In the language of medical specialists around the world, ankylosing spondylitis has different names: ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Strumpell-Bekhterev-Marie disease. All of these concepts indicate a general pathology: inflammation of the intervertebral joints with a subsequent decrease in their mobility - ankylosis. This complication is caused by fusion of the articular ends due to their increase in size as the inflammatory process progresses. The fusion of the vertebrae locks the spinal column into a rigid bony sheath, making it immobile. The disease causes the patient to assume the classic bowed position (the so-called “begging pose”) and causes pain when trying to change the position of the body.
Statistics and etiology of the disease
The first mentions of cases of ankylosing spondylitis are found in medical records of the European Middle Ages. Doctors of that time were quite surprised to discover skeletons with characteristic ossification of the spine, the individual elements of which formed a strong “bone” column. In the mid-19th century, the disease became the subject of general medical study, as evidenced by surviving records of patient complaints and examinations of deceased people. The works of the Russian doctor Vladimir Bekhterev, the German Adolf Strumpel and the Frenchman Pierre Marie are accepted as the basis of etiology and are currently being studied in medical institutions.
Current statistics on ankylosing spondylitis indicate a gender link. In men it occurs 4-6 times more often and has a more aggressive, accelerated course than in women. The latter note:
- low degree of pain syndrome;
- preservation of full spinal function for a long time;
- arthritis occurs with long-term remission;
- signs of sacroiliitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joint) are recorded relatively rarely.
The area of development of the pathological process is the spine, large joints of the lower extremities and the sacroiliac joint. With extra-articular localization, the first signs of the disease are damage to the eyeballs in the form of redness of the sclera, inflammation of the iris or cornea. Characteristic signs are observed in 5-10% of patients, which in some cases makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis at the initial stage of development of ankylosing spondylitis. Less common is an alternative onset of pathology in the form of inflammation of the walls of the aorta or muscle fibers of the heart muscle, developing against the background of an actively occurring pathological process in the joints of the spinal column.
Contraindications to surgery
Surgical interventions for the consequences of ankylosing spondylitis cannot always be used. Contraindications to spinal surgical correction are:
- history of cancer;
- post-stroke and post-infarction period;
- cerebral encephalopathy;
- severe degree of nervous disorders;
- infectious processes within the spine;
- abscesses, infections, dermatoses, wounds of supravertebral soft tissues at the intended site of intervention;
- any active infections in any part of the body (dental, genitourinary, respiratory, etc.);
- serious chronic pathologies in the stage of decompensation (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, bronchial asthma, sinusitis, etc.);
- severe thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities;
- blood clotting diseases;
- unacceptably reduced bone density in the problem segment;
- the inability to choose a safe type of anesthesia due to the patient’s intolerance to all possible anesthetics.
It cannot be said that all of the listed contraindications are absolute. Many simply require a targeted course of treatment before surgery. For example. In case of caries – provide high-quality dental treatment. In case of uncompensated diabetes mellitus and hypertension, receive competent preoperative treatment for stable stabilization of blood sugar or blood pressure. If there is an infection in the body, eliminate it with the necessary medication, and so on. After complete elimination of the lesion, bringing the concomitant medical problem to full compensation and remission, the patient in some cases is allowed to undergo surgery.
Mechanism of disease development
Despite active study and collected statistics, the origin of the disease remains unclear. Most experts are inclined to the version of genetic predisposition: the presence of the HLA-B27 antigen in patients passes to first-degree relatives in 25-30%, and occurs within the family only in 7-8% of cases. In residents of the equatorial regions, the pathology is practically not diagnosed, and as we move towards the poles, its frequency increases to 30-40%.
Describing the causes of ankylosing spondylitis, experts talk about an inadequate immune response to the musculoskeletal system of the spinal column. Its tissues are perceived by the body as foreign, and the effect of their rejection occurs, characteristic of all autoimmune diseases. The subsequent inflammatory process is triggered by a cytokine substance consisting of TNF-α peptide signaling molecules called tumor necrosis factor alpha. Due to its active influence, the spine gradually becomes ossified and immobilized. Confirmation of the negative effect of the TNF-α molecule is the maximum concentration of the cytokine in the sacroiliac joint.
