Author - Sergey Aleksandrovich Tverezovsky
, surgical oncologist, mammologist, oncodermatologist, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category.
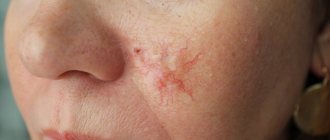
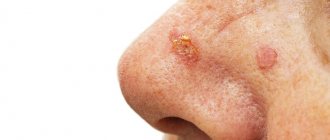
Cutaneous keratoma
is a general collective name for several types of benign skin tumors. In fact, it is a benign tumor growing from the surface layer of the skin - the epidermis. The cells of this layer are called keratinocytes, and tumors from them are called keratomas.
Normally, there is a certain balance between the formation of new skin cells and their desquamation. When this balance is disturbed, due to various reasons, a special type of benign skin tumors is formed in such places - keratomas.
Types of keratomas
Senile (age-related, senile) keratoma
is a gray-whitish formation that goes through stages from a spot to a plaque with crusts on the surface. With equal frequency, senile keratoma occurs in both men and women and is localized on any area of the skin.
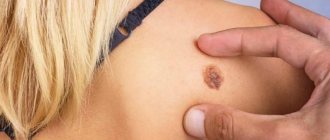
Seborrheic keratoma
– a slow-growing and slowly rising above the skin level (corresponding to the process of keratinization of the surface) plaque-like structure, often with clear, less often with blurred contours. The surface becomes keratinized and cracks, the color of the keratoma changes towards dark - gray-brown.
Horny keratoma or cutaneous horn
- a formation that has a conical or linear shape, rising above the skin level in the form of a horn or spike. A feature of this type of tumor, as well as transitional tumors similar to it, is an increased risk of malignancy into squamous cell carcinoma.
Follicular keratoma
- a rarer formation of gray-pink color, more often occurring in women, localized on the upper lip and on the skin of the forehead, neck, and near the hairline.
Solar, solar keratoma
or
actinic keratosis
- these neoplasms appear on areas of the skin exposed to direct sunlight (face, neck, outer side of the upper and lower extremities, upper back and chest), in the form of multiple dense foci of hyperkeratosis of light brown and dark brown color which are covered with grayish dry scales. Solar keratoma can also degenerate into basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma of the skin. Any of the above types of formations can be either single or multiple.
How dangerous is a keratoma?
For the most part, keratomas do not pose an oncological risk.
As mentioned above, keratoma keratoma and solar keratoma have an increased risk of malignancy. But what else is the danger of these skin formations? The fact is that even an experienced doctor is not always able to distinguish a keratoma from a malignant neoplasm using clinical methods.
Many malignant tumors at various stages of their development are similar to keratomas. Therefore, in all cases it is necessary to contact a dermatologist-oncologist; only a specialist can correctly diagnose and determine treatment tactics.
Also, keratomas can be dangerous due to complicated course. In the early stages of development, they cause only aesthetic inconvenience (which is important for women or when multiple keratomas are located in open areas of the body). But after the appearance and intensification of keratinization on the surface of the formations, additional complaints may occur - itching, pain, tingling in the area of the keratoma, with deep cracks and injury - the addition of an infection and the occurrence of inflammation, suppuration, with trauma and part of the crusts coming off the surface - severe bleeding.
To summarize: treatment of keratoma is necessary if malignant degeneration is suspected, with a complicated course, with rapid growth, as well as with aesthetic problems.
Classification of keratomas
Keratoma is a group of skin pathologies, among which there are several options:
- Senile keratoma is the most common type of neoplasm of this type. Looks like a brown spot. Tends to increase in size and at the same time change its structure, for example, becoming convex and soft, and may become loose. Its surface begins to peel off over time. This type of keratoma can disappear spontaneously, or it can transform into a cutaneous horn, which is prone to malignancy.
- Seborrheic keratoma. It grows slowly, and seborrheic multilayer crusts form on its surface. At the initial stages, the keratome looks like a yellowish spot, then, when the work of the sebaceous glands in them is disrupted, scales appear on the surface. Their thickness can reach one centimeter. The spots increase in size, merge with each other and change color to brown. If the keratoma is damaged, it bleeds and becomes painful.
