Interferons are a special class of drugs that affect the immune system and have antiviral, antitumor and immunomodulatory effects.
Interferon preparations are similar to natural human interferons, which are complex proteins produced in our body in response to viruses. Interferons prevent viruses from entering cells and also block the proliferation of viruses in the body.
In addition to viruses, interferons are able to neutralize cancer cells, preventing the progression of tumor diseases.
Interferons also act as immunomodulators - agents that normalize immunity. Interferons increase decreased immunity and slightly inhibit increased immune response.
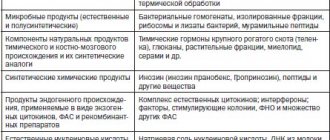
In addition to drugs, in fact, interferons themselves, there is a separate class of drugs: inducers of interferon synthesis, which increase the body’s production of its own (endogenous) interferons.
Indications for use
Interferon preparations are used for the prevention and treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections (including in newborns), as well as for the treatment of viral eye diseases (conjunctivitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis, keratouveitis caused by herpes viruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses), acute and chronic viral hepatitis B, C and D, genital warts, tick-borne encephalitis, meningoencephalitis.
In addition, interferon preparations are used in the treatment of oncological diseases (hairy cell leukemia, multiple myeloma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Kaposi's sarcoma due to AIDS, chronic myeloid leukemia, melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, cancer of the bladder, kidney, ovary, larynx, reticulosarcoma).
Interferon preparations are also used in women for urogenital infections, including sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, mycoplasmosis).
Interferon beta preparations are also used in the complex treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Inducers of interferon synthesis are used for viral hepatitis A, B and C, infectious-allergic and viral encephalomyelitis, for the prevention and treatment of influenza and other colds, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, chlamydia.
Inducers of interferon synthesis are additionally indicated for the treatment of chronic sluggish infections of the respiratory and urinary tract, as well as in patients who have suffered acute colds with incomplete recovery (bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis), who are often ill in the autumn-winter period.
Counteracting viruses to the body's immune system
Different types of viruses have learned to block the first signaling pathway – the induction of interferon synthesis. Moreover, they block the second signaling pathway – the action of interferon itself. Violation of interferon synthesis leads to severe viral diseases.
To fight viruses that block the action of interferon, humanity has learned to make additional interferon molecules. These genetically engineered molecules are completely identical to endogenous ones. With their help we can overcome the blocking effect of viruses.
When the influenza virus, coronavirus, or MS virus infect the upper respiratory tract, the synthesis of just a few cytokines is activated.
If the lower respiratory tract is infected by these viruses, hypersecretion of mucus, collapse of the alveoli, infiltration of immune cells, and impaired air exchange as a result of pulmonary edema may develop. In this case, the synthesis of most cytokines increases. This suggests that in severe cases, infection with the virus leads to activation of the immune system, and if there is a lack of interferon alpha, it can lead to severe clinical manifestations.
pharmachologic effect
Interferon preparations have an immunomodulatory effect, affecting the activity of T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, as well as the formation of antibodies.
In addition, interferons, as well as inducers of interferon synthesis, have a pronounced antiviral effect.
Interferon preparations additionally have an antitumor effect.
Enisamium iodide, in addition to its immunostimulating and antiviral effect, also has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects.
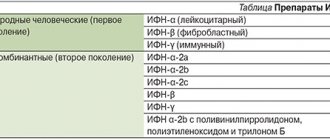
Types of interferons
Interferons are the main antiviral proteins in the body. They are part of the cytokine family.
Based on the similarity of biological activity in the human body, there are 3 types of interferons. A variety of interferons of the same type is needed to duplicate the antiviral defense function in the body.
| Interferon | Number of genes | Homology | Interferon type |
| IFN-alpha | 13 | 80% | Type I |
| IFN-beta | 1 | 60% | Type I |
| IFN-omega | 1 | 40% | Type I |
| IFN-kappa | 1 | 30% | Type I |
| IFN-lambda 1 | III type | ||
| IFN-lambda 2 | III type | ||
| IFN-lambda 3 | III type | ||
| IFN- lambda 4 | III type | ||
| IFN-gamma | Type II |
Interferons of one type are determined by binding to specific cellular receptors. In the cytoplasm of cells, the same molecules are associated with them.
The task of type 1 and 3 interferons is cell activation and expression of interferon-stimulated genes.
Type 2 interferon (interferon gamma) has different receptors, different signaling and different activation of signaling pathways. This is due to the fact that it is not an antiviral interferon, but more of an immunomodulator. The name “interferon” was given to it historically, since it was discovered simultaneously with type 1 and 3 interferons.
