Home » Services for women » Gynecology » Inflammation of the appendages in women
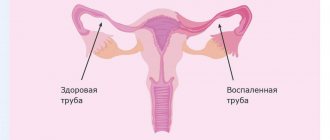
Adnexitis is the name given to inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. The disease often occurs in women after thirty, as well as in women who frequently change sexual partners. In the absence of therapy, inflammation of the appendages in women has sad consequences - infertility, associated diseases of the genital area or oncology. Therefore, if symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process occur, you should immediately visit an experienced gynecologist and consult with him.
Causes
The appendages become inflamed under the pathological influence of cocci (streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci), Escherichia coli, Koch bacillus (mycobacterium tuberculosis), actinomycetes (radiant fungi). Koch's bacillus, a pale spirochete, enters the tubes and ovaries from infected organs through the bloodstream. This route of infection is called hematogenous. The remaining bacteria penetrate the appendages along the ascending path.
The vagina is inhabited by opportunistic microorganisms. When certain factors appear, they become pathogenic, causing adnexitis. Pathagents penetrating from outside displace beneficial microflora from the vaginal area. Bacteria spread along an ascending path, reaching the tubes and gonads, leading to their inflammation and corresponding symptoms. Pathogens can also be carried through the lymphatic system.
Provoking factors:
- promiscuity in intimate partners, their frequent change;
- sex without a barrier contraceptive. A regular partner may not be sick himself, but may be a carrier of the infection. If a woman has a weak immune system and/or menstruation, she will most likely become infected;
- STD;
- stagnation of blood in the pelvis caused by irregular sexual intimacy, physical inactivity, obesity, constipation;
- tuberculous damage to any organ;
- chronic infectious process in the absence of treatment during relapse (tonsillitis, caries, sinusitis, bronchitis, cystitis, endometritis, vulvitis, vaginitis, others);
- low immune status, susceptibility to frequent colds;
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- having sex during menstruation. Through the open cervical canal with regulation, microorganisms easily penetrate into the appendages, causing inflammation;
- stress negatively affects the production of hormones;
- severe illnesses that weaken the body;
- lack of treatment for urogenital infections;
- hormonal imbalance;
- unsuccessfully installed IUD. The intrauterine contraceptive itself is not the cause of salpingoophoritis, but it aggravates the course of the pathological process. Therefore, before treatment, the IUD is removed;
- regular physical fatigue;
- constant diets, fasting, as a result - vitamin deficiency, deficiency of microelements;
- ignoring hygiene procedures;
- using other people's towels, napkins, linen for hygiene;
- improper hygiene when the pathogen is introduced from the intestines;
- swimming in open water, especially during menstruation;
- intimacy after surgical treatment, when the gynecologist’s recommendations are not followed;
- surgical interventions on the reproductive organs;
- childbirth, especially complicated ones;
- invasive diagnostic procedures.
Pregnant women are less at risk of inflammation of the appendages. This is due to changes in the composition and quality of cervical mucus. During pregnancy, it thickens, performing a barrier function, trapping bacteria. If a woman has chronic adnexitis, then a relapse is possible. This is explained by intense hormonal changes during the gestational period.
Why Central Clinical Hospital RAS
Even for a regular preventive examination, it is better to go to a highly qualified, experienced gynecologist. And when health problems arise, this becomes especially relevant. The hospital's excellent equipment with equipment from leading global manufacturers allows the cause of the disease to be quickly and accurately determined. It has its own clinical diagnostic laboratory - you don’t have to wait long for tests, and most of them are ready on the day of your visit.
But the most important thing is that doctors who are in love with their profession work here. Many of them have an academic degree - these are C.M.N., professors, doctors of the highest category. Gynecology is one of the most important medical areas of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. All specialists constantly improve their skills and use the latest achievements of researchers in various fields. In complex and controversial cases, the question of prescribing the necessary treatment is decided by the council.
A warm, friendly atmosphere, affordable prices, convenient registration by phone or online are pleasant additional advantages. In addition, you can always be sure that at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences you are welcome and ready to help in the most difficult situation.
Classification
Inflammation of the appendages is classified as follows:
| By localization | With the flow | By pathogen type |
| Left-handed | Acute – abrupt onset, severe symptoms. Recovery in a few days | Bacterial – caused by different groups of bacteria |
| Right-handed | Subacute – lasts several days or months | Fungal – the cause is a fungal infection |
| Two-way | Chronic – occurs if acute inflammation is not treated. Characterized by an undulating course, unexpressed symptoms |
Tetracyclines
These drugs are used to treat inflammation in the appendages. But the sensitivity of infectious pathogens to the drug is lost as antibiotics are taken. Tetracyclines have severe side effects.
