Pharmacological properties of the drug Cephalexin
Semi-synthetic antibiotic of the 1st generation cephalosporin group. Acts bactericidal. The following are sensitive to the drug: gram-positive microorganisms - staphylococci (coagulase-positive, coagulase-negative and penicillinase-forming strains), streptococci (with the exception of enterococci, which are highly resistant to the drug), pneumococci; gram-negative microorganisms - E. coli, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Neisseria spp., Proteus mirabilis , various strains of Haemophilus influenzae (about 75%) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (about 50%), pale spirochetes and radiant fungi. The mechanism of bactericidal action is due to damage to the cell membrane of bacteria during the reproduction stage of the latter (specific inhibition of membrane enzymes). Stable in acidic environments. When taken orally on an empty stomach, it is quickly (after 1.5–2 hours) and almost completely adsorbed, somewhat more slowly when taken after a meal. Bioavailability when taken orally is over 90%. The therapeutic concentration in the blood after a single oral dose persists for 4–6 hours. A significant amount is excreted unchanged in the urine, a small part is excreted in the bile. Poorly penetrates the BBB.
Use of the drug Cephalexin
Inside, regardless of food intake. A single dose of cephalexin for adults is 0.25–0.5 g, a daily dose is 1–2 g. Children are prescribed at a dose of 25–50 mg/kg/day. In case of severe infection, the dose for adults can be increased to a maximum of 4 g/day, for children - up to 100 mg/kg/day. The daily dose is divided into 4 doses. The duration of treatment is usually 7–14 days; for streptococcal infections, the duration of therapy is at least 10 days. In case of renal failure, the dose should be reduced.
Cephalexin caps 500 mg x16 Hemofarm
Trade name: Cefalexin International name: Cefalexin Pharmacological group: antibiotic-cephalosporin Pharmacological group according to ATC: J01DB01. Cephalexin Pharmacological action: antibacterial Pharmacodynamics: Cephalosporin antibiotic of the first generation. It has a bactericidal effect and disrupts the synthesis of the cell wall of microorganisms. Quite resistant to penicillinases of gram-positive microorganisms, destroyed by beta-lactamases of gram-negative microorganisms. Wide spectrum of action: active against gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus spp., non-producing and producing penicillinase, Staphylococcus epidermidis (penicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus spp. (including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes), Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Clostridium spp., Bacillus anthracis, Actinomyces israelii, gram-negative microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp. (including Klebsiella pneumoniae), Moraxella catarrhalis (Branhamella), Proteus mirabilis, Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Shigella spp., Salmonella spp., Treponema spp. Does not affect Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pseudomonas of other species, Proteus spp. (indole-positive strains), Mycobacterium tuberculosis, anaerobic microorganisms, Enterococcus faecalis, Haemophilus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Aeromonas spp., Acinetobacter spp., methicillin-resistant staphylococcal strains.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption - 90%, acid-resistant, food intake slows down absorption, but does not affect its completeness. Bioavailability - 95%. TCmax - 1-2 hours. After oral administration in doses of 250, 500 and 1000 mg Cmax - 9, 18, and 32 mcg/ml, respectively. Distributed relatively evenly in various tissues and body fluids: lungs, bronchial mucosa, liver, heart, kidneys. Does not pass the BBB, penetrates the placenta, and is excreted in small amounts in breast milk. Distribution volume - 0.26 l/kg. Bonding with plasma proteins is 5-15%. T1/2 - 0.9-1.5 hours. 90% is excreted unchanged by the kidneys (2/3 - by glomerular filtration, 1/3 - by tubular secretion), with bile - 0.5%. Total clearance - 380 ml/min, renal clearance - 210 ml/min. Cmax in urine after oral administration in doses of 250, 500 and 1000 mg is 1, 2.2 and 5 mg/ml, respectively. If renal function is impaired, the concentration in the blood increases, and the elimination time lengthens, T1/2 - 20-40 hours.
