Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
The pharmacy is closed on Sundays and holidays.
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online, this is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: medicine delivery , medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
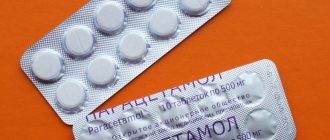
PARACETAMOL 250MG SUPPORTS No. 10
Instructions
Trade name of the drug: Paracetamol
Active ingredient (INN): paracetamol
Dosage form: rectal suppositories
Compound:
1 suppository contains:
Active substance: paracetamol – 50 mg, 100 mg or 250 mg;
Excipients: base for suppositories: solid fat, sufficient amount to obtain a suppository with an average weight of 1.25 g.
Description: suppositories of white or white with a yellowish or white with a creamy tint, torpedo-shaped.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Analgesic-antipyretic.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics:
Paracetamol has analgesic and antipyretic effects. The drug blocks cyclooxygenase in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation. In inflamed tissues, cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on cyclooxygenase, which explains the lack of a significant anti-inflammatory effect.
The absence of a blocking effect on the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues determines the absence of a negative effect on water-salt metabolism (sodium and water retention) and the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is high, quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The period to achieve maximum concentration is 30-60 minutes. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. The amount of bioavailability in children and neonates is similar to that in adults. Metabolized in the liver. The half-life is 2-3 hours. Within 24 hours, 85-95% of paracetamol is excreted by the kidneys in the form of glucuronides and sulfates, 3% unchanged. There is no significant age-related difference in the rate of elimination of paracetamol and in the total amount of the drug excreted in the urine.
Indications for use
Used in children from 3 months to 12 years as:
- an antipyretic for acute respiratory diseases, influenza, childhood infections, post-vaccination reactions and other conditions accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- an analgesic for pain of mild to moderate intensity, including: headaches and toothaches, muscle pain, neuralgia, pain from injuries and burns.
In children from 1 to 3 months, a single dose of the drug can be taken to reduce fever after vaccination; the use of the drug for all indications is possible only as prescribed by a doctor.
Directions for use and doses
Rectally. After spontaneous bowel movement or a cleansing enema, the suppository is released from the contour cell packaging and inserted into the rectum. The dosage of the drug is calculated depending on age and body weight, in accordance with the table. A single dose is 10-15 mg/kg of the child’s body weight, 2-3 times a day, every 4-6 hours. The maximum daily dose of paracetamol should not exceed 60 mg/kg of the child's body weight.
Age Weight Single dose
1-3 months 4-6 kg 1 suppository of 50 mg
3-12 months 7-10 kg 1 suppository of 100 mg
1-3 years 11-16 kg 1-2 suppositories of 100 mg each
3-10 years 17-30 kg 1 suppository of 250 mg
10-12 years 31-35 kg 2 suppositories of 250 mg each
Duration of treatment: 3 days as an antipyretic and up to 5 days as an anesthetic.
Extend the course of treatment if necessary after consultation with a doctor.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, neonatal period (up to 1 month).
Carefully
Renal and liver failure, benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert's syndrome), viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, alcoholism, pregnancy, lactation, genetic absence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, simultaneous use of other paracetamol-containing drugs.
Side effects
Allergic reactions (including skin rash).
special instructions
If fever persists for more than 3 days and pain persists for more than 5 days, you should consult your doctor.
The simultaneous use of paracetamol with other paracetamol-containing drugs should be avoided, as this may cause an overdose of paracetamol.
When using the drug for more than 5-7 days, peripheral blood counts and the functional state of the liver should be monitored. Paracetamol distorts laboratory results in the quantitative determination of glucose and uric acid in plasma.
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children and not used after the expiration date.
