Today, more than 380 million people have been diagnosed with diabetes, more than 10.9 million of them live in Russia. It is not always possible to diagnose on time; in 46% of cases the disease remains unrecognized. Self-monitoring is essential for optimal blood sugar control. The results help calculate insulin doses, the amount of sugar in food and physical activity.
The purpose of using a glucometer is not just to control blood sugar levels, but to reduce the incidence of late complications such as damage to the retina, kidneys and nervous system. No less dangerous is the risk of hypoglycemia associated with taking tablets and injectable forms of insulin. This contributes to a high risk of pathology of the heart and blood vessels. Before you buy a glucometer, let's talk about what is important in its use and what problems you may encounter along the way.
How to measure glucose levels?
To determine the concentration of sugar in the blood, you must:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water and wipe dry;
- insert the test strip into the device and turn it on;
- pierce the pad of the middle, index or ring finger, after moving it to speed up blood circulation;
- wipe off the first drop with a cotton swab and apply the second onto the test strip;
- remove and discard the test strip;
- turn off the device.
The result will be known in 5-60 seconds (depending on the model).
To obtain accurate results, you must strictly follow the rules for using the glucometer:
- Before taking measurements, calibrate the device;
- After the puncture, lightly massage your finger without squeezing out the blood;
- Store test strips correctly, observing the expiration date;
- check that the numbers on the test strip packaging correspond to the code on the screen;
- clean the device in a timely manner;
- Change lancets after each blood draw.
Every diabetic should have an individual glucometer. You should not use someone else's device.
About glucometers
The device for measuring blood glucose levels is a portable device equipped with a display and functional buttons. According to the technical characteristics, the following glucometers are used today:
- photometric – indicators are assessed by changes in the color indicator;
- electrochemical - according to current strength;
- non-invasive devices, i.e. without punctures of the skin (thermal, spectral, ultrasound, tonometric).
The latest version of glucometers allows you to avoid permanent injury to the skin and accidental infection of the puncture wound. The disadvantage of this type of device is the high price category. In addition, not all non-invasive models are certified in the Russian Federation. The most common assistant for Russian diabetics is an electrochemical glucometer.
The prerogative aspects of the device include:
Tests for diabetes
- price;
- accuracy (minimum error of results);
- ease of operation;
- high speed of obtaining results;
- auto-encoding of strips (test strips);
- “blood drop” function (0.3 µl is enough to check sugar levels);
- memory function (you can save the results of previous measurements);
- customization function;
- availability of consumables (strips).
Depending on the specific model, the meter may be equipped with additional capabilities for measuring ketone bodies and cholesterol. Popular among diabetics are the functions of calculating the average glycemic value per day (week, month), and automatic connection with a home computer.
Devices differ from each other in color, shape, font size (numbers displayed on the display). Among domestic models, the Satellite Express glucometer (manufactured by Elta, Russia) is considered the leader. The device is distinguished by high accuracy of results and an affordable cost. Equipped with functions:
- auto-on;
- memory;
- uninterrupted use more than 2 thousand times.
Another plus is the Russian-language menu.
The range of possible values for which the device is oriented is 1.8 - 35 mmol/l
The most popular imported devices are glucometers of the AccuChek line (Accu-Chek), manufactured in Switzerland:
- Mobile;
- Assets;
- Performa.
The price of foreign devices is an order of magnitude higher than domestic ones.
Measurement frequency
It is recommended to measure sugar concentration:
- in the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed;
- before eating;
- 1-2 hours after eating;
- before, during and after physical activity;
- 5 hours after insulin administration;
- before driving a car;
- before bedtime.
If there is a high probability of hypoglycemic risk, it is advisable to additionally take a control measurement at 3-4 am.
In some cases, more frequent monitoring may be required:
- for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia;
- when changing the dosage of the medicine;
- at the beginning of taking a new drug;
- when introducing new products into the diet;
- when you feel unwell.
For type 1 diabetes, it is necessary to take measurements several times daily, and for type 2 diabetes, it is enough to measure glucose levels 4-7 times a week and do daily monitoring once every 7-10 days.
All readings received should be recorded in the Self-Control Diary and taken with you before visiting your doctor.
Content:
- What is a glucometer and how it works?
- How to properly set up a glucometer?
- How to use a glucometer correctly?
- Short description
Any disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, including diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2, require monitoring of blood glucose levels. For this purpose, a glucometer is used. How to use the strips and the device itself, and calibrate it to obtain reliable results is indicated in the instructions. In general, most devices have similarities in the principle of glucose determination and use.
Why measure your sugar level?
Self-monitoring of glucose will allow you to:
- determine the effectiveness of medications at night, after meals and between meals;
- calculate the optimal dose of insulin and dosage of medications;
- adjust nutrition and physical activity;
- assess the dynamics of the disease;
- ensure driving safety;
- prevent the development of diabetic crisis, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
It should be noted that self-monitoring cannot replace laboratory diagnostics. Therefore, you should visit the clinic every month for a blood test.
Blood sugar levels
A key role in the proper absorption of glucose as a source of energy for the body is played by insulin, an intrasecretory hormone of the pancreas that ensures the delivery and distribution of glucose to the tissues and cells of the body. The high-quality work of the pancreas in producing insulin and the full ability of cells to absorb this hormone ensure normal carbohydrate metabolism in the body.
