pharmachologic effect
Expectorant, mucolytic agent.
Ambroxol is an active N-demethylated metabolite of bromhexine. It has secretomotor, secretolytic and expectorant effects. Stimulates the work of the bronchial glands, increases the motor activity of the ciliated epithelium by influencing type 2 pneumocytes in the alveoli and Clara cells in the bronchioles, enhances the formation of endogenous surfactant - a surfactant that ensures the sliding of bronchial secretions in the lumen of the respiratory tract. Ambroxol increases the proportion of the serous component in the bronchial secretion, improving its structure and helping to reduce viscosity and thin the sputum; as a result, mucociliary transport (mucociliary clearance) improves. Increasing mucociliary clearance improves the removal of sputum from the bronchial tree and alleviates cough.
On average, when taken orally, the effect of the drug occurs within 30 minutes, the duration of action is 6-12 hours, depending on the dose taken.
Orvis Broncho Ambroxol solution for oral administration 7.5 mg/ml fl 100 ml
Active substance:
ambroxol
Dosage form
Solution for oral administration and inhalation
Release form, packaging and composition of the drug Orvis® Broncho
The solution for oral administration and inhalation is transparent, colorless to brown, with a slight characteristic odor.
1 ml
ambroxol 7.5 mg
Excipients: sodium chloride - 6.22 mg, sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate - 4.35 mg, citric acid monohydrate - 2 mg, benzalkonium chloride - 0.225 mg, purified water - 989.705 mg.
50 ml - orange glass bottles (1) - cardboard packs complete with a measuring cup.
100 ml - orange glass bottles (1) - cardboard packs complete with a measuring cup.
Clinical and pharmacological group:
Mucolytic and expectorant drug
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Expectorant mucolytic agent
pharmachologic effect
Mucolytic and expectorant drug.
Ambroxol is a benzylamine metabolite of bromhexine. It differs from bromhexine in the absence of a methyl group and the presence of a hydroxyl group in the para-trans position of the cyclohexyl ring. It has secretomotor, secretolytic and expectorant effects.
After oral administration, the effect occurs within 30 minutes and lasts for 6-12 hours (depending on the dose taken).
Preclinical studies have shown that ambroxol stimulates the serous cells of the glands of the bronchial mucosa. By activating ciliated epithelial cells and reducing sputum viscosity, it improves mucociliary transport.
Ambroxol activates the formation of surfactant, having a direct effect on type 2 alveolar pneumocytes and Clara cells of the small airways.
Studies on cell cultures and in vivo studies on animals have shown that ambroxol stimulates the formation and secretion of a substance (surfactant) active on the surface of the alveoli and bronchi of the embryo and adult.
Also, preclinical studies have proven the antioxidant effect of ambroxol.
Ambroxol, when used together with antibiotics (amoxicillin, cefuroxime, erythromycin and doxycycline), increases their concentration in sputum and bronchial secretions.
Indications of the active substances of the drug Orvis® Broncho
Diseases of the respiratory tract with the production of viscous sputum and difficulty in clearing sputum.
Dosage regimen
The method of administration and dosage regimen of a particular drug depend on its release form and other factors. The optimal dosage regimen is determined by the doctor. The compliance of the dosage form of a particular drug with the indications for use and dosage regimen should be strictly observed.
For inhalation, ambroxol is used in the form of a solution for oral administration and inhalation
Adults and children over 5 years of age are recommended to inhale 15-45 mg of ambroxol 1-2 times a day.
Children under 5 years of age are recommended to inhale 15-30 mg of ambroxol 1-2 times a day.
The inhalation solution can be used using any modern inhalation equipment (except steam inhalers). The drug is mixed with saline; to achieve an optimal level of air humidification in the respirator, the drug can be diluted in a 1:1 ratio. Since during inhalation therapy, a deep breath can provoke coughing impulses, inhalations should be carried out in normal breathing mode. Before inhalation, it is usually recommended to warm the inhalation solution to body temperature. For patients with bronchial asthma, inhalation may be recommended after taking bronchodilators.
Before use, consultation with a specialist is required. Storage mode, interactions and side effects are indicated in the instructions.
