Description of the medicine
ACC is available in several dosage forms:
- effervescent tablets with a dosage of 100 and 200 mg;
- effervescent tablets with an increased dosage of 600 mg (ACC Long);
- syrup with a dosage of 20 mg in 1 ml;
- powder for preparing a solution with a dosage of 100, 200 and 600 mg.
All types of the drug contain acetylcysteine as the main active ingredient.
Effervescent tablets have the shape of a flat cylinder and a score, white color and blackberry aroma. The finished medicine is colorless, transparent with a light berry aroma. Sold in cylindrical tubes of 10 or 20 pieces, which are placed in a cardboard box along with instructions.
The powder is white granules without inclusions, with a characteristic orange aroma. Sachets with powder are placed in boxes of 6 or 20 pieces, depending on the dosage of the main substance.
ACC syrup is colorless, transparent, and has a cherry aroma. Sold in 100 ml darkened glass bottles, placed in boxes, with an additional syringe or measuring cup.
ACC powder for the preparation of a solution for oral administration 200 mg in bags No. 20
Name
ACC por. dpr. orally 200 mg No. 20
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. The shelf life of granules for the preparation of oral solution (200 mg, 600 mg) is 3 years. The shelf life of granules for preparing an oral solution (orange) is 4 years. The shelf life of the syrup is 2 years; Once opened, the bottle should be stored for no more than 18 days at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Expiration date from date of manufacture
3 years
Product description
Granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration are white, homogeneous, without agglomerates and mechanical impurities, with the smell of lemon and honey; When sifting through a 1.5 mm sieve, no particles should remain on the sieve.
pharmachologic effect
Mucolytic drug. Acetylcysteine is a derivative of the amino acid cysteine. It has a mucolytic effect, facilitates the discharge of sputum due to a direct effect on the rheological properties of sputum. The action is due to the ability to break the disulfide bonds of mucopolysaccharide chains and cause depolymerization of sputum mucoproteins, which leads to a decrease in sputum viscosity. The drug remains active in the presence of purulent sputum. It has an antioxidant effect due to the ability of its reactive sulfhydryl groups (SH groups) to bind to oxidative radicals and thus neutralize them. In addition, acetylcysteine promotes the synthesis of glutathione, an important component of the antioxidant system and chemical detoxification of the body. The antioxidant effect of acetylcysteine increases the protection of cells from the damaging effects of free radical oxidation, which is characteristic of an intense inflammatory reaction. With the prophylactic use of acetylcysteine, there is a decrease in the frequency and severity of exacerbations in patients with chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and distribution Absorption is high. Bioavailability when taken orally is 10%, which is due to the pronounced “first pass” effect through the liver. The time to reach Cmax in blood plasma is 1-3 hours. Binding to blood plasma proteins is 50%. Penetrates through the placental barrier. There are no data on the ability of acetylcysteine to penetrate the BBB and be excreted in breast milk. Metabolism and excretion Rapidly metabolized in the liver to form a pharmacologically active metabolite - cysteine, as well as diacetylcysteine, cystine and mixed disulfides. Excreted by the kidneys in the form of inactive metabolites (inorganic sulfates, diacetylcysteine). T1/2 is about 1 hour. Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases Impaired liver function leads to an extension of T1/2 to 8 hours.
Indications for use
Respiratory diseases accompanied by the formation of viscous, difficult to separate sputum (acute and chronic bronchitis, obstructive bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngotracheitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, COPD, bronchiolitis, cystic fibrosis); acute and chronic sinusitis; Otitis media
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Due to insufficient data, the use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated. For syrup: use of the drug during pregnancy is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. If it is necessary to use the drug during lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding should be decided.