The most popular drug from this group is doxycycline, which has minimal side effects and is quickly eliminated from the body. Solutab is a good remedy. Its active substance is placed in microspheres filled with a special filler. Under its influence, microspheres dissolve in an alkaline environment, and not in an acidic one.
Signs of inflammation of the appendages
In 2/3 of patients there is an acute onset. In 1/3, the disease begins “sluggishly”, with “erased” symptoms, characteristic of many genitourinary infections.
The acute stage is characterized by:
- cramping or nagging severe pain in the lower abdomen or only on the affected side. Pain increases during coitus, lifting weights, and playing sports. Irradiation to the lumbar region and anus is noted. This is the main symptom of the pathology;
- fever 38 degrees or higher;
- joint, headache, muscle pain;
- sweating, weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- dyspeptic disorders due to intoxication;
- severe vaginal itching, which intensifies during urination, after sex, and hygiene procedures with soap. A burning sensation in the vagina is another characteristic manifestation of inflammation;
- frequent urination;
- problems with the menstrual cycle. Regulations may increase or, on the contrary, become scarce. The regularity of the cycle is disrupted;
- bleeding outside the cycle;
- when the process is started, an unpleasant odor from the genitals and purulent-serous discharge appear.
With chronic inflammation of the appendages, an asymptomatic course is often observed.
May occur:
- unexpressed periodic aching pain;
- painful sex and bowel movements;
- non-cyclic bleeding;
- mucous vaginal discharge;
- unpleasant odor that increases during menstruation;
- Lack of treatment leads to cycle disruption. With purulent inflammation, amenorrhea sometimes occurs;
- low-grade fever during relapse.
Pain syndrome worsens the quality of intimate life. Libido decreases, irritability and emotional tension appear. A woman may refuse intimacy without knowing the reasons for her condition. You just need to see a doctor, undergo an examination and a therapeutic course.
Chronic stage
The chronic form of the disease is the result of an untreated acute form. Characterized by a recurrent course. The inflammatory process can develop as a result of exposure to nonspecific factors, such as overwork, stressful, conflict situations, hypothermia.
Chronic adnexitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- deterioration in general health;
- malaise;
- the appearance or intensification of pain in the lower abdomen;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees;
- the appearance of mucous or purulent discharge.
After a week, the symptoms of the disease usually subside, leaving only moderate pain in the lower abdomen.
Almost half of women with this disease complain of menstrual irregularities. Menstruation becomes painful, discharge is abundant or, conversely, scanty. In addition, many suffer from sexual function disorders: pain during sexual intercourse, decreased or complete absence of sexual desire.
Diagnostics
With inflammation of the female organs, consult a gynecologist. At the appointment, the patient is asked what is bothering her, her medical history is ascertained, and a gynecological examination is performed. Using a mirror, the doctor detects enlargement, thickening, swelling of the appendages, redness of the mucous membrane, and uneven surface. There is a change in tissue structure, pathological discharge, unpleasant odor, and pain on palpation.
It turns out whether abortions, curettage, or operations were performed. Was there pregnancy and childbirth, method of delivery. How does menstruation happen and how long does it last? Questions are asked about intimate life.
After examination and conversation, a diagnostic complex is prescribed:
- blood biochemistry;
- general urine test;
- PCR testing to exclude STDs;
- a smear from the infected area for bacterial culture to determine the type of microflora so that an effective antibiotic can be selected;
- transvaginal ultrasonography. For pregnant women, ultrasound is performed transabdominally;
- pregnancy test. In some cases, ectopic pregnancy may have symptoms similar to inflammation of the appendages.
If a tuberculous form of adnexitis is suspected, menstrual blood is taken for bacterial culture and a Pirquet or Mantoux test is performed.
For differential diagnosis of inflammation of the appendages or in case of an unclear diagnosis, the following can be performed:
- hysterosalpingography - X-ray contrast examination of the fallopian tubes and uterus;
- colposcopy – a detailed examination of the uterine cavity using a colposcope (binocular with a lighting device);
- hysteroscopy – the uterus and appendages are examined using a hysteroscope. As with colposcopy, biopsy material can be taken;
- Laparoscopy – allows you to simultaneously examine organs and perform surgical procedures.
A biopsy is needed to exclude atypical cell degeneration and assess the risk of neoplasms. MRI and computed tomography with contrast can be performed.