Concomitant pathologies or unfavorable external factors can accelerate the transition of ankylosing spondylitis to new stages. These usually include chronic infectious diseases, hypothermia, pelvic or spinal injuries, the consequences of which could not be completely eliminated. At risk are persons with hormonal disorders, infectious and allergic diseases, chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic and intestinal organs.
conclusions
It is impossible to completely cure ankylosing spondylitis. A person with such a diagnosis will have to be constantly monitored by a specialist, and during periods of exacerbation should be hospitalized in a traumatology or rheumatology department.
Rehabilitation is the most important part of therapy. It is necessary to regularly perform special exercises selected by qualified specialists in the field of rehabilitation, as well as use such accessible physical therapy products as the Lyapko applicator at home.
Ankylosing spondylitis, when treated properly, usually has a good prognosis with milder symptoms and significantly slower progression.
The use of Lyapko application devices is an excellent preventive measure and the key to your health, vitality and good mood!
Symptoms in men and women
Among the signs of the disease, all patients without exception note pain in the back, legs and buttocks with a simultaneous feeling of stiffness in the spine. Discomfort increases in the second half of the night due to prolonged lying down. Also among the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis are chest stiffness, pain in the heel bones, and discomfort when trying to change body position.
In most cases, signs of ankylosing spondylitis are detected without visible external causes. But pathology has a number of precursors that cannot be ignored. Among them:
- stiffness of the back, noticeable limitation of movements, which can be overcome with the help of a hot shower;
- weakness in the morning, fatigue;
- mild back pain without clear localization;
- pain in the sacrum, pelvis and ribs, which gets worse when coughing, sneezing or talking;
- discomfort when sitting on a hard surface;
- changes in gait associated with heel pain;
- redness of the eyes, accompanied by itching and burning.
- decreased range of motion of the cervical spine.
Often, ankylosing spondylitis “hides” under the signs of rheumatoid arthritis with pain in the heart and small joints of the extremities. Sometimes a disease at the acute stage can be discovered by chance during a comprehensive diagnosis of the body or when other diseases are suspected. X-rays show ossification and fusion of the intervertebral joints, which allows us to speak with confidence about the development of pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Are you experiencing symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Description of ankylosing spondylitis
The disease is chronic in nature, manifesting itself systemically in the body. Belongs to the group of seronegative polyarthritis. The mechanics consist of active damage to the joints of the spine, large and rarely small joints of the extremities. There is damage to the connection of the sacrum with the iliac bone of the pelvis. As a result, the patient is completely immobilized. Ankylosing spondylitis ICD 10 affects not only the osteoarticular system, but can develop in internal organs: kidneys, heart, iris. The combination of lesions is different.
Bekhterev's joint disease has the following features:
- Moderate and moderate pain is observed in the area of the femur, lower back, and back. Occurs in the morning and evening;
- Due to daily physical activity, back discomfort is somewhat reduced;
- The first sign that ankylosing spondylitis in men affects the joints appears between the ages of 15 and 30;
- As the pathology develops, an increase in pain is observed;
- In approximately 10% of cases, the disease manifests itself at an early age. Children suffer from damage to the knees, hip joints, and big toes. As you get older, your spine becomes affected.
Ankylosing spondylitis code according to ICD 10 manifests itself differently in men and women. In the stronger sex it manifests itself brightly, with a sharp aggravation of pain. Calm periods are short. Small joints are predominantly affected. The period of manifestation before the first signs of pathology lasts from 4 to 5 years. Men are susceptible to damage to all parts of the spine, which leads to curvature and limited mobility. Accompanied by damage to the vascular system and internal organs.
Ankylosing spondylitis develops in women after 40 with mild symptoms and rare acute pain. Long periods of calm occur. The time until the first symptoms appear lasts from 10 to 20 years. Mainly the spine and large joints are affected. Pain and pathology are localized in the sacral and lumbar regions. Damage to internal organs and blood vessels is rare.
Often ankylosing spondylitis ICD indicates the development of concomitant diseases, which include:
- Acute purulent arthritis;
- Inflammation of the bone - osteomyelitis;
- Sepsis;
- Limitation of foot mobility;
- Pathological dislocation.