Directions for use and doses
Oral administration (1 ml = 25 drops)
- Adults and children over 12 years of age: the first 2-3 days, 4 ml (100 drops) 3 times a day (which corresponds to 90 mg of ambroxol per day), then 4 ml 2 times a day (which corresponds to 60 mg of ambroxol per day) .
- Children from 6 to 12 years old: 2 ml (50 drops) 2-3 times a day (which corresponds to 30 or 45 mg of ambroxol per day).
- Children from 2 to 6 years old: 1 ml (25 drops) 3 times a day (which corresponds to 22.5 mg of ambroxol per day).
- Children under 2 years of age: 1 ml (25 drops) 2 times a day (which corresponds to 15 mg of ambroxol per day).
- For children under 2 years of age, the drug is prescribed only under the supervision of a doctor.
Maximum daily dose when taken orally: for adults – 90 mg, for children
6-12 years old – 45 mg, for children 2-6 years old – 22.5 mg, for children under 2 years old – 15 mg.
The drug is used after meals, adding to water, tea, milk or fruit juice.
During treatment, it is necessary to drink plenty of fluids (water, tea, juice) to enhance the mucolytic effect of the drug.
Inhalations
- Adults and children over 6 years of age: 1-2 inhalations of 2-3 ml (50-75 drops) of solution per day (which corresponds to 15-45 mg of ambroxol per day).
- Children under 6 years of age: 1-2 inhalations of 2 ml (50 drops) of solution per day (which corresponds to 15-30 mg of ambroxol per day).
The drug can be used using any modern equipment for inhalation (except steam inhalers). To achieve optimal hydration during inhalation, the drug is mixed with 0.9% sodium chloride solution in a 1:1 ratio. Since during inhalation therapy a deep breath can provoke a cough, inhalations should be carried out in normal breathing mode. Before inhalation, it is usually recommended to warm the inhalation solution to body temperature. Patients with bronchial asthma are recommended to carry out inhalation after taking bronchodilators to avoid nonspecific irritation of the respiratory tract and their spasm.
If symptoms of the disease persist within 4-5 days from the start of treatment, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Orvis Broncho Ambroxol
Orvis Broncho solution for intravenous priming and inhalation 7.5 mg/ml 100 ml x1, ATX code: R05CB06 (Ambroxol) Active substance: ambroxol Rec.INN registered by WHO
Dosage form
ORVIS® BRONCHO
solution for oral administration and inhalation 7.5 mg/ml: bottles of 50 or 100 mlreg. No.: LP-004198 dated 03/17/17 - Valid
Release form, composition and packaging
The solution for oral administration and inhalation is transparent, colorless to brown, with a slight characteristic odor.
1 ml
ambroxol 7.5 mg
Excipients: sodium chloride - 6.22 mg, sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate - 4.35 mg, citric acid monohydrate - 2 mg, benzalkonium chloride - 0.225 mg, purified water - 989.705 mg.
Clinical-pharmacological group: Mucolytic and expectorant drug Pharmaco-therapeutic group: Expectorant mucolytic drug The scientific information provided is general and cannot be used to make a decision about the possibility of using a specific drug.
pharmachologic effect
Mucolytic agent with expectorant action. Stimulates the serous cells of the glands of the bronchial mucosa, increasing the content of mucous secretion and, thus, changing the disturbed ratio of serous and mucous components of sputum. At the same time, hydrolyzing enzymes are activated and the release of lysosomes from Clara cells is enhanced, which leads to a decrease in the viscosity of sputum. Ambroxol increases the content of surfactant in the lungs, which is associated with an increase in its synthesis and secretion in alveolar pneumocytes, as well as a violation of its breakdown. Increases mucociliary transport of sputum. Slightly suppresses cough.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, ambroxol is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after approximately 0.5-3 hours. It does not accumulate. Plasma protein binding is about 90%.
After oral and parenteral administration, ambroxol is quickly distributed in the tissues of the body, the highest concentration is determined in the lungs.
Penetrates through the BBB and placental barrier, excreted in breast milk.