Treatment
In severe cases, hospitalization is required, in others it can be treated on an outpatient basis. The main way to eliminate inflammation of the appendages is antibacterial therapy. For effective treatment, broad-spectrum drugs are needed. The duration of the course, medications, dosage, and frequency of administration are selected individually. For mild salpingoophoritis, the patient takes the tablets for 5-7 days. In severe cases, antibiotics are administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
To relieve symptoms, painkillers, antihistamines, antifever, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Multivitamin complexes are used to strengthen the immune system. Local treatment must be carried out in combination with systemic treatment. Hygienic baths with antiseptic solutions are made, vaginal suppositories or tablets with an antibacterial effect are prescribed, and the uterine cavity is sanitized.
After the acute phase of inflammation is removed, physiotherapy is used.
| Highly effective physiotherapeutic methods | Action |
| Medicinal electrophoresis | Relieves pain, swelling |
| Laser therapy | Improves microcirculation, shortens recovery period, normalizes metabolism |
| Ultrasound | Helps soften adhesions and normalize hormonal levels |
| Ural Federal District | Kills bacteria |
| Paraffin therapy | Stimulates ovarian hormone production |
| Magnetotherapy | Accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues |
During the rehabilitation period, gynecological massage is useful. It improves muscle tone and blood circulation in the pelvic organs. Massage helps to resolve adhesions, normalize menstrual function, hormonal balance, and increase libido. Physiotherapy has a calming effect and has a beneficial effect on the emotional background. For chronic inflammation of the appendages, sanatorium treatment helps to prolong remission. Balneotherapy and mud tampons have a good effect.
In case of a complicated course, the patient is hospitalized for surgical intervention. In modern gynecological surgery, organ-preserving techniques are used. This is especially true for women of reproductive age planning pregnancy.
Laparoscopy is most often used. Under systemic anesthesia, the patient is given 3-4 small punctures in the abdominal wall. Gas is injected into the peritoneum to expand the surgical space. A laparoscope and microinstruments are inserted into the incisions. The surgeon uses manipulators to eliminate the problem. It can dissect adhesions, remove damaged tissue, polyps, cysts, myomatous nodes, and small tumors. A biopsy sample is taken for morphological examination. The entire procedure is displayed on the screen. The doctor visualizes the organs under significant magnification. Therefore, with a proven technique, errors are practically eliminated.
If inflammation of the appendages is advanced, there is a risk of pipe rupture, a purulent abscess has developed, or there is a danger to the woman’s life, then the appendages are removed in older patients.
To quickly restore the menstrual cycle, oral contraceptives are prescribed in minimal doses.
After surgery it is recommended:
- temporary abstinence from sexual intercourse. In each case, a specific period is determined;
- do not eat hot, spicy, pickled, sour foods. Do not drink alcohol or hot drinks;
- do not take hot baths, do not visit baths, saunas, do not swim in open reservoirs and public pools;
- you cannot lift weights;
- do not engage in active sports;
- don't get too cold.
Minor physical activity is allowed so that there is no stagnation in the pelvic organs. You need to drink plenty of fluids: non-hot tea, non-acidic fruit drinks, compotes, juices, clean water. Ultrasonography is prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Complications
Inflammation of the appendages develops rapidly.
If not treated in time, it can become complicated by the following pathological conditions:
- various forms of menstrual cycle disorders. Oligomenorrhea occurs in 3% of women who have recovered from the disease;
- pain syndrome;
- hydrosalpinx - sacs with fluid;
- pyosalpinx - purulent exudate (in the tube), pyovar (ovary);
- cicatricial adhesive process;
- tubo-ovarian tumor - the tube enlarges due to the accumulation of pus and becomes similar to a tumor. It has nothing to do with neoplasm;
- hypofunction, ovarian depletion;
- sexual dysfunction;
- hormonal imbalance;
- damage to the pelvic tissue.
- ectopic pregnancy (up to half of cases).
Infertility is the most severe consequence of inflammation for women of childbearing age. The most dangerous thing is an abscess. It can lead to rupture of the fallopian tube. If purulent contents enter the abdominal cavity, peritonitis will develop. This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate surgery.
When to see a doctor
A visit to the doctor should take place in the first 1-2 days after a woman discovers at least one of the above symptoms of a painful condition of the appendages. A gynecologist treats inflammatory diseases of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
If sexually transmitted infections are detected, a venereologist is involved in the diagnostic and treatment process. Delay in examination and treatment of diseases of the appendages entails a deterioration in health and the development of a large number of complications.
