Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Eutirox is a drug created on the basis of a synthetic levorotatory isomer of thyroxine . Its use affects the growth and development of tissues and metabolic processes.
Small dosages can have an anabolic effect on fat and protein metabolism. Medium doses stimulate growth and development, metabolic processes, normalize the need for oxygen in tissues, as well as the functioning of the heart, blood vessels and nervous system. The development of the therapeutic effect appears after 7-12 days, remaining stable during this time and after treatment is discontinued.
Absorption of levothyroxine sodium occurs in the small intestine, directly in its upper section. Eating food affects the absorption of the active substance, significantly reducing it. The maximum concentration of the component is achieved 5-6 hours after application.
The main part of the drug binds to serum proteins. Thyroid hormones are then metabolized, primarily in the kidneys, liver, brain and muscle tissue. Excretion of metabolites occurs through the kidneys and intestines.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Eutirox
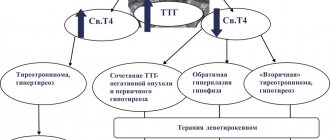
Synthetic levorotatory isomer of thyroxine. After partial conversion to triiodothyronine (in the liver and kidneys) and passage into the body’s cells, it affects tissue development and metabolism. In low doses it has an anabolic effect on protein and fat metabolism. In medium doses, it stimulates growth and development, increases tissue oxygen demand, stimulates the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and increases the functional activity of the cardiovascular system and central nervous system. In high doses, it inhibits the production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone of the hypothalamus and thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland. The therapeutic effect develops after 7–12 days, during which time the effect persists after discontinuation of the drug. The clinical effect for hypothyroidism appears after 3–5 days. Diffuse goiter decreases or disappears within 3–6 months. After oral administration, levothyroxine is almost completely absorbed in the upper small intestine. Up to 80% of the dose taken is absorbed. Eating reduces the absorption of levothyroxine. Maximum serum concentrations are achieved approximately 5–6 hours after oral administration. After absorption, more than 99% of the drug binds to serum proteins (thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxine-binding prealbumin and albumin). In various tissues, approximately 80% of levothyroxine is monodeiodinated to form triiodothyronine (T3) and inactive compounds. Thyroid hormones are metabolized mainly in the liver, kidneys, brain and muscles. A small amount of the drug is deaminated and decarboxylated, and is also conjugated with sulfuric and glucuronic acids (in the liver). Metabolites are excreted in urine and bile. The half-life is 6–7 days. With thyrotoxicosis, the half-life is reduced to 3–4 days, and with hypothyroidism it is extended to 9–10 days.
Contraindications for use
Taking the drug is contraindicated if:
- high sensitivity to its constituent substances;
- untreated thyrotoxicosis, pituitary and adrenal insufficiency;
- pregnancy in combination with antithyroid drugs.
It is not recommended to use Eutirox for the treatment of patients with acute forms of myocardial infarction, myocarditis and pancarditis . The lactose content in the drug makes it prohibited for use by patients with rare hereditary diseases associated with galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Caution in use requires such diseases as: coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia .
Instructions for Eutirox (Method and dosage)
As the instructions for use of Eutirox indicate, this medicine is taken orally. In this case, the daily dose is set individually, taking into account the indications and characteristics of the patient.
It is recommended to take the daily dosage in the morning, on an empty stomach. The tablet must be swallowed whole with liquid. When replacement therapy for hypothyroidism is carried out, the dose is determined depending on the weight of the patients. When treating children under 3 years of age, the medicine is given half an hour before the first feeding. The tablet must be dissolved in water until a thin suspension is formed.
Severe and long-term form of hypothyroidism requires initiation of treatment with caution and in small dosages. Then the dose is gradually increased to 25 mcg or more. In such cases, the drug is usually taken constantly, but strictly as prescribed by the attending physician.
