Urologist
Belkin
Andrey Ivanovich
19 years of experience
Urologist of the first category, member of the European Association of Urology
Make an appointment
Urolithiasis (urolithiasis) refers to diseases of the urinary system. Its main feature is the deposition in the sections of this system of various compactions, which are called stones. Most often, the bladder and kidneys are susceptible to stone formation. The disease is dangerous not only because it affects internal organs and significantly reduces the standard of living. It is also fraught with a number of extremely undesirable complications.
It is difficult to say which group of people is more susceptible to this disease. The disease occurs in very young people of 20 years old, and in adults from 50 years old. It occurs more often in men, but in women the stones are larger, so the disease is more complicated. People who live in cities are more likely to get sick, which is related to the environment and water quality.
The disease can be chronic, with periodic relapses, or it can manifest itself only once and, after the patient recovers, never return.
Symptoms
The first signs of urolithiasis include sensations of colic or dull pain in the kidney area, as well as the bladder. Frequent urination should also alert you. When the disease progresses to a serious level, other symptoms appear:
- renal colic - sharp pain. It is very difficult to endure such pain; it is difficult for patients to tolerate;
- nausea and vomiting due to attacks of pain;
- painful sensations during urination;
- lack of urination. This is the case if the stone blocks the urinary system;
- blood particles in the urine. This symptom does not occur in only 8% of patients;
- increased weakness, fatigue;
- chills;
- temperature increase.
If symptoms of urolithiasis are detected, do not treat yourself under any circumstances, do not try to wait out the pain - immediately call an ambulance.
Are you experiencing symptoms of urolithiasis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
General information
The peculiarity of urolithiasis is that it often occurs without any symptoms. This is its danger, because vivid symptoms appear already at the stage of disease progression.
KSD can develop at any age, but the disease is more common in patients between 20 and 55 years old. In this case, men are most often affected, but in women the course of urolithiasis is more acute, which leads to a number of complications (the formation of stones that occupy the entire cavity of the kidney).
Urolithiasis leads to the formation of stones in various parts of the urinary tract. In elderly patients and children, they most often form in the bladder, in middle-aged people - in the ureters or kidneys. The size of the stones, as well as their number, can vary - from 1 mm to large stones whose weight exceeds 500-600 grams.
Complications
Urolithiasis, if the patient is not treated in time, can lead to more serious consequences:
- penetration, development and spread of infections in the urinary tract;
- pyelonephritis and other kidney diseases;
- nephrosclerosis. These are transformations of kidney tissue that are associated with degenerative processes;
- problems with the intestines - in particular, paresis;
- accumulation of purulent formations;
- renal failure and bacterial shock.
If the stone is not removed, then as the disease develops the kidney may even die - this is extremely dangerous and risky, so the disease requires effective and thorough treatment.
Pathogenesis
The insidiousness of urolithiasis lies in the fact that for a long time a person does not notice any signs indicating the presence of stones.
The situation begins to worsen the moment the stone begins to move, interfering with the normal process of urine outflow. A severe pain syndrome appears - the so-called “renal colic”.
Urinary infection aggravates urolithiasis, being one of the factors stimulating the development and relapse of this disease. This is explained by the fact that the infection affects the composition of urine, leading to the formation of crystals and stones.
Causes
There are many causes of urolithiasis, the main ones are as follows:
- drinking water with plenty of minerals. It is also called hard water. Water supersaturated with calcium salts most strongly contributes to the development of the disease;
- a menu rich in high-protein foods, as well as too sour and spicy dishes;
- deficiencies of individual vitamins - most often belonging to group B and vitamin A;
- physical inactivity – that is, an insufficiently active lifestyle also contributes to urolithiasis;
- some bad habits. Thus, the development of stones is promoted by excessive alcohol consumption;
- taking certain medications not according to instructions, in excessive quantities;
- structural features of the urinary system. We are talking about anomalies such as a narrowed lumen of the urinary tract;
- various inflammations, including urethritis, cystitis, etc.;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe and regular dehydration;
- increased acidity of the body itself.