special instructions
For bronchial asthma and obstructive bronchitis, acetylcysteine should be prescribed with caution under systematic monitoring of bronchial patency. Severe allergic reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome have been very rarely reported with the use of acetylcysteine. If changes in the skin and mucous membranes occur, the patient should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a doctor. It is not recommended to prescribe the drug to patients with renal and/or liver failure to avoid additional formation of nitrogenous compounds. When dissolving the drug, it is necessary to use glass containers and avoid contact with metals, rubber, oxygen, and easily oxidized substances. You should not take the drug immediately before bedtime (the preferred time of administration is before 18.00). When prescribing the drug to patients on a diet aimed at limiting sodium intake, it is necessary to take into account that 1 ml of ACC® syrup contains 41.02 mg of sodium. There is no need for special precautions when disposing of unused ACC®. Instructions for patients with diabetes mellitus When treating patients with diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to take into account that ACC® in the form of granules for the preparation of oral solution (200 mg, 600 mg, orange 100 mg and 200 mg) contains sucrose. ACC® in the form of granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration /orange/ 100 mg and 200 mg: 1 sachet of 100 mg corresponds to 0.24 XE, 1 sachet of 200 mg - 0.23 XE. ACC® in the form of granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration 200 mg: 1 sachet corresponds to 0.21 XE. ACC® in the form of granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration 600 mg: 1 sachet corresponds to 0.17 XE. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery There is no information on the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
With caution (Precautions)
The drug should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers; for bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis; liver and/or kidney failure; histamine intolerance (long-term use of the drug should be avoided, since acetylcysteine affects the metabolism of histamine and can lead to signs of intolerance, such as headache, vasomotor rhinitis, itching); varicose veins of the esophagus; diseases of the adrenal glands; arterial hypertension. Contraindications Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase; hemoptysis; pulmonary hemorrhage; pregnancy; lactation period (breastfeeding); children under 2 years of age (syrup, granules for the preparation of solution for oral administration /orange/ 100 mg and 200 mg); children under 6 years of age (granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration 200 mg); children under 14 years of age (granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration 600 mg); fructose intolerance, because the drug contains sorbitol (granules for the preparation of an oral solution /orange/ 100 mg and 200 mg, granules for the preparation of an oral solution 200 mg and 600 mg); sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, glucose-galactose deficiency (granules for oral solution /orange/ 100 mg and 200 mg, granules for oral solution 200 mg and 600 mg); hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine and other components of the drug. The drug should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastric and duodenal ulcers; for bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis; liver and/or kidney failure; histamine intolerance (long-term use of the drug should be avoided, since acetylcysteine affects the metabolism of histamine and can lead to signs of intolerance, such as headache, vasomotor rhinitis, itching); varicose veins of the esophagus; diseases of the adrenal glands; arterial hypertension.
Directions for use and doses
Granules for preparing an oral solution (orange) 100 mg and 200 mg, granules for preparing an oral solution 200 mg. Adults and adolescents over 14 years of age are recommended to prescribe the drug 200 mg 2-3 times a day. The daily dose is 400-600 mg. Children aged 6 to 14 years are recommended to take 100 mg 3 times a day or 200 mg 2 times a day. The daily dose is 300-400 mg. Children aged 2 to 5 years are recommended to take the drug 100 mg 2-3 times a day. The daily dose is 200-300 mg. For cystic fibrosis, children over 6 years of age are recommended to take the drug 200 mg 3 times a day. The daily dose is 600 mg. Children aged 2 to 5 years - 100 mg 4 times a day. The daily dose is 400 mg. For patients weighing more than 30 kg with cystic fibrosis, the dose can be increased to 800 mg/day if necessary. For short-term colds, the duration of use is 5-7 days. For chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, the drug should be used for a longer period of time to prevent infections. For long-term illnesses, the duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician. The drug is