- Cutaneous horn. It begins as a red spot, in its place the epidermis thickens and a tubercle forms. It is dense and rises above the skin (cases of cutaneous horn about 10 cm in height have been described). Its surface is uneven and peeling. Can transform into cancer. Horny keratoma can act as an independent disease or be a symptom of another pathology.
- Follicular keratoma is localized at the base of the hair. It looks like a flesh-colored knot. Its size does not exceed one and a half centimeters. In the center there is a cone-shaped depression with scales.
- Solar keratoma. At the initial stages it looks like multiple scaly pink papules. Gradually they grow and transform into plaques, around which there is an area of inflammation. The plaques are covered with scales, which have a dense structure, but are easily removed from the keratome. The disease is considered a precancerous condition because it is prone to spontaneous malignant transformation. At the same time, it can also disappear spontaneously, but then a relapse occurs in the same place. Solar keratoma is localized in open areas of the skin.
- Angiokeratoma is a group of neoplasms originating from skin capillaries with symptoms of keratinization disorder (hyperkeratosis). They look like burgundy elevations, dense to the touch.
Removal of keratomas: choice of treatment method
How to get rid of keratomas?
The doctor always chooses a method of elimination depending on the type of keratoma, its size, location, as well as the patient’s preference, his qualifications and equipment.
The appointment is conducted by an expert class doctor - oncologist surgeon, oncodermatologist, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category Sergey Aleksandrovich Tverezovsky.
Diagnostics
An appointment with a dermatologist begins with taking an anamnesis. The doctor clarifies how long ago the formation was, asks the patient about sensations - painful manifestations, itching, and studies the symptoms. Next, the skin is examined to determine the size and location of the keratoma. The instrumental method - dermatoscopy - allows you to clarify the diagnosis and exclude other skin diseases.
A special device allows you to identify the formation, examine the structure of its tissues, and the depth of its occurrence. The dermatoscope magnifies the image many times, so errors are excluded. And if there is a risk of the keratoma degenerating into a tumor, the doctor will determine this. In some cases, histology is recommended - the formation is sent to the laboratory to determine the cellular composition.
Laser removal of keratoma
The most common, delicate, low-cost and aesthetic option for eliminating keratoma is laser removal (our clinic uses a fractional CO2 laser).
We also use radio wave, electrocoagulation and surgical methods for removing skin keratoma, and use a combination of laser and radio wave elimination methods. The procedure for removing keratoma should be quick, painless, and least expensive, so that the patient receives the maximum aesthetic effect with a minimum recovery period. Both the laser or radio wave method and their combination completely solve these issues.
Laser removal of keratomas is performed on an outpatient basis, immediately after examination and digital dermatoscopy and has many advantages:
- Speed. Removal occurs not even in a matter of minutes, but literally in seconds;
- Painless. We use local anesthesia, and for small forms of keratomas, an application method of pain relief is possible;
- Complete sterility;
- Ease of wound care;
- Fast healing. For small keratomas it is 4-5 days, and for large ones - 2-3 weeks.
What is a keratoma and why does it appear?
Keratoma is a specific skin formation that is formed from epidermal surface cells. It can have different sizes - from a few millimeters to 3-5 centimeters in diameter. Typically, keratomas are brown, gray or brown in color, and may look like freckles. Over time, its surface becomes keratinized.
Content:
- What is a keratoma and why does it appear?
- Types of cutaneous keratomas known to doctors
- Why are keratomas dangerous and why do they need to be treated?
- Treatment of keratosis: what methods exist
- Treatment of neoplasms at home, traditional medicine
The formation grows precisely from epithelial cells, which have a multilayer structure, where each layer lies on top of each other. The outer layer of cells gradually dies, becomes horny and turns into scales, which fall off under mechanical influence, for example, during washing. They are replaced by deeper layers, which also die and fall away over time - this is how the continuous process of renewal of the skin takes place.
