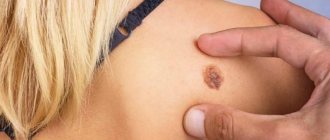
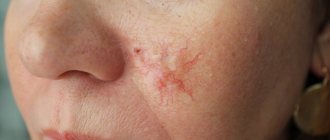
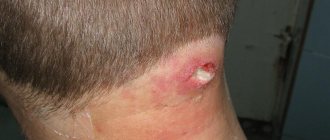
Keratoma is a benign formation on the skin that appears due to a local accumulation of horny cells of the epidermis. Outwardly, such manifestations resemble convex pigment spots with hard scales on the surface. And they are often located on the face, forearms, upper back, and arms.
Single or multiple keratomas are typical for mature people over 40 years of age. This skin pathology is rarely encountered in children and young people. They appear equally in men and women. Cases of self-healing have been recorded when formations of this type disappeared by themselves. But often raised dark spots reappear in the same areas of the skin.
Are keratomas dangerous? Do they need to be treated or not? How to get rid of keratomas at home? The specialists of the Medical Center for the Diagnostics of Moles “Lazersvit” have the answers to all these questions.
Keratomas: causes of appearance?
Keratoma, according to dermatologists, develops for one of two reasons - excessive ultraviolet radiation and the physiological processes of aging of the skin. The predisposition to the development of pathology, according to medical experts and geneticists, is inherited. But there are no clear reasons for the appearance of a formation, such as, for example, in condyloma, which is caused by the human papillomavirus. At one point, an accumulation of cells is observed, which leads to an anomaly.
Skin keratoma, as a rule, does not pose a threat to health. But dermatologists strongly recommend observing the spots. After all, individual formations have a tendency to reproduce and grow. And in rare cases, they degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
Causes of keratoma formation
Keratomas have a multifactorial etiology. First of all, age-related degeneration of skin cells is important. In addition, the following factors are important:
- Excess ultraviolet radiation.
- Age-related decrease in immune defense. As a consequence, intensive growth of epidermal cells and the formation of areas of hyperkeratinization and keratinization occur.
- Neuroendocrine pathology.
- Vitamin A deficiency.
- Endocrine disorders and sexual involution (menopause).
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Skin exposure to chemicals.
Why should a keratoma be observed?
The skin disease keratoma is considered by oncologists to be a borderline formation, especially in patients with an increased risk of cancer. The probability of malignancy into melanoma or basal cell carcinoma varies in different age groups in the range of 8-35%. For this reason, people who have one or more formations of this type are recommended to see a dermatologist. Regular visits to the doctor allow you to notice signs of degeneration in the early stages and begin treatment in a timely manner. Well, it’s better to remove the protruding spot in order to prevent even the minimal likelihood of pathological processes.
The risk of cancer is not the only reason to see a doctor. Keratoma on the face is perceived as a cosmetic defect, attracts the attention of others, and becomes the cause of complexes. A convex formation on the body can be injured by tight clothing or accessories. In this case, there is a threat of secondary infection.
Age-related keratoma “loves” to grow on the scalp. The formation is often damaged by a comb and hairdresser's accessories during cutting and styling.
Each case of keratoma requires an individual approach. And only a qualified doctor can give recommendations to the patient - treat or remove, ignore or observe.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of keratoma
Traditional medicine recipes can be used as additional therapy and only after consultation with a doctor!
Celandine ointment and a mixture of fir and sea buckthorn oil will help slow down the growth of the tumor. You need to lubricate the keratoma three times a day for two weeks. In parallel with the main treatment, you need to adjust your diet - doctors recommend consuming more citrus fruits, blueberries, beans, soy and green tea. According to recent studies, these products contain large amounts of vitamin P, which slows down the development of keratoma.
With timely diagnosis and qualified treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. For prevention purposes, doctors recommend minimizing exposure to direct sunlight and using body scrubs twice a week.
Classification
Keratomas are classified as follows:
- Seborrheic keratoma appears most often on the chest, back and scalp. Initially, this is a yellow-brown spot, the diameter of which can reach 3 cm. Over time, the surface of the formation becomes dense, and scales appear on it. The color changes to dark brown or black. Externally, this skin pathology looks like dried raisins stuck in the skin.