Use of the drug Eutirox
The daily dose is determined individually, depending on the indications. Eutirox in a daily dose is taken as one whole tablet orally in the morning on an empty stomach 30 minutes before meals, washed down with a small amount of liquid (1/2 cup of water). When carrying out replacement therapy for hypothyroidism, patients under the age of 55 years in the absence of cardiovascular diseases are prescribed Eutirox at a daily dose of 1.6–1.8 mcg/kg, over 55 years of age or with concomitant cardiovascular diseases - 0.9 mcg/kg . In case of significant obesity, the dose should be calculated based on ideal body weight. Initial replacement therapy for hypothyroidism:
| Patients without cardiovascular disease or under the age of 55 years | Initial dose: women - 75-100 mcg/day, men - 100-150 mcg/day |
| Patients with cardiovascular disease or over 55 years of age | The initial dose is 25 mcg/day. The dose is increased by 25 mcg at intervals of 2 months until the TSH level in the blood normalizes. If the severity of cardiac symptoms increases, cardiac therapy should be adjusted |
Recommended doses of thyroxine for congenital hypothyroidism:
Age | Daily dose of thyroxine, mcg | Thyroxine dose per body weight, mcg/kg |
| 6 months | 25–50 | 10–15 |
| 6–12 months | 50–75 | 6–8 |
| 1–5 years | 75–100 | 5–6 |
| 6–12 years | 100–150 | 4–5 |
| 12 years | 100–200 | 2–3 |
Indications | Recommended doses of Eutirox, mcg/day |
| Treatment of euthyroid goiter | 75–200 |
| Prevention of relapse after surgical treatment of euthyroid goiter | 75–200 |
| In complex therapy of thyrotoxicosis | 50–100 |
| Suppressive therapy for thyroid cancer Thyroid suppression test | 50–300 4 weeks before the sample — 75 3 weeks before the sample — 75 2 weeks before the sample — 150–200 1 week before the sample — 150–200 |
For infants, the daily dose of Eutirox is given in one dose, 30 minutes before the first feeding. The tablet is dissolved in water until a suspension forms immediately before taking the drug. In patients with severe, long-term hypothyroidism, treatment should be started with extreme caution, with low doses of 12.5 mcg/day. The dose is increased to maintenance at longer intervals - by 12.5 mcg / day every 2 weeks and the level of TSH in the blood serum is determined more often. For hypothyroidism, Eutirox is used throughout life. For thyrotoxicosis, Eutirox is used in complex therapy with thyreostatics after achieving a euthyroid state. In all cases, the duration of treatment with the drug is determined individually.
Overdose
In case of an overdose of Eutirox, a significant increase in the rate of metabolic processes is possible. This leads to the development of hyperthyroidism , and especially when the individual threshold of tolerance to levothyroxine sodium , as well as a too rapid increase in the therapeutic dose.
In this case, such symptoms of overdose develop as: arrhythmia, tachycardia , heartbeat irregularities, angina pectoris , muscle and headaches, tremor, hyperemia, fever , vomiting, benign intracranial hypertension , anxiety, insomnia , hyperhidrosis , weight loss and so on.
Treatment depends on the symptoms that appear. It is possible that the doctor will reduce the daily dose or recommend taking a break or prescribing beta-blockers . As a result of taking excessively high doses, plasmapheresis . When the symptoms of overdose have resolved, treatment is resumed with caution, using small doses.
special instructions
Before starting replacement therapy with thyroid hormones and performing a thyroid suppression test, diseases or abnormalities such as acute coronary insufficiency, angina pectoris, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension , pituitary insufficiency or adrenal insufficiency should be excluded or treated. This also applies to the functional autonomy of the thyroid gland.
It is recommended to exclude the development of hyperthyroidism during treatment in patients suffering from coronary and heart failure, tachyarrhythmias . For this reason, it is necessary to regularly monitor the concentration of thyroid hormones.
If there is a suspicion of the occurrence of functional autonomy of the thyroid gland, then before treatment it is necessary to perform reactions to the administration of thyroid hormone-releasing hormone, known as the TRH test, as well as suppressive scintigraphy.
Postmenopausal women with diagnosed hypothyroidism and an increased risk of osteoporosis should not have high physiological concentrations of the active component in the serum. In this case, it is necessary to regularly monitor the functioning of the thyroid gland.