taken orally after meals. Additional fluid intake enhances the mucolytic effect of the drug. ACC® in the form of granules for oral solution (orange) 100 mg and 200 mg dissolved in water, juice or iced tea. ACC® in the form of granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration, 200 mg, is dissolved with stirring in 1 glass of hot water and drunk, if possible, hot. If necessary, you can leave the prepared solution for 3 hours. Granules for preparing a solution for oral administration 600 mg Adults and adolescents over 14 years of age are recommended to prescribe the drug at a dose of 600 mg (1 sachet) 1 time/day. For short-term colds, the duration of use is 5-7 days. For chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, the drug should be used for a longer period of time to prevent infections. For long-term illnesses, the duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician. The drug is taken orally after meals. Additional fluid intake enhances the mucolytic effect of the drug. The granules are dissolved with stirring in 1 glass of hot water and drunk, if possible, hot. If necessary, you can leave the prepared solution for 3 hours. Syrup Adults and adolescents over 14 years of age are prescribed 10 ml of syrup 2-3 times a day (400-600 mg of acetylcysteine). Children aged 6 to 14 years - 5 ml of syrup 3 times a day or 10 ml of syrup 2 times a day (300-400 mg of acetylcysteine). Children aged 2 to 5 years are prescribed 5 ml of syrup 2-3 times a day (200-300 mg of acetylcysteine). For cystic fibrosis, children over 6 years of age are recommended to take the drug 10 ml of syrup 3 times a day (600 mg acetylcysteine); children aged 2 to 5 years - 5 ml of syrup 4 times a day (400 mg acetylcysteine). For short-term colds, the duration of use is 4-5 days. For chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, the drug should be used for a longer period of time to prevent infections. For long-term illnesses, the duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician. The drug is taken orally after meals. Additional fluid intake enhances the mucolytic effect of the drug. ACC® syrup is taken using a measuring syringe or measuring cup contained in the package. 10 ml of ACC® syrup corresponds to 1/2 measuring cup or 2 filled syringes. Using a measuring syringe 1. Open the cap of the bottle by pressing on it and turning it counterclockwise. 2. Remove the cap with the hole from the syringe, insert it into the neck of the bottle and press in until it stops. The stopper is designed to connect the syringe to the bottle and remains in the neck of the bottle. 3. It is necessary to insert the syringe tightly into the stopper. Carefully turn the bottle upside down, pull the syringe plunger down and draw the required amount of syrup (ml). If air bubbles are visible in the syrup, press the plunger all the way and then refill the syringe. Then return the bottle to its original position and remove the syringe. 4. The syrup from the syringe should be poured onto a spoon or directly into the child’s mouth (into the cheek area, slowly, so that the child can swallow the syrup). While taking the syrup, the child should be in an upright position. 5. After use, rinse the syringe with clean water.
Overdose
Acetylcysteine when taken at a dose of 500 mg/kg/day does not cause signs and symptoms of overdose. Symptoms: in case of an erroneous or intentional overdose, phenomena such as diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, heartburn, and nausea are observed. Treatment: symptomatic therapy
Side effect
According to WHO, undesirable effects are classified according to their frequency of development as follows: very often (?1/10), often (?1/100,
Compound
Active substance: acetylcysteine 200 mg; Excipients: sucrose - 2507 mg, ascorbic acid - 25 mg, sodium saccharinate - 8 mg, lemon flavor - 130 mg, honey flavor - 130 mg.
Interaction with other drugs
With the simultaneous use of acetylcysteine and antitussives, sputum stagnation may occur due to suppression of the cough reflex. With the simultaneous use of acetylcysteine and oral antibiotics (penicillins, tetracyclines, cephalosporins, etc.), the latter may interact with the thiol group of acetylcysteine, which can lead to a decrease in antibacterial activity. Therefore, the interval between taking antibiotics and acetylcysteine should be at least 2 hours (except for cefixime and loracarbef). Concomitant use with vasodilators and nitroglycerin may lead to an enhanced vasodilator effect.
Release form
Granules for the preparation of a solution for oral administration are white, homogeneous, without agglomerates and mechanical impurities, with the smell of lemon and honey; When sifting through a 1.5 mm sieve, no particles should remain on the sieve. 1 pack Active substance: acetylcysteine 200 mg; Excipients: sucrose - 2507 mg, ascorbic acid - 25 mg, sodium saccharinate - 8 mg, lemon flavor - 130 mg, honey flavor - 130 mg. 3 g - bags made of three-layer material (20) - cardboard packs.