Without diabetes
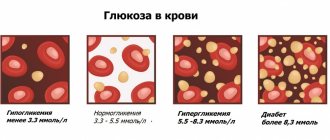
In the absence of metabolic and hormonal disruptions, the level of fasting glycemia ranges from 3.5 to 5.5 mmol/l. Maximum sugar levels (up to 8.9 mmol/l) are recorded an hour after food enters the stomach, then sugar gradually decreases and is completely normalized after 3 hours.
For optimal assessment of carbohydrate metabolism, measurement is performed 120 minutes after eating. Ideal values do not exceed the accepted norm of 7.8 mmol/l. Minor fluctuations in indicators do not relate to endocrine pathology:
- in women during the perinatal and menopausal periods, which is due to changes in hormonal status;
- after 60 years (regardless of gender), due to an age-related decrease in the sensitivity of body tissues to insulin.
Fasting blood glucose standards by age
For diabetes
In diabetics, the processes of metabolism and production of the hormone insulin are disrupted. In type 1 of the disease, the pancreas does not produce insulin; in type 2, the body's cells refuse to adequately perceive it.
In both cases, glucose synthesized from incoming food accumulates in the blood. In diabetes mellitus, indicators of 4-6 mmol/l before meals, and no more than 8.5 mmol/l after meals, are considered good compensation for the disease.
Acceptable glycemic values for diabetes
| Type 1 (values in mmol/l) | Type 2 (values in mmol/l) | |
| on an empty stomach | 7,8 — 9 | 7,8 – 8,2 |
| +60 min | ≤11,0 | ≤9,0 |
| +120 min | ≤10,0 | 8,5 – 8,9 |
| +180 min | ≤9,0 | ≤7,5 |
Guidelines for diabetics
Device coding
This is a procedure on which the accuracy of the results depends. It allows you to bring the device itself and the test strips that come with it into maximum compliance. Older models required manual coding. It was replaced by electronic chips.
The most advanced devices do not require coding. It occurs automatically when the test strip enters the housing. The glucometer reads the code and configures itself.
No Coding technology was developed because it became apparent that most patients were not completing the necessary adjustments. The coding procedure cannot be ignored, as this reduces the accuracy of measurements. As a result, it is not possible to accurately determine the dose of insulin that needs to be administered to the patient.
Rating of the best devices
A high-quality glucometer can only be purchased at a pharmacy or medical equipment store that has the appropriate license. There are numerous manufacturers on the market that receive positive reviews. Their ranking is as follows:
| Manufacturer | Popular models |
| Accu-Chek (Germany) |
|
| OneTouch (Switzerland) |
|
| Bayer (Germany) |
|
| Diamedical (Taiwan) |
|
| Bioptik (Taiwan) |
|
| 77 Elektronika Kft (Hungary) |
|
| iHealth (USA) |
|
| CareSens (South Korea) |
|
| Satellite (Russia) |
|
| AgaMatrix (Germany) |
|
Tokareva Lyudmila Georgievna, therapist, medical offices 36.6
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, BEFORE USE YOU MUST CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST
Don't forget about memory!
The expert considers the memory of a glucometer to be one of the important parameters: “It is important that the device remembers the result, date and time of the analysis. For example. Our Satellite Express stores up to 60 of the latest results. For the attending physician, and the diabetic himself, it is very important to be able to perform a statistical analysis of measurements, as well as systematize data for further monitoring of indicators. This makes it possible to predict events to some extent and make important decisions related to treatment adjustments.”
The principle of choosing a portable device
Pharmacies offer a wide range of modern glucometers. To ensure that your purchase does not disappoint, before purchasing, it is recommended to monitor online reviews of various models, sites comparing the cost of devices, and manufacturers’ sites with detailed descriptions of the devices.
It would be useful to compare prices in online pharmacies with the cost of glucometers in regular city pharmacies. If in doubt, you can consult your treating endocrinologist. When choosing a device, you should focus on the following parameters:
- the highest possible accuracy of the result;
- availability of consumable strips for constant sale;
- additional functions that will be useful for a particular patient (large font or sound signal for the visually impaired, cholesterol measurement, data transfer to a PC, etc.);
- ease of everyday use;
- price of glucometer and test strips;
- presence of auto-tuning function;
- Possibility of use in hiking conditions, ease of transportation;
- special storage case;
- speed of obtaining results;
- device warranty.
Thanks to the efforts of manufacturers, you can choose the design of the device to your liking.
Results
Checking your glycemic level at home using a glucometer is an integral part of the life of a patient with diabetes. Thanks to this, a diabetic can control his condition, correctly calculate the dose of medication, and take timely measures to prevent critical risks.
The measurement results must be saved to a computer (or recorded) in the “Diabetes Diary”. Analysis of the patient’s records will help the doctor analyze the dynamics and predict the course of endocrine pathology, and, if necessary, adjust treatment tactics.
Against the background of independent measurements, one should not forget about regular visits to the endocrinologist and donating blood in the laboratory. The accuracy of laboratory diagnostics is always higher than that of portable glucometers.
Is it possible to take blood from something other than a finger?
Traditionally, blood for testing is taken from a finger or from a vein. In the case of assessing sugar levels, venous is not very preferable. It contains more glucose than capillary, and there is a high risk of incorrect interpretation of the analysis. Therefore, blood for sugar is taken from a finger.
But there are many nerve endings in the fingertip. For many people, piercing is too painful. Therefore, there are high-quality glucometers that include the ability to analyze blood from:
- shoulder;
- forearms;
- shins;
- hips.
It's not that painful to pierce them. However, blood circulation in these parts of the body is slower than in the fingers. Therefore, changes in glucose levels do not always appear in a timely manner according to analyzes from alternative sites.