Hawthorn is a tall shrub from the Rosaceae genus. It grows in temperate latitudes and grows wild in North America and Eurasia. On the territory of the Russian Federation, two types are most common: large-fruited hawthorn and blood-red hawthorn (popularly known as the so-called garden hawthorn, the benefits and harms of which will be discussed). No less famous is the black hawthorn, which grows in the Czech Republic, Hungary and the Balkan Peninsula.
It is a valuable medicinal plant, planted for decorative purposes, and is considered a good honey plant.
Wild hawthorn berries were used for health benefits back in Ancient China and Asia, first to treat diarrhea, and then to improve the functioning of blood vessels and the heart. Cultivated plant species were bred in the 16th century.
What does hawthorn help with and how is it useful, how to take it correctly and to whom herbal medicine with plant preparations can cause harm, read our new article.
Features of a medicinal plant
Hawthorn is a deciduous, semi-evergreen, tall shrub (rarely a small tree) from the Rosaceae family.
In the wild, it occurs either singly or in compact groups. His “favorite” places are forest edges, clearings, clearings, and screes. In excessively moist soil, hawthorn roots can rot, so it grows mainly in deep, moderately moist and well-drained soil. The perennial plant is unpretentious, so homeowners willingly use it for decoration. Delicate hawthorn flowers are attractive in spring, and tart red fruits are attractive in autumn. Both of them have medicinal properties. So, the plant not only decorates gardens, but is also used to combat various diseases.
Chemical composition of hawthorn
In medicine and pharmacology, hawthorn fruits are especially valued - spherical, pear-shaped, elongated, with one or several large, strong triangular seeds. And also flowers with five white, round petals with a short nail. They contain a lot of dimethylamine, a substance that in its pure form smells like stale fish. But in hawthorn flowers it is practically not felt. The pulp of the berries and flower petals are saturated with biologically active substances. The chemical composition of the medicinal plant is represented by the following organic compounds:
- essential oil;
- bioflavonoids - quercetin, hyperoside, vitexin;
- organic acids - citric, oleanic, ursolic, crotegusic, caffeic, chlorogenic;
- carbohydrates - glucose, fructose, sucrose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, galactose;
- carotenoids;
- tannins;
- fatty oils;
- pectins;
- monoterpenoids;
- triterpene and flavonoid glycosides;
- choline;
- sugars;
- vitamins;
- steroids;
- sesquiterpenoids;
- lignanans;
- hydroxycinnamic acid.
And each of these substances exhibits its own therapeutic activity. Hawthorn fruits with a large amount of lupeol, p-sitosterol, betulin, and betulinic acid are indispensable for loss of strength. However, like its flowers, which contain a lot of potassium, iron, sulfur, iodine, tocopherol, B vitamins, ascorbic acid, oligomeric and polymeric procyanidins.
Release forms
Pharmacies sell hawthorn fruits in bulk cardboard boxes - whole or crushed. Plant materials are dark burgundy in color, with a rough surface, mostly without stalks. To make tea, highly crushed fruits are sold, packaged in filter bags. Hawthorn also represents the composition of many preparations: for the heart and blood vessels, antihypertensive, restorative, tonic, and anti-cold. Flowers can also be purchased in bulk, in filter bags, or in medicinal mixtures.
A popular drug is an alcoholic tincture of hawthorn, which helps with heart rhythm problems. In folk medicine, mixed with other tinctures, it is used to prevent surges in blood pressure, weakness, and fatigue. There are many dietary supplements with hawthorn in the pharmacy assortment:
- tablets;
- capsules;
- syrups;
- balms;
- elixirs
This useful plant is often included in cosmetics to improve complexion and even out skin texture. Hawthorn extract is found in shampoos, toothpastes, hair balms, and bath salts.
The benefits and harms of dry hawthorn
The fruits of this useful plant help in the treatment of the following pathologies: shortness of breath, obesity, poisoning, prostatitis, heart pain, insomnia, neurasthenia, infertility, kidney and liver diseases, angina pectoris, migraine, etc. The benefits of hawthorn are great, but the berries can also cause harm to the body.
There are contraindications for the use of hawthorn: age under 12 years, pregnancy, lactation, hypotension, abnormalities of the genitourinary system.
If consumed in excess, berries can cause the following side effects:
- increased heart rate;
- migraine, renal dysfunction;
- stomach upset.
How to store hawthorn? The medicinal plant can be stored in dried form, in the form of jam, infusion, or frozen.
Which hawthorn is healthier, dried or frozen? Both options for preserving berries allow you to preserve as many useful, medicinal and nutritional properties of the fresh plant as possible, therefore, the storage method can be chosen based on the comfort of preparing the product for the winter, as well as the convenience of its further use. The shelf life of the product, regardless of its form, is six months.
How to store dried hawthorn at home? Dried fruits should be placed in fabric bags (providing air circulation) and stored in a dry, dark place at a temperature of +20 and above.
How to use? Berries can be added to baked goods, prepared teas, infusions, prepared sauces for meat, added to nourishing and healing masks, etc. There are a lot of ways to use the product, and one of the most common is brewing.