Most patients testify that ankylosing spondylitis in women and men manifests itself in the form of pain for a period of at least three months. Inflammatory processes manifest themselves in various combinations, up to damage to the iris of the eyes.
Expert opinion
Author:
Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Difficulties in diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis are associated with the similarity of the pathology in the early stages with other degenerative lesions of the musculoskeletal system. According to world statistics, ankylosing spondylitis is detected in 0.5-2% of the population. The ratio of sick men to women is 9:1. In the structure of disability, ankylosing spondylitis occupies a leading position. Without correct treatment, the pathology leads to persistent impairment of self-care and loss of ability to work.
The Yusupov Hospital uses the latest CT and MRI equipment to diagnose ankylosing spondylitis. In a modern laboratory, blood parameters are determined, changes in which indicate the possible development of ankylosing spondylitis. All necessary tests are prescribed by experienced neurologists. Treatment is selected for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the disease. The task of doctors is not only to stop the exacerbation of symptoms, but also to select preventive therapy. At the moment, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. Doctors have the power to achieve stable remission and prevent the condition from worsening. In the conditions of the Yusupov Hospital, it is possible to carry out innovative therapy using stem cells.
Possible complications
In the absence or voluntary refusal of the patient to treat ankylosing spondylitis, the pathology develops as follows:
- pain in the back and hips becomes constant, intensifying with prolonged rest of the body;
- the spinal column loses flexibility and the patient’s movements become difficult;
- it is more difficult for the patient to breathe;
- the inflammatory process moves from the pelvic area higher to the chest.
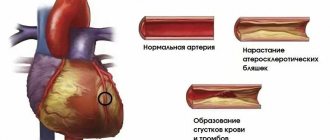
With moderate physical activity, the pain becomes less pronounced, while in a prolonged state of rest the discomfort intensifies. In the absence of treatment and ignoring the signs of the disease, the spine takes on a slightly bent shape, the arms are deformed at the elbows, the back is slouched, and the legs are bent at the knees. Over time, these changes become irreversible. The pathology significantly complicates the work of internal organs, as a result of which pneumonia, osteoporosis, eye damage with loss of vision, damage to the vascular system with an increased risk of myocardial infarction, and renal failure develop.
Types of operations
A surgical approach is a necessary measure when long-term ankylosing spondylitis has seriously aggravated a person’s quality of life. Since the scenario of the consequences of the disease can be different, and the characteristics of each patient’s body are different, there is no uniform algorithm for selecting the type and technique of surgery. The specialist, strictly based on the specific clinical picture, develops the most promising and less aggressive plan for surgical care.
Pain management during surgical procedures largely involves the use of general anesthesia with an element of intubation. The leading surgical approach is microsurgical open with posterior, anterior, posterolateral or anterolateral exposure of the surgical field. Correction of the spinal axis for this diagnosis is a complex of complex manipulations, which for the most part requires rather long incisions and wide expansion of the musculocutaneous tissue.
The most complex multi-stage intervention in the spinal column and hip joint.
Depending on the characteristics of the diagnosis, any one technique can be used or several operational tactics can be used simultaneously. For ossification of the spine and ankylosis of large joints, neurosurgical operations and orthopedic interventions are used today, among which the following have become increasingly popular:
- vertebrotomy;
- spinal fusion;
- spinal decompression;
- prosthetics.
The primary goals of operations are the maximum possible improvement of the patient’s functions and the prevention of life-threatening consequences. Surgery also has an aesthetic effect, correcting ugly back shapes.
Vertebrotomy
Corrective vertebrotomy involves straightening the deformed area of the back by intersecting and resection of the posterior vertebral structures. It is used primarily for pathological kyphotic, shear, rotational bends or a combination thereof. In order to segmentally align the spine, the surgeon resects the articular processes, pedicle and/or vertebral arches at the root. After removal, extension (straightening) of the vertebral bodies is performed in the closest to their physiological position. Subsequently, in the position of the achieved correction, tight marginal contact of the vertebrae is ensured with their interconnection with special metal stabilizers.