- Senile keratoma affects the skin of people over 35 years of age. A spot with a diameter of up to 2.5 centimeters appears on the skin. Over time, it thickens, becomes crusty, cracks, and changes color from yellow to black. The growth grows slowly, but over time it can protrude above the skin by a centimeter or even more. Senile keratoma, as this type of neoplasm is also called, is often localized on the shoulders, head, and back. Less common on the face and neck. Senile keratomas can grow in colonies. They also often become inflamed due to physical damage.
- Horny keratoma, which dermatologists often call “cutaneous horn,” has an increased risk of degeneration. First, a gray or brown spot appears on the skin, which eventually becomes covered with scales. A convex tubercle with a rough surface is suitable for placement of the arms, chest, and back. But other parts of the body are no exception. Sometimes patients are diagnosed with multiple horny keratomas.
- Follicular keratoma appears on the cheeks, lips, nose, eyelids. The skin first turns pink, then small tubercles grow at the site where the spot appears.
- Angiokeratoma is a nodular formation of red, black or blue color. Its size can reach 10 centimeters, but most often the growth grows to 2-3 centimeters. Often such skin pathologies form on the back, abdomen, legs and genitals.
- At the first stage, solar keratoma looks like a flat mole. Gradually it begins to peel off. Scales form on its surface. Dense lesions are often found in men over 40 years of age. Location: back, face, feet. Education is rarely singular. As a rule, this is a whole colony of growths. In some cases, degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma is diagnosed.
The type of keratoma and its risks for the patient are diagnosed by a dermatologist after examining the formation.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist
Removal of keratoma: main methods and their features
Keratoma removal is a surgical operation, a destructive method of treating skin diseases, which involves excision of excess epithelial formations. Keratoma is a special formation of the epidermis that is dark brown or yellowish in color, resembling a pigment spot. The size of a keratoma can range from small (a few millimeters) to large (several centimeters). Usually this is a single spot, but sometimes they can form small groups. Keratomas are not dangerous to health and usually do not cause significant discomfort to a person. They can go away on their own when the keratinized cells completely exfoliate and fall off.
Doctors say that keratoma is not hereditary, but is the result of the influence of negative environmental factors. The main one is exposure to ultraviolet radiation during uncontrolled exposure to the sun, due to which skin cells die and become keratinized, forming keratomas. Over time, they grow and change color to dark or yellow.
Keratoma is not at all life-threatening and is not a cause for concern. However, it can cause significant physical and aesthetic discomfort to a person. In addition, there is a possibility that when exposed to certain negative factors, it will degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The procedure for removing keratoma has multiple positive reviews. This is the best way to get rid of complexes and prevent the development of serious health problems. It is not recommended to remove keratoma at home. An operation to get rid of a skin tumor must be carried out in a medical clinic only by certified specialists in a way that is most suitable for the patient due to the individual characteristics of his body.
Diagnostics
An appointment with a dermatologist begins with taking an anamnesis. The doctor clarifies how long ago the formation was, asks the patient about sensations - painful manifestations, itching, and studies the symptoms. Next, the skin is examined to determine the size and location of the keratoma. The instrumental method - dermatoscopy - allows you to clarify the diagnosis and exclude other skin diseases.
A special device allows you to identify the formation, examine the structure of its tissues, and the depth of its occurrence. The dermatoscope magnifies the image many times, so errors are excluded. And if there is a risk of the keratoma degenerating into a tumor, the doctor will determine this. In some cases, histology is recommended - the formation is sent to the laboratory to determine the cellular composition.
For what reasons do acquired keratoses occur?
The main cause of almost all keratoses is said to be chronic exposure to ultraviolet rays. In the literature, all changes associated with sun exposure are often grouped under the term dermatoheliosis. Thus, the damaging effect can affect the epidermis (senile, actinic keratosis), dermis (solar elastosis), blood vessels (telangiectasia), sebaceous glands (porokeratosis) and melanocytes (dyschromia).
