulty in sputum discharge; - bronchiectasis.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, after eating, take with liquid. Adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed 1 tablet (30 mg) 3 times a day in the first 2-3 days, then 1 tablet 2 times; if necessary, to increase the therapeutic effect, you can prescribe 2 tablets 2 times a day (120 mg /day); children 6-12 years old – 1/2 tablet (15 mg) 2-3 times a day. During treatment, it is necessary to drink plenty of fluids (juices, tea, water) to enhance the mucolytic effect of the drug. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor individually and depends on the severity of the disease. If it is necessary to use the drug for more than 4-5 days, consultation and supervision of a doctor is required.
Side effect
The incidence of possible side effects is indicated as: very often (≥1/10); often (from ≥1/100 to The drug is usually well tolerated.
From the digestive system: rarely - abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea.
From the immune system: rarely - hypersensitivity reactions. Frequency unknown: anaphylactic reactions, including anaphylactic shock, angioedema, itching.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rarely - rash, urticaria. Not known: severe skin reactions (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis)
From the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: very rarely - increased mucus secretion in the nasal cavity, increased salivation, as well as dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and respiratory tract.
Contraindications
— I trimester of pregnancy; - hypersensitivity to ambroxol or other components of the drug; - children under 6 years of age (due to the high content of the active substance in the 30 mg tablet). Children under 6 years of age are prescribed ambroxol in liquid form.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, during lactation (breastfeeding), and in patients with renal and/or liver failure.
Overdose
Severe symptoms of overdose in humans have not been described. Transient nervous excitability and diarrhea have been reported. Ambroxol was well tolerated when taken orally up to 25 mg/kg/day. Possible symptoms (based on preclinical studies): increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia and hypotension.
Treatment: Symptomatic therapy. Inducing artificial vomiting and gastric lavage in the first 1-2 hours after administration are carried out only in cases of extreme overdose.
Interaction with other drugs
Ambroxol increases the penetration of amoxicillin, cefuroxime, erythromycin, and doxycycline into the bronchial secretions.
The drug is compatible with drugs that inhibit labor.
It should not be used in combination with antitussives (for example, those containing codeine), as this complicates the passage of liquefied sputum from the bronchi and its accumulation in them against the background of suppression of the cough reflex.
special instructions
In extremely weakened patients, patients with anatomical narrowing of the bronchi and increased mucus secretion, when using ambroxol, difficulties may arise in the evacuation of bronchial secretions. In these cases, measures should be taken to suck out the secretions.
The drug should be prescribed with caution for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. In case of severe renal and liver dysfunction, lower doses should be used or the interval between doses should be increased.
There have been reports of severe skin reactions, such as erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis in patients taking ambroxol.
You should immediately stop taking the drug if symptoms of a progressive skin reaction (sometimes associated with the development of blisters and damage to the mucous membranes) appear.
Pregnancy and lactation
Ambroxol penetrates the placental barrier. Experimental studies on animals did not reveal direct or indirect adverse effects on pregnancy, embryonic, prenatal and postnatal development and childbirth. Extensive clinical experience with the use of ambroxol after 28 weeks of pregnancy does not indicate harmful effects on the fetus. However, the usual precautions should be taken when using the drug during pregnancy. The drug should be used with caution during breastfeeding, since ambroxol is excreted in breast milk. The use of the drug in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy and in breastfeeding mothers is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Transport and machinery management.
No special studies have been conducted regarding the effect of ambroxol on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Release form:
Tablets 30 mg in blister packs No. 10x2, No. 10x5 and in jars No. 20, No. 50. Together with the package insert, two or five blister packs or a jar are placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions.
Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date:
2 years. The expiration date is indicated on the packaging. This medicine should not be used after the date stated on the package.