The use of levothyroxine sodium in metabolic disorders accompanied by hyperthyroidism. Exceptions include concomitant use of antithyroid drugs in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. In case of switching to treatment with another drug, dose adjustment is required taking into account the therapeutic effect and laboratory data.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Eutirox
In case of hypothyroidism caused by damage to the pituitary gland, it is necessary to find out whether there is insufficiency of the adrenal cortex. If present, corticosteroid replacement therapy should be started before treating hypothyroidism with thyroid hormones to avoid the development of acute adrenal insufficiency. The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles. The drug should be prescribed with caution for diseases of the cardiovascular system, such as atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction), arrhythmia; for diabetes mellitus, severe long-term hypothyroidism, malabsorption syndrome (dose adjustment may be required). During pregnancy, therapy with the drug prescribed for hypothyroidism should be continued. During pregnancy, it is necessary to increase the dose of the drug due to the increased level of thyroxine-binding globulin. The amount of thyroid hormone that is secreted in breast milk during lactation (even when using the drug in high doses) is not enough to cause problems in the child. Use during pregnancy in combination with thyreostatics is contraindicated, since the use of levothyroxine may require an increase in doses of thyreostatics. Thyrostatics, unlike levothyroxine, can cross the placenta, causing the development of hypothyroidism in the fetus. During breastfeeding, the drug should be used with caution, only in recommended doses and under medical supervision.
Interaction
Concomitant use of this drug with tricyclic antidepressants may enhance their effect.
Levothyroxine sodium reduces the effectiveness of cardiac glycosides.
Combination with cholestyramine, colestipol, aluminum hydroxide reduces the concentration of the active substance in plasma due to inhibited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, between doses of these drugs you need to maintain an interval of 4-5 hours.
The simultaneous use of Eutirox and anabolic steroids, asparaginase, tamoxifen can lead to pharmacokinetic interaction at the level of binding to plasma proteins. It has also been found that protease inhibitors, namely ritonavir + lopinavir and indinavir , can affect the effectiveness of this drug. It is necessary to monitor the concentration of thyroid hormones and make timely dosage adjustments.
Combination therapy with phenytoin often increases the concentration of levothyroxine sodium, accelerating its metabolism. This drug may reduce the effectiveness of hypoglycemic agents and enhance the effect of anticoagulants.
Use with sevelamer reduces the absorption of the active substance, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors, aluminum-containing, iron-containing drugs and calcium carbonate reduce its effectiveness. When consuming products containing soy, a decrease in the absorption of the active component in the gastrointestinal tract was noted.
Euthyrox®
The use of tricyclic antidepressants with levothyroxine sodium may lead to increased effects of the antidepressants.
Levothyroxine sodium reduces the effect of cardiac glycosides.
With simultaneous use of cholestyramine and colestipol (ion exchange resins), as well as aluminum hydroxide, they reduce the plasma concentration of levothyroxine sodium by inhibiting its absorption in the intestine. In this regard, levothyroxine sodium must be used 4-5 hours before taking these drugs.
When used simultaneously with anabolic steroids, asparaginase, tamoxifen, pharmacokinetic interaction is possible at the level of binding to plasma proteins.
Protease inhibitors (eg, ritonavir, indinavir, lopinavir) may affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium.
Close monitoring of thyroid hormone concentrations is recommended. If necessary, the dose of thyroxine sodium should be adjusted. Phenytoin may affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium due to the displacement of levothyroxine sodium from plasma proteins, which can lead to increased concentrations of free T4 and T3. On the other hand, phenytoin increases the rate of metabolism of levothyroxine sodium in the liver. Close monitoring of thyroid hormone concentrations is recommended.
Levothyroxine sodium may reduce the effectiveness of hypoglycemic drugs. Therefore, frequent monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is necessary from the start of thyroid hormone replacement therapy. If necessary, the dose of the hypoglycemic drug should be adjusted.