Spinal fusion
Spondylodesis is prescribed for developed pathological lordosis and kyphosis, and vertebral instability. The operation is performed, as a rule, through a posterior or dorsal approach created in the projection of the defect. Next, the abnormally fused segments are separated and aligned relative to each other. A bone graft is placed between the vertebrae of interest. The principle of wedge osteotomy can also be used previously. In the planned position, the spine is sequentially screwed together with metal knitting needles. Two or more vertebrae fixed to each other will fuse into a single bone a couple of months after the operation. In fact, this is also ankylosis, but it is artificially created by a doctor in order to restore the normal angle of the vertebral curves.
Prosthetics
Prosthetics are necessary when, instead of a non-viable part of the musculoskeletal system, it is possible to install an implant that maximally imitates its functions and structure. The specific prosthetic technique for facet joints is difficult to implement in practice, but intervertebral discs and vertebrae are naturally often replaced with implants. This type of high-tech medical care, however, is more acceptable for ankylosing spondylitis lesions of non-vertebral joints - joints of the knee, pelvis and hip, shoulder, ankle, etc.
The natural limb joint that has become subject to deformation and ankylosis is first resected. After its removal, endoprosthesis components made from high-quality and safe materials are installed on the prepared ends of the articular bones. They are fixed to the bones using acrylic cement and/or “clean” hammering. The installed components of the endoprosthesis are adjusted into each other. Thus, a single functional structure is formed that provides the required range of movements in the operated part of the limb. In operation, the joint prosthesis will be practically no different from the native joint of the leg or arm. The service life of artificial joints (hips, knees, etc.) is quite long - 15 years or more.
Spinal decompression
Decompression techniques occupy the first place in spinal neurosurgery (in general) in terms of frequency of use. They are often used to solve neurological problems that have developed due to ankylosing spondylitis. Their purpose is to eliminate the main cause of compression of the spinal canal, spinal roots and blood vessels. Decompression is performed in several ways, depending on the factor exerting pressure on the relevant components of the central nervous system.
So, if the compression is caused by an intervertebral hernia, microdiscectomy (often in combination with disc implantation) and nucleoplasty are used. If oppression of the spinal cord, nerve structures, blood vessels and arteries occurs due to overgrown osteophytes, the latter are removed. In the case of subluxations of the vertebrae and intervertebral joints, decompression is performed by realigning the displaced element, after which it is secured in the corrected position with a stabilizing system. In the presence of a spinal fracture, the integrity of the vertebrae is highly effectively and minimally traumaticly restored by kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty.
Classification of forms
Based on research data, experts distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- central, localized on the spine;
- kyphosis, in which inflammation affects the vertebrae of the cervical and thoracic spine;
- rigid, leading to smoothing of the natural curves of the back;
- rhizomelic, the area of localization of which is the spine and root joints;
- peripheral, involving the joints of the lower extremities;
- Scandinavian, which is characterized by damage to the joints of the hands;
- visceral, which combines the symptoms of any of the listed forms with simultaneous inflammation of the kidneys, heart or arteries.
Diagnostics
It is possible to obtain a comprehensive picture of the disease and clarify the area of its localization using the following research methods:
- radiography, which will show pathologies of the sacroiliac region, where the development of the disease begins;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- gene diagnostics for the presence of HLA-B27 antigen in the body;
- a general clinical blood test, where the inflammatory process is indicated by a sharp increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Other operations
A separate type of surgical invasions belongs to methods that are not associated with orthopedics and spinal neurosurgery. They are used if the patient has problems localized in two still vulnerable parts of the body with this pathology: the cardiovascular system and the visual center.
Pacemaker.
To help with serious heart damage, the patient undergoes aortic valve replacement, sometimes (less commonly) an implantation of an artificial heart pacemaker system is required. A cardiac aortic implant is implanted from the anterior chest wall after opening the aorta and removing the diseased valve. An implanted mechanical prosthetic valve with three semilunar leaflets is secured at the junction of the aorta and the left ventricle with a ligature (sutures). After installation, the backflow of blood from the aorta into the ventricle is prevented.
