This hormone is produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries every month after ovulation and is responsible for regulating the menstrual cycle. Progesterone also helps the body prepare for pregnancy if the egg is fertilized.
After ovulation, the hormone progesterone causes the uterus to thicken and prepare to fertilize an egg. If the fertilized egg implants, it is responsible for maintaining the lining of the uterus throughout pregnancy. However, if the egg is not fertilized, the level of progesterone in the body drops, and this leads to the fact that women begin to menstruate. Progesterone is also responsible for breast growth during pregnancy. It also prevents lactation until the baby is born. Men produce a small amount of it, which contributes to the development of sperm.
What to do if there are already problems
All of them can be solved with the help of aesthetic gynecology. This branch of medicine can completely restore orgasmic function in those 70% of women who cannot live a full life.
Hyaluronic acid
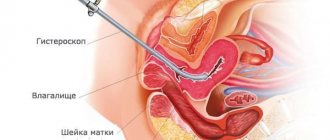
The injection of hyaluronic acid into the “G-spot” (clitoral legs) is very similar to the procedure for injecting fillers into the lips, which young girls love so much.
It is inserted into the legs of the clitoris to make them larger - in this case they will hang more into the vagina. As a result, during frictions the “G-spot” will finally be activated, due to which an orgasm will occur. Hyaluronic acid also helps when estrogens leave a woman. The mucous membrane immediately becomes dry, does not moisturize and does not produce natural lubrication. The procedure for intimate vaginal plastic surgery is carried out with a preparation that is not dense hyaluronic acid, which we inject into the lips, but, on the contrary, more liquid.
It literally pulls all the water onto itself, and if we insert it into the vagina, it will simply pull up all the moisture. In this case, there is no need for lubricants.
Kegel exercises
Regular Kegel exercises solve most problems - they prevent pelvic organ prolapse, strengthen muscles, and the vagina becomes more capacious.
As a result, the “G-spot” becomes easily accessible to the penis, which automatically eliminates anorgasmia. The same exercise is indicated if a woman has relaxed vaginal syndrome - muscle turgor improves, and the woman begins to feel something that she did not feel before.
Plasmolifting
During vaginal plasmolifting, we inject the woman with her own fibroblasts, which themselves are a source of their own hyaluronic acid.
The woman's blood is taken, passed through a centrifuge, and after some time we draw plasma into a syringe, which will remain on top of the tube. After this, we inject plasma into the vagina, and hyaluronic acid begins to do its job, that is, attract water to itself.
Often, after this procedure, women also no longer need artificial lubricants - we can renew the epithelium, moisturize it and “feed it with goodies.” Then both the clitoris and vagina will begin to please us again.
Laser treatment
The laser is a unique tool that can correct almost all problems.
Very often, patients who seek laser help have suffered from cancer. Often, due to the disease, women are forced to remove the uterus along with the ovaries, so estrogen ceases to be produced. Accordingly, the vaginal mucosa is very dry, and such women simply cannot be sexually active - when everything is removed, the vagina has nowhere to get hormones for its hydration. Due to dryness, the vagina becomes very thin - like the peel of an apple that should be juicy. New laser technologies turn a thin vagina into a thick one, because the better it is estragonized, the better - the vagina begins to moisturize again and produce its own hyaluronic acid.
The laser also combats vaginal relaxation syndrome - it is an ideal alternative to classical surgery. In fact, it does not affect the muscles in any way, but it can tighten the mucous membrane - it becomes elastic and contracts more strongly. Under the influence of a laser, the vagina narrows by 20%, and often this is enough for women.
At the top of the list of reasons why women end up in the gynecologist's office is vaginal discharge. They recur - patients are given treatment, and in the best case scenario we see them with the same problem six months later. Therefore, when we cannot cope with the problem with local treatment (suppositories, etc.), we move on to laser.
The vaginal tract as a whole, as well as the microbes in it, reflect the general condition of the body - we eat incomprehensibly what, we live in cities where only the name of ecology remains. All this is reflected in the vaginal tract. There are 10,000 germs in the vagina, and when this number increases, a woman begins to experience such problems. The laser renews the epithelium in the vagina - thanks to its effect, the vaginal walls begin to secrete glycogen, a nutrient material for lactobacilli.
They live only where they can eat, and leave the place where they cannot survive - then microbes take their place, which manifest themselves in secretions. The laser stimulates the layer of the vaginal walls and triggers the production of glycogen - lactobacilli begin to return, and the discharge goes away.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, member of the Association of Gynecologists and member of the Russian Association of Endometriosis Inna Davidovna Dzhidzhoeva.
Progesterone norms
Progesterone levels can be determined using a simple blood test. A progesterone test in men can be done at any time; the normal range is 0.2-1.38 ng/ml. On the other hand, progesterone testing in women should be done during a specific phase of the menstrual cycle.
Progesterone - role in the body, norms and excess
Progesterone levels in women are as follows:
- follicular phase of the ovarian cycle: 0.28 – 0.72 ng/ml
- periovulatory period: 0.64 – 1.63 ng/ml
- luteal phase of the ovarian cycle: 4.71-18.0 ng/ml.
The rate of progesterone in women after menopause is slightly different - then its concentration in the blood ranges from 0.07 to 1.25 ng / ml. On the contrary, the rate of progesterone in pregnant women is constantly increasing, and at 40 weeks it can even reach more than 150 ng/ml.
Why are high values dangerous?
Long-term hormonal imbalances can cause significant harm. Increased progesterone is no exception.
