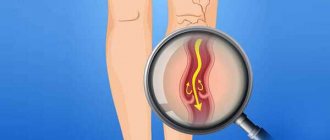
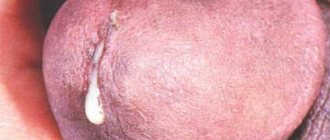
Varicocele is a varicose dilation of the vessels of the testicle or spermatic cord. The pathology impairs the functioning of blood vessels, increases venous pressure in the genital area, and often causes infertility in men.
The course is often asymptomatic or symptoms are not clearly expressed. In this case, varicocele can be diagnosed during a routine examination or when determining the causes of infertility.
Causes:
- genetic predisposition to varicose veins;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- regular physical activity, namely lifting heavy objects;
- the presence of tumors in the groin;
- excess body weight.
Statistics
Due to the anatomical features of the veins in the testicular area, varicocele most often forms on the left side. 80-95% are allocated to these cases. Right-sided testicular varicose veins are not so common (up to 8%). On both sides, varicocele occurs in 2-12 cases out of a hundred. Male disease is “linked” to the age of the patients. A large percentage (19) of problems with testicular veins are noted by doctors in adolescents. If we consider the reproductive age of men, then the statistics of varicose veins reach 35%. These are sad numbers, because... Varicocele in sexually mature men can cause infertility. Treatment of the disease should begin at the earliest stages.
What does it look like
A photo of a varicocele clearly demonstrates a male problem - the scrotum on one side (usually the left) is slightly lower. The skin covering the testicle does not hide the contours of the veins. When self-palpating the venous vessels, a man can feel their expansion. The patient may not even be aware of other symptoms of the disease. Palpation of the scrotum and visual examination are necessary actions for all men who care about their health. This is especially true for males planning fatherhood. You need to be regularly examined by a urologist. Medical examinations and consultations with qualified specialists are offered by the Global Clinic Center, which has extensive experience in the treatment of varicocele.
Postoperative period
During the first month after surgery, it is recommended to limit physical activity. It is also considered advisable to wear thick panties or swimming trunks for 2-3 weeks.
Subsequently, the patient should be regularly observed by an andrologist for at least 1 year.
At the discretion of the doctor, courses of antioxidant therapy, venoprotectors, and hyperbaric oxygenation can be used.
After the operation, strict observance of clinical follow-up is necessary.
History of the disease
Varicocele is a disease with deep historical roots. The first mention of the problem dates back to the 16th century and is associated with the name of Paré, a famous surgeon of the Renaissance. He drew attention to the pathology of the venous vessels near the male testicle. Many medical historians speak of the involvement of Hippocrates and Celsius in establishing the facts about this problem. The topic of varicocele is very closely related to infertility. In the 19th and 20th centuries, scientists confirmed the possibility of curing male infertility in direct proportion to the elimination of testicular varicose veins.
Preventive measures
An annual visit to the urologist, even in the absence of any complaints or symptoms, in combination with a healthy lifestyle, decisive and unconditional cessation of bad habits (primarily smoking) and active sports is the best set of preventive measures at any age. You should also pay attention to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and take care to exclude fatty, fried and spicy foods from your diet. Clothing should be comfortable and not constrict the genitals. It is important to remember that hypothermia of the body is an additional provoking factor for the occurrence of varicocele or its progression.
Varicocele. Symptoms
The danger of the first stages of the disease is that it is asymptomatic. The problem is discovered by chance, during medical examinations or when patients address other male issues (for example, in connection with infertility). Symptoms of varicocele characteristic of other degrees of the disease:
- nagging pain and discomfort in the left side of the scrotum, testicle and groin area;
- drooping left (mostly) testicle, interfering with walking;
- decrease in the size of the testicle on the left;
- manifestation of the contours of venous vessels;
- appearance of pain.
Varicocele is characterized by symptoms manifested in a decrease in the number of sperm and a decrease in their motility, in this case it is worth talking about male infertility. When doctors try to find out the cause of male infertility and analyze various symptoms in a patient, they often discover a varicocele, using the most modern diagnostic methods.
Causes and risk factors for the disease
In the veins surrounding the spermatic cord, a malfunction of the valve occurs, which prevents blood from flowing back. Instead of rising upward, the blood stagnates, because... is transmitted in the opposite direction. Because of this, the venous vessels become dilated and weak. The causes and risk factors of varicocele are associated with the appearance of primary and secondary reflux. The abnormal structure of the veins associated with congenital pathology leads to the complete absence of valves for the reverse outflow of blood or their atypical operation. During puberty, blood pressure on the vessels increases, and varicose changes occur in the veins near the spermatic cord. The weak walls of blood vessels inherited from birth by boys cannot cope with the flow of blood during physiological changes. As a rule, varicocele is inherited, so this should be taken into account in case of male infertility and comprehensive treatment of testicular varicose veins should be carried out. Secondary reflux occurs when the blood outflow valves stop functioning normally due to problems in the renal or vena cava. Varicose veins most often occur on the left side, because it is on the left that the venous vessels meet the renal vein. Narrowing of the lumen in the latter structure can cause varicocele. Unfavorable factors for testicular varicose veins:
- haemorrhoids;
- phlebeurysm.