For severe eye injuries with the development of cataracts, surgical treatment may also be recommended. It is based on opening the PC lens, cataract extraction, partial removal of the vitreous body with further implantation of a three-part intraocular lens (IOL) into the capsular bag. This ophthalmic surgical session is characterized by a low degree of surgical aggression. After the procedure, visual acuity improves, intraocular pressure normalizes, and the likelihood of repeated uveal exacerbations is minimized. The prognosis is favorable.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment of the disease is necessary throughout the patient’s life with adjustment of the set of drugs depending on the results achieved and visible changes in the patient’s condition. The complex includes:
- hormonal drugs to relieve inflammation;
- immunosuppressants to suppress the process of inhibition of “foreign” spinal tissues by the body’s immune system;
- methods of physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
A new page in the history of treatment of ankylosing spondylitis was opened after the creation of TNF inhibitor drugs that block the activity of TNF-α molecules. They do not affect the immune system, but stop the synthesis of substances that activate the inflammatory process in the joints. Thanks to their use, it is possible to stop the spread of inflammation and maintain the mobility of bone joints, while simultaneously eliminating the process of their fusion. Additional recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis include cryotherapy, massage and manual therapy, and sodium chloride baths. Their combination increases the duration of remissions and makes it easier for the patient to go through the exacerbation phase.
Application therapy Lyapko
Lyapko applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, application belts, application tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic capabilities.
Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
Mechanisms of action of the applicator
The high healing effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvano-electric;
- immunological.
Application therapy has a pronounced analgesic and antispasmodic effect. Improves blood circulation, lymph flow, microcirculation, reduces tissue swelling. Activates tissue mechanisms of immune defense, increases the level of its own opiate peptides and anti-stress hormones in the blood, reduces the level of sensitivity of pain receptors, has a positive psycho-emotional effect and, as a result, stimulates general human adaptation mechanisms. In contact with the skin, the applicator needles stimulate the release of a person’s internal medicines, engaging his “inner doctor” in the work.
Applicators are widely used in medical institutions, health centers and sanatoriums, and are compatible with all types of medication and physiotherapeutic treatment.
Ease of use, safety, high efficiency with minimal effort allow us to recommend applicators for independent use at home.
It is important to note that local (local) improvement of blood circulation during application therapy occurs without additional stress on the heart, since the work of peripheral circulation increases and the heart rests at this time. This is very important for all categories of patients and, especially, with coronary heart disease, circulatory failure of 1-2 degrees, and elderly people.
The therapeutic effect of the applicators is enhanced if they are applied to the skin, previously moistened with water, a hypertonic solution, or on a gauze pad with a decoction of medicinal herbs, water-based medications. After removing the applicator, all skin pores at the site of its application are opened and the application of medicinal oils, ointments and compresses is most effective.
How to use the applicator, application zones
In 90% of cases it is necessary to act on the pain zone, and to increase efficiency on additional and auxiliary zones.
The general formulation should always include the core area (spine area).
The main zones are located on the back surface of the torso, head, and neck.
They are named the main ones due to the fact that the areas of skin on both sides of the spine and directly above the spine are closest to the exits of the roots of the cranial and spinal nerves and other structures.
Auxiliary zones are the anterior surface of the torso, head and neck.
Due to the fact that the internal organs and endocrine glands are located directly under the anterior abdominal wall, under the chest, in the neck, face, exposure to them or to individual skin areas (metameres) in these areas using different metal needle applicators helps regulate, normalization, restoration, improvement and activation of the activities of these bodies. The result is achieved faster when using auxiliary zones simultaneously with the main and additional zones.
Accessory zones: zones of the skin of the lower and upper extremities, which are secondary (peripheral) in relation to the (central) structures of the spinal cord and brain.
Important. Since a common cause of all autoimmune diseases is past infectious diseases of the intestines or genitourinary system, it is imperative to restore the movement of lymph and blood in the abdomen.
Lyapko's application therapy is indicated for improving the functioning of the abdominal organs and intestines, where the largest amount of lymphoid tissue responsible for the functioning of the immune system is located.
To do this, it is recommended to use flat applicators on the lower thoracic and lumbosacral spine, in addition to the auxiliary area - the anterior abdominal wall (simultaneously or alternately), you can also wrap these areas with the “Health Magic Tape” for 20-30 minutes or roll these areas with application rollers for 10-15 minutes.
