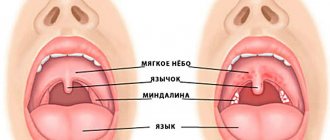
If you have pain, dryness, soreness, a feeling of a “lump” in the throat, painful swallowing, then most likely it is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx - pharyngitis . The throat with pharyngitis is red and inflamed.
Treatment of this disease must begin as early as possible, when the first symptoms appear. This will help avoid serious complications. Our clinic receives daily consultations from experienced otolaryngologists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences.
Why is pharyngitis dangerous?
Untimely treatment of pharyngitis is dangerous because the disease becomes chronic and has serious complications, including sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media, kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis), etc. But the most dangerous possible consequences are rheumatic lesions of the heart and joints.
1 Diagnosis of pharyngitis in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of pharyngitis in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of pharyngitis in MedicCity
Treatment of pharyngitis should be carried out only under the supervision of an ENT doctor! Acute pharyngitis may be the first manifestation of infectious diseases (measles, rubella, scarlet fever), requiring a different treatment regimen than for pharyngitis.
Chronic pharyngitis may not be an independent disease, but a manifestation of chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal pathologies. With gastroesophageal reflux disease, for example, acidic gastric contents often enter the throat during sleep, which causes the development of chronic catarrhal pharyngitis . Until the underlying cause of the disease is eliminated, local treatment in this case will not produce results.
Where to treat chronic pharyngitis in Moscow?
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis in Moscow is carried out in various medical institutions, ranging from district clinics to large multidisciplinary network clinics. The cost of treatment and the quality of services in this case cannot be the same everywhere.
The most affordable way to treat the disease is to enroll in a clinic at your place of residence. Affordable, but not the simplest or most effective. As a rule, in district clinics, appointments with an otorhinolaryngologist are quite dense, and it is very difficult to get a ticket “here and now.” You will have to wait about two weeks for an appointment (during this time, the exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis will only gain momentum), or try to get through the “live” queue, sitting all day at the ENT doctor’s office. By the way, it is not always possible to do this the first time.
Now about the quality of treatment - the doctor in the clinic has the task of accepting as many patients as possible. Everything is logical: there are many patients, one doctor. This means that the consultation time is very limited in time. But in the 10 minutes allocated for each patient, it is impossible to fully collect anamnesis and conduct an examination, let alone give effective prescriptions and carry out therapeutic manipulations. Another problem of district clinics is the lack of sophisticated, modern equipment, so the choice of treatment procedures used by the doctor is very limited. Treatment often comes down to prescribing medications that only relieve symptoms for a short time. Treatment for chronic pharyngitis can be very long and tedious.
Many patients are treated in multidisciplinary network clinics, with which they have an agreement to provide treatment under the VHI policy. In such clinics, the treatment process itself often becomes a secondary issue. It takes a doctor a lot of time to fill out medical documentation correctly, because filling it out incorrectly can lead to problems with the insurance company. Therefore, an impressive part of the reception is spent on “paper” work. Another drawback of such clinics, which patients often complain about, is the appointment of unnecessary procedures and unnecessary consultations. Network clinics need a constant flow of patients: the more people come, the more doctors or services they visit, the better. The quality of treatment under such conditions fades into the background.
The third option is treatment in highly specialized private clinics that deal with one particular medical area. Insurance companies are not interested in such clinics, so there will be no flow of people here. Highly specialized clinics, as a rule, are well equipped with medical equipment, which allows high-quality diagnostics and treatment to be carried out in one place. For the treatment of chronic pharyngitis, which requires increased attention and experience of an ENT doctor, this option is the most acceptable.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Common causes of pharyngitis are inhalation of cold or polluted air, exposure to chemical irritants (alcohol, tobacco).
Infectious pharyngitis can be caused by various microbes (strepto-, staphylo-, pneumococci), viruses (influenza, adenovirus) and fungi (candida). The disease can also develop as a result of the spread of infection from a nearby source of inflammation (for example, sinusitis, rhinitis, dental caries).
Difficulty in nasal breathing and overuse of vasoconstrictor drops can also cause pharyngitis.
Symptoms of pharyngitis may be present with the so-called postnasal syndrome (the English term is “postnasal drip”), when the constant flow of pathological secretion from the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses along the back wall of the pharynx causes discomfort and a sore throat. This condition may be accompanied by wheezing, so it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with bronchial asthma.
Tablets and lozenges and sprays
A resorption remedy for pharyngitis must include an antiseptic drug, a throat tissue softener and a moisturizing component. Some medications also include an anesthetic component to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Also, tablets for pharyngitis may contain plant extracts or essential oils.