How does ACC work?
According to the instructions, ACC is classified as a means of thinning mucus and facilitating its removal.
Acetylcysteine can make bronchial secretions less viscous. The mucolytic effect persists even if the sputum is mixed with pus.
This substance can also increase cell protection from the effects of severe inflammation and have a detoxic effect on the body.
In people diagnosed with cystic fibrosis or chronic bronchitis, preventive treatment helps reduce the number of exacerbations and make them easier to progress.
ACC®
A mucolytic agent that thins sputum, increases its volume, and facilitates the separation of sputum. The action is associated with the ability of free sulfhydryl groups of acetylcysteine to break intra- and intermolecular disulfide bonds of acidic mucopolysaccharides of sputum, which leads to depolymerization of mucoproteins and a decrease in sputum viscosity.
In addition, it reduces induced hyperplasia of mucoid cells, enhances the production of surfactants by stimulating type II pneumocytes, and stimulates mucociliary activity, which leads to improved mucociliary clearance.
Remains active against purulent sputum, mucopurulent and mucous sputum.
Increases the secretion of less viscous sialomucins by goblet cells, reduces the adhesion of bacteria to the epithelial cells of the bronchial mucosa. Stimulates mucous cells of the bronchi, the secretion of which is lysed by fibrin. It has a similar effect on the secretion formed during inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs. It has an antioxidant effect due to the presence of an SH group that can neutralize electrophilic oxidative toxins.
Acetylcysteine easily penetrates into the cell and is deacetylated to L-cysteine, from which intracellular glutathione is synthesized. Glutathione is a highly reactive tripeptide, a powerful antioxidant, cytoprotector that traps endogenous and exogenous free radicals and toxins.
Acetylcysteine prevents exhaustion and helps increase the synthesis of intracellular glutathione, which is involved in the redox processes of cells, thus promoting the detoxification of harmful substances. This explains the effect of acetylcysteine as an antidote for paracetamol poisoning.
Paracetamol exerts its cytotoxic effect through the progressive depletion of glutathione.
The main role of acetylcysteine is to maintain proper levels of glutathione concentration, thereby providing protection to cells. Protects alpha1-antitrypsin (elastase inhibitor) from the inactivating effects of HOCl, an oxidizing agent produced by myeloperoxidase of active phagocytes.
It also has an anti-inflammatory effect (by suppressing the formation of free radicals and reactive oxygen-containing substances responsible for the development of inflammation in the lung tissue).
What diseases does ACC help with?
Regardless of the form of release, ACC is used in the treatment of respiratory diseases, which are characterized by the formation of viscous secretions that are difficult to cough up.
The medication is prescribed for:
- tracheitis and laryngotracheitis;
- bronchitis (chronic, acute, obstructive);
- inflammation or abscess of the lungs;
- cystic fibrosis;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- bronchial asthma;
- inflammation of bronchioles;
- bronchiectasis;
- sinusitis in chronic or acute form;
- otitis media.
When ACC is contraindicated, possible adverse reactions
The drug in any dosage form is not prescribed for hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine or other substances included in the composition.
The manufacturer also lists general contraindications as:
- age up to two years;
- aggravated gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- coughing up blood, bleeding from the lungs;
- state of pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Effervescent tablets with a dosage of 100 mg are contraindicated in case of lactase deficiency, impaired absorption of substances in the intestines, or lactose intolerance.
According to the instructions, ACC 600 mg tablets and higher dosage powder are contraindicated for children under 14 years of age.
The powder is contraindicated in case of fructose intolerance, intestinal malabsorption syndrome, or sucrose deficiency.
Possible side effects of ACC have been studied in great detail. The main ones include:
- manifestations of allergies. In rare cases, itching, rashes, angioedema, increased heart rate, and a drop in blood pressure are possible. Anaphylactic shock is extremely rare;
- deterioration of the respiratory system: bronchospasms, breathing disorders;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract: the appearance of heartburn, pain in the abdomen, attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Very rarely, tinnitus, headache, and fever may occur.
