Ketoacidosis in diabetes is a condition that occurs when this disease decompensates due to an increase in the concentration of glucose and ketone bodies in the blood. It is characterized by the development of thirst, an increase in the volume of daily diuresis, dry skin, the presence of an acetone odor in the exhaled air and abdominal pain. On the part of the central nervous system, patients, as a rule, note headaches, increased irritability or lethargy, decreased performance, and lethargy. Ketoacidosis can be diagnosed based on laboratory biochemical tests.
Mechanism of development of decompensation
The development of ketoacidosis in diabetes is associated with insufficient insulin in the body. Without the influence of this pancreatic hormone, the utilization of glucose is impossible, so a situation develops that can be called “hunger among plenty.” In this pathological condition, there is enough sugar in the body, but its use as a source of energy is impossible.
At the same time, the release of adrenaline, cortisol, somatotropic and adrenocorticotropic hormone, and glucagon increases. This leads to a rapid increase in glucose levels in the body. Once the renal threshold is exceeded, it begins to be excreted through the kidneys along with a large volume of fluid and ions.
Due to blood thickening, tissue hypoxia develops, due to which glucose molecules are oxidized through the anaerobic pathway. This contributes to an increase in lactate concentration and the subsequent development of lactic acidosis. At the same time, the body tries to use fatty acids as an alternative source of energy, which serve as the basis for the formation of ketone bodies, which leads to the development of acidosis.
Causes of the pathological condition
Ketoacidosis appears in the following cases:
- When a very low dose of insulin is administered.
- Eating large amounts of carbohydrates.
- Missing a dose of insulin.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Severe stress.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- The presence of an infectious disease.
- Using ecstasy or cocaine.
When blood sugar levels are significantly higher than normal, hyperglycemia occurs in the body and the number of ketone bodies increases.
Causes of ketoacidosis
A number of factors can provoke the development of this condition, among the main ones:
- Disorders associated with injection administration of insulin. This may occur due to incorrect dosage, use of a drug that has expired, or unexpected malfunction of the syringe or pump.
- Wrong choice of therapy by the attending physician. In clinical practice, there are situations when the patient used tableted hypoglycemic drugs, while needing insulin therapy.
- Taking drugs with an effect that is opposite to insulin. Hormones and diuretics can cause high blood sugar levels.
- Associated with an increase in the interval between breakfast, lunch and dinner or an increase in the number of bread units in the diet.
- The use of antipsychotics, which reduce the body's sensitivity to insulin.
- A history of nervous disorders or alcohol dependence, since these diseases may interfere with receiving adequate treatment.
- Use of alternative treatment methods if insulin injections are necessary.
- The presence of concomitant somatic pathologies.
- Traumatization of the pancreas during surgery.
- Pregnancy occurring with severe toxicosis.
In every 4th patient, it is impossible to identify the true cause that served as the trigger for the development of ketoacidosis, since this condition cannot be associated with any of the factors that were listed. An increased need for insulin also occurs due to increased growth of the body, hormonal changes or nervous strain.
Who can develop ketoacidosis?
- Type 1 diabetes, especially in children, is often recognized when the patient is admitted to the hospital in a state of ketoacidosis. The patient feels unwell several days or even several weeks before, but does not suspect that the poor health is due to increased blood sugar.
- Ketoacidosis develops in all patients with type 1 diabetes if they stop taking insulin. As a rule, less than a day passes from stopping insulin administration to the development of ketoacidosis.
- In patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus with severe infections, purulent processes, heart attacks, strokes and other severe concomitant diseases.
- In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus during pregnancy.
- In case of inadequate treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus - infrequent control of blood sugar, skipping insulin doses, poor diet, use of spoiled or expired insulin.
Most patients with type 1 diabetes will experience diabetic ketoacidosis at least once during their lifetime.
Symptoms of ketoacidosis
Every patient with a history of this disease should be familiar with the clinical picture of decompensated diabetes mellitus. Among the main symptoms, special attention should be paid to:
- Increased thirst. This sign is the first alarm bell. If the concentration of glucose and ketone bodies is disturbed, a person begins to drink more water without getting full.
- Increased daily diuresis. Frequent visits to the toilet due to an increased urge to urinate are a symptom of the initial stage of ketoacidosis, since as it progresses, the amount of urine produced will rapidly decrease.
- The appearance of a specific odor. With the development of this pathological condition, the smell of acetone may be felt in the exhaled air.
- Drowsiness, decreased ability to work. Patients become slow and lethargic.
- Headache and slight dizziness.
As ketoacidosis progresses, loss of consciousness may occur.
Worsening of the patient's condition and decreased photoreaction of the pupils may signal the development of ketoacidotic coma.
Symptoms and warning signs
Signs and symptoms of fasting ketoacidosis may include:
- decrease in muscle mass
- decrease in body temperature
- minimal amount of body fat
- low heart rate
- obvious thinness
- caries
- sparse, thin, dry hair
- low blood pressure
The 2021 case report provides information on patients with mental disorders and starvation ketoacidosis. The authors conclude that making an accurate diagnosis may be more challenging for people with mental disorders because they may be unable to provide an accurate history of their health or eating habits. As a result, there may be a delay in treatment.
