The duodenum is the initial section of the large intestine. It is located immediately after the pylorus of the stomach. The intestine got its name due to the fact that its length is twelve transverse fingers of the hand.
The special structure of the mucous membrane of the organ allows its epithelium to remain resistant to the aggressive effects of digestive juice, bile secretions, and pancreatic enzymes. The bulb, the rest of the intestine and the head of the pancreas have a common blood circulation. In this article, we will take a closer look at the features of the structure and location of the intestine, and also find out how it can hurt.
Anatomy
Most people have a variety of shapes. Even in the same person, the shape and location of the organ can change over time. First, let's talk about the structure of the duodenum.
Structure
The organ has several layers:
- outer shell;
- muscle layer with longitudinal and circular layers;
- submucosa, thanks to which the mucous membrane can be collected in layers;
- mucous layer covered with villi.
Location
The organ has four main parts:
- Upper, or initial. It is located approximately at the level of the first lumbar vertebra or even the last thoracic vertebra.
- Descending. It is located to the right of the lumbar region and touches the kidney.
- Bottom, or horizontal. It goes from right to left, and then passes next to the spine and bends upward.
- Rising. Forms a bend and is located at the level of the second lumbar vertebra.
Where is the duodenum located? Most often it is located at the level of the second or third lumbar vertebrae. The location may differ for each person and is influenced by a large number of factors, such as age and weight. For example, in elderly and thin people the organ is located slightly lower than in young and well-fed subjects.
The photo clearly shows where the duodenum is located in humans
The intestine is in contact with other abdominal organs on all sides:
- liver;
- bile ducts;
- pancreas;
- right kidney;
- ureter;
- ascending colon.
The length of the duodenum is 25-30 cm.
Classification of chronic duodenitis
Classification of chronic duodenitis:
1) chronic duodenitis , mainly bulbitis , of acidopeptic origin;
2) chronic duodenitis, combined with atrophic gastritis or enteritis;
3) chronic duodenitis that developed against the background of duodenostasis;
4) local duodenitis (papillitis, peripapillary diverticulitis).
According to the endoscopic picture there are:
1) superficial chronic duodenitis;
2) atrophic chronic duodenitis;
3) interstitial chronic duodenitis;
4) erosive-ulcerative chronic duodenitis.
Functions
Let us highlight the main functions of the duodenum:
- production of enzymes and duodenal juice necessary for normal digestion;
- motor and evacuation function, that is, responsible for moving food gruel;
- secretory;
- regulation of bile pancreatic enzymes;
- supporting communication with the stomach. She is responsible for opening and closing the gatekeeper.
- adjusting the acid-base balance of food. It makes the food bolus alkaline.
Since the duodenum is the initial section of the entire intestine, it is here that the processes of absorption of nutrients that come with food and drink actively occur. This is where the stage of intestinal digestion begins.
Digestion
After the food bolus enters the initial part of the colon, it mixes with bile, secretions of the intestinal walls, as well as fluid from the pancreatic ducts. The acidic environment of food is then neutralized by bile, thereby protecting the mucous membrane. In addition, bile breaks down fat and breaks it down into small emulsions, which speeds up the digestion process.
Under the influence of bile secretion, fat breakdown products dissolve and are absorbed into the intestinal walls, and complete absorption of vitamins and amino acids occurs. It is also worth noting that bile regulates intestinal motility, stimulating the contraction of its muscles. Thanks to this, the food bolus moves faster through the intestinal lumen and is promptly evacuated from the body.
Pancreatic juice also plays an important role, with the help of which starch is digested, as well as proteins and fats. The duodenal glands produce intestinal juice, which mostly consists of mucus. This secret promotes better breakdown of proteins.
Considering all of the above, we can say that the duodenum plays a huge role in the digestive process. It saturates the food bolus with the necessary enzymes and ensures further digestion.
DPC ensures the normal course of digestive processes
Chronic duodenitis, symptoms of chronic duodenitis
What are the signs, manifestations, symptoms of chronic duodenitis ? The clinical picture of chronic duodenitis is characterized by such signs as constant, dull or ulcer-like pain in the epigastrium , a feeling of fullness or distension in the upper abdomen after eating, decreased appetite (poor appetite), vomiting, nausea. On palpation, pain is noted in the epigastric region.
With proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. With the erosive-ulcerative form of duodenitis, various complications can often occur, most often intestinal bleeding.
The clinical picture of duodenitis is diverse and nonspecific. Isolated chronic duodenitis is rare. It is combined with chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, enteritis, pancreatitis, and diseases of the biliary tract.
How does the duodenum hurt?
Considering the fact that the duodenum starts from the stomach, and the ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas also open into it, many of its diseases are associated with the malfunction of these organs:
Stomach pain and belching of air
- increased acidity of the stomach leads to the fact that hydrochloric acid begins to corrode the mucous membrane of the duodenum;
- Low stomach acidity means that rough food that has not been processed well gets into the intestine. This causes mechanical damage;
- with pancreatitis and cholecystitis, the production of digestive enzymes is disrupted, because of this, food is poorly crushed in the duodenum;
- With hepatitis and cirrhosis, blood circulation is impaired and, as a result, nutritional deficiency occurs.
But sometimes the occurrence of duodenal diseases is influenced not by existing pathologies of other organs, but by a person’s lifestyle. Snacking on the go and in a hurry, insufficient chewing of food, overeating, too long breaks between meals - all this negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
You can identify the reason why an organ is suffering by how it hurts:
- duodenitis caused by Helicobacter pylori. The pain occurs at night and on an empty stomach. It disappears after taking antisecretory and antacid drugs, as well as after eating. Unpleasant sensations may be accompanied by heartburn, belching and constipation;
- duodenitis caused by diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. Painful sensations occur in the right or left hypochondrium and intensify after eating fatty foods. Patients complain of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, and constipation, which is replaced by diarrhea;
- inflammation associated with stomach cancer or atrophic gastritis. Pain and heaviness in the stomach;
- peptic ulcer. Pain in the form of colic, which is a consequence of spasm of the smooth muscles of the muscles.
By the way the duodenum hurts, you can understand the reason from which the organ is suffering
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum. The disease can be acute or chronic, which occurs with relapses. In almost all recorded cases of duodenitis, a chronic process is observed.
Poor nutrition, bad habits, chronic gastrointestinal diseases - all this can serve as an impetus for the activation of the inflammatory response. Patients are concerned about pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, belching, heartburn, and weakness. Inflammation of the duodenum can lead to peptic ulcers and even cancer.
Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is also accompanied by inflammation of the organ, only the appearance of ulcers on the surface of the mucous membrane is added to everything else. This is a chronic pathology with frequent relapses. If the disease is left to chance, it can lead to atrophic changes, as well as fistulas and bleeding.
A duodenal ulcer can even cause death. Poor nutrition, taking potent drugs, chronic duodenitis - all this can lead to ulcers. But the most common cause is still the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
The infectious agent seriously damages the mucous membrane of the organ with its metabolic products. A characteristic symptom is hunger or night pain, which disappears half an hour after eating. The danger of a peptic ulcer is that it can develop into cancer.
Duodenostasis
These diseases affect the motor function of the organ, leading to the development of congestion. As a result, a mass consisting of undigested food, gastric juice and digestive enzymes accumulates in the lumen of the duodenum. This leads to pain, nausea and vomiting.
These are chronic pathologies characterized by alternating periods of remission and relapse. During exacerbation, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating. The patient loses his appetite and may also be bothered by constipation.
Tumor
A tumor in the duodenum can be either benign or malignant. For a long time, the pathological process may not manifest itself in any way. Cancer usually appears due to tumor growth from other organs, most often the stomach.
According to statistics, the disease most often appears in older people. The first symptoms of the disease resemble gastrointestinal disorders or digestive disorders. Then abdominal pain, weakness, lack of appetite, and depression appear.
Untreated organ inflammation can lead to cancer
When treating diseases of the duodenum, antibiotics, analgesics, and also agents that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid can be used. Traditional recipes can be used as an auxiliary therapy to relieve pain and strengthen the immune system. Proper nutrition and sufficient fluid intake play an important role in the treatment process.
Parasites
Helminths can enter the body along with food if basic personal hygiene rules are not observed. Parasites can affect any organ, but for a long period of time they may not manifest themselves in any way. Most often, the duodenum is affected by nematodes. Larvae can be transmitted not only through the fecal-oral route, but even through skin pores.