Lyapko's application therapy is used both as an independent procedure and as a preparation for relaxing the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall for visceral abdominal massage.
These procedures improve the functioning of internal organs, relieve congestion and inflammation in them, restore the functioning of the lymphatic system, and increase immunity.
It is recommended to use flat applicators of large sizes on the back area: Applicator “Large Mat”, “Large Needle Massage Mat”, “Chance 6.2x4”, “People’s”.
“Chamomile M”, “Quadro”, “Duet”. The larger the impact area, the better the effect.
It is also possible to use flat applicators of smaller sizes: “Needle massage pillow”, “Insoles plus”, “Chance”, “Sputnik plus”, which are placed on the pain area. In addition to the back area, to enhance the effect, it is recommended to use applicators on auxiliary zones on the front surface of the body, in the area of pain projection. For example: pain in the lumbosacral spine - place the applicator on the lower abdomen. In addition, the use of applicators on the kidney area, adrenal glands (under control of blood pressure - do not use with high blood pressure), and on the abdominal area improves the functioning of the immune system. The exposure time is 20–30 minutes, the course of treatment is 10–14 days, which can be repeated after a break after 1–2 weeks. Such procedures can be used in courses for a long time.
It is better to complete the session by treating the feet using the Insole Plus applicator, which can also be used on all parts of the body.
In addition to flat applicators, you can roll the area of the back, front surface of the body, arms, legs with the “Large Roller M” or “Universal Roller M” until the skin becomes uniformly pink in color. They can also be used to warm up the body before a massage.
First, roll along the spine, along the intercostal spaces on one side, until a uniform pink color appears. Then we roll the second side in the same way. Exposure time is 3–7–10 minutes depending on the individual skin reaction.
Belt “Baby”, Belt “Universal M” is attached across and along the spine to areas of pain or applied in a lying position, like a regular applicator.
You can also wrap the pain area with the “Health Magic Tape”.
The “Speck” applicator can be fixed on the pain area. Considering the small area of influence, wearing is long - 1 - 3 hours.
You can use either a manual back massage or a massage using the Pharaoh massager, which can be used through thin fabric or over the body lubricated with oil or cream. The duration of the massage and its intensity determines the desired effect. Long lasting, up to 15 minutes. and more, massage promotes complete relaxation of muscles and creates a sedative (calming) effect.
After the massage, we recommend laying on a flat applicator for rest and relaxation.
For joint pain
If the joints of the upper extremities are affected, you need to use the applicators on the cervical-collar spine, from where the innervation comes to the upper extremities, then on the joint area.
If the joints of the lower extremities are affected, apply applicators to the lumbosacral spine, from where the innervation goes to the lower extremities, then to the joint area.
You can act simultaneously or alternately.
The “Chamomile M” applicator is especially convenient to use, which, thanks to its flexible “petals,” acquires relief for any part of the body. They can have an impact on any part of the spine, hip and knee joints (fixed with an elastic bandage); apply to calves and feet.
The exposure time for flat applicators is 20-30 minutes.
You can also use static-dynamic applicators: “Magic tape “Health”, belt “Universal M”, belt “Baby”. Uniform pressure to the surface of the body and ease of fixation allows you to move freely, do normal activities and receive treatment at the same time.
It is recommended to fix the applicator to the areas of damaged joints for 20-30 minutes; Additionally, you can use the areas of the opposite healthy side for 10-15 minutes. The procedure time is 20–40 minutes, the course of treatment is 1–2 weeks, treatment can be repeated after 2–4 weeks.
It is also necessary to massage the upper and lower extremities, the corresponding areas of the spine, joints, for example, using the Pharaoh massager, but you must avoid direct impact on the diseased joint, as this can increase the inflammatory reaction in it, work above and below the joint .
How to make an appointment with a specialist at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in Moscow
You can make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) on the website - the interactive form allows you to select a doctor by specialization or search for an employee of any department by name and surname. Each doctor’s schedule contains information about visiting days and hours available for patient visits.
Clinic administrators are ready to accept requests for an appointment or call a doctor at home by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60.
Convenient location on the territory of the central administrative district of Moscow (CAO) - 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10 - allows you to quickly reach the clinic from the Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Belorusskaya metro stations .