Therapeutic effect
Hawthorn normalizes heart rhythm, promotes dilation of coronary vessels and increased coronary circulation, reducing myocardial excitability. After taking a decoction or infusion, blood pressure decreases and the functional activity of the walls of blood vessels, including those representing the venous bed, increases. The pronounced therapeutic effect of hawthorn is due to the expansion of peripheral vessels and those that supply blood to the internal organs. The herbal remedy also exhibits the following therapeutic activity:
- soft soothing;
- anti-inflammatory;
- moderate analgesic;
- antimicrobial;
- disinfectant;
- antiseptic;
- decongestant;
- antispasmodic;
- immunostimulating;
- immunomodulatory.
Hawthorn helps with excessive nervous excitability of the central nervous system, insomnia or daytime sleepiness. Under the influence of its bioactive substances, blood vessels are cleared of cholesterol plaques, the gastrointestinal tract is cleared of undigested food particles and mucus, and the liver is cleared of toxic substances. Relatively recently, the ability of flowers to maintain optimal blood glucose levels and increase the body’s immunity to negative factors was discovered.
Beneficial features
Content
- Chemical composition of the product
- Beneficial features
- The benefits and harms of dry hawthorn
- Rules for brewing hawthorn
Teas and infusions made from dried hawthorn berries have incredible beneficial properties, including tonic, calming and rejuvenating effects on the body. The product perfectly supports the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. The product also perfectly lowers blood pressure and is recommended for use for skin diseases, menopause, heart disease, liver disease, increased fatigue, atherosclerosis, and insomnia.
In cooking, dried berries add a pleasant aroma and interesting flavor notes to dishes.
The product has: anti-stress, immunomodulatory, blood purifying, astringent, cleansing, sedative, hypocholesterol, vasodilator, antispasmodic, venotonic, cardiotonic, tonic, antioxidant, vitaminizing, antimicrobial, diuretic, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, hypotensive beneficial properties.
What is hawthorn for?
The medicinal plant is recommended for the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system. For pathologies of the first degree of severity, only an infusion or decoction is used, including for the prevention of disruptions in myocardial function, increased blood pressure, and cardiac pain. For diseases of moderate or severe severity, herbal remedies with hawthorn are used only as part of complex therapy with pharmacological drugs. For medicinal purposes, doctors prescribe fruits and (or) flowers to patients with the following pathologies:
- functional disorders of the heart;
- hypertension;
- angina pectoris;
- antigioneuroses;
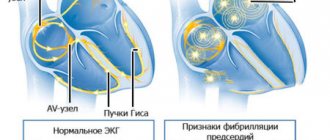
- atrial fibrillation;
- paroxysmal tachycardia;
- atherosclerosis;
- climacteric neurosis;
- increased secretion of hormones by the thyroid gland;
- diarrhea;
- febrile conditions;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- chronic fatigue;
- low immunity;
- frequent colds;
- wounds and inflammatory processes on the skin;
- dermatitis and eczema;
- hair loss;
- swelling.
This is one of the best means for preventing hypertension. The use of hawthorn helps to avoid its development in the presence of provoking factors, such as excess weight, hereditary predisposition, and kidney pathologies. Such preventive measures improve the tone of blood vessels and reduce the load on the heart muscle.
Hawthorn has proven itself well in the treatment of diseases affecting one of the organs of the urinary system. Doctors recommend taking kidney infusions with fruits or flowers to patients with cystitis, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, and nephritis. Pectins, contained in large quantities in hawthorn, cleanse the gastrointestinal tract of toxins. This ability of medicinal raw materials is used in folk medicine to stop the processes of putrefaction and fermentation characteristic of dyspeptic disorders with pancreatitis, gastritis, and irritable bowel syndrome.
How to use hawthorn correctly
A course of decoction can restore heart function and strengthen blood vessels. To prepare it, you need to pour a tablespoon of crushed raw materials with a glass of water, bring to a boil in a water bath and simmer for a quarter of an hour. Then strain the broth and cool. The optimal dosage regimen is a teaspoon three times a day before meals. A medicinal drink for hypertension should be prepared somewhat differently:
- pour two tablespoons of whole fruits into a thermos;
- pour in two glasses of boiling water;
- leave for 7-8 hours, cool, strain;
- drink in small portions throughout the day.
For preventive purposes, it is more convenient to use tea from filter bags - from them the drink is prepared much faster. In addition, you can always take them with you to work or on trips. One filter bag should be poured with a glass of boiling water, cool after 15 minutes, strain, and squeeze out the bag with a spoon.
The doctor determines the volume of infusion or decoction and the duration of treatment. When calculating doses, he takes into account the type of disease, the cause of its development, the intensity and nature of the symptoms. As a rule, the duration of therapy is individual. Treatment can last from two weeks to a month, if necessary, resume after a 1-2 week break.
If after a month your health does not improve, the symptoms of the pathology do not become less pronounced, you must inform your doctor about this. He will replace hawthorn with another herbal remedy or a preparation with synthetic ingredients.
Traditional medicine recipes
Fresh fruits
You can consume no more than 1 glass of fresh fruits per day. Exceeding the recommended dose may lead to heart rhythm disturbances.