Helminths ultimately cause atrophic changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum. As the pathological process progresses, patients develop skin rash, itching, abdominal pain, heartburn, and diarrhea.
Erosion
The pathology causes an inflammatory reaction on the surface of the mucous membrane, without affecting the muscle layer of the organ. During ultrasound examination, erosive areas appear as thickened walls. Stressful situations, smoking, Helicobacter pylori, dietary errors and much more can cause erosion.
The pain syndrome is accompanied by problems with stool, belching, and a burning sensation in the esophagus.
Obstruction
Chronic organ obstruction can develop for a number of reasons: developmental defects, abnormal rotation of the organ, vascular abnormalities. The pathology manifests itself in the form of a painful outbreak in the right hypochondrium. Gallstone obstruction is most often diagnosed in older women. The stone migrates through the digestive canal and gets stuck in the small intestine.
To summarize, we can say with confidence that the duodenum is the most important organ of the digestive tract, facilitating normal digestion of food. You can maintain the health of this organ with proper nutrition, which should become your lifestyle.
If you experience discomfort in the duodenal area, immediately contact a specialist for examination. Early diagnosis will help avoid serious intestinal problems.
Causes and risk factors
Expert opinions differ regarding the reasons for the development of oncology in the duodenum. There is evidence that the causes of cancer in this location are similar to the causes of stomach tumors.
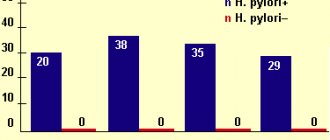
It is believed that there is a connection with a long-term infection caused by H. Pilori, an acid-fast bacteria. Ulcerative defects caused by this microorganism occur more often than in the stomach area. They occur in 8 out of 10 patients, while in the stomach only 6 out of 10 people. Duodenal ulcers are more common in women, although the incidence of cancer in them is equal to that in men. There are publications about the connection between cancer and obesity, dietary habits, including some national cuisines of the world.
Malignant tumors of the duodenum can occur against the background of certain provoking factors. These include:
- chronic inflammatory processes (duodenitis) and ulcerative lesions, the presence of Crohn's disease;
- diffuse intestinal polyposis (benign lesions - polyps of different sizes on the intestinal walls);
- poor nutrition with a predominance of animal fat and a deficiency of fiber;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- decreased immune defense, including antitumor.
In addition, some of the risk factors include viral infections, diabetes, and pancreatitis. Unfavorable heredity also plays a role.
Treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis
Complex differentiated treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of patients with chronic duodenitis and gastroduodenitis with the widespread use of new reflexology techniques allows you to achieve satisfactory results even with a pronounced clinical picture of the disease! Sarklinik knows how to treat duodenitis, how to cure duodenitis, how to get rid of duodenitis.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Wacpan | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Heartburn, burning in the stomach, treatment in Saratov, how to get rid of heartburn, what to do
Reflux esophagitis: symptoms, treatment, gerb, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Belching, treatment, frequent rotten belching of air, eggs, food
Stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer: treatment in Saratov
Chronic gastritis: treatment in Saratov, how to treat inflammation of the stomach
Comments ()
Diagnosis of chronic duodenitis, differential diagnosis
Diagnosis of chronic duodenitis is carried out using diagnostic methods such as fibrogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy, duodenoscopy, pH-metry, floor-by-floor manometry, impedance measurement. In parallel with the diagnosis of duodenitis, other digestive organs are examined.
Often duodenitis simulates duodenal ulcer. People of all age groups suffer from duodenitis. More often, inflammation of the duodenum occurs in young women, in whom duodenitis can be severe, accompanied by various disturbances in the activity of the central nervous system and endocrine glands. Duodenitis often occurs in childhood, which is facilitated by the inherited weakness of the hormonal apparatus of the duodenum, the variability of its shape, mobility and location in relation to the axis of the body.
The duodenum does not have a mesentery. In the case where the embryonic mesentery is preserved, the intestine is abnormally mobile and forms additional loops. Part of the liquid food mass flowing through the duodenum gets stuck in the additional elbow, creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms in the intestinal cavity. When exposed to alcoholic drinks or irritating foods, an inflammatory process occurs. An obstacle to the passage of food through the duodenum also appears when it is located in the opposite direction relative to the axis of the body.