The following are considered as a trigger for the appearance of varicocele:
- Hard physical labor.
- Extreme loads in sports or weight lifting.
- Lack of normal sex life.
- Professions that require long periods of standing.
- Chronic constipation.
Prevention
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Simple physical exercises aimed at improving blood circulation and relieving congestion in the pelvic organs, avoiding heavy physical activity, and regular sexual relations can stop the development of the disease. Normalization of stool, avoidance of alcoholic beverages, and consumption of fortified foods or vitamin preparations prevent the appearance of varicocele.
A healthy lifestyle and good nutrition help get rid of many problems, including preventing varicocele.
Complications
The main thing that patients suffering from testicular varicose veins need to understand is the serious situation with the appearance of offspring. Infertility can become a sad complication of varicocele, so you should not delay going to the clinic for diagnosis and treatment. Doctors from the Global Clinic Center can provide qualified assistance. Statistics show that patients diagnosed with varicocele in 60 cases out of a hundred are faced with the problem of sperm dysfunction. 40% of men with testicular varicose veins become infertile.
Statistics on varicocele: why you need to see a urologist during puberty
The content of the article
Typically, pathology develops in young men during puberty. It is during this period that the disease reaches its peak, which, with timely detection and treatment, can be prevented.
Statistics show how high the risk of remaining infertile is for any young man who does not attend routine examinations with a urologist. According to her data, every fifth man over the age of 17 suffers from varicocele. In a third of cases, the pathology reduces the ability to conceive (fertility).
Diagnostics
To effectively treat the disease, you need to use all diagnostic methods. To detect varicocele, experienced specialists only need to visually examine the patient and palpate the plexus of testicular venous vessels in the form of a cluster. The man is examined in a standing position, in a calm state. To clarify the results of palpation, the patient is asked to tense the abdominal muscles (Valsalva maneuver) to improve the filling of testicular vessels with blood. In this case, the study of the enlarged area will be more complete. This will help in diagnosing grade 2-3 varicocele; if the problem is not expressed, you will need the help of modern equipment. Ultrasound and doplegraphic examination of the scrotum is necessary to clarify the diagnosis. The patient must be examined in two positions - standing and sitting. To rule out infertility, a man needs to have a spermogram. One semen examination is not enough; examination in the interval from 4 to 12 weeks will make the diagnosis more accurate. This diagnosis is very informative; it can be used to determine the type of varicocele, obtain data on the size of the testicle, the location of diseased veins, and thickening of the spermatic cord.
Advantages of Marmara microsurgery:
- A small cosmetic incision in the groin area, in the hair growth area (the scar is almost invisible)
- The greatest efficiency of the operation is achieved through the use of operating binoculars and microsurgical instruments
- Lowest percentage of relapses and complications (less than 5 percent)
- Can be performed on an outpatient basis, without hospitalization
- Short and easy postoperative and recovery period
I am aware of my responsibility for preserving the main thing that my patient trusts me, and I will do everything to justify the trust!
Classification
The degrees of the disease are classified based on the dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord and testicle. The development of varicocele is divided into 4 degrees. They speak of zero degree if the symptoms of the disease cannot be determined visually or by manual palpation. Only instrumental examination (most often when diagnosing other problems) reveals varicocele. Grade 1 is diagnosed when the dilation of the veins cannot be palpated with the patient lying down, only standing. In patients with the 2nd degree of the disease, the doctor feels with his hands an increase in the venous vessels of the spermatic cord and testicle in men who are sitting and standing. To determine the third degree of varicocele, a visual examination of the patient is sufficient. If we consider testicular varicose veins from the point of view of the location of the pathology, then we distinguish left-, right- and bilateral varicoceles. Subclinical and clinical types of the disease are classified depending on physical examination methods.
Stages of development of testicular varicose veins
Varicocele begins with a mild form and gradually progresses. At the same time, the pathology does not always reach its climax; varicose veins can stop developing, remaining undetected.
The disease occurs in 4 stages:
- Symptoms of varicocele are hidden.
The veins of the testicle are not visible or palpable. Dilatation of the veins is detected on ultrasound of the scrotum. That is why preventive ultrasound examination is recommended for all young men at the age of 17-18 years. - The veins are palpated in a horizontal position.
In the supine position no changes are noticeable. - Veins can be palpated in any position.
- Dilated veins are greatly enlarged and visible
. If severely disturbed, they may even hang down. Pain appears.
Spermagenesis is disrupted gradually, which leads to infertility. The brighter the signs, the more reasons to suspect a male factor in infertility.
Treatment
The problem of varicose veins in the vessels of the spermatic cord and testicle cannot be eliminated. Improper operation of the blood outflow valves can be corrected through surgery. Surgical treatment of varicocele is the main method. The effectiveness of medication use is insignificant. Only the first stages of the disease can be treated conservatively. Consultation with a doctor and a joint decision on surgery for varicocele are mandatory. Surgical intervention is not always necessary for the patient. If the disease does not bother the man too much, or the patient is of advanced age, then doctors advise not to undergo surgery. A variety of surgical methods helps doctors find the only correct method. The essence of the operation for varicocele is to ligate the venous pathological vessels and normalize the outflow of blood. To save the results obtained during the operation, you should:
- limit physical and sexual stress;
- come to your doctor for examination.