Basics of treatment with interferon drugs
Interferon preparations are used intranasally (drops, nasal spray) for the prevention and treatment of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. This route of administration is especially applicable in children, including young children. The course of treatment is on average 2-3 days.
In the treatment of eye diseases caused by viruses, interferons are used topically in the form of eye drops. Apply until the symptoms of the disease disappear completely (usually 5-10 days).
Interferon preparations for the treatment of urogenital infections in women are prescribed in the form of vaginal or rectal suppositories for a course of 10 days. It is also worth noting that interferon preparations are safe for use even in pregnant women.
For the treatment of viral hepatitis, tumor diseases, multiple sclerosis, interferon preparations are used subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. The course of treatment ranges from 3 to 6 months.
Inducers of interferon synthesis are used orally (inside). The course of treatment, depending on the disease, can range from 4 days to 6 weeks.
Virus life cycle
The first stage is entry into the cell, the second stage is replication, the third stage is exit from the cell. Antiviral defense proteins fight the virus at all stages and block its replication. It is important that all these proteins are synthesized under the influence of interferons.
When a virus enters a cell, it activates the signaling pathway and type 1 interferons are expressed. Next are two ways:
- One leads to the expression of interferons, and interferon triggers the expression of interferon-stimulated genes.
- The second path leads to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes - the inflammatory response is triggered.
In most cells, between 200 and 500 genes are activated in response to interferon, all of which are involved in antiviral defense.
| Major interferon-stimulated genes | Mechanisms of antiviral defense |
| PKR | Viral protein translation block |
| MX1 | Transcription suppression |
| OAS1 | Activation of RNase L for viral genome degradation |
| APOBEC3G | Replication suppression, cytidine deamination |
| TRIM5 | Capsid formation block |
| ZAP | Binding to viral RNA |
| ISG15 | Binding to viral proteins |
| ADAR | Suppression of RNA virus replication |
| IFITM1/2/3 | Helicase block, replication suppression |
Features of treatment with interferon drugs
Interferon drugs often cause a flu-like syndrome - fever, chills, weakness, muscle pain. This side effect is easily eliminated by taking paracetamol.
Inducers of interferon synthesis enhance the effect of antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal agents, which makes it possible to take them together.
Enisamium iodide contains iodine, so its use in patients with thyroid diseases can lead to an imbalance of thyroid hormones. Also, the presence of iodine in the composition of the drug is associated with such a side effect as a bitter, metallic taste in the mouth.
Imbalance of innate and acquired immune responses
The task of innate immunity is to block viral replication through the synthesis of interferon and to induce adequate synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines to activate acquired antiviral immunity.
However, highly pathogenic influenza viruses induce a hyperinflammatory response with hypersynthesis of proinflammatory cytokines. A state of acute hypercytokinemia develops. It happens that it is not supported by a sufficient level of endogenous interferon and the development of effective acquired immunity. Then inappropriately strong inflammation occurs, the development of respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema and death of patients in especially severe cases.
Effect of endogenous interferon levels on protection against influenza virus
In 2021, it was experimentally proven that restoration of intestinal microflora improved the synthesis of interferon by lung epithelial cells.
The study was conducted on mice. Antibiotics disrupted the composition of the intestinal microflora. As a result, the level of interferon in the lungs decreased and resistance to experimental infection with the influenza virus decreased. A severe course of the disease was observed as the virus replication became more active.
Normalization of the microbiota restored interferon synthesis and protection against the influenza virus. The study proved that the stimulating effects of intestinal microflora provide tonic signals to activate the expression of interferon genes.
Scientific and clinical effectiveness of interferon alpha for the prevention and treatment of ARVI
A 2014 study on human cell cultures using electron microscopy proved the antiviral effect of interferon alpha.
In 2013, treatments for experimentally infected monkeys were studied. Treatment with interferon alfa and ribavirin demonstrated a significant reduction in the development of symptoms of viral pneumonia, respiratory failure and a decrease in the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines.
To date, the clinical effectiveness of intranasal interferon alpha for viruses has already been shown:
- Adenovirus
- Coronavirus
- Rhinovirus
- Influenza A virus (H1N1, H3N2)
- Influenza B virus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Respiratory syncytial virus
Recombinant interferon alpha, administered externally into the respiratory tract, can enhance the antiviral effect.
Local application of interferon alfa allows the drug to be administered exactly where the drug is intended to act. Now there are various dosage forms: nasal drops, aerosol, spray. Local rather than systemic use can significantly reduce the dose of interferon alpha and eliminate side effects.
The use of intranasal interferon alpha can give a good preventive effect during an epidemic of influenza, coronavirus and other respiratory viruses.
