An umbilical hernia is a protrusion of internal organs through the fibrous ring of the navel. Most often, intestinal loops, the stomach wall, or the greater omentum come out. In children, this problem occurs mainly in the first months of life, which is associated with the anatomical features of the abdominal muscles and intrapartum complications. Mostly girls get sick. In total, about 12% of newborns have an umbilical hernia. However, surgical treatment is necessary for 30-40% of such children.
Causes of the disease and predisposing factors
Premature babies are more often affected by the disease. According to statistics, every third child who was born prematurely is predisposed to the appearance of an umbilical hernia. Pathology is found in newborns, one-year-olds, and even those aged 6 to 8 years. Let's look at the issue “umbilical hernia in children - causes” in detail.
A congenital disease can be caused by the following factors:
- being born prematurely;
- heredity;
- infection in the womb;
- negative environmental factors, poor ecology in the region;
- weakness of the child's abdominal muscles inherited through genes.
What causes acquired pathology? The disease can occur due to the following conditions:
- colic in the abdomen;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract (constipation, gas, bloating);
- lactase deficiency;
- early walking;
- hysterical crying or severe and frequent coughing, other reasons.
The disease can appear without certain prerequisites.
Hernia is inherited
Plastic surgery of the anterior abdominal wall for hernias in children
- Cost: 52,000 - 80,000 rubles.
More details
Hernias of the anterior abdominal wall account for up to 30% of all surgical diseases in children. The name of individual types of hernia usually corresponds to the location of its anatomical location. According to the frequency of treatment, they are distributed approximately as follows: inguinal hernias - 81%, umbilical hernias - 15%, hernias of the white line of the abdomen - 3.5%, femoral hernias - 0.5%. According to modern concepts, the causes of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall in children are: 1. Violation of genetic information (many hereditary pathological syndromes include a hernia). 2. Various external influences on the fetus during pregnancy (physical, chemical, biological, and more often infectious). 3. Deficiency of differentiating hormones of mother and fetus (imbalance between “male” and “female” hormones). The listed factors, affecting the connective tissue of the fetus, cause general intrauterine growth retardation. This delay is expressed, in particular, in the insufficient development of collagen fibers of connective tissue, which in turn manifests itself in the improper formation of various tissues, primarily of mesenchymal origin - skin, aponeurosis, muscles, bones, including the structures of the inguinal and femoral canals. In girls, hernias are observed 9-10 times less often than in boys, which is due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the body.
Symptoms
Many parents are interested in what an umbilical hernia looks like in a child? It looks like a round formation in the navel area. The shape of the protrusion resembles a ball. The hernia is easily reduced inside. However, the above symptoms are typical if the umbilical ring is greatly expanded. If its expansion is not very large, then in the normal state of the child the protrusion is unnoticeable. It can only be detected when the baby cries a lot, laughs or coughs, i.e. for any tension in the child's tummy.
With an umbilical hernia in children, the symptoms may be as follows. Increased anxiety in the baby, especially when the weather changes. The child is more capricious than all other children. This is explained by the fact that infant colic is more painful for him.
Parents should be alert to such changes in the child’s well-being: vomiting, changes in sensitivity in the hernia area, and also if the location of the pathology has changed color and density. These signs may indicate a strangulated hernia. You should immediately contact a pediatric surgeon.
Surgical treatment of pediatric umbilical hernia at the Laser Medicine Center
or why you shouldn’t be afraid to go to a pediatric surgeon
If the time allotted by nature to your baby’s health for self-healing is coming to an end, if all your conscientious efforts to help your child cope with this harmless pathology have not yielded results, then you should not hesitate and gather your courage and make a decision on surgical treatment of the hernia.
Please note that the uniqueness of a child for parents does not apply to his illness for a doctor. If a pediatric surgeon has several dozen operations to repair an umbilical hernia, then his professional experience is a sufficient guarantee of the success of the operation. When you are dealing with a doctor who has performed hundreds of similar operations, the child’s parents have an objective reason to be completely confident in the successful surgical treatment of their child.
Dear Parents.
You can get qualified help regarding the treatment of an umbilical hernia, as well as hernial protrusions of other origins, in the pediatric surgery department of the multidisciplinary clinic “Laser Medicine Center”.