ACC syrup
Release form
Syrup . Transparent, colorless, slightly viscous, with a cherry odor.
Compound
Active ingredient: acetylcysteine (20 mg/ml).
Excipients: methyl parahydroxybenzoate, sodium benzoate, disodium edetate, sodium saccharinate, sodium carmellose, sodium hydroxide, 10% aqueous solution, “Cherry” flavor, purified water.
Pharmacological group
Secretolytics and stimulants of motor function of the respiratory tract.
Action
Mucolytic agent with expectorant action. Acetylcysteine increases the volume of sputum, facilitates its discharge due to a direct effect on the rheological properties of sputum, and has an anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the formation of free radicals and reactive oxygen-containing substances responsible for the development of inflammation in the lung tissue.
Acetylcysteine: description of the substance
Indications
Respiratory diseases and conditions accompanied by the formation of viscous and mucopurulent sputum: acute and chronic bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngotracheitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, COPD, interstitial lung diseases and atelectasis due to blockage of the bronchi by mucus plug, sinusitis (to facilitate the passage of secretions), cystic fibrosis.
Inflammation of the middle ear, acute and chronic sinusitis, rhinosinusitis.
Contraindications and restrictions
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase,
- hemoptysis, pulmonary hemorrhage,
- lactation period (breastfeeding),
- children under 2 years of age,
- hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine and other components of the drug.
Carefully
- history of gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- bronchial asthma;
- liver and/or kidney failure;
- histamine intolerance (long-term use should be avoided);
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- arterial hypertension.
Application and dosage
Orally with additional fluid intake after meals.
The syrup is taken using a measuring syringe or measuring cup contained in the package.
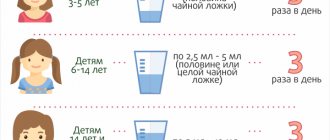
- Adults and children over 14 years of age: 10 ml of syrup 3 times a day;
- children from 6 to 14 years old: 5 ml of syrup 3-4 times a day;
- children from 2 to 6 years: 5 ml of syrup 2-3 times a day.
For cystic fibrosis
- Adults and children over 14 years of age: 10 ml of syrup 3 times a day;
- children from 6 to 14 years old: 5 ml of syrup 4 times a day;
- children from 2 to 6 years: 5 ml of syrup 3 times a day.
For long-term illnesses, the course of therapy is determined by the attending physician. For chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, the drug should be taken for a longer period of time to achieve a preventive effect against infections.
special instructions
1 ml of syrup contains 41.02 mg of sodium, which must be taken into account when using the drug in patients on a diet with limited sodium/salt intake.
Storage
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C. Shelf life: 3 years. Once opened, store the bottle for no more than 18 days at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Production
- Sandoz d.d. (Slovenia)
- Salutas Pharma GmbH (Germany)
- Pharma Wernigerode GmbH (Germany)
Package
A bottle of 100 or 200 ml along with a dosing device in a cardboard box.
Recipe
Available without a prescription.
How to take ACC
The dosage regimen and dosage of the drug depend on the patient’s age. ACC is taken orally and always after meals.
Syrup:
- adults and adolescents over 14 years of age - 10 ml twice or thrice a day;
- children 6-14 years old - 5 ml 3-4 times or 10 ml twice a day;
- children 2-6 years old - 5 ml twice or thrice a day.
ACC 100 mg (one tablet or one sachet):
- adults and adolescents over 14 years of age – 2 tablets/2 sachets twice or thrice a day;
- children 6-14 years old – 1 tablet/1 sachet three times a day or 2 tablets/2 sachets twice a day;
- children 2-6 years old - 1 tablet/1 sachet twice or thrice a day.
ACC Long adults and adolescents from 14 years of age take one effervescent tablet once a day.
Patients with cystic fibrosis are allowed to increase the dose of acetylcysteine to 800 mg per day.
Effervescent tablets must be dissolved in 200 ml of water; the solution should be drunk immediately after preparation. The powder is dissolved in non-hot tea, water or juice.
