Humulin NPH, 100 IU/ml, suspension for subcutaneous administration, 3 ml, 5 pcs.
PC,
in the area of the shoulder, thigh, buttock or abdomen. IM administration is allowed.
The dose of Humulin® NPH is determined by the doctor individually, depending on the concentration of glucose in the blood. IV administration of Humulin® NPH is contraindicated.
The temperature of the administered drug should be at room temperature. Injection sites should be rotated so that the same site is used no more than approximately once a month. When administering insulin subcutaneously, care must be taken not to enter a blood vessel. After the injection, do not massage the injection site.
Patients should be trained in the correct use of the insulin delivery device. The insulin administration regimen is individual.
Preparing for the introduction
For the drug Humulin® NPH in vials.
Immediately before use, vials of Humulin® NPH must be rolled between the palms several times until the insulin is completely resuspended until it takes the form of a homogeneous cloudy liquid or milk. Do not shake vigorously as this may cause foam to appear, which may prevent the dose from being delivered correctly. Do not use insulin if, after mixing, there are flakes or hard white particles stuck to the bottom or walls of the bottle, creating a frosty pattern effect. Use an insulin syringe that matches the concentration of insulin injected.
For the drug Humulin® NPH in cartridges.
Immediately before use, Humulin® NPH cartridges should be rolled between the palms 10 times and rocked, turning 180° also 10 times until the insulin is completely resuspended until it takes the form of a homogeneous cloudy liquid or milk. Do not shake vigorously as this may cause foam to appear, which may prevent the dose from being delivered correctly. Inside each cartridge there is a small glass ball that makes it easier to mix the insulin. Do not use insulin if there are flakes in it after mixing. The design of the cartridges does not allow mixing their contents with other insulins directly in the cartridge itself. Cartridges are not intended to be refilled. Before giving the injection, you must read the manufacturer's instructions for using a syringe pen for administering insulin.
For the drug Humulin® NPH in the KwikPen™ syringe pen.
Before performing an injection, you must read the Instructions for Use of the KwikPen™ syringe pen.
Instructions for using the KwikPen™ syringe pen
The KwikPen™ syringe pen is easy to use. It is a device for administering insulin (insulin syringe pen) containing 3 ml (300 units) of an insulin preparation with an activity of 100 IU/ml. You can administer from 1 to 60 units of insulin per injection. You can set the dose with an accuracy of one unit. If too many units are set, the dose can be adjusted without losing insulin. The QuickPen™ syringe pen is recommended for use with needles manufactured by Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
for syringe pens. Before using the pen, you must ensure that the needle is completely attached to the pen.
In the future, the following rules should be followed.
1. Follow the rules of asepsis and antisepsis recommended by the attending physician.
2. Wash your hands.
3. Select the injection site.
4. Wipe the skin at the injection site.
5. Rotate injection sites so that the same site is used no more than approximately once a month.
Preparation of the KwikPen™ syringe pen and administration
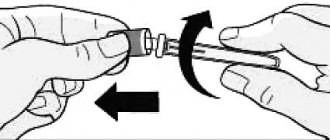
1. Pull the pen cap to remove it. Do not rotate the cap. Do not remove the label from the syringe pen. Make sure the insulin is checked for insulin type; expiration date; appearance. Carefully roll the pen 10 times between your palms and turn the pen over 10 times.
2. Take a new needle. Remove the paper sticker from the outer needle cap. Use an alcohol swab to wipe the rubber disc at the end of the cartridge holder. Place the needle in the cap straight along the axis onto the syringe pen. Screw the needle until completely connected.
3. Remove the outer cap from the needle. Don't throw it away. Remove the inner needle cap and discard it.
4. Check the KwikPen™ syringe pen for insulin supply. You should check your insulin supply every time. Checking the delivery of insulin from the pen should be performed before each injection until a stream of insulin appears to ensure that the pen is ready to administer a dose.
If you do not check your insulin before the trickle appears, you may receive too little or too much insulin.
5. Fix the skin by stretching it or gathering it into a large fold. Insert the needle subcutaneously using the injection technique recommended by the attending physician. Place your thumb on the dose button and press firmly until it stops completely. To administer a full dose, hold the dose button and slowly count to 5.
6. Remove the needle and gently press the injection site with a cotton swab for a few seconds. Do not rub the injection site. If insulin drips from the needle, the patient most likely did not hold the needle under the skin long enough. It is normal to have a drop of insulin at the tip of the needle and will not affect your dose.
7. Using the needle protective cap, unscrew the needle and discard it.
Even numbers are printed in the dose indicator window as numbers, odd numbers are printed as straight lines between even numbers.
If the dose required to deliver exceeds the number of units remaining in the cartridge, you can inject the remaining amount of insulin in the pen and then use a new pen to complete the required dose, or administer the entire dose required using a new pen.
Do not attempt to inject insulin by rotating the dose button. The patient will not receive insulin if he rotates the dose button. It is necessary to press the dose button along a straight axis in order to receive a dose of insulin.
Do not try to change the insulin dose during the injection.
Note.