What to do with ketoacidosis and ketoacidosis coma?
It is important to understand that when this critical condition develops, the patient needs emergency medical care, which can only be provided in a hospital setting. The clinic uses the following areas to stabilize a person’s condition:
- Insulin infusion.
- Rehydration aimed at replenishing fluids, electrolytes, and pH correction.
- Treatment of concomitant somatic diseases.
Insulin therapy is aimed at eliminating biochemical changes in the body that led to the development of ketoacidosis. To increase concentration, it is administered in short doses of 4-6 units every hour. This helps to slow down lipolysis, the formation of ketone bodies and inhibition of glucose release by the liver, which has a beneficial effect on glycogen synthesis.
To rehydrate the body, the introduction of 0.9% saline solution with sodium chloride is used. With an increased level of sodium in the blood, fluid replenishment is carried out using a 0.45% solution. As the deficiency is eliminated, kidney function is restored, and glucose levels decrease due to its active excretion in the urine.
Correction of acidity also remains an important point. With adequate sugar concentration and sufficient fluid supply, stabilization of the acid-base balance occurs independently. The pH shifts toward the alkaline level, the synthesis of ketone bodies stops, and the restored excretory system copes with their removal.
How to check your ketone levels?
As DKA develops, symptoms appear quickly. If one or more signs are present, blood and urine are tested for ketone bodies. They appear in the blood much faster than in the urine. To prevent poisoning of the body, perform the following measures:
- A blood test is performed to check for the presence of ketone bodies. If your home glucose meter can do this, use it. All you have to do is insert the required test strip.
- Study the result obtained. A value up to 0.6 mmol/l does not require any action. This indicator is considered the norm. An average level of 0.6-1.5 mmol/l indicates the beginning of the formation of ketone bodies in the body. Over the next 1.5-2 hours, you may need the help of a doctor. A high content of ketone bodies (more than 1.5 mmol/l) requires immediate medical attention and behavioral caution.
The attending physician is informed of the diagnosis and adheres to the prescribed recommendations.
Prevention of ketoacidosis
With a timely and correct treatment plan, ketoacidosis can be stopped in a hospital setting. However, in the absence of the possibility of therapeutic measures, the pathological condition quickly develops into a coma. Mortality during its development is 5%, and in elderly patients (over 60 years old) - up to 20%.
Prevention of the development of ketoacidosis is based on education of people suffering from diabetes. Patients should know the initial symptoms of this pathological condition, the rules for injecting insulin, and the basics of monitoring glucose concentrations. Obtaining the maximum amount of information about the disease will help a person maintain a healthy lifestyle and adhere to the diet compiled by a nutritionist. It is important to remember that when the first signs of decompensation appear, you need to seek medical help to prevent the development of complications.
Diagnostics
Fasting ketoacidosis is uncommon in healthy people, as it occurs due to a lack of glucose in the diet after long periods of fasting.
Therefore, when fasting ketoacidosis occurs, the doctor may look for other causes of weight loss, which may delay diagnosis and treatment.
If you experience unexplained weight loss, be sure to tell your doctor about:
- any other symptoms
- your diet
- any underlying diseases
According to the 2021 article, the doctor first needs to stabilize the patient before performing necessary tests, including blood tests to check for electrolyte abnormalities and vitamin deficiencies. If a patient is diagnosed with fasting ketoacidosis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Fasting ketoacidosis is an uncommon form of ketoacidosis. It occurs when you don't eat enough food regularly or your body can't absorb nutrients properly.
A doctor can check for fasting ketoacidosis with blood tests and will need to monitor the patient as they begin to eat again.
Most healthy people are not at risk. However, those who suffer from eating disorders and those who have undergone certain medical procedures may be at higher risk of developing fasting ketoacidosis.
Full recovery is usually possible after treatment.
Video on the topic
About the causes, symptoms and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in the video:
To avoid the occurrence of a dangerous condition, the patient is recommended to become familiar with possible complications at an early stage when diagnosing diabetes. If, however, you were unable to control the situation in time, and ketoacidosis did occur, take immediate action.
If the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates, you should not self-medicate. Seek help from specialists to avoid dire consequences such as disability or death.
Treatment
Fasting ketoacidosis occurs when the body is deprived of essential food and energy for an extended period. While food may seem like an obvious treatment, it can be dangerous for those who have been undernourished for a long time.
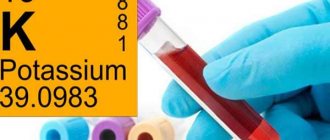
When a doctor treats a patient for fasting ketoacidosis, he or she needs to carefully monitor electrolytes. During the process of introducing food, doctors will need to check and restore the patient's potassium, phosphate and magnesium.
One case study involved an anorexic patient who developed fasting ketoacidosis. Doctors treated him with dextrose solution for 15 hours, during which time his ketoacidosis improved.
With proper treatment, including treatment for underlying conditions such as anorexia, the patient should make a full recovery.