Metabolized in the liver by conjugation to form pharmacologically inactive metabolites.
T1/2 is 7-12 hours. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys in the form of metabolites - 90%, unchanged - 5%.
T1/2 increases in severe chronic renal failure.
Indications Acute and chronic diseases of the respiratory tract, accompanied by the release of viscous sputum (chronic bronchitis with broncho-obstructive syndrome, bronchial asthma, bronchiectasis). Respiratory distress syndrome in newborns and premature infants. ICD-10 codes
Dosage regimen
Orally for adults and children over 12 years old - 30 mg 2-3 times a day.
Orally for children aged 5 to 12 years - 15 mg 2-3 times / day, from 2 to 5 years - 7.5 mg 3 times / day, for children under 2 years - 7.5 mg 2 times / day.
In the form of inhalations, adults and children over 5 years old - 15-22.5 mg 1-2 times a day.
Adults parenterally (i.m., i.v.) - 15 mg, in severe cases - 30 mg 2-3 times a day.
Children IM - 1.2-1.6 mg/kg 3 times a day, IV - 1.2-1.6 mg/kg/day.
For children under 2 years of age, intravenous dosage is 15 mg/day, frequency of administration is 2 times/day.
Children from 2 to 5 years old intravenously - 22.5 mg/day, frequency of administration - 3 times/day.
For children over 5 years old, intravenous dosage is 30-45 mg/day, frequency of administration is 2-3 times/day.
For the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in premature and newborn babies, ambroxol is administered intravenously or intramuscularly at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day, the frequency of administration is 3-4 times/day, if necessary, the dose can be gradually increased to 30 mg/kg /day
Side effect
From the digestive system: rarely - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, urticaria, angioedema.
Other: rarely - weakness, headache.
Contraindications for use: Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, convulsive syndrome of various etiologies, first trimester of pregnancy, hypersensitivity to ambroxol.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Ambroxol is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. If it is necessary to use it in the second and third trimesters, the potential benefits of therapy for the mother and the possible risk to the fetus should be assessed.
If it is necessary to use ambroxol during lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be decided.
Use in children Use is possible according to the dosage regimen.
Use in elderly patients Use is possible according to the dosage regimen.
Special instructions In patients suffering from bronchial asthma, in order to avoid nonspecific irritation of the respiratory tract and their spasm, bronchodilators can be used before inhalation of ambroxol.
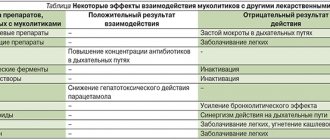
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with antitussive drugs, it becomes difficult to separate sputum while reducing cough; with amoxicillin, doxycycline, cefuroxime, erythromycin, their penetration into the bronchial secretion increases.
special instructions
Ambroxol should not be combined with antitussives that make it difficult to remove mucus.
To maintain the secretolytic effect during the period of use of the drug, it is necessary to ensure that a sufficient amount of fluid enters the body.
In patients with bronchial asthma, ambroxol may increase cough.
The drug contains benzalkonium chloride (a preservative), which, when inhaled, can cause bronchospasm in sensitive patients with increased respiratory tract reactivity.
The drug is not recommended to be mixed with cromoglycic acid and alkaline solutions.
Patients on a hyposodium diet should take into account that 1 ml of the drug contains 10 mg of sodium. The maximum daily dose (12 ml) for adults and children over 12 years of age contains 120 mg of sodium.
There are isolated reports of the detection of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome, which coincided with the administration of ambroxol, but there is no cause-and-effect relationship with the drug. In most cases, they can be explained by the severity of the underlying disease and/or concomitant therapy. Patients with Stevens-Johnson or Lyell syndrome may experience fever, body pain, rhinitis, cough and sore throat in the early phase. During symptomatic treatment, it is possible to erroneously prescribe mucolytic agents such as ambroxol hydrochloride. If the above syndromes develop, it is recommended to stop treatment with ambroxol and immediately seek medical help.
In severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), the risk of accumulation of ambroxol metabolites must be taken into account.
The drug does not affect the performance of potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions (driving a car, working with driving mechanisms, etc.).