We widely use modern effective treatment methods to achieve positive results. The department is equipped to the most modern standards, so your stay in the hospital will be as comfortable as possible.
Diagnostic methods
Only an experienced specialist can diagnose pathology. You need to visit a pediatrician. The doctor will make a preliminary conclusion and, if necessary, refer you to a pediatric surgeon for a final clarification of the diagnosis. However, one examination is not enough, since the hernia is not always noticeable and clearly visible. It can also be similar in appearance and symptoms to other diseases. Therefore, an additional examination is prescribed, which includes the following diagnostic methods:
- ultrasonography;
- general blood analysis;
- radiography;
- herniography (the area of the hernia is examined using x-rays).
This examination is necessary to accurately prescribe treatment for an umbilical hernia in children.
Accurate diagnosis allows you to determine whether surgical intervention is needed or whether the problem can actually be solved in other ways. For example, with the help of therapeutic exercises, massage or using a fixing patch.
Features of treatment of umbilical hernia in children
If an umbilical hernia is detected in a child, how to treat it is the first question that interests parents. You should understand what determines the choice of treatment method. If the hernia is small, minimal in size, and does not increase, it is quite possible to eliminate it without surgery. The well-being of the little patient is also important. If nothing bothers the baby, he feels well, the doctor will prescribe massage, gymnastics, and medication.
Taking medications is one of the treatment methods that a specialist can prescribe. The purpose of the medications in this case is to strengthen the walls of the child’s tummy. Often this treatment is accompanied by therapeutic massage, gymnastics, and wearing a bandage. When such therapy is unsuccessful, surgical removal of the umbilical hernia in children is required.
At the slightest sign of illness, you should contact your pediatrician. Experienced and caring specialists from JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) provide consultations in the center of Moscow, not far from the Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya metro stations. If you need to clarify the diagnosis with a surgeon, your pediatrician will refer you to this specialist. Due to the fact that our clinic employs doctors from 66 medical specialties, you can undergo all examinations and receive consultations from highly specialized specialists in one building.
Umbilical hernia
21247 November 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Umbilical hernia: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
An umbilical hernia is a protrusion of abdominal organs through a defect in the abdominal wall in the navel area.
Causes of umbilical hernia
After the umbilical cord falls off in newborns, the umbilical ring normally closes, and the hole is filled with scar-connective tissue. The umbilical fascia and peritoneum are directly adjacent to the skin in the area of the umbilical ring, and the muscles of the abdominal wall additionally tighten the ring.
A congenital defect in the anatomical structure of the umbilical ring, underdevelopment or absence of the umbilical fascia can cause an umbilical hernia, which occurs with the slightest increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
The contents of an umbilical hernia can be loops of the small and large intestines, the greater omentum, the liver, and part of the stomach.
Umbilical hernias can occur during the embryonic development of the fetus, in childhood and in adults, therefore they are distinguished:
- embryonic hernias,
- childhood hernias,
- adult hernias.
Embryonic hernia (omphalocele) is a severe congenital malformation of the anterior abdominal wall, in which internal organs fall out through its defect and delamination of the tissues of the initial section of the umbilical cord.
Three factors play a major role in the origin of an embryonic hernia of the umbilical cord: impaired intestinal rotation in the first period of rotation, underdevelopment of the abdominal cavity, and impaired closure of the anterior abdominal wall. Depending on the period of occurrence of the defect, embryonic hernias are divided into actual embryonic hernias
(occur during the period of development when the anterior abdominal wall is not yet fully formed),
fetal hernias
(occur when the anterior abdominal wall is finally formed, and the umbilical ring from the abdominal cavity is covered by the peritoneum) and
mixed hernias
.
In the first months of a child’s life (usually up to 6 months), umbilical hernias of childhood may occur, which are twice as common in girls as in boys. Cough, flatulence, and straining can be factors that cause an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and provoke the appearance of an umbilical hernia.
Umbilical hernia in adults occurs in 2-6% of the adult population and is more often detected after 40 years, and in 90% of cases in women who have given birth multiple times with concomitant obesity. Factors that contribute to increased intra-abdominal pressure and stretching of the abdominal wall, which can lead to the appearance of an umbilical hernia in adults, include pregnancy, obesity, ascites, constipation, rapidly growing abdominal tumors, and heavy physical labor.