During therapy, it is advisable to drink more fluid to better thin the mucus.
The duration of treatment for coughing against the background of ARVI is no more than a week.
Chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis are indications for longer courses.
ACC powder
Release form
Powder for the preparation of solution for oral administration. White or yellowish in color, partially agglomerated, with an odor of orange or lemon and honey.
Compound
Active ingredient: acetylcysteine (100 or 200 mg for orange scent, 200 or 600 mg for lemon-honey scent).
Excipients:
- Lemon-honey - sucrose, ascorbic acid, sodium saccharinate, lemon flavor, honey flavor.
- Orange - sucrose, ascorbic acid, saccharin, orange flavor.
Pharmacological group
Secretolytics and stimulants of motor function of the respiratory tract.
Action
Mucolytic agent with expectorant action. Acetylcysteine increases the volume of sputum, facilitates its discharge due to a direct effect on the rheological properties of sputum, and has an anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the formation of free radicals and reactive oxygen-containing substances responsible for the development of inflammation in the lung tissue.
Acetylcysteine: description of the substance
Indications
Respiratory diseases and conditions accompanied by the formation of viscous and mucopurulent sputum: acute and chronic bronchitis, obstructive bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngotracheitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis. Inflammation of the middle ear, acute and chronic sinusitis.
Contraindications and restrictions
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase,
- hemoptysis, pulmonary hemorrhage,
- pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding),
- children's age up to 2 years (for a dosage of 100 mg), up to 6 years (for a dosage of 200 mg), up to 14 years (for a dosage of 600 mg),
- sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose deficiency,
- hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine and other components of the drug.
Carefully
- History of gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- bronchial asthma;
- obstructive bronchitis;
- liver and/or kidney failure;
- histamine intolerance (long-term use should be avoided);
- varicose veins of the esophagus;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- arterial hypertension.
Application and dosage
Inside after meals. Additional fluid intake enhances the mucolytic effect of the drug.
- Hot drink . Lemon and honey powder is dissolved in 1 glass (150-200 ml) of hot, but not boiling, water. Drink hot, but if necessary, the solution can be left for 3 hours.
- Cold drink . Orange powder is dissolved in 1 glass (150-200 ml) of water at room temperature.
Adults and teenagers over 14 years of age:
- ACC 600 mg. 1 sachet 1 time per day.
- ACC 200 mg. 1 sachet 2-3 times a day (400-600 mg per day).
- ACC 100 mg. 2 sachets 2-3 times a day (400-600 mg per day).
Children from 6 to 14 years old:
- ACC 200 mg. 1 sachet 2 times a day or 1/2 sachet 3 times a day (300-400 mg per day).
- ACC 100 mg. 1 sachet 3 times a day or 2 sachets 2 times a day (300-400 mg per day).
Children from 2 to 6 years old:
- ACC 100 mg. 1 sachet 2-3 times a day (200-300 mg per day).
- ACC 200 mg. 1/2 sachet 2-3 times a day (200-300 mg per day).
For short-term diseases, the course of treatment is 5-6 days. For long-term illnesses, the course of therapy is determined by the attending physician. For chronic bronchitis and cystic fibrosis, the drug should be taken for a longer period of time to achieve a preventive effect against infections.
For cystic fibrosis:
- Adults and children weighing ≥30 kg: if necessary, the daily dose can be increased to 800 mg per day.
- Children over 6 years: 600 mg per day.
special instructions
The drug contains sucrose, which must be taken into account when treating patients with diabetes.
When working with the drug, you must use glass containers and avoid contact with metals, rubber, oxygen, and easily oxidized substances.
Storage
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Shelf life - 3 years (lemon-honey), 4 years (orange).
Production
- Sandoz d.d. (Slovenia)
- Salutas Pharma GmbH (Germany)
- Lindopharm GmbH (Germany)
Package
Powder 3 g in a bag of three-layer material, 6, 10, 20 or 50 bags in a cardboard box.
Recipe
Available without a prescription.