Indications for use: Infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract (bronchitis, acute pneumonia and exacerbation of chronic pneumonia, empyema and lung abscess), genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, endometritis, gonorrhea, vulvovaginitis, etc.), ENT -organs (pharyngitis, otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.), skin and soft tissues (furunculosis, abscess, phlegmon, pyoderma, lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, etc.), bones and joints (including osteomyelitis).
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity (including to other beta-lactam antibiotics).
Dosage regimen: Orally, 30-60 minutes before meals, with water. The average dose for adults is 0.25-0.5 g every 6 hours. If necessary, the daily dose is 4-6 g. Duration of treatment is 7-14 days. For children - preferably in the form of a suspension. For body weight less than 40 kg, the average daily dose is 25-50-100 mg/kg, frequency of administration is 2, 3, 4 times a day. For otitis media - dose 75 mg/kg/day, frequency of administration - 4 times a day. For streptococcal pharyngitis, skin and soft tissue infections in adults, adolescents, and children over 1 year of age, the dosage frequency is 2 times a day. In case of severe infections, the daily dose can be increased to 100 mg/kg, and the frequency of administration - up to 6 times a day. For infections caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the minimum duration of treatment is 10 days. For adult patients with impaired renal function, the daily dose is set taking into account the CC value: with CC 5-20 ml/min, the maximum daily dose is 1.5 g/day, with CC less than 5 ml/min - 0.5 g/day.
Side effects: Allergic reactions: urticaria, angioedema, erythematous rashes, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), anaphylaxis, arthralgia, arthritis, eosinophilia, itching of the genitals and anus. From the nervous system: dizziness, weakness, headache, agitation, hallucinations, convulsions. From the genitourinary and urinary system: vaginitis, vaginal discharge, genital candidiasis, interstitial nephritis. From the digestive system: abdominal pain, dry mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, diarrhea, toxic hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, intestinal candidiasis, oral cavity, rarely - pseudomembranous enterocolitis. From the hematopoietic organs: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia. Laboratory indicators: increased activity of liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase, increased prothrombin time. Overdose. Symptoms: vomiting, nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhea, hematuria. Treatment: activated charcoal (more effective than lavage), maintaining airway patency, monitoring vital signs, blood gases, electrolyte balance.
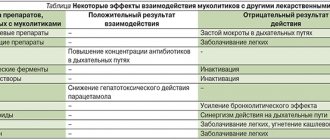
Interaction: Enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants. Increases the nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides, polymyxins, phenylbutazone, furosemide. Salicylates and indomethacin slow down the excretion of cephalexin by the kidneys. Drugs that reduce tubular secretion increase the concentration of the drug in the blood and slow down its elimination.
Special instructions: Patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins and carbapenems may have increased sensitivity to cephalosporin antibiotics. During treatment with cephalexin, a positive direct Coombs test is possible, as well as a false positive urine test for glucose. During the treatment period, it is not recommended to consume ethanol. The use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation is justified only in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped. In patients with impaired renal function, accumulation is possible (adjustment of the dosage regimen is required). In staphylococcal infections, cross-resistance exists between cephalosporins and isoxazolylpenicillins. Carefully. Renal failure, pseudomembranous colitis (history), pregnancy, lactation, infancy (up to 6 months).