Classification of the disease
By origin
I. Congenital hernia (embryonic):
a) actually embryonic; b) fetal hernias (umbilical cord); c) mixed hernias.
II. Purchased:
1. Hernias of childhood. 2. Adult hernias: a) direct; b) oblique.
Based on the possibility of hernia reduction:
- reducible,
- irredeemable.
According to the presence of complications:
- complicated,
- uncomplicated.
To size:
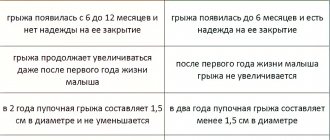
- small hernias (up to 5 cm in diameter),
- medium hernias (from 5 to 10 cm in diameter),
- large hernias (over 10 cm in diameter).
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia
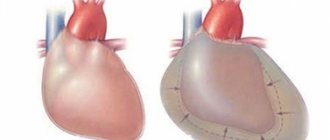
The clinical picture of an umbilical hernia depends on the size of the hernial protrusion and hernial orifice, the severity of the adhesive process, and the presence of complications. The size of the hernia varies from 4-5 to 20-30 cm in diameter.
In adults, a hernia can form gradually - a small spherical protrusion appears in the navel area when standing, when coughing or straining. In a horizontal position, the protrusion disappears. When palpated, the contents of the hernia “fall” into the hole in the abdominal wall. The hernial sac consists of peritoneum; on the outside it is covered with skin, subcutaneous tissue and fascia. After the hernia has been reduced, you can palpate the umbilical ring (hernia orifice). If the hernial orifice is narrow, reduction of the hernia contents may be difficult. Over time, the hernia tends to increase and begins to cause discomfort and pain.
An umbilical hernia can also occur suddenly during physical activity. In this case, the person feels a sharp pain in the navel or in the middle abdomen.
If the hernia stops being reduced, pain occurs, or signs of inflammation appear, you should consult a doctor. These symptoms may indicate a strangulated hernia.
Umbilical hernias can be oblique or straight. Direct hernias occur due to thinning of the transverse fascia adjacent to the umbilical ring. In this case, the hernial sac enters the subcutaneous tissue directly through the umbilical ring. When oblique hernias occur, a hernial protrusion forms above or below the umbilical ring, passes through the gap between the linea alba and the transverse fascia (umbilical canal), then exits into the subcutaneous tissue through the umbilical ring.
The characteristic signs of an umbilical hernia in children are the same as in adults: protrusion in the navel in an upright position and/or with increased intra-abdominal pressure, which disappears with pressure, expansion of the umbilical ring.
Umbilical hernias in children most often do not become strangulated, but parents should be informed of the signs of a strangulated hernia and the need for immediate hospitalization if strangulation does occur.
As the abdominal wall develops and strengthens, self-healing from a small umbilical hernia is possible in children under 6 years of age. Therefore, if the hernia does not cause concern to the child, expectant management is used. If cure does not occur, surgical treatment is planned.
With small embryonic hernias, the general condition of children usually remains quite satisfactory. The contents of small hernias are always only intestinal loops, which can be easily inserted into the abdominal cavity without causing a reaction on the part of the child.
Medium-sized hernias contain a significant number of loops of the small and large intestine, in 1/3 of cases - part of the liver. An attempt to immerse the organs is difficult. Cooling of these organs, as well as infection of the membranes of the hernial sac, worsen the child’s condition.
Large hernias may contain a significant portion of the liver. Immersion of organs is difficult or often impossible. The condition of the children is severe; cyanosis (blueness of the skin), adynamism, lethargy, often elevated body temperature and chronic intestinal obstruction are observed.
Diagnosis of umbilical hernia
A patient with an umbilical hernia is examined in a vertical and horizontal position. The reducibility of the contents of the hernial sac, the size, shape of the hernial orifice, and the consistency of the hernial contents are determined (the intestinal loop has an elastic consistency, the lobed structure of the soft consistency is the greater omentum).
For large hernias, to determine the nature of the hernial contents, an x-ray examination of the digestive tract is performed: - a survey x-ray of the abdominal organs.