Lozenges have less therapeutic activity than tablets. At the same time, you can consume quite a lot of them during the day, combining them with tablets. The main medications for resorption in case of illness are:
- Falimint is an effective anti-inflammatory drug with an analgesic effect;
- Lizobact - the medicine must be sucked, and not chewed or cracked. In order for the drug to act on the mucous membrane for as long as possible, it is necessary to swallow saliva and try to retain it in the throat area;
- Septolete are popular lozenges that contain an antiseptic and essential oils. The components of the drug slowly act on the mucous membrane, which allows for maximum therapeutic effect. They are recommended as an aid;
- Septogal is a medicine that has antiviral and antiseptic effects. The preparation also contains essential oils. The effect of using the product is felt after the first time.
There are also a large number of drugs that have similar effects, but are less popular.
Sprays for irrigating the throat for pharyngitis are most often prescribed as an auxiliary element of therapy. The most popular are Chlorophyllipt and Inhalipt.
This category of drugs is one of the few that can be used without medical prescription, since it is not capable of causing harm if all contraindications are taken into account.
Classification of pharyngitis
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form.
Acute pharyngitis develops as a result of exposure to the mucous membrane of the pharynx by an aggressive factor (infection, chemicals, etc.). The course of the disease is favorable.
Chronic pharyngitis can develop as a consequence of untreated acute pharyngitis or be an independent disease resulting from prolonged irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa. The course of chronic pharyngitis is characterized by phases of exacerbation and remission.
1 Throat examination
2 Throat sanitation
3 Diagnosis of pharyngitis in MedicCity
Literature
- Gostry A.V., Mikhailova N.A., Simonova A.V. Chronic pharyngitis: etiology, pathogenesis, treatment. New approaches to assessing etiopathogenesis // Archives of Internal Medicine. —2019. - No. 1. - P. 32-43.
- A.V. Gurov, M.A. Yushkina, O.A. Guseva Local therapy of inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx // Difficult patient No. 3, VOL. 16, 2021, p. 41-46.
- S. Ya. Kosyakov, I. B. Angotoeva. Non-infectious causes of chronic pharyngitis. Medical Council, No. 20, 2021, pp. 112-115.
- Sobolev V.P., Karpova O.Yu., Artamonova P.S. New possibilities for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the pharynx. // Consilium Medicum. 2018; 20 (11): 30–32.
- Deryabin P.G. Study of the antiviral properties of the drug “hexoral” in vitro against a number of viruses that cause acute respiratory infections and herpes [Electronic resource] / P.G. Deryabin, G.A. Galegov // Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. - 2015. - No. 9. — P. 72-75.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL ®TABS:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®CLASSIC:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®TABS EXTRA:
Symptoms of pharyngitis
The symptoms of pharyngitis (acute and chronic) are similar to each other, but there are still slight differences:
Acute pharyngitis
- dryness and sore throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- less often – general malaise, increased body temperature;
- possible irradiation of pain to the ears.
Chronic pharyngitis
- dryness, sore throat;
- sensation of a lump in the throat, which makes you want to cough;
- dry cough.
What happens with pharyngitis?
The primary link in the development of pharyngitis symptoms is damage to the pharyngeal mucosa. In this case, the mechanism of epithelial destruction depends on the underlying cause of the disease.
Burns lead to massive tissue necrosis with the development of inflammation around the lesion. Viruses penetrate cells and use their structures to reproduce their own genetic material. The release of many newly formed viral particles is accompanied by irreversible destruction of cell walls. Bacteria most often infect cells from the outside, although some pathogens are capable of intracellular existence (for example, chlamydia and mycoplasma). Bacterial endo- and exotoxins also contribute to tissue damage.
The destruction of cells of the pharyngeal mucosa leads to the activation of local nonspecific protective forces. Mucus secretion increases and the cough reflex is stimulated. There is also a release of biologically active substances, which provokes tissue swelling and impaired blood microcirculation at the site of inflammation. Subsequently, specific antibodies begin to be released. In some cases, they are destructive not only for pathogens, but also for the cells affected by them.
Accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the walls of the pharynx undergo reactive hyperplasia. Regional cervical lymph nodes may also enlarge. They act as natural barriers to the lymphogenous spread of infection.
The inflammatory process and reactive tissue changes can persist even after the infection is eliminated. In this case, the symptoms of pharyngitis can be supported by the action of various irritating factors. In response to prolonged inflammation, the pharyngeal mucosa may atrophy or overgrow.
Pharyngitis in children
Pharyngitis in children is easy to recognize. Symptoms of pharyngitis in children may be as follows. The child complains of scratching and sore throat, it is difficult for him to swallow, and he coughs. The back wall of the throat is red, covered in small tubercles, but the tonsils on both sides of the tongue are in normal condition, pink and clean. With pharyngitis, the child experiences weakness, headache and sore throat, lack of appetite, and difficulty swallowing.