Manufacturer: Hemofarm AD, Serbia Registration certificate holder: Hemofarm AD, Serbia Forms of release: granules for the preparation of oral suspension 250 mg|5 ml, dark glass bottles, granules for the preparation of oral suspension 250 mg/5 ml, dark glass bottle with a notch, sealed with a plastic or metal lid with first opening control. Composition: cephalexin hydrate 250 mg [in terms of cephalexin] - 5 ml of ready suspension Belongs to VED Conditions of release: by prescription Shelf life: 3 years Registration data: P N011645/02 dated 09/02/2011, 03/20/2008 Status of the registration certificate: current Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-10564-05, ND 42-10564-99, P N011645/02-020911
Manufacturer: AVVA RUS OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: AVVA RUS OJSC, Russia Release forms: 250 mg capsules, cellular contour packs, 250 mg capsules, polymer jars, 250 mg capsules, polymer bottles Ingredients: cephalexin 250 mg Belongs to VED Dispensing conditions : by prescription Shelf life: 2 years Registration data: LS-002617 dated 04/21/2010 Status of the registration certificate: valid (until 2011) Pharmaceutical article number: FS 42-3118-95, FSP 42-0236-6944-05
Manufacturer: Belmedpreparaty RUP, Belarus Registration certificate holder: Belmedpreparaty RUP, Belarus Release form: 250 mg capsules, cellular contour packaging Composition: cephalexin 250 mg Belongs to the Vital and Essential Drugs Dispensing conditions: by prescription Shelf life: 2 years Registration data: LS-000864 from 07/27/2010 Registration certificate status: valid Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-8883-05, ND 42-8883-06, ND 42-8883-98
Manufacturer: Severnaya Zvezda ZAO, Russia Registration certificate holder: Severnaya Zvezda ZAO, Russia Release forms: 250 mg capsules, plastic bags, 250 mg capsules, cellular contour packaging, 250 mg capsules, polymer jars, 250 mg capsules, dark glass jars, capsules 250 mg, polymer bottles Composition: cephalexin monohydrate 250 mg [in terms of 100% substance] Belongs to the Vital and Essential Drugs Dispensing conditions: by prescription Shelf life: 2 years Registration data: LSR-002246/07 dated 08.17.2007 Registration certificate status: valid Pharmaceutical article number: FS 42-3118-95, FSP 42-7967-06
Manufacturer: Hemofarm AD, Serbia Registration certificate holder: Hemofarm AD, Serbia Release forms: 250 mg capsules, blister packs, 500 mg capsules, blister packs, 250 mg capsules, PVC/aluminum blister, 500 mg capsules, PVC/aluminum blister Composition: cephalexin hydrate 263/525.9 mg [euv.250/500 mg cephalexin] Belongs to the VED Conditions of release: by prescription Shelf life: 3 years Registration data: P N011645/01 dated 04/20/2011, 03/20/2008 Registration certificate status: current Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-10563-05, ND 42-10563-99
Manufacturer: Shchelkovo Vitamin Plant OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: Shchelkovo Vitamin Plant OJSC, Russia Release form: 250 mg capsules, contour cell packaging, 250 mg capsules, polymer jars Ingredients: cephalexin 250 mg Dispensing conditions: by prescription Shelf life: 2 years Registration data: P N003253/01 dated July 14, 2004 Registration certificate status: inactive (since 2009) Pharmaceutical article number: FS 42-3118-95, FSP 42-0055-4788-03
Manufacturer: Sintez OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: Sintez OJSC, Russia Forms of release: powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 125 mg, heat-sealable bags made of Buflen material, powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 125 mg, polyethylene bottles 150 ml, powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 125 mg|5 ml, heat-sealable bags made of Buflen material, powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 125 mg|5 ml, polyethylene bottles 150 ml, powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 250 mg, bags heat-sealable from the material "Buflen", powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 250 mg, polyethylene bottles 150 ml, powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 500 mg, heat-sealable bags from the material "Buflen", powder for the preparation of an oral suspension 500 mg, polyethylene bottles 150 ml Composition: cephalexin 0.125/0.25/0.5/2.5 g - 1.75/3.5/7/35 g Belongs to the Vital and Essential Drugs Dispensing conditions: by prescription Shelf life: 2 years, after preparation - 6 days (at room temperature), 14 days (in the refrigerator) Registration data: P N000563/01 dated December 29, 2006 Status of the registration certificate: valid (until 2011) Pharmaceutical article number: FSP 42-0054-0590-00, FSP 42-0054-0590-06