Many of these causes of urolithiasis can act in combination, in a complex manner - it all depends on the situation.
Diet
Diet is the basis of treatment not only for urolithiasis, but also for other diseases. Here are some basic principles:
- Diet variety (while the total amount of food consumed is reduced).
- Exclusion from the diet of foods that contain large amounts of stone-forming substances.
- Drink plenty of fluids (2-2.5 liters per day).
Regarding foods that need to be excluded from the diet, it all depends on the chemical composition of the stones. Naturally, alcohol, fatty and spicy foods will have to be excluded in any case, but there are foods whose intake will also have to be limited.
For example, with phosphorus-calcium stones, milk, alkaline mineral waters, and spices are excluded. It is better to limit the consumption of potatoes, cheese, legumes and green vegetables.
Diagnostics
As in many other cases, the diagnosis of urolithiasis begins with collecting an anamnesis and analyzing the patient’s complaints. Already based on the information that the patient feels severe pain and has problems with urination, certain conclusions can be drawn.
The following are assigned:
- general blood analysis;
- general urinalysis and biochemistry;
- CT;
- Ultrasound of the urinary and kidneys.
When making a diagnosis, it is important to exclude other diseases that have similar symptoms, for example, acute cholecystitis or appendicitis.
Questions about the article
Vitaly
March 14, 2021 at 04:29 pm
Hello, Anton Evgenievich! At work, my blood pressure rose sharply to 170/100, shortness of breath, cold sweat, anxiety, dizziness and a nagging, subtle pain in the left side in the area of the lower ribs and lower back. When I took tests, my blood was normal, my urine was normal, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs did not reveal anything other than an inflection of the bile duct and moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas. Ultrasound of the heart is normal. Only on an ultrasound of the kidneys they found a stone of 5 mm in the left upper calyx and sand up to 3 mm in the right. I rarely went to the toilet, but there was no discomfort, the urine was of a normal color, now I am worried about almost imperceptible pain on the left in the area of the lower ribs and lower back and also lack of air. Fluorography is normal without pathologies. The urologist said that my case should not provoke hypertension and a feeling of shortness of breath. Can stones cause these problems?
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
March 15, 2021 at 09:33
I agree with your urologist. Stones of this size and location are unlikely to cause a serious increase in pressure
Treatment
The treatment regimen for urolithiasis is influenced by the parameters of the cystolithiasis stone: composition, location, and impact on the general condition of the patient. The characteristics of the course of the disease are also taken into account. The main task in the treatment of cystolithiasis is to remove stones from the urinary system. They are either dissolved or removed through surgery.
Thus, treatment of urolithiasis comes down to several points:
- taking certain medications;
- physiotherapy;
- diet;
- operation.
To restore the patient’s quality of life, pain is relieved and antispasmodics are prescribed. In some cases, very strong painkillers are required.
The process of dissolving stones is not fast, some methods do not give results immediately - the program is selected according to the situation and is constantly monitored by doctors.
Diet for urolithiasis is important: high-quality drinking regimen, limiting fatty, spicy, spices, coffee, tea, chocolate. Legumes, citrus fruits, dairy products and many other types of food are also not recommended - each patient is given a detailed reminder.
As for surgical intervention, the types of operations are also different - there are more than five techniques that are selected based on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the stone(s).
Various herbal mixtures are used as folk remedies. But under no circumstances should you drink them on your own, without consulting a doctor - first get the doctor’s permission.
Urolithiasis disease
Category: Prevention.
Urolithiasis is a disease characterized by the appearance of hard stone-like formations in the urinary organs (kidneys, ureters, bladder). At their core, urinary stones are crystals formed from salts dissolved in urine.
The appearance of foreign bodies in the urinary tract leads to damage to the mucous membrane and inflammation, causing a typical clinical picture of the disease.