Treatment of COVID-19
Interferon is a highly active molecule, so treatment with systemic drugs is carried out only by qualified specialists.
Early treatment with interferon reduces mortality and accelerates recovery, later it worsens the disease
A number of studies on the effectiveness of interferon for COVID-19 have revealed a dependence: the timing of treatment initiation is critical - up to 5 days from the onset of symptoms .
Interferon type 1
Chinese experts studied the results of treatment of 1,401 patients with coronavirus infection with nebulized IFN-1 “Inhalation of interferon-α2b improves clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19.” The best treatment results were when the drug was started 0 to 2 days after the onset of symptoms: adverse clinical outcomes were less than 1%. If treatment was started after 6 days, then severe or critical form of the disease occurred in almost 6% of cases. The details were published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
Doctors from the UK also studied the effectiveness of nebulized IFN-1 "Inhaled interferon β-1a reduces mortality in COVID-19 and speeds recovery." On day 28, the chances of recovery in the placebo group were 3 times lower than in the group receiving interferon. Details of the study were published in The Lancet.
Iranian doctors studied the safety and effectiveness of subcutaneous administration of IFN-1 to patients with coronavirus infection “Systemic therapy with interfron-beta-1a reduces mortality from COVID-19 by 2 times.” The best clinical outcome was in patients receiving IFN:
- on day 14, 67% of patients were discharged compared to 44% of patients who did not receive injections;
- The 28-day mortality rate was 19% in the interferon group and 43% in the no-IFN group;
- early administration of interferon reduced the risk of death by 13 times.
Details were published in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
Indian scientists investigated the effectiveness of a single intramuscular injection of IFN-1 to treat patients with COVID-19 “Interferon alfa-2b is approved for the treatment of COVID-19 in India.” These people required less oxygen support than patients receiving standard therapy: 56 hours versus 84. Symptoms resolved 1 day faster in the IFN group. The details were published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Russian scientists studied the combined use of rectal suppositories and IFN-1 nasal gel as part of complex therapy for coronavirus infection. In the group receiving additional interferon treatment, recovery occurred 7 days earlier than in patients receiving only standard treatment. The details were published in the journal Infectious Diseases.
Interferon type 2
Another group of Russian specialists studied the effectiveness of IFN-2 against COVID-19. Doctors used subcutaneous injection in addition to standard therapy. The duration of hospitalization in the interferon group was 2 days less than in the group receiving standard therapy only. Also, in the IFN group, respiratory failure did not progress and the need for intensive care decreased. The details were published in the journal Virology Issues.
Use of interferon in risk groups: type 2 diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of severe COVID-19. A common cause is a cytokine storm, which causes tissue destruction and multiple organ failure. The main role in the development of a cytokine storm is played by key cells of the innate immune system—macrophages.
One of the properties of macrophages is plasticity. At the stage of infection development they:
- destroy viral particles and infected cells, and thus stimulate inflammation;
- under the influence of cytokines, they produce additional cytokines to increase inflammation and quickly suppress the infection.
During the recovery phase after the acute phase of the disease, macrophages change their functions and suppress inflammation, promoting tissue healing.
In type 2 diabetes, the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus suppresses the plasticity of macrophages. Macrophages continue to increase cytokine storm and hyperinflammation rather than suppress inflammation and support organ repair. Interferon beta restores macrophage plasticity. However, during coronavirus infection in people with type 2 diabetes, IFN-beta levels are reduced to almost zero.
As a result of laboratory studies, scientists from the University of Michigan (USA) showed that early administration of IFN-beta reduces inflammation and prevents cytokine storm caused by macrophages in people with type 2 diabetes. “Interferon prevents cytokine storm in coronavirus in diabetic patients.” Details of the study are published on the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA website.
Antiviral treatments targeting the interferon system
Increasing the effectiveness of interferon is an important strategy to combat COVID-19. The antiviral drug imidazolylethanamide pentanedioic acid (IPA) increases the susceptibility of body cells to IFN molecules. The mechanism of action is based on stimulation of the synthesis of interferon receptors on the surface of cells.
Russian scientists studied the effectiveness of the drug against COVID-19 as part of complex therapy. Research results:
| Index | Standard treatment + IPC | Standard treatment |
| Time until body temperature normalizes (days) | 4,5 | 7,1 |
| Time until disease severity decreases by 3 levels on the WHO scale (days) | 10,3 | 15,0 |
| % of patients whose disease severity decreased by 3 levels on the WHO scale on day 6 | 44,4 | 10,5 |
| Time to reach SpO2 ≥95% (days) | 3,6 | 6,4 |
Details of the study were published in the journal Therapy.