Acute pharyngitis is more common in children and adolescents. Typically, acute pharyngitis occurs against the background of colds.
Treatment of pharyngitis in children
How to treat pharyngitis in children? Before starting treatment, you need to establish the cause of the disease. Then remove too hot and cold foods, cold drinks (especially soda) from the child’s diet, and refrain from spicy, salty and solid foods.
You can apply warm compresses to the neck, warm the child’s feet, drink warm milk with honey and butter. Gargle with a decoction of chamomile, oak bark and other anti-inflammatory herbs.
Inhalations and rinses
Inhalations for pharyngitis, as well as rinses, help to significantly speed up recovery. An action directly aimed at the inflamed mucosa gives a quick result, especially if the pathology is not advanced.
Inhalations can be carried out using steam using essential oils and medicinal plants or using a nebulizer, which is filled with the necessary medications. In this case, specific medications are prescribed by the doctor. Using a nebulizer, cold inhalations can be carried out with antibiotics, saline (if it is necessary to soften and moisturize mucosal tissue), as well as mucolytics.
Antiseptic agents are used for rinsing. This can be a simple saline solution or decoctions of eucalyptus, sage or calendula. Pharmacy antiseptics are also used, such as hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, furatsilin, propolis tincture and other agents that can destroy pathogenic bacteria without irritating a sore throat.
Pharyngitis in adults
Unlike children, chronic pharyngitis is most common in adults.
Patients are bothered by pain, dryness and soreness in the throat, they find it difficult to swallow, they often want to cough, but the contents are difficult to cough up. With chronic pharyngitis, headaches occur, sleep deteriorates, and general weakness is noted.
The main causes of pharyngitis include:
- untreated colds;
- remaining caries in the mouth;
- smoking;
- frequent stress;
- weakened immune system;
- drinking cold (straight from the refrigerator) and too hot drinks;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- allergy;
- poor environment and work in hazardous production.
Antiviral agents
Antiviral medicine for pharyngitis is required if the throat infection is viral in nature. In this case, there is no bacterial infection attached, and antibiotics will not be effective. Antiviral drugs can even be homeopathic, but they are prescribed much less frequently due to the rather long period of their accumulation in the body before the action begins.
For the use of antiviral drugs to be effective, it must be established that the disease is viral in nature. It will not be possible to determine the causative agent of the disease on your own, so you need to contact an ENT doctor. A specific antiviral drug will be prescribed depending on what pathogen has affected the mucosa.
Treatment of pharyngitis
When treating pharyngitis, qualified diagnostics are required, including examination by an otorhinolaryngologist, a smear from the oropharynx for flora with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages, and also, if necessary, consultation with a gastroenterologist, general and biochemical blood tests, general urinalysis, and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
1 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
2 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
3 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
Treatment of pharyngitis includes general measures and local therapy .
General events
It is necessary to sanitize the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity - eliminate adenoids, rhinitis, deviated nasal septum, sinusitis, caries, etc. It is also important to cure gastrointestinal diseases, which are often the cause of the development of pharyngitis.
Medicines aimed at increasing immunity (hardening procedures, vitamin therapy, etc.) are also prescribed.
It is recommended to reduce the impact of negative environmental factors on the pharyngeal mucosa (smoking, dust, chemicals, etc.).
Local treatment
Drug therapy includes antibiotic therapy as indicated, irrigation of the pharynx with medications, lubrication of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall, etc.
Alkaline, oil-alkaline, herbal inhalations are very effective against pharyngitis. It is also important to gargle frequently with antiseptic solutions (the patient can do this at home independently).
The course of treatment for chronic pharyngitis usually includes 10-14 treatment procedures performed daily or every other day. It is also recommended to carry out maintenance courses of treatment 2-3 times a year.
Remember that tobacco smoke, strong alcohol, household dust, cold air can cause exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis! During your illness, avoid drinking alcohol, smoking, and walking in cold, damp weather!
For pharyngitis, treatment should only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist! Medicines purchased at random or on the recommendation of friends may turn out to be useless or harm your health!
Prevention of chronic pharyngitis
Prevention of chronic pharyngitis includes significant adjustments to habits and lifestyle - this is the only way you will reduce the risks of developing the disease.
Preventive measures to prevent the development of chronic pharyngitis include:
- timely treatment of acute pharyngitis and other inflammatory ENT diseases;
- reducing cases of contact with irritating harmful substances at work and allergens;
- cessation of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- treatment of gastrointestinal diseases;
- limiting the consumption of spicy and sour foods;
- strengthening the immune system;
- avoiding crowded places during ARVI epidemics;
- maintaining the required level of humidity and temperature in the room.