Massage
This procedure is allowed within a couple of weeks after the baby is born. Namely: as soon as the umbilical wound has healed well. A pediatrician at our clinic can teach you this. Having mastered the principle and technique of therapeutic massage, you will be able to carry out the procedure yourself at home. What is the difference between massage for an umbilical hernia in a child? Its peculiarity is that before the manipulation, the hernia site is sealed with an adhesive plaster. This action is necessary in order not to injure the hernia and prevent its prolapse. Massage movements of the hands should be light and not forceful. There is no need to put pressure on the baby’s belly; try to do everything gently and carefully.
Carrying out the operation
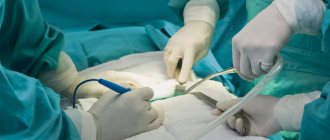
At the First Children's Medical Center, it is possible to perform an operation using open access (through an incision in the abdominal wall).
During the operation, the surgeon excises the hernia and pushes the contents into the abdominal cavity. Then manipulations are carried out with the tissues of the umbilical ring (strengthening the tissues to prevent relapse). After this, the navel is given an aesthetic appearance. As a rule, this type of operation lasts no more than half an hour.
Physiotherapy
Often, umbilical hernia in newborn children can be well cured with the help of therapeutic exercises. In our clinic, experienced specialists will select the necessary set of exercises for the child.
You can also do some exercises on your own at home. For example:
- before feeding the baby, place the baby on his tummy (for a couple of minutes);
- turn the child onto the left and right side alternately for a couple of seconds;
- turn the child to face you and, holding his head, tilt him back slightly;
- when the baby is lying on his back, carefully lift him by the arms, while supporting his back (the head and legs hang freely);
- Also, while lying on your back, carefully turn the baby onto his tummy;
- Place the baby on a bulky ball and roll it around, holding it by the legs.
Children under 8 years old can visit a trainer and do exercises with him. Such services are also available in our clinic.
Using an adhesive patch
This remedy can be used for newborns as soon as their umbilical wound has healed. The patch is glued so that a small fold is formed. The course of wearing the patch is 10 days. Typically, three courses are required with breaks in order to completely eliminate a hernia in an infant. The patch must be selected from a hypoallergenic material that allows air to pass through, so as not to irritate the baby’s sensitive skin. To ensure that the treatment of the disease is as effective as possible, it is recommended to combine the use of the patch with other methods. In this case, the result is more stable.
Rehabilitation period
This operation belongs to the so-called outpatient surgery. After direct surgery, the child spends 6 to 12 hours in the hospital, after which he is sent home. Before discharge, it is imperative to consult with your doctor to receive recommendations for caring for your child. It is very important to clean the wound daily and keep it clean. After a week (or 10 days), you must come to the Center to remove the stitches and observe the surgeon. It is worth noting that the rehabilitation period is quite easy, since almost all children tolerate such surgical procedures well.
Operation
Sometimes elimination of pathology is only possible through surgery. In our clinic, umbilical hernia surgery in children is performed using gentle and safe methods.
The surgeon prescribes surgical intervention in the following cases:
- the umbilical ring is 2 cm in diameter or more;
- the hernia is strangulated and must be removed immediately;
- the child in whom the pathology is detected is more than one year old, and the disease is constantly progressing;
- the child is 4-5 years old, but treatment of the hernia did not produce results.
If the protrusion is small, the operation is quick, about 20 minutes. Here an incision is made above the navel, then the umbilical ring is tightened. You can use laparoscopy instead of this method. This method of surgical intervention usually has no complications, and there are no scars after it.
If the protrusion is large enough, hernioplasty is used. In this case, the formation is first reduced, and then a special synthetic mesh (like a patch) is installed on the hernial orifice. Subsequently, the mesh fuses with the tissues of the body and prevents the formation of a new formation.
Surgery without hospitalization...