Manufacturer: Lupin Ltd., India Registration certificate holder: Lupin Ltd., India Release form: substance-powder, two-layer polyethylene bags Registration data: P N013276/01 dated 02/11/2008 Registration certificate status: valid Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-5244 -01, ND 42-5244-03, ND 42-5244-07, ND 42-5244-95
Manufacturer: Orchid Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India Registration certificate holder: Orchid Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India Release form: substance-powder, two-layer polyethylene bags Ingredients: cephalexin hydrate Shelf life: 4 years Registration data: P N012110/01 dated 29.02. 2008 Status of the registration certificate: valid Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-10995-00, ND 42-10995-07
Manufacturer: Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd, India Registration certificate holder: Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd, India Release form: powder substance, multilayer polyethylene bags Ingredients: cephalexin hydrate Shelf life: 3 years Registration data: P N015962/01 dated 10/15/2004 Registration certificate status : inactive (since 2009) Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-7125-04, ND 42-7125-97
Manufacturer: Unimark Remedies Ltd, India Registration certificate holder: Unimark Remedies Ltd, India Release form: substance-powder, double-layer polyethylene bags Ingredients: cephalexin Shelf life: 4 years Registration data: LSR-004598/09 dated 06/09/2009 Registration certificate status : current Pharmaceutical article number: ND 42-14736-07
Manufacturer: Biokhimik OAO, Russia Registration certificate holder: Biokhimik OAO, Russia Release form: film-coated tablets 250 mg, tablet Dispensing conditions: by prescription Registration data: P N003669/01 dated 08/31/2009 Status of the registration certificate: valid Pharmaceutical article number: РN003669/01-131011
Special instructions for the use of the drug Cephalexin
Use with caution in case of impaired renal and liver function, as well as in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins. There is a possibility of cross-allergy between penicillins and cephalosporins with hypersensitivity to penicillin (approximately 5-10% of patients). Treatment with cephalexin should be discontinued if allergic reactions occur and appropriate therapy should be prescribed. It is not recommended to prescribe during pregnancy in the absence of vital indications (potential teratogenicity has not been sufficiently studied). While taking an antibiotic, a urine test may reveal a false positive reaction to glucose.
List of pharmacies where you can buy Cephalexin:
- Moscow
- Saint Petersburg
Cephalexin capsules 500 mg No. 10x2
Name
Cephalexin caps. 500 mg in container pack No. 10x2
Description
Each capsule of Cephalexin contains the active substance - cephalexin, 500 mg, and excipients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate. The capsule contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, brilliant blue E133, orange yellow E110, quinoline yellow E104, water. This drug belongs to the group of cephalosporins, antimicrobial agents for systemic use. Suppresses the growth of microorganisms that cause infections.
Main active ingredient
Cephalexin
Release form
capsules
Dosage
500 mg
Indications for use
Infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug: otorhinolaryngological infections (pharyngitis, otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis); respiratory tract infections (bronchitis, pneumonia, empyema and lung abscess); infections of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, endometritis, gonorrhea, vulvovaginitis); infections of the skin and soft tissues (furunculosis, abscess, phlegmon, pyoderma); infections of bones and joints (osteomyelitis).