Levothyroxine sodium may enhance the effect of anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives) by displacing them from plasma proteins, which may increase the risk of bleeding, such as hemorrhage in the central nervous system or gastrointestinal bleeding, especially in elderly patients. Therefore, regular monitoring of coagulation parameters is necessary both at the beginning and during combination therapy with these drugs. If necessary, the dose of the anticoagulant should be adjusted. Salicylates, dicumarol, furosemide in high doses (250 mg), clofibrate and other drugs can displace levothyroxine sodium from binding to plasma proteins, which leads to an increase in the concentration of the free T4 fraction.
Orlistat: When orlistat is taken concomitantly with levothyroxine sodium, hypothyroidism may develop and/or decreased control of hypothyroidism may occur. The reason for this may be decreased absorption of iodine salts and/or levothyroxine sodium.
Sevelamer may reduce the absorption of levothyroxine sodium. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, imatinib, sunitinib) may reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, at the beginning or at the end of a course of concomitant therapy with these drugs, it is recommended to monitor changes in thyroid function in patients. If necessary, the dose of levothyroxine sodium is adjusted.
Medicines containing aluminum, iron and calcium salts: Aluminum-containing medicines (antacids, sucralfate) are described in the literature as potentially reducing the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, it is recommended to take levothyroxine sodium at least 2 hours before using aluminum-containing medications. This recommendation applies to the use of medications containing iron and calcium salts.
Somatropin, when used simultaneously with levothyroxine sodium, can accelerate the closure of epiphyseal growth plates.
Propylthiouracil, glucocorticosteroids, beta-sympatholytics, iodinated contrast agents, and amiodarone inhibit the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. Due to the high iodine content, the use of amiodarone may be accompanied by the development of both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Particular attention should be paid to nodular goiter with the possible development of unrecognized functional autonomy.
Sertraline, chloroquine/proguanil reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium and increase serum TSH concentrations.
Drugs that induce hepatic enzymes (eg, barbiturates, carbamazepine) may enhance the hepatic clearance of levothyroxine sodium.
In women using estrogen-containing contraceptives or in postmenopausal women receiving hormone replacement therapy, the need for levothyroxine sodium may be increased.
Consumption of soy-containing products may reduce the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, dosage adjustments may be necessary, especially when starting or stopping consumption of soy-containing products.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Thyroidin
Levothyroxine
Thyrotome
Tyreocomb
L-Thyroxine
The main analogues of the drug are represented by L-thyroxine and Levothyroxine sodium . Also have a similar effect: Thyroidin and Triiodothyronine hydrochloride.
Eutirox and weight
Many women suffering from thyroid disorders are concerned about the question: can weight gain occur during treatment with Eutirox. But reviews show that the use of hormonal drugs has different effects on both the weight of patients and their general condition. Therefore, in some women it increases, while in others it decreases.
For this reason, some believe that Eutirox can be used for weight loss, especially since at one time a number of hormonal drugs were actually used to adjust body weight, for example, in athletes. However, experts say that Eutirox for weight loss should not be taken without specific indications for this. Sometimes reviews for weight loss report successful cases, but usually this method of eliminating excess weight leads to serious deviations in the functioning of the body.
EUTIROX TAB 25MCG N100
The use of tricyclic antidepressants with levothyroxine sodium may lead to increased effects of the antidepressants.
Levothyroxine sodium reduces the effect of cardiac glycosides.
With simultaneous use of cholestyramine and colestipol (ion exchange resins), as well as aluminum hydroxide, they reduce the plasma concentration of levothyroxine sodium by inhibiting its absorption in the intestine. In this regard, levothyroxine sodium should be used 4–5 hours before taking these drugs.
When used simultaneously with anabolic steroids, asparaginase, tamoxifen, pharmacokinetic interaction is possible at the level of binding to plasma proteins.
Protease inhibitors (eg, ritonavir, indinavir, lopinavir) may affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium. Close monitoring of thyroid hormone concentrations is recommended. If necessary, the dose of levothyroxine sodium should be adjusted. Phenytoin may affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium due to the displacement of levothyroxine sodium from plasma proteins, which can lead to increased concentrations of free T4 and T3. On the other hand, phenytoin increases the rate of metabolism of levothyroxine sodium in the liver. Close monitoring of thyroid hormone concentrations is recommended.