Prevention
Inflammation of the appendages in its clinical picture and symptoms is similar to many diseases of the genitourinary system, especially of infectious etiology. Therefore, there is no specific prevention; you need to follow some rules:
- treat inflammation without allowing the process to become chronic or develop complications;
- refuse to have sex during menstruation;
- be selective in sexual relationships;
- It is advisable to use a condom during sexual intercourse. This will not only protect you from infection, but also from unwanted pregnancy. Curettage of the uterus is a risk factor. A barrier contraceptive will not prevent infection;
- do not overcool;
- treat colds in a timely manner;
- visit the dentist - microbes in the oral cavity from caries, unhealthy teeth or gums can be a source of infection that enters the genital tract through the bloodstream;
- be physically active to prevent stagnation in the pelvis;
- maintain hygiene regularly;
- do not use other people’s towels or hygiene products;
- do not swim in unfamiliar bodies of water, especially during menstruation;
- strengthen the immune system: harden yourself, make sure that your diet contains enough useful microelements and that your food is fortified. It’s good to take vitamin courses every six months or a year. Only a doctor can prescribe medications. Hypervitaminosis is as dangerous as vitamin deficiency.
If alarming symptoms appear, it is better to immediately get checked by a doctor so as not to start the inflammatory process. Medical examinations cannot be ignored. Once a year you need to undergo a gynecological examination.
Human papillomavirus
Recently, this infection has received the attention of most researchers, as well as practitioners. This is due to the fact that the ability of this infection to cause cancer of the genital organs in both women and men has been proven.
Human papillomavirus infection, like many other STDs, very often occurs without symptoms, thereby contributing to its even greater spread in the human body. Not all cases of HPV cause cancer, but almost every case of cancer is caused by HPV.
Currently, more than 120 types of HPV have been identified, 34 of which affect the genitals, as well as the perineal area. Moreover, each virus is responsible only for its own “area”.
How does a person become infected with this virus?
HPV can be transmitted during direct contact of mucous membranes and skin when:
- traditional sexual intercourse (the main route of transmission of infection);
- non-traditional sexual intercourse (anal or homosexual sex). It is also believed that HPV transmission is possible through oral-genital contact;
- during childbirth during the passage of the fetus through the infected genital tract of the mother;
- The household route of transmission is also possible: through hands, bath accessories, dirty clothes.
Factors that provoke the development of HPV
These factors include:
- promiscuity, early sexual activity, a large number of partners;
- repeated abortions;
- the presence of other STDs (chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma);
- smoking;
- chronic diseases of the genital organs (inflammation of the uterus, appendages, vagina);
- anal sex;
- aggravated medical history (cervical cancer in close relatives).
The incubation period ranges from 1 to 8 months. People aged 17-26 years are most often susceptible to HPV infection, which is associated with increased sexual activity at this age. But this does not mean that older people cannot be infected.
Sometimes there are cases that the virus leaves the body on its own, without treatment. This happens most often in young people over 30 years old. If the virus enters the body after 35 years, then the likelihood that it will leave the body on its own is, unfortunately, small.
Forms of infection
This infection can occur in 3 forms:
- Latent form. It is asymptomatic. In this case, there are no changes or abnormalities, but the infected partner can transmit the infection through sexual contact.
- Subclinical form. Patients may have the following symptoms: vaginal discharge, a feeling of discomfort and dryness in the external genital area, which intensifies after sexual intercourse, itching, burning. At the same time, an ordinary gynecological examination will not reveal changes in the genital area. They can only be detected through a detailed examination (for example, colposcopy).
- Clinical form. Finally, the most common symptom of HPV is condylomas. This is a type of wart that is located on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, namely: at the entrance to the vagina, in the area of the clitoris, anus, urethra, and on the walls of the vagina. Occasionally they can be found on the skin of the perineum and labia.
Condylomas are skin growths that resemble a cockscomb in appearance. They can be on a stem or on a base. The color of condylomas is no different from the color of the surrounding tissues.
HPV is detected using the PCR diagnostic method.
Treatment
Condylomas are removed chemically (using various medications), using a laser, and also by cryodestruction. Then treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the body's immunity. In this case, vaginal and rectal suppositories are prescribed for local immunity and various drugs that stimulate general immunity - tablets or intramuscular injection.
It is also necessary to screen your partner for this disease. Sexual intercourse during treatment is possible only with the use of a condom.