The pen will not allow the patient to set an insulin dose greater than the number of units remaining in the pen. If you are not sure that the full dose has been administered, do not administer another one. You should read and follow the instructions contained in the instructions for use of the drug. The label on the pen should be checked before each injection to ensure that the drug has not expired and that the patient is using the correct type of insulin; Do not remove the label from the syringe pen.
The color of the dose button of the QuickPen™ syringe pen corresponds to the color of the stripe on the label of the syringe pen and depends on the type of insulin. In this manual, the dose button is shown in gray. The beige color of the body of the QuickPen™ syringe pen indicates that it is intended for use with the Humulin® line of drugs.
Storage and disposal
The syringe pen cannot be used if it has been out of the refrigerator for more than the time specified in the instructions for use.
Do not store a pen with a needle attached to it. If the needle is left attached, insulin may leak out of the pen, the insulin may dry out inside the needle, causing the needle to become clogged, or air bubbles may form inside the cartridge.
Syringe pens that are not in use should be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2 to 8 °C. Do not use the pen if it has been frozen.
The pen currently in use should be stored at room temperature, away from heat and light, and out of the reach of children.
Dispose of used needles in a puncture-resistant, lockable container (such as a biohazard or waste container), or as directed by your healthcare provider.
The needle must be removed after each injection.
Dispose of used pens without needles attached as directed by your healthcare provider and in accordance with local medical waste disposal regulations.
Do not recycle a filled sharps container.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Humulin NPH is a DNA recombinant human insulin with an intermediate duration of action, the main effect of which is to regulate glucose metabolism . The drug also exhibits anabolic effectiveness.
In the tissues of the human body (except for brain tissue), insulin Humulin NPH activates the transport of amino acids and glucose , and also accelerates the processes of protein anabolism . In parallel, in the liver, the drug promotes the formation of glycogen from glucose , stimulates the transformation of excess glucose into fat , and inhibits gluconeogenesis .
The onset of action of Humulin NPH insulin is observed 60 minutes after administration, with maximum effectiveness achieved in the period from 2 to 8 hours and a duration of action within 18-20 hours.
Observed individual differences in insulin depend on the choice of dose, injection site, and physical activity of the patient.
special instructions
decide whether to switch the patient to another drug or type of insulin . This change must take place under strict control of the patient's condition.
A change in the type of insulin activity (Regular , M3 , etc.), its type ( human , porcine , analogue ) or production method ( animal origin or DNA recombinant ) may require dose adjustments, both at the first administration and during therapy , gradually over weeks or months.
Insulin dependence may decrease with insufficiency of kidney , pituitary, adrenal , thyroid, and liver .
With emotional stress and certain pathologies, there may be an increased need for insulin .
Sometimes dosage adjustments are appropriate when changing your diet or increasing your physical activity .
In some patients, when using human insulin , the symptoms preceding hypoglycemia may differ from those when using animal insulin or be less severe.
Normalization of plasma glucose levels , due to intensive insulin therapy , leads to the disappearance of all or some manifestations of hypoglycemia , about which the patient must be informed.
Symptoms of advancing hypoglycemia may be smoothed out or changed in the case of concurrent use of beta-blockers , diabetic neuropathy or prolonged diabetes mellitus .
In some cases, local allergic manifestations may develop for reasons unrelated to the effects of the drug (for example, skin irritations due to the use of a cleansing agent or improper injection).
Rarely, systemic allergic reactions may require immediate therapy ( desensitization or insulin replacement ).
Due to the potential for symptoms of hypoglycemia , every precaution should be taken when performing hazardous work or driving a vehicle.
Side effects
The main side effect is hypoglycemia , which in severe cases can cause loss of consciousness and even death (rarely).
There is also a minimal likelihood of developing lipodystrophy .
Allergic manifestations of a systemic nature:
- generalized itching;
- dyspnea;
- labored breathing;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased sweating ;
- increased heart rate.
Local allergic manifestations:
- swelling or itching in the injection area (usually disappears within a few weeks);
- hyperemia.
Interaction
The hypoglycemic effectiveness of Humulin NPH decreases with concomitant use oral contraceptives , thyroid hormones, glucocorticoids , thiazide diuretics , tricyclic antidepressants , Diazoxide .
The combined use of ethanol , hypoglycemic drugs (oral), salicylates , MAO inhibitors, sulfonamides , beta-blockers enhance the hypoglycemic effects of Humulin NPH.
Reserpine , clonidine and beta-blockers can alleviate the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Overdose
As such, there is no specific overdose of Humulin NPH. Symptoms are considered to be manifestations of hypoglycemia , accompanied by increased sweating , lethargy, tachycardia , headache, pale skin, trembling , confusion , and vomiting.
In some cases, the symptoms that precede hypoglycemia ( long-term diabetes or its intensive control) may change.
Manifestations hypoglycemia are usually relieved by oral intake of sugar or glucose ( dextrose ). In the future, you may need to adjust your diet, insulin , or physical activity.
Correction of hypoglycemia is carried out by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of glucagon , followed by oral intake of carbohydrates .
Manifestations of severe hypoglycemia may be accompanied by coma , neurological disorders or seizures , which are localized by intravenous injection of concentrated glucose ( dextrose ) or subcutaneous or intramuscular administration of glucagon . In the future, in order to prevent recurrence of symptoms, it is necessary to eat foods rich in carbohydrates .