CAUSES OF URINOLOGICAL DISEASE
This disease is polyetiological, that is, several factors lead to its development. Most often, urolithiasis develops in people aged 20–45 years, and men suffer from it 2.5–3 times more often than women.
Factors that contribute to kidney stone formation include:
- genetic predisposition;
- drinking water rich in certain mineral salts;
- insufficient water regime - consumption of a small amount of liquid;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- eating foods rich in purine compounds (meat, vegetables - spinach, beans).
A special place among the causes of urolithiasis is occupied by diseases of various organs:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract: pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis.
- Diseases of the stomach and other organs of the digestive tract: hepatitis, gastritis, pancreatitis and others.
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of the kidneys and ureters.
- Metabolic diseases: gout, hyperparathyroidism.
All of the above conditions lead to changes in the acid-base balance in the body, which leads to the formation of kidney stones.
URINOLOGICAL DISEASE: SYMPTOMS OF THE DISEASE
Signs of urolithiasis vary in their diversity - from the complete absence of clinical symptoms to such serious phenomena as renal colic and kidney block.
The leading symptoms of urolithiasis, or what patients complain about:
- burning and pain above the pubis and in the urethra during urination - are explained by the spontaneous release of small pebbles, the so-called “sand”;
- lower back pain associated with a sudden change in body position, sudden shaking, heavy drinking (especially after drinking liquids such as beer and pickles). Pain occurs due to slight displacement of stones;
- hyperthermia (high temperature) - indicates a pronounced inflammatory reaction to the stone at the site of its contact with the mucous membranes, as well as the addition of infectious complications;
- renal colic is the most unpleasant complication of urolithiasis, manifested by sharp pain in the lower back with irradiation (spread) along the ureter, irradiation of pain may be noted in the leg, in the abdomen;
- patients often note cloudiness of the urine, as well as the appearance of blood in it (typical of renal colic).
The nature of the pain and its location can give the doctor information about the location of the stones: in the kidney itself, ureter or bladder. X-rays and ultrasound can help confirm this assumption.
In the earliest stages, the disease may not manifest itself in any way - kidney stones are often discovered by chance during a medical examination. Sometimes even large stones do not show up until the patient experiences an attack of renal colic.
TREATMENT OF URINOLOGICAL DISEASE
We recommend reading:
- Treatment of kidney stones: features of surgical and conservative treatment
- In the treatment of urolithiasis, both conservative methods are used - using tablets and injections, and surgical methods - operations are performed to remove stones.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF URILOSTICAL DISEASE
Analgesics are used to eliminate pain; even narcotic drugs can be used in the ambulance and in the hospital. Antispasmodic drugs also relieve pain - with good antispasmodic therapy, the stone can come out on its own.
To dissolve stones, drugs are used that change the acid-base balance of the blood and change the acidity of the urine. The drug is selected taking into account the type of stones, of which there are several types: cystine, oxalate, phosphate.
Thiapramine, Uralit can be used to dissolve cystine stones; oxalate - Prolit, renal collections No. 7 and 8; phosphate - Marilin.
Important: the drug is selected by a urologist or nephrologist based on urine and blood tests of the patient!
Among the conservative methods of treatment, physiotherapy is also used: patients are prescribed magnetic therapy, amplipulse therapy, inductothermy and other methods.
URILOSTICAL DISEASE: TREATMENT AT HOME
At home, in the absence of pain, and also to prevent relapses, you can use traditional methods. For phosphate stones, the effect is observed with regular drinking of rosehip or barberry decoctions. Combined herbal preparations are also used, consisting of several herbs that have moderate diuretic, antispasmodic and uroseptic effects.
Important: only the attending physician can give accurate recommendations!