The effects of sun damage to the skin gradually accumulate as the total amount of time spent exposed to UV rays increases year after year. This leads to the fact that the peak incidence of this nosology occurs at the age of 50 years and older.
However, nowadays, actinic keratosis has become much more common in young people. As a rule, these are people of the first and second phototypes (with fair skin, blond or red hair, and blue, green or gray eyes). There is a high likelihood of developing keratoses in young people exposed to sunlight for a long time.
The incidence is slightly higher in men because they tend to use little or no sun protection. Clinical studies estimate that about 60 percent of predisposed individuals by the age of forty have at least one element of actinic keratosis. Some experts believe that almost everyone over the age of 80 suffers from some form of keratoses.
In addition, persons whose immune defenses are weakened by chemotherapy, extensive exposure to x-rays or a number of industrial chemicals, patients with AIDS, patients who have undergone organ transplants, patients with disorders of the nervous and endocrine systems, etc. less able to combat the effects of radiation and, therefore, more prone to developing keratoses.
Keratoma: how to treat?
To help the patient get rid of keratoma or actinic keratosis, the doctor prescribes a conservative or surgical treatment method. If drug therapy does not produce results, if the location of the formation is unsuccessful, if it is perceived as a cosmetic defect, surgery to remove the keratoma is prescribed.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment involves the use of various ointments, solutions or emulsions with active substances. It is immediately important to note that such methods are effective in the initial stages, when the stain has just appeared. Therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly not recommended, as it can cause complications in the form of damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Keratoma: how to remove surgically?
The keratoma is surgically removed using one of the following methods:
- laser method;
- cryodestruction;
- radiosurgery method.
The leader of choice is laser removal, since it minimizes the risks of negative consequences, bleeding, wound infection, and relapses. In a few minutes the formation is completely removed. And the wound heals within a few days.
Possible risks
Attempts to remove the keratoma yourself by tying it with thread or cauterizing it with aggressive media are strictly prohibited. This can lead to serious consequences, including the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer.
Treatment
Treatment includes drug therapy and surgical removal. Drug therapy involves the local use of cytostatics or other antitumor drugs selected according to an individual regimen. Treatment may require hospital stay.
Surgical methods for removing keratomas are varied:
- Traditional excision within healthy tissue using a scalpel. Used in cases of suspected cancer.
- Curettage of the hair follicle - the keratoma is scraped out with special instruments with sharp edges.
- Laser removal - using laser radiation, the tumor is evaporated layer by layer. In its place, a crust remains, which disappears after healing, and “young” skin remains in its place.
- Electrocoagulation - the tumor is excised under the influence of high-frequency electric current. It leads to local heating of tissues and their evaporation. At this point, they separate and form a cut. After removal, a wound with a crust remains in place, healing occurs, as after exposure to a laser.
- Radio wave surgery is a non-contact method of removal using radio waves. A modern, effective method with minimal risk of the formation of rough scars.
- Cryodestruction is the effect of liquid nitrogen on the keratoma, which leads to its immediate freezing and necrosis. After a few days it disappears on its own.
Surgical removal is performed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient can leave the clinic almost immediately.
Our clinic has all the necessary equipment for keratoma removal, and experienced specialists will offer treatment based on specific clinical features.
Book a consultation around the clock +7+7+78
Removal using radio waves
Radioknife, or radio wave surgery (Surgitron device) is the most universal method for removing dermatological tumors, which can be used even in hard-to-reach locations. As in the previous case, the method is based on heating and evaporation of cells under the influence of radio frequency waves. The technology allows for targeted effects down to several millimeters. The surrounding tissues are not affected. Another advantage of the method is a good cosmetic result - healing occurs practically without the formation of noticeable marks and scars.
Are there any new developments in this direction on the world market?
Well, for example, from 1998 to the present, the Australian biopharmaceutical company Peplin has been studying the topical treatment of actinic keratosis with the drug Ingenol Mebutate, which is the first in a new class of formulations and is derived from milkweed juice. This ingredient has a long history of traditional use for a variety of skin conditions, including the topical treatment of skin cancer and precancerous skin lesions. The company plans to enter the third phase of the trial soon.