Directions for use and doses
Cephalexin is taken as prescribed by a doctor, who determines the individual dose and duration of treatment. The drug is taken orally, 30-40 minutes before meals, without chewing the capsules, with 150-200 ml of water. Adults and children over 12 years of age: For most infections: 500 mg every 8 hours or 1 g every 12 hours. Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections, streptococcal pharyngitis and uncomplicated urinary tract infections: 250 mg every 6 hours or 500 mg every 12 hours. Treatment of complicated urinary tract infections: 1 g twice daily. In case of severe infections, especially those caused by less sensitive microorganisms, the dose should be increased to 1 g three times a day or 2 g twice a day. Treatment of gonorrhea: As a rule, one dose of 3 g with 1 g probenecid for men or 2 g with 0.5 g probenecid for women is sufficient. Concomitant use with probenecid delays the elimination of cephalexin and increases serum concentrations by 50 to 100%. Children: Cephalexin capsules are not prescribed for children under 7 years of age due to the difficulty of swallowing capsules. The recommended daily dose for children is 25-60 mg/kg. For most infections in children 7–12 years of age, a dose of 250 mg every 8 hours is suggested. For chronic, severe infections, the dose can be doubled (maximum daily dose - no more than 4 g/day). Clinical studies have shown that a dose of 75-100 mg/kg/day, divided into 4 doses, is required for the treatment of otitis media. For more accurate dosing, it is necessary to use a medicine with a lower dosage or a release form suitable for children. Maximum daily dose: for adults - 4000 mg, for children - 100 mg/kg (in four doses). Duration of treatment: depends on the nature and severity of the disease, determined by the doctor. Usually the duration of treatment is 7-14 days, but for severe infectious diseases longer therapy may be required. For most infectious diseases, treatment continues for at least another 48-72 hours after the symptoms of the disease disappear and/or according to the results of a bacteriological study. For infections caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the minimum duration of treatment is 10 days. Patients with impaired renal function: Cephalexin should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal function. If there is a significant deterioration in renal function, a dose reduction is required. Close clinical observation and laboratory monitoring are recommended in such patients. Standard recommended doses should be halved only in patients with creatinine clearance (CR)? 50 ml/min. The maximum recommended dose (i.e. 4 mg/day) should be reduced to 50% for mild (creatinine clearance 40-50 ml/min), to 25% for moderate (creatinine clearance 10-40 ml/min) and to 12. 5% for severe (creatinine clearance ≤ 10 ml/min) renal failure. Patients on dialysis: Adult patients receiving intermittent dialysis should take an additional 500 mg of Cephalexin after each dialysis, up to a total dose of 1 g on that day. Children should receive an additional 8 mg/kg. Patients with impaired liver function: No dose adjustment is required. Elderly patients: There is no need to adjust the dose of the drug in elderly patients with normal renal function.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, use is possible if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
Precautionary measures
The use of cephalexin is possible only as prescribed by a doctor! Before you start taking Cephalexin, be sure to inform your doctor if you have had hypersensitivity reactions to taking cephalosporins, penicillins or other antibiotics in the past. Use with caution in patients with hypersensitivity to penicillins, as cross-hypersensitivity to cephalosporins is possible. If any allergic reactions occur during treatment, you should stop taking Cephalexin and consult a doctor. After taking a single dose of the drug, hypersensitivity reactions are possible, including anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions - life-threatening conditions. There have been reports of the development of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis with the use of cephalexin. Generalized exanthematous pustulosis appears when you start taking cephalexin as a red, scaly, widespread rash with bumps under the skin and blisters, and is accompanied by fever. The most common location: skin folds, trunk and upper extremities. The risk of this serious skin reaction is highest during the first week of use. If you develop a rash or other skin symptoms, you should stop taking cephalexin and seek immediate medical attention from your doctor. When prescribing almost all broad-spectrum antibiotics (including macrolides, semisynthetic penicillins and cephalosporins), cases of pseudomembranous colitis are possible. If you suspect pseudomembranous colitis (loose stools for a long time, possibly with blood or mucus in it), you should immediately stop taking the drug and immediately consult a doctor for appropriate treatment! You should not use medications that inhibit intestinal motility. Long-term use of Cephalexin can lead to the development of microorganisms that are not sensitive to this drug. If the treatment is ineffective, inform your doctor. Taking Cephalexin may cause a decrease in prothrombin activity, especially in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, low body weight, recent use of anticoagulants, intake of vitamin K or long-term antibacterial therapy. Monitoring of prothrombin time is indicated in these patients. While taking Cephalexin, a false positive reaction to sugar in the urine is possible. During a laboratory urine test, inform your doctor about taking Cephalexin. During treatment, you should not drink alcohol or medications containing alcohol. The shell of the Cephalexin capsule contains auxiliary components - dyes (E 133, E 110, E 104), which can cause allergic reactions. The drug contains lactose, so it should not be used in patients with galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption. The drug contains a small amount of sodium: less than 23 mg (1 mmol) per capsule, that is, almost free of sodium.