Up to 80% of all operations for surgical diseases in children can be performed in a one-day hospital setting. The specialists of the CELT Children's One-Day Hospital came to this opinion a long time ago—one of the first in our country. The advantages of a one-day hospital are obvious: reducing the waiting time for surgery, eliminating the psycho-emotional trauma of the child from separation from parents and maintaining the usual biorhythm during postoperative rehabilitation, reducing treatment costs due to the elimination of costs for a long hospital stay and paying for additional staff, eliminating the risk of intra-hospital infections. This primarily applies to diseases such as hernia. In the postoperative period, children do not require medical care, observation, regimen or diet. Rehabilitation at home is much faster and easier. The use of medications at home is limited to a single dose of an analgesic tablet on the first day.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Recovery after surgery varies. Children recover the fastest after laparoscopy. Since this method is the most gentle of all, rehabilitation here takes 2-3 days maximum. Most often, babies are discharged within a day after such an operation.
Now we’ll tell you how a child feels after an umbilical hernia operation performed in other ways. If the surgical intervention was planned and timely, then the rehabilitation period takes no more than 14 days. This means that the child was operated on while still in preschool age. In this case, there should be no complications. The doctor will prescribe the wearing of a postoperative bandage, as well as the diet necessary for the little patient. You will not be able to eat foods that can cause gas in the intestines for some time. Physical activity will also need to be temporarily reduced.
The rehabilitation process takes the longest for those children who were urgently hospitalized. If the operation was unplanned, the hernia was strangulated or the hernia sac ruptured, then a longer recovery will be required. Usually, a course of medications and physical therapy are also prescribed.
One day and no hernia!
Operations are performed under general anesthesia, specially designed for one-day hospitals. All medications used during surgery and for postoperative pain relief do not cause adverse or perverse reactions, which makes it possible to treat children with increased allergies and concomitant diseases. After the operation, the small patient is brought to the ward in a state of medicated sleep, where his parents or other loved ones are waiting for him, and where he is under the supervision of medical staff until he fully awakens. This achieves psychological comfort for both children and their parents, ensures the safety of postoperative awakening, and also neutralizes the elements of excitement characteristic of the post-anesthesia period. Treatment ends a week later with a visit to our Center for a follow-up examination of the child and removal of the suture.
How dangerous is a hernia, what are the complications?
It is important to know why an umbilical hernia is dangerous in a child. This will help avoid unpleasant consequences in the future.
If a hernia is strangulated or ruptured, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. This situation poses a threat to the baby's life. Although hernia rupture is uncommon, it is best not to neglect precautions.
Parents should be alert to the following signs of a possible strangulated hernia:
- the child feels sick and/or vomits;
- there are traces of blood in the stool;
- the hernia cannot be reduced in a supine position.
You should immediately seek medical help if your child is crying particularly hysterically and has a very swollen tummy. You need to pay attention to whether the color of the hernial sac or its density has changed. If you have one or more symptoms, it is important not to waste time, but to seek help from a clinic.
What leads to the formation of intervertebral hernias in children and adolescents?
- Injuries, blows to the spine, falls.
- Strength sports, excessive stress on the spine.
- Insufficient development of the child’s muscle corset, skeletal bones and connective tissue.
- Strong flexion and twisting of the spine in games or sports - for example, in gymnastics, somersaults, etc.
- Weakness of the body due to poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, environmental factors, and previous illnesses.
- Anatomical and genetic factors.
- Underweight or overweight.
Prevention
Many people are interested in the question of how to remove an umbilical hernia in a child? In this regard, disease prevention is very effective. Here are some preventive measures to help your baby stay healthy:
- breast-feeding;
- diet of a nursing mother, which excludes the consumption of foods that cause gas formation;
- It is necessary that the mother who is breastfeeding her baby eats a balanced diet, eats healthy and nutritious food;
- if the child is bottle-fed, it is necessary to carefully select the milk formula;
- it is necessary to ensure that the baby does not catch a cold and cries as little as possible - coughing and crying can also cause a hernia;
- It is useful to engage in physical education, swimming, and therapeutic massage sessions with your child.
Classification
There are several classifications of the disease according to certain criteria. The main thing is to distinguish types based on origin. There are two types:
- congenital or embryonic defects that occur in a child even at the stage of intrauterine development, they are caused by disturbances in the formation of the abdominal wall;
- acquired or postnatal hernias that develop in infants during the first 1–4 months of life.
Additionally, direct and oblique hernias are distinguished depending on the direction of the protrusion, as well as reducible and irreducible.