For urate stones, you can use oatmeal decoction. For cystine and struvite stones, traditional methods in the treatment of urolithiasis are ineffective, as well as conservative treatment, since these stones almost do not dissolve.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
Large urinary stones that cannot be dissolved are broken into small fragments, which either come out on their own or are removed surgically. Stones are destroyed by lithotripsy, affecting them with a shock wave. There are several types of lithotripsy:
- ESWL - external shock wave lithotripsy - is a non-invasive method in which the impact on kidney stones is carried out without any skin incisions or other invasive techniques.
- Contact lithotripsy - an endoscopic device is brought to the stone through the urethra and bladder, the active part of which comes into contact with the stone (which is why the method is called contact). A shock wave is formed at the point of contact.
- Percutaneous lithotripsy - with this technique, a lithotripter is inserted into the kidney through an incision in the lumbar region. Used for crushing giant and coral-shaped stones.
- In cases where the stone cannot be crushed, surgery is performed. Depending on the volume of the operation, the following types of operations for urolithiasis are distinguished:
- Pyelolithotomy - a kidney stone is removed through a small incision in the renal pelvis.
- Nephrolithotomy - an incision is made directly through the kidney. This operation is indicated for stones that cannot be removed by other methods and when lithotripsy is ineffective. It is the most difficult operation for the patient.
- Ureterolithotripsy is an operation to remove a stone from the ureter.
PREVENTION OF URILOSTICAL DISEASE
It is easier to prevent kidney stones than to treat them later. There is a whole range of preventive measures aimed at reducing the rate of stone formation and getting rid of them. It is recommended for all patients who have had at least one attack of renal colic to adhere to simple prevention tips.
Prevention Tips:
- Proper drinking regime. Water consumption per day should be at the level of two liters. In summer, you can increase this volume to three liters. But you should first consult a doctor, since for some heart diseases large amounts of fluid are contraindicated.
- Prevention of dehydration (dehydration). In extreme conditions (in the heat, when playing sports, during illnesses with high fever), you should drink more liquid in small portions of 100–150 grams every half hour to hour.
- Diet for urolithiasis. A balanced diet, in which the ratio of different types of meat, dairy and plant products is selected individually, can reduce the risk of stone formation. Ideally, the diet should be selected by a doctor. Food requires sufficient levels of microelements and vitamins of different groups. If necessary, you can take multivitamin complexes.
Diet option for urolithiasis:
- Limiting salt intake. It is better to under-salt food than to over-salt it. Excess table salt puts a strain on the kidneys, causing urolithiasis.
- Physical activity. The load on the abdominal and back muscles improves renal blood flow, which stimulates metabolic processes in the kidneys and improves their detoxification function.
- Timely treatment of diseases. Pay attention to the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system - these organ systems should be periodically examined, since disturbances in their functioning are one of the leading factors predisposing to urolithiasis.
- Prevention of diseases of the genitourinary system. Pyelonephritis and urethritis can cause exacerbation of urolithiasis, so it is better not to get sick with them, and if there are symptoms of the disease, start treatment.
- Spa treatment. Patients with kidney stones during remission are recommended to visit resorts where treatment with mineral waters is carried out 1–2 times a year. This is one of the most effective methods of prevention. In Russia, dispensaries specializing in the treatment of this disease are available in Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk, and Zheleznovodsk. A doctor will help you choose a specific sanatorium, since certain mineral waters are suitable for each type of stone.
COMPLICATIONS OF URILOSTICAL DISEASE
Delayed consultation with a doctor and abuse of traditional methods of treating urolithiasis without the consent of a doctor can lead to serious complications in the urinary system.
Complications often include:
- Infections of the urinary system can not only provoke urolithiasis, they can also be its complication. Often the following diseases occur against the background of the disease: pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis.
- Kidney block and hydronephrosis - blockage of the ureter by a calculus makes it impossible for urine to flow out. As a result, it accumulates in the kidney, causing it to enlarge. This condition can lead to kidney failure and kidney loss.
- Nephrogenic hypertension. Against the background of renal pathology, an uncontrolled increase in blood pressure is often observed - symptomatic hypertension.