Hyperprogesteronemia causes complications and other diseases , which are then quite difficult to treat. The most dangerous are tumors and cysts of the pelvic organs.
With such an advanced hormonal disorder, an ovarian corpus luteum cyst is usually diagnosed.
This is a benign neoplasm that is formed as a result of the accumulation of fluid in the ovarian tissue. The cyst begins to intensively produce the hormone, so its high concentration is found in the blood serum.
This pathology can be successfully treated with drugs , and in rare cases, surgery is possible. In the worst case scenario, it may rupture, but this is an uncommon occurrence in clinical practice.
Dangerous consequences are malignant tumors, but they occur very rarely. These include lipid cell neoplasms or chorionepithelioma, which forms during pregnancy or after childbirth.
However, such serious pathologies account for only 1-3% of all gynecological diseases.
Hyperprogesteronemia can also manifest itself in the urological field. Adrenal dysfunction or kidney failure are possible consequences of late consultation with a doctor. Each person has an individual body, so it is impossible to say exactly what the consequences will be.
The mechanism of occurrence of some diseases has not yet been studied. In advanced cases of hyperprogesteronemia, the following clinical manifestations are possible:
- ovarian corpus luteum cyst;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- diseases of the adrenal glands, including oncology;
- renal failure;
- infertility;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- obesity.
All of these diseases can be treated with medication and surgery. But the main thing for the patient is not to start the pathological process. Early consultation with a doctor will avoid many complications and symptoms.
Low progesterone when planning pregnancy
home
Articles
Low progesterone when planning pregnancy
Much in a person’s life is determined by his hormones. They affect aspects of his life. And, naturally, during pregnancy they play one of the main roles.
Progesterone, or, as it is called, the pregnancy hormone, has a great influence on the process of implantation, growth and development of the fertilized egg, and on gestation in general. Low levels can cause interruption or delay in fetal development. Therefore, it is better to determine low progesterone when planning pregnancy, rather than during pregnancy.
It is produced even before fertilization and has a huge impact on the chance of conceiving a child, because it prepares the woman’s body. It is he who “holds” the zygote against the wall of the uterus. In other words, without progesterone, the body would reject the fertilized egg. By reducing the activity of the uterus, normal hormone levels during planning eliminate the possibility of miscarriage. It also helps the mammary glands produce milk.
To summarize, we can say the following about progesterone:
- Necessary for conception, and the survival of the fertilized egg, normal implantation.
- A normal level supports the embryo during gestation, strengthening the secretory endometrium in the uterus.
- It prevents the body from rejecting the fertilized egg and does not prevent miscarriages.
Therefore, identifying low progesterone levels at the stage of pregnancy planning allows a woman to bring the amount back to normal before fertilization.
A course of drug treatment to normalize the amount of progesterone in the blood is prescribed by a doctor individually based on blood tests. Remember that every body is unique and there are no universal methods. Entrust your treatment to specialists. Planning will help you prepare for conception.
Along with others, the list of mandatory studies during pregnancy includes TTG. It responds to any changes related to the thyroid gland.
During pregnancy, TSH stimulates the corpus luteum, preserving it in the early stages. Fetal organs, including the brain, develop under TSH control.
A low level of TSH leads to miscarriage, impossibility of conception, gestosis, placental abruption, and delayed fetal development.
Therefore, low TSH when planning pregnancy is a signal for treatment. Treating it before conception is much safer than putting the embryo at risk.
Get tested at the planning stage and the doctor will choose the best treatment strategy for you, tailored to your body, to correct low hormone levels.
Return to list
Progesterone levels after embryo transfer
Doctors recommend very carefully checking progesterone after embryo transfer, doing this on the day of transfer, then on days 3, 5, 7, 9 and 14. It is important to repeat the analysis many times, because even if the first 2-3 tests showed a good result, it does not mean that implantation has already taken place (this can happen up to 10 days inclusive).
To get the most accurate results, you need to donate blood in the morning, after 8-10 hours of fasting.
Progesterone should be maintained within normal limits, that is, not lower than 38.15 nmol/l (or 12 ng/ml in other units of measurement), but not higher than 57.8 nmol/l (or 18.2 ng/ml ).
The most dangerous situations are when the hormone level is low: there is a high risk of miscarriage. This should be corrected immediately with progesterone medications - in the form of injections, tablets or vaginal gel.
Less dangerous, but not very good when progesterone is elevated. It causes pathological changes in the endometrium, which also reduces the likelihood of implantation.
Diet
The clinical manifestation of the disease is sudden weight gain. Therefore, dietary nutrition plays an important role in the treatment and restoration of hormonal levels . It is necessary to strictly limit the consumption of protein foods, which slightly increase the hormone.
Protein foods include:
- cottage cheese;
- milk;
- cheese;
- beef meat;
- seeds;
- legumes;
- nuts;
- flour products;
- rice.
Eating these foods will not immediately increase progesterone levels, as they do not directly affect progesterone production. But there is an indirect effect on hormonal synthesis.
Foods rich in protein and cholesterol activate processes in the body that stimulate hormonal increases. In this case, it is advisable to consume carbohydrates (peas, potatoes, carrots, parsley, beets, onions).
Fruits and dried fruits are also beneficial for hyperprogesteronemia . They contain many vitamins and nutrients. Decoctions of red rowan, mint, and cloves are effective in restoring hormonal levels.
During pregnancy, it is not necessary to adhere to such a diet , except for the strict recommendations of a doctor who knows the clinical picture of the expectant mother.
But diet therapy is an auxiliary means of correcting the disease. This does not in any way replace the main treatment, which should play a major role in normalizing hormonal levels.