Interaction with other drugs
Aminoglycoside antibiotics, loop diuretics (ethacrynic acid, furosemide), polymyxins - the risk of nephrotoxicity increases. Monitoring of renal function is recommended. Erythromycin - the effectiveness of both drugs decreases. Metformin - the concentration of metformin in the blood plasma increases; a dose adjustment of metformin may be required. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid), probenecid, phenylbutazone - the elimination of cephalexin slows down. Anticoagulants - possible prolongation of prothrombin time. PTI control is recommended. Antithrombotics and vitamin K antagonists potentiate the action of these drugs. Cytotoxic drugs - may decrease potassium levels in the blood. Monitoring potassium levels in the blood is recommended. Oral contraceptives - decreased contraceptive effect; when taken with cephalexin, additional methods of non-hormonal contraception (for example, a condom) are recommended. Laboratory tests to determine creatinine - a false increase in creatinine concentration is possible. Use during pregnancy and lactation During pregnancy, use is possible if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to cephalexin, any of the auxiliary components of the drug or other cephalosporins; Severe immediate hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis) to penicillins.
Compound
Each capsule of Cephalexin contains the active substance - cephalexin, 500 mg, and excipients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate. The capsule contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, brilliant blue E133, orange yellow E110, quinoline yellow E104, water. This drug belongs to the group of cephalosporins, antimicrobial agents for systemic use. Suppresses the growth of microorganisms that cause infections.
Overdose
If the number of capsules per day you take exceeds the number recommended by your doctor, or your child swallows the capsules, consult a doctor or call an ambulance! Stop taking the medicine! An overdose can be manifested by nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the epigastric region, diarrhea, and the appearance of blood in the urine. As first aid, it is recommended to rinse the stomach and take antacids.
Side effect
Like all medicines, Cephalexin may cause side effects at varying rates, regardless of whether you have previously taken it. If the following side effects occur, stop taking the medication and immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance: swelling of the hands, face, lips, tongue; difficulty breathing; sudden appearance of rashes, damage, redness, peeling of the skin; sore throat; severe dizziness or weakness; acute abdominal pain; yellowness of the skin or eyes! Immune system: urticaria, skin rash, itching, angioedema, erythematous rash, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), anaphylaxis, serum sickness-like reaction (skin rash, urticaria, itching , arthralgia, fever, malaise, swollen lymph nodes). From the nervous system: dizziness, weakness, malaise, headache, sleep disturbance, agitation, hallucinations, convulsions, hyperactivity, hypertonicity. From the genitourinary and urinary system: vaginitis, vaginal discharge, genital candidiasis, interstitial nephritis, toxic nephritis, renal dysfunction, acute tubular necrosis. From the digestive system: abdominal pain, dry mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, diarrhea, gastritis, toxic hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, intestinal/oral candidiasis, rarely - pseudomembranous colitis. From the hematopoietic system: neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia/thrombocytosis, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, lymphopenia, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, bleeding. Laboratory indicators: transient increase in the level of liver enzymes, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, urea, creatinine in the blood serum; prolongation of prothrombin time. If you take a larger dose of Cephalexin than your doctor recommends: If the number of capsules per day you take exceeds the number recommended by your doctor, or your child swallows the capsules, contact your doctor or call an ambulance! Stop taking the medicine! An overdose can be manifested by nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the epigastric region, diarrhea, and the appearance of blood in the urine. As first aid, it is recommended to rinse the stomach and take antacids.
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from moisture and light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Buy Cephalexin caps. 500 mg in container pack No. 10x2 in the pharmacy
Price for Cephalexin caps. 500 mg in container pack No. 10x2
Instructions for use for Cephalexin caps. 500 mg in container pack No. 10x2