Levothyroxine sodium may reduce the effectiveness of hypoglycemic drugs. Therefore, frequent monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is necessary from the start of thyroid hormone replacement therapy. If necessary, the dose of the hypoglycemic drug should be adjusted.
Levothyroxine sodium may enhance the effect of anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives) by displacing them from plasma proteins, which may increase the risk of bleeding, such as hemorrhage in the central nervous system or gastrointestinal bleeding, especially in elderly patients. Therefore, regular monitoring of coagulation parameters is necessary both at the beginning and during combination therapy with these drugs. If necessary, the dose of the anticoagulant should be adjusted. Salicylates, dicumarol, furosemide in high doses (250 mg), clofibrate and other drugs can displace levothyroxine sodium from binding to plasma proteins, which leads to an increase in the concentration of the free T4 fraction.
Orlistat: When orlistat is taken concomitantly with levothyroxine sodium, hypothyroidism may develop and/or decreased control of hypothyroidism may occur. The reason for this may be decreased absorption of iodine salts and/or levothyroxine sodium.
Sevelamer may reduce the absorption of levothyroxine sodium. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (eg, imatinib, sunitinib) may reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, at the beginning or at the end of a course of concomitant therapy with these drugs, it is recommended to monitor changes in thyroid function in patients. If necessary, the dose of levothyroxine sodium is adjusted.
Medicines containing aluminum, iron and calcium salts: Aluminum-containing medicines (antacids, sucralfate) are described in the literature as potentially reducing the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, it is recommended to take levothyroxine sodium at least 2 hours before using aluminum-containing medications. This recommendation applies to the use of medications containing iron and calcium salts.
Somatropin, when used simultaneously with levothyroxine sodium, can accelerate the closure of epiphyseal growth plates.
Propylthiouracil, glucocorticosteroids, beta-sympatholytics, iodinated contrast agents, and amiodarone inhibit the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. Due to the high iodine content, the use of amiodarone may be accompanied by the development of both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Particular attention should be paid to nodular goiter with the possible development of unrecognized functional autonomy.
Sertraline, chloroquine/proguanil reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine sodium and increase serum TSH concentrations.
Drugs that induce hepatic enzymes (eg, barbiturates, carbamazepine) may enhance the hepatic clearance of levothyroxine sodium.
In women using estrogen-containing contraceptives or in postmenopausal women receiving hormone replacement therapy, the need for levothyroxine sodium may be increased.
Consumption of soy-containing products may reduce the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine sodium. Therefore, dosage adjustments may be necessary, especially when starting or stopping consumption of soy-containing products.
Reviews about Eutirox
As reviews of Eutirox show, this drug is often used in clinical practice, since thyroid disorders worry many patients.
Basically, reviews of Eutirox 50 mcg report that this particular dosage is used in the treatment of most diseases. However, it is important to start therapy with small doses, for example, 12.5 mcg, then increase to 25 mcg and so on. The main thing is to do it gradually.
A large number of questions arise from patients who have recently been prescribed the drug. Therefore, they are interested in how to take tablets and Eutirox - is it a hormonal drug or not? Women are also concerned about whether various side effects actually develop during treatment and whether it can be used for weight loss?
Often, patients who take this medication report that it is well tolerated and has minimal side effects. Of course, important conditions are: strict adherence to dosage, timely testing and lifestyle changes.
Unfortunately, you can find messages in which patients report that they continue to experience severe pain, drowsiness, and depression. It has also been noted that some people experience weight loss or gain. In any case, all questions should be discussed with your doctor, which will allow you to replace the treatment or adjust the dosage.
Eutirox - treatment of thyroid diseases
Eutirox is a hormonal drug, the active substance of which is levothyroxine sodium, and belongs to the thyroid drugs. Eutirox is synthesized in the form of tablets. The tablets have a flat shape, on one side there is an engraving EM + dose of the drug.