Interaction with other drugs
Stimulators of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, flumecinol, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which makes it possible to develop severe intoxications, even with a slight overdose. Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. When taken together with salicylates, the nephrotoxic effect of paracetamol increases. Combination with chloramphenicol leads to an increase in the toxic properties of the latter. Strengthens the effect of indirect anticoagulants, reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Overdose
Symptoms: during the first 24 hours after administration - pallor of the skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain; impaired glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis. Symptoms of liver dysfunction may appear 12-48 hours after an overdose. In case of severe overdose - liver failure with progressive encephalopathy, coma, death; acute renal failure with tubular necrosis (including in the absence of severe liver damage); arrhythmia, pancreatitis. The hepatotoxic effect in adults occurs when taking 10 g or more.
Treatment: administration of SH-group donors and precursors for the synthesis of glutathione - methionine 8-9 hours after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine - after 12 hours. The need for further therapeutic measures (further administration of meteonine, intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as the time elapsed after its administration.
Release form
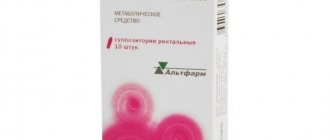
Rectal suppositories 50 mg, 125 mg, 250 mg.
Suppositories of 5 pieces are placed in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film.
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ºС.
Best before date
3 years.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Over the counter.
Paracetamol 125 mg No. 6 sup. rect.
APPROVED by the Order of the Chairman of the Committee for Control of Medical and Pharmaceutical Activities of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated "______" __________ 201___ No. ________ Instructions for the medical use of the drug PARACETAMOL Trade name Paracetamol International nonproprietary name Paracetamol Dosage form Rectal suppositories 125 and 250 mg Composition One suppository contains the active substance paracetamol 125 or 250 mg, excipients: base for suppositories Suppotsir (semi-synthetic glycerides) (Hard fat) - up to 1 g. Description Suppositories of a cylindrical conical shape, white or white with a yellowish tint. The cut is allowed to have an airy and porous rod and a funnel-shaped depression. Pharmacotherapeutic group: Analgesics, antipyretics. Anilides. ATC code N02B E01 Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics Absorption is fast and complete. The maximum concentration of paracetamol in plasma after using rectal suppositories is achieved after 0.5-2 hours. Penetrates into most tissues and biological fluids of the body. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Plasma protein binding is weak - 10-15%. The main part of paracetamol is metabolized in the liver along the glucuronide and sulfate pathways with the formation of inactive metabolites, a small part (about 5%) - by hydroxylation with the formation of a reactive metabolite - N-acetyl-p-aminobenzoquinone (this biotransformation occurs in the liver and kidneys), which in in turn is inactivated by glutatitone. It is excreted in the urine in the form of metabolites; less than 5% of paracetamol is excreted unchanged. The half-life of paracetamol after the use of rectal suppositories is about 1-4 hours. In elderly patients, the clearance of the drug decreases and the half-life increases. Pharmacodynamics It has antipyretic, analgesic and weak anti-inflammatory effects. Paracetamol blocks COX-1 and COX-2 mainly in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of thermoregulation and pain. In inflamed tissues, cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX, which explains the weak anti-inflammatory effect. The absence of a blocking effect on the synthesis of prostaglandin in peripheral tissues determines the absence of its negative effect on water-salt metabolism and on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Metabolized in the liver. Excreted by the kidneys. Indications for use - pain syndrome of weak and moderate intensity of various origins: arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, migraine, headache and toothache, algodismenorrhea, etc. - febrile syndrome of various origins - acute respiratory viral diseases, influenza, childhood infections, infectious diseases inflammatory diseases, etc. Method of administration and dose Rectal. Children: single dose - 15 mg/kg body weight; the maximum daily dose is 60 mg/kg body weight. From 6 months to 1 year (8 to 10 kg): single dose from 60 mg to 125 mg. If necessary, use 2-3 times a day with an interval of 4-6 hours between doses. From 1 