If normally the speed of the process of development of new cells and death of old ones is balanced in such a way that the number of newly appeared cells corresponds to the number of keratinized and dead cells, then in cases when a disorder occurs in this system, various formations are formed on the skin, including benign tumors from keratocytes - cells of the epidermis.
The formation is benign because it consists of unchanged cells, and appears only due to their excess quantity. However, on average, in 8-20% of cases, a keratoma can degenerate into a cancerous tumor if some external factors contribute to this, for example, excessive tanning or work associated with contact of toxic substances with the skin.
Keratomas can be single or localized in groups. They can be located on any part of the body, most often on the chest, neck, face, arms, and less often on the lower extremities.
The reasons for the appearance of these tumors are not yet fully known to medicine, but doctors emphasize that frequent and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays, on the beach or in a solarium, promotes the growth of keratomas.
Radio wave removal of keratoma
A modern and effective method that has advantages similar to laser. Removal of keratomas using the radio wave method does not require special preparation. It is bloodless and non-contact; it can be used to eliminate skin tumors in delicate areas, for example, to remove keratoma on the face without scars.
Is it possible to remove a keratoma surgically?
Surgical treatment of keratomas is also used, although very rarely.
Excision is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis, accompanied by the application of a neat cosmetic suture. An oncologist surgeon and oncodermatologist at our clinic uses excision for large keratomas - more than 4-5 cm, as well as when a malignant process is suspected. In all other cases, it is advisable to use more delicate, low-traumatic and aesthetic methods - laser and/or radio wave removal.
At the end of the discussion of removal methods, it is necessary to clarify once again - removal of keratomas should be carried out by an oncologist-dermatologist only after the required minimum preoperative examination (digital dermatoscopy, sometimes biopsy). Only after making sure that the skin formation is not malignant can you begin to eliminate it.
In each specific case, we decide on the need to send a remote lesion for histological analysis.
What are destructive (ablative) methods?
All skin tumors must be examined by a dermatologist before removal due to the risk of skin cancer. Treatment performed in a timely manner will help prevent the development of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) or squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (SCC).
- Cryosurgery using liquid nitrogen is the most common method for treating keratoses, but is not suitable for hyperkeratotic lesions. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed directly onto the affected areas of the skin using a cryodestructor or applied using the “reed” method (application with a cotton swab on a wooden stick). Cryosurgery is easily performed on an outpatient basis, shows excellent cosmetic results and is well tolerated.
- Radio wave, electro- and diathermo-laser destruction.
- Photodynamic therapy involves the application of a photosensitizing agent, methyl aminolevulinate, and then exposure to light of a specific wavelength, which leads to tissue necrosis. Photodynamic therapy is well tolerated and has excellent cosmetic results.
- Surgical removal . The surface of the skin is cleaned with a special instrument (curette).
- Chemical peeling:
- Jessner's solution (resorcinol, lactic and salicylic acids in ethanol);
- trichloroacetic acid solution 35%.
- Dermabrasion . The affected areas of skin are removed using a fast-moving abrasive brush.
- Phototherapy (IPL) and fractional photothermolysis - coagulation of keratosis elements using light energy. Suitable for the initial manifestations of actinic keratosis.
Prices for keratoma removal:
- Initial appointment with an oncologist-dermatologist
- 2,400 rubles. (candidate of medical sciences, surgeon, doctor of the highest category). The appointment includes digital dermatoscopy. - Removal of keratomas on the body
- from 900 rubles. (per unit, laser or radio wave method). - Removal of keratomas on the face and delicate areas
— from 1,300 rub. (per unit, laser or radio wave method).* when removing 4 or more tumors - a 10% discount on the initial price (for education of lesser cost).
- Histological examination of skin neoplasms
- RUB 3,500.
Removing keratomas at home
Removing keratomas at home is categorically unacceptable, since the patient is not able to independently assess the degree of aggressiveness of the process, as well as adequately eliminate the formation. The risk of getting a serious and sometimes life-threatening complication is extremely high. Do not self-medicate, trust your health to professionals.