The main therapeutic effect of the drug is to compensate for the lack of hormones secreted by the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is the main hormone of the gland; after absorption into the blood, it is transformed into the active hormone - triiodothyronine. The synthesis of thyroxine is carried out by gland cells under the direct control of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Eutyrox is an isomer of thyroxine, that is, it has the same composition and molecular weight compared to thyroxine, but differs in the arrangement of atoms in space, in particular, eutirox is a levorotatory isomer. The medicine also functions as the thyroid hormone thyroxine, which is synthesized by the body itself. In the liver, as well as the kidneys, eutirox is partially transformed into another hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). After this, T3 enters the cells, causing various effects. Eutirox causes dose-dependent effects. Thus, in small dosages, eutirox causes anabolic effects on various body metabolisms. With an average dosage of the drug, it accelerates cell growth, increases the need for tissues to receive oxygen, and in addition, stimulates metabolic processes, which is manifested by an increase in the functioning of the heart and nervous processes. If the doses are very large, the production of other substances is blocked (thyrotropin-releasing hormone of the hypothalamus, TSH of the pituitary gland).
The main therapeutic effect begins to appear a week and a half after eutirox enters the body. When you stop taking the medicine, the effect also remains for the same time. When treating diffuse goiter, a decrease in its volume occurs only after six months.
When compared with other drugs, eutirox, entering through the upper gastrointestinal tract, is absorbed into the blood only in the small intestine. It must be remembered that the medicine must be taken before meals, since food reduces the absorption of the drug. After entering the body, approximately six hours later, the concentration of the drug reaches its maximum in the blood. Eutirox, entering the blood, binds to proteins. Eutirox is deactivated in the liver, brain, muscles, and kidneys using various enzyme systems. The drug is excreted through the kidneys and intestines.
The main diseases for which a specialist prescribes eutirox are:
- hypothyroidism - a condition in which there is a long-term lack of thyroid hormones, due to a decrease in its work
- euthyroid goiter - proliferation of the thyroid gland,
— after surgery, in particular, removal of the thyroid gland, it is also necessary to constantly replenish the level of the hormone in the blood,
- with neoplasms of the gland, when there is a disruption of the thyroid gland,
- diffuse toxic goiter in a corrected state, when the patient is in a euthyroid state after taking antithyroid drugs.
Considering the effect of the drug on basic metabolic processes, it is very important to remember that the drug should not be taken in the following conditions:
Untreated thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism is a condition in which there is an increased production of thyroid hormones. The use of eutirox in this case will only worsen the patient's condition.
In case of uncorrected pituitary insufficiency, eutirox is also contraindicated. The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is responsible for the synthesis of T3 and thyroxine. In various diseases of the pituitary gland, the synthesis of many hormones is disrupted, so when prescribing eutirox, you need to know what the cause of the disturbances is and only after correcting them should you prescribe the drug.
Diseases of the adrenal glands, which can cause insufficiency of their work, are also a contraindication to the prescription of eutirox. If the adrenal glands malfunction, the production of hormones is disrupted, which have a negative effect on the heart and blood vessels, causing various rhythm disturbances. When taking Eutirox, the effect increases, which can lead to serious complications.
In addition, the drug is contraindicated in pregnant women who are taking antithyroid drugs.
You should also take the drug with extreme caution in the following conditions:
- for various heart diseases
- myocardial infarction, as it can aggravate the condition due to its effect on the heart and blood vessels,
- myocarditis - inflammatory processes in the heart
- pancarditis, with inflammation of all the membranes of the heart muscle.
In addition, the drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its various components. Eutirox should be taken with great caution in diseases such as myocardial ischemia, high blood pressure, cardiac dysfunction, and diabetes mellitus.
A feature of taking eutirox during pregnancy at different stages is an increase in dosage, which must be adjusted by the doctor based on test results. The dose is usually increased due to the fact that the level of thyroxine-binding globulin increases in pregnant women.
During lactation, if a woman takes the recommended doses of eutyrox, hyperthyroidism or suppression of TSH synthesis will not occur in the child. In addition, at therapeutic doses there are no teratogenic or fetotoxic effects. However, if the dosage is too high, there may be adverse effects on the fetus. If the dosage of eutirox is correct, no side effects were noted. There have been several cases of allergies to medication.
The use of eutirox requires a correctly selected dose of other medications taken, as it affects their concentration in the blood. Thus, it causes an enhanced effect of antidepressants. Eutyrox reduces the effectiveness of cardiac glycosides, so any specialist should know that the patient is taking levothyroxine. In addition, levothyroxine reduces the effectiveness of hypoglycemic drugs.
In any case, when taking levothyroxine, constant monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is required. In addition, when taking other medications, it is necessary to monitor their plasma concentrations or their effectiveness. Thus, levothyroxine enhances the effect of blood thinning drugs, which can increase bleeding from various sources (stomach, brain, and others).
Taking estrogen-containing contraceptives or postmenopausal women requires dose adjustment of eutirox.
The dosage of the medicine is selected individually depending on the disease, stage of the process, clinical picture, age and weight of the patient. The drug must be taken orally half an hour before meals.
If hypothyroidism lasts for a long time, the drug is usually given based on minimal dosages. After which, the dosage of the drug is increased every week, while the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone, as well as other metabolic indicators, is determined. If hypothyroidism is diagnosed, eutirox must be taken for life with constant monitoring of hormone concentrations in the blood. For other conditions, the duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
If the dose is chosen incorrectly, an overdose of the drug may occur. In this case, there is a significant increase in the rate of metabolism of various substances in the body. In this case, interruptions in the functioning of the heart may occur, muscle pain and headaches may appear, the temperature rises, and vomiting may occur.
If signs of overdose occur, it is necessary to either reduce the dosage of the drug or take a break from treatment. At significant high doses of the drug, plasmapheresis is required.
Another feature when taking eutirox is its possibility of developing psychosis. Therefore, predisposed patients require monitoring of hormone levels in the blood, as well as dynamic medical supervision.
Thus, the drug eutirox is the most effective remedy for the treatment of various pathological conditions of the thyroid gland.
treatment of thyroid diseases
Eutirox price, where to buy
The price of Eutirox 50 mcg for 50 pieces in Moscow pharmacies is 130-150 rubles.
You can buy Eutirox 50 mcg in online pharmacies for 106-130 rubles.
The price of Eutirox 100 mcg varies between 117-150 rubles, and Eutirox 25 mcg can be purchased for 86-100 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Eutirox tablets 125 mcg 100 pcs. Merck KGaA
153 rub. order - Eutirox tablets 88mcg 100 pcs.Merck KGaA
124 RUR order
- Eutirox tablets 25 mcg 100 pcs. Merck KGaA
98 RUR order
- Eutirox tablets 150mcg 100 pcs. Merck KGaA
RUB 159 order
- Eutirox tablets 112mcg 100 pcs.Merck KGaA
148 RUR order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Eutirox (tab. 88 µg No. 100) Merck KgaA
125 rub. order
- Eutirox (tab. 75 µg No. 100) Merck KgaA
127 RUR order
- Euthyrox (tab. 100 µg No. 100) Merck KgaA
127 RUR order
- Euthyrox (table 50 µg No. 100) Merck KgaA
106 rub. order
- Eutirox (tab. 137 µg No. 100) Merck KgaA
RUB 144 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Eutirox 25 mcg No. 100 tablets Merck KGaA, Nimechchina
107 UAH. order - Eutirox 50 mcg No. 100 tablets Merck KGaA, Nimechchina
121 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Eutirox tablets Eutirox tablets 150 µg No. 100 Germany, Merck KGaA
180 UAH order
- Eutirox tablets Eutirox tablets 25 µg No. 100 Germany, Merck KGaA
111 UAH order
- Eutirox tablets Eutirox tablets 50 µg No. 100 Germany, Merck KGaA
128 UAH order
- Eutirox tablets Eutirox tablets 125 µg No. 100 Germany, Merck KGaA
175 UAH order
- Eutirox tablets Eutirox tablets 100 µg No. 100 Germany, Merck KGaA
149 UAH order
show more