year to 3 years (from 10 to 15 kg): single dose -125 mg. If necessary, apply 4 times a day with an interval between doses of 4-6 hours. From 3 years to 6 years (from 16 to 21 kg): single dose - 250 mg. If necessary, apply 2-3 times a day with an interval between doses of 4-6 hours. From 6 years to 12 years (from 21 to 35 kg): single dose - from 250 mg. If necessary, apply 3-4 times a day with an interval of 4-6 hours between doses. Adults and children over 12 years old (with body weight more than 60 kg): minimum single dose - 500 mg, maximum single dose - 1 g. Frequency of administration - 4 times a day with an interval between doses of 4-6 hours. The maximum daily dose is 4 g. The duration of treatment is 3 days when used as an antipyretic and 5 days when used as an analgesic. Side effects Rarely - anemia, thrombocytopenia, methemoglobinemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia - skin rash, itching, urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic reactions, including shock. - with long-term use in high doses, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects are possible - irritation of the rectal mucosa, tenesmus. Contraindications - hypersensitivity to paracetamol or any other ingredient of the drug - simultaneous use of other paracetamol-containing drugs - recent inflammation or bleeding in the rectum (contraindication related to the route of administration) - severe renal and / or liver dysfunction - deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase - blood diseases - proctitis - children under 6 months (for a dose of 125 mg) - children under 3 years of age (for a dose of 250 mg) Drug interactions Paracetamol enhances the effect of anticoagulants. Concomitant use with salicylates significantly increases the risk of nephrotoxicity. Concomitant use with inducers of microsomal oxidation and hepatotoxic drugs (barbiturates, anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, rifampicin, isoniazid, butadione, ethanol) increases the risk of hepatotoxic action of the drug. Concomitant use with metoclopramide may increase the absorption of paracetamol. Concomitant use with probenecid reduces the clearance of paracetamol and increases the half-life. When used together with cholestyramine for less than 1 hour after taking paracetamol, the absorption of paracetamol may be reduced. Simultaneous use with chloramphenicol leads to an increase in the toxic properties of the latter. Special instructions: Use with caution in benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert's syndrome), in diseases of the liver (including alcohol damage) and kidneys, as well as in elderly patients. Taking paracetamol may distort laboratory test results for the quantitative determination of glucose and uric acid in blood plasma. When using the drug for more than 7 days, it is necessary to monitor the peripheral blood picture and the functional state of the liver. Pregnancy and lactation Use with caution during pregnancy and lactation. Features: influence of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and control potentially dangerous mechanisms. Does not affect. Overdose Symptoms: pale skin; anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, increased liver transaminases in the blood plasma, increased prothrombin time, later pain in the liver appears, impaired glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis. In severe cases, liver failure, hepatonecrosis, encephalopathy and coma develop. Rarely, liver failure develops at lightning speed and can be complicated by acute renal failure against the background of tubular necrosis. Pancreatitis. Treatment: administration of SH-group donors and precursors of glutathione synthesis - methionine, orally, no later than 10 hours after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine, intravenously within 8 hours after an overdose (immediately 150 mg/kg, after 50 mg/kg every 4 hours and after 100 mg/kg for 16 hours); symptomatic therapy; in case of severe intoxication, they resort to hemodialysis. Release form and packaging: 6 suppositories in contour cell packaging made of polyvinyl chloride film laminated with polyethylene. 1 blister pack together with instructions for use in the state and Russian languages are placed in a cardboard pack. Storage conditions Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 15º to 25º C. Keep out of the reach of children! Shelf life 3 years Do not use after the expiration date Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies Without a prescription Manufacturer LLC FARMAPRIM MD-2028, Republic of Moldova, Chisinau, st. G. Tudor, 3 Name and country of the owner of the registration certificate FARMAPRIM LLC, Republic of Moldova Address of the organization receiving complaints from consumers regarding product quality: Representative of the company: Abulkhairova Tatyana Alaty, microdistrict Ainabulak-1, building 20, apartment 67 Telephone/ fax: 252-64-13, 8-777-242-46-49 Email