- Nephrosclerosis is the degeneration of kidney tissue due to constant disturbances in urine metabolism. This is the most common cause of chronic renal failure.
- Purulent complications that occur when pathogenic microorganisms enter the kidney (abscess and pyonephrosis). Kidney stones make these diseases worse and can lead to septic shock and death.
The information is provided for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor. There are contraindications, a doctor's consultation is required.
Based on materials from the site: www.oceydoc.ru
Prevention
Measures to prevent urolithiasis are the following:
- Consult a doctor if colic occurs even very rarely and does not particularly bother you. It is better to study the problem at the very beginning and prescribe effective treatment;
- undergo routine examinations if you have already had any urological diseases;
- eat healthy foods, reducing the amount of spicy, salty, fatty foods;
- eliminate or minimize alcohol consumption as much as possible;
- drink the daily amount of water, do not violate the drinking regime. The water must be of high quality, purified through a filter;
- move every day, devote time to physical activity.
These simple recommendations for the prevention of urolithiasis will help significantly reduce your risks.
Surgery
When choosing surgical treatment, preference should be given to the least traumatic methods. There are two types of operations - endoscopic and laparoscopic. The essence of endoscopic surgery is to crush stones using medical instruments. Most often used:
- Cystolithotripsy. It is carried out for stones localized in the bladder. First, the stone is crushed, and then it is removed.
- Ureterolithotripsy. Used for stones in the ureter. To carry it out, a ureteroscope is used.
- Flexible retrograde nephrolithotripsy. Used to remove kidney stones (diameter at least 2 cm).
Laparoscopy is a modern surgical treatment method that involves performing surgery through small holes.
Urolithiasis is a serious pathological condition, so treatment is carried out immediately after the first symptoms are identified. It should be borne in mind that relapse is possible even after surgery. Therefore, long-term observation by a urologist is required, as well as following his recommendations.
Prevention involves changing your diet, excluding “junk” foods (fast food, processed foods), engaging in some kind of active hobby (especially during sedentary work), and drinking enough water per day.
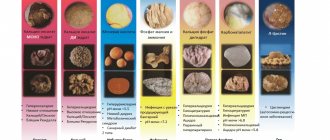
Classification of stones
The classification can be based on the shape, location, chemical composition and size of the stones. Stones formed in the urinary system can have the following forms:
- round;
- oblong;
- flat;
- combined (from different configurations);
- coral-shaped.
If the systematization is based on the chemical composition inherent in stones, then the following types can be distinguished:
- protein;
- from inorganic compounds (we are talking about carbonates, phosphates, oxalates);
- magnesium;
- from derivatives of uric acid;
- polymineral.
The size range of stones can range from one millimeter to ten-centimeter “giants”; the weight of some specimens reaches a kilogram or more. Doctors performing operations to extract substances have to deal with stones of various appearances.
| Stone type | Color | Surface |
| Uric acid (urate) | Yellow-brown | Smooth |
| Oxalate | Brown-black | Uneven, with thorns |
| Phosphate | Whitish gray | With pores |
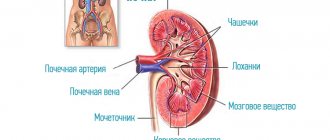
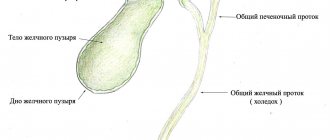
If we consider stones according to their location, then doctors identify substances that have settled in the renal pelvis, in the bladder area, in the ureter, in the kidneys.
Genesis of formal type
The basis of the stone is its matrix, which has a protein structure. The matrix is formed as a result of metabolic disorders, infection of the body, various inflammatory diseases, and atypical blood circulation in the kidneys. Insoluble compounds (calculi) are deposited in the components of the urinary system, which accumulate and increase over time. The kidneys and other organs that remove urine from the body are in conditions of insufficient blood flow, which reduces their nutrition and leads to malfunctions.