Fresh Juice
Freshly squeezed juice from hawthorn fruits, diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio, is taken to improve blood circulation and normalize the digestive system (several teaspoons before meals).
Juice can also be prepared from thawed berries, but in this case there is no need to dilute it with water.
Berry pulp can be used for brewing as an infusion.
Vitamin tea from hawthorn
It is useful even for those who do not have indications for treatment with hawthorn. Helps saturate the body with vitamins, strengthen the immune system and heart muscle.
Take 1 tbsp. dry fruits and pour a glass of boiling water over them, cover with a lid, leave for 20 minutes and filter. Add the resulting infusion in an amount of 40-50 ml to a glass of green tea. Take 1-2 times a day.
The second recipe (it turns out more concentrated). Take 20-30 dried hawthorn fruits, a few rose hips and pour 1 liter of boiling water in a thermos and leave overnight. You can drink it in the morning.
Alcohol tincture of hawthorn
Improves heart function, recommended for atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. Prescribed as a mild sedative, for stress, as a tonic and immunomodulatory agent.
Take 1 part of dried hawthorn fruits and add 10 parts of 70° alcohol, leave in a dark, closed bottle for 21 days, filter. How to take: 30 drops, diluted in ½ glass of boiled clean water, three times a day, half an hour before meals. Course 30 days.
Hawthorn decoction
Recommended for heart neuroses, cardiac cough, nervous overload, shortness of breath, asthma, rheumatism, hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances such as atrial fibrillation. Relieves hot flashes.
Take 15 g. dry berries and pour a glass of hot water, simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes. Cool the mixture for about 45 minutes, then filter. Bring the decoction to a volume of 200 ml with chilled boiled water. Take 100 ml twice a day for 30 minutes. before meals.
Water infusion of hawthorn
Take a couple of handfuls of dry fruits, chop and brew with boiling water (1 l). Leave overnight. Take 1/3 cup 60 minutes before meals 3-4 times a day. Useful for arrhythmia, angina pectoris, increased nervous excitement.
Alcohol tincture of hawthorn for blood pressure
It is prepared from dried crushed fruits or flowers. Take 4 tbsp. vegetable raw materials, add 500 ml of vodka and leave in a dark place for 14 days. Then strain. Drink 25-30 drops diluted with water an hour before meals for hypertension and angina.
Tea balm
Recommended for heart failure. Take 100 gr. good black tea, add 2 tbsp. rose hips, 1 tsp. hawthorn fruit, 1 tbsp. motherwort herb, 1 tbsp. peppermint and 1 tsp. valerian rhizomes and chamomile flowers. Brew like regular tea. You can drink 1 glass 2 times a day.
Infusion for hypertension
Take 1 tsp. crushed hawthorn fruits, motherwort, dried cucumber and chamomile flowers. Brew a glass of boiling water and filter after 60 minutes. Take 1 tbsp an hour before meals.
Restorative agent after myocardial infarction
Patients who have had a heart attack are recommended to take half a glass of diluted hawthorn juice with 1 tsp. vegetable oil.
Remedy for weak vascular tone
Take 3 tsp. hawthorn flowers, 2 tbsp. herbs medicinal letter and pour the mixture with three glasses of cold water. Boil and leave to steep for 5 hours. Drink 1 glass an hour before meals.
Skin lotion
An aqueous infusion of hawthorn is recommended to be used as a lotion to restore the natural moisture of the skin, increase skin tone, eliminate puffiness and fine wrinkles. The infusion can be frozen and rubbed into cubes on the skin before bed and in the morning.
Contraindications
Hawthorn flowers and fruits are not prescribed by doctors to patients with hypersensitivity to them. Taking infusions and decoctions from medicinal plants is not recommended for people predisposed to the development of allergic reactions. It is not used in pediatrics. The exception is fees intended specifically for children. Plants from their composition undergo additional purification from harmful impurities.
An absolute contraindication to treatment with hawthorn is persistently low blood pressure. Most manufacturers warn against taking this herbal remedy during pregnancy and breastfeeding. But some include hawthorn in their preparations to enhance lactation.
Possible side effects
Systemic side effects during the treatment of hawthorn are not excluded, since its bioactive substances are absorbed into the blood and distributed to all organs and tissues. They are observed rarely, usually when the dosage regimen determined by the doctor is not followed or when the decoction, tea, or infusion is inappropriately taken. Systemic reactions are clinically manifested as follows:
- nausea;
- increased heart rate;
- drop in blood pressure;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- flatulence;
- disorders of intestinal motility.
Local adverse reactions are manifested by angioedema and irritation of the skin and mucous membranes. If any negative effect occurs, you should stop using hawthorn and seek medical help to eliminate symptoms.
How to use berries
Dried berries are already ready for use - they are equally useful as long as they are stored in the house. Tinctures, teas, and vitamin solutions for external use are prepared from the dried product.
Tinctures and tea can be drunk or pre-infused so that the solution is more concentrated. Another option is to grind the berries using a coffee grinder and then pour boiling water over them. After the mixture has infused, it is filtered or drunk finely ground. A cold, fortified drink is useful in summer; it also quenches thirst well.