Reasons for appearance
The exact causes of the disease have not yet been established. The main one is regular exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It affects the dermis, epidermal layers, blood vessels, sebaceous glands, and melonocytes.
Gradually, under the influence of sunlight, the disturbances increase, reaching the peak of the disease.
The following factors contribute to the development of pathology:
- genetic predisposition;
- weakened immune system;
- influence on the skin of chemicals (resinous substances, oil, sand, etc.);
- past infections;
- age-related changes (the disease most often affects people over 50 years of age).
Due to weak immunity, AIDS carriers, people with problems with the nervous and endocrine systems, as well as patients who have undergone chemotherapy or complex operations are more prone to the appearance of keratosis.
Some types of keratoses often affect young people. This usually applies to red-haired or fair-haired people with gray, blue or green eyes. Research shows that by the age of 40, 60% of the population has at least one element of keratosis.
Over the age of 80, everyone has some type of this pathology.
Our recommendations for gentle skin care:
- Do not expose your skin to friction or pressure.
- Avoid contact with chemicals, including household chemicals, on your skin.
- Be careful when working in the country - juices and pollen of harmful poisonous plants should not come into contact with the keratoma.
- Senile keratoma should not be exposed to ultraviolet irradiation. Apply sunscreen, wear wide-brimmed hats, closed clothing made of lightweight fabrics, in short, choose the protection methods that suit you.
- Try to eat as little junk food as possible that contains carcinogens and other harmful substances. Give preference to plant foods, reduce your consumption of meat (especially red).
And finally, we note once again - if you have a keratoma, do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor.
But following the general principles of proper nutrition, trying not to injure the tumor, not exposing it to sunlight and following other methods of preventing its growth is not only possible, but also necessary. We are always there and ready to help. Book a consultation with an oncodermatologist right now by calling the clinic: +7 (812) 952-83-73, and you will be able to undergo a thorough diagnosis and remove skin keratomas in 1 visit.
What are the symptoms of this disease? In what areas do they appear most often?
The patient, as a rule, may miss the onset of the disease and not pay attention to small irregularities, roughness, sometimes invisible to the eye, on the skin of the cheeks, bridge of the nose, ears, forearms, upper arms and forearms, back of the hands, back of the neck, upper chest, even on the scalp. Moreover, actinic keratosis can also develop on closed areas of the body that have been repeatedly exposed to the sun.
Developed actinic keratosis is represented by neoplasms from 0.1 cm to 2 cm or more. Over time, the spots become red or brownish in color and flake, and may rise above the skin in the form of growths. We most often see such patients at clinic appointments. Actinic keratosis usually develops very slowly and usually does not cause any discomfort other than aesthetic ones. Itching or burning in the affected area usually occurs in areas of long-term and severe keratinization. Most often, elements of skin keratosis develop slowly, but can disappear and reappear with repeated exposures that damage the skin. They can become inflamed and, in rare cases, even bleed.
Keratoma: how to treat?
To help the patient get rid of keratoma or actinic keratosis, the doctor prescribes a conservative or surgical treatment method. If drug therapy does not produce results, if the location of the formation is unsuccessful, if it is perceived as a cosmetic defect, surgery to remove the keratoma is prescribed.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment involves the use of various ointments, solutions or emulsions with active substances. It is immediately important to note that such methods are effective in the initial stages, when the stain has just appeared. Therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly not recommended, as it can cause complications in the form of damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Keratoma: how to remove surgically?
The keratoma is surgically removed using one of the following methods:
- laser method;
- cryodestruction;
- radiosurgery method.
The leader of choice is laser removal, since it minimizes the risks of negative consequences, bleeding, wound infection, and relapses. In a few minutes the formation is completely removed. And the wound heals within a few days.
Possible risks
Attempts to remove the keratoma yourself by tying it with thread or cauterizing it with aggressive media are strictly prohibited. This can lead to serious consequences, including the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer.