Description of the disease
Hypospadias is one of the most common congenital urological pathologies in children. It is detected immediately after birth and does not go away on its own. This problem is most relevant for boys, since without surgical correction the condition inevitably leads to disruption of the genitourinary system and problems with intimate life.
Displacement of the external opening of the urethra may also be accompanied by curvature of the penis, as well as narrowing of the opening, which also aggravates urination problems.
Complications
Early complications include bleeding, inflammation, dehiscence, skin flap necrosis, and swelling. Late complications - urethral fistula, narrowing of the urethra, secondary curvature of the penis. The number of complications in the treatment of proximal forms of hypospadias is higher than with distal ones. Postoperative bleeding rarely occurs and is usually controlled by a compression bandage on the penis.
Urethral fistulas are long-term complications and are most often detected after removal of the catheter draining the urinary tract. The probability of fistula formation for most one-stage operations is about 10% according to world literature. When reconstructing proximal forms of hypospadias, the probability of fistula formation approaches 40%. Fistulas rarely close spontaneously and most often require reoperation after 6 months. The probability of fistula recurrence is about 10%.
Another complication is meatal stenosis, or narrowing of the urethra. Urethral strictures can occur in the long term and require bougienage; if ineffective, surgical treatment. Urethral diverticula may appear after urethral reconstruction using preputial skin. The created urethra does not have a frame base, therefore, when resistance to the flow of urine appears in the distal sections, a diverticulum-like expansion of the urethra occurs. This complication usually requires removal of excess skin tissue and suturing of the urethral tube onto an age-appropriate catheter. It is optimal to create the same diameter throughout.
One of the complications is the growth of hair in the urethra when using skin bearing hair follicles. As a result, stones appeared in the urethra, which required multiple repeated operations. Despite the fact that skin flaps with hair follicles have ceased to be used, such patients are still encountered in urologist practice.
Consultation with an endocrinologist
If a violation of sex formation is suspected in a patient with hypospadias, or if hypospadias is combined with cryptorchidism or micropenia, consultation with an endocrinologist is indicated.
Classification
There are several options for classifying the disease. Depending on the position of the external opening of the urethra, the following forms of hypospadias in children are distinguished:
- capitate: the opening is shifted to the base of the head of the penis; this form of hypospadias is most common in boys;
- coronal: the urethra is located in the area of the coronary sulcus;
- stem: the external opening is located on the shaft of the penis;
- scrotal: the urethra ends in the scrotum;
- perineal: the opening of the urethra is located in the perineum.
A special pathology stands out, which is called “hypospadias without hypospadias” - with it, the position of the external opening of the urethra is not disturbed in the child, but the urethra itself is shortened in comparison with the cavernous bodies. As a result, the penis becomes curved, which becomes especially noticeable during an erection.
The position of the external opening of the urethra in a child also allows us to distinguish anterior hypospadias (capitate and coronal form), middle (trunk) and posterior (perineal and scrotal).
Causes and frequency of hypospadias
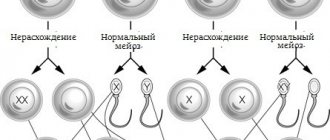
The causes of hypospadias are hormonal changes in the body of the mother and fetus, as well as genetic defects. Hormonal changes can also be genetically programmed, but can also be a consequence of external and internal influences on the body of the mother and fetus. Genetically determined variants of the defect generally constitute a more severe group.
The question of possible causes of hypospadias requires a separate discussion. We are currently doing a lot of work together with endocrinologists, geneticists and gynecologists to more accurately answer questions about the reasons for the birth of children with hypospadias and the possibility of preventing similar defects in future offspring.
Hypospadias occurs in 1:100 to 1:1500 male newborns. Capitate and coronal hypospadias occur in approximately half of the cases. Truncal hypospadias in a third of cases. Severe forms of hypospadias occur in 10-20% of patients.
After artificial insemination, children with hypospadias are born 2-3 times more often. However, according to our data, there is no direct connection with the process of artificial insemination itself, and the characteristics of pregnancy, the threat of miscarriage, the degree of maturity of the child at birth and the phenomena of hormonal imbalance are of greater importance.
Forms of hypospadias
The forms of hypospadias differ depending on the location of the external opening of the urethra - the meatus: on the head - capitate, in the area of the coronary groove - coronal, on the shaft of the penis - stem, in the area of the scrotum - scrotal or perineum - perineal.
Capitate form - at the site of the normal location of the external opening of the urethra, a urethral plate or longitudinal depression to the coronary groove is determined. The external opening of the urethra, the meatus, is often narrowed, which is called meatostenosis. Curvature of the penis is rare. Complaints arise when the external opening of the urethra narrows or when the head tilts down. The curvature of the head may increase during sexual activity.
Coronal form of hypospadias - the external opening of the urethra is located in the area of the coronary groove. More often than with the capitate form, there are complaints of impaired urination and curvature of the penis. Children urinate in a thin, tense stream. Often urine gets on your feet. Therefore, during urination it is necessary to raise the penis.
If the curvature of the cavernous bodies of the penis is pronounced, then during surgical straightening the coronal form becomes more severe - the trunk or even the scrotal-trunk, which must be taken into account when planning the operation.
Trunk form of hypospadias - in patients, the location of the external opening of the urethra is noted at different levels of the stem part of the penis. Complaints of impaired urination (the stream is directed downwards), which makes it difficult to urinate in an upright position. Children urinate while sitting on the potty or are forced to strongly lift their penis upward to correct the stream. Characteristic is curvature of the penis, sometimes with rotation and deviation to the side. As a rule, there is a narrowing of the external opening of the urethra - meatostenosis, but there are narrowings located along the urethra. Truncal hypospadias is often divided into distal trunk - the external opening of the urethra - the meatus is located on the trunk closer to the coronary groove and proximal trunk - when the meatus is located closer to the scrotum. This division is carried out to more accurately determine surgical tactics.
The penoscrotal form of hypospadias or scrotal-trunk is distinguished by the fact that the opening of the urethra is located on the border of the scrotum and the shaft of the penis.
Scrotal hypospadias is one of the most severe forms of hypospadias. The urethra opens between the halves of the split scrotum. Characterized by severe underdevelopment and curvature of the penis. The penis resembles an enlarged clitoris. The split scrotum enhances the resemblance to female genitalia. Urination is possible only while sitting. Urine gets on the skin of the scrotum, often causing irritation and inflammation. Newborns with scrotal hypospadias are often mistaken for girls or girls with adrenogenital syndrome.
Perineal form of hypospadias - The urethra opens behind the bifurcated scrotum. The penis is sharply reduced in size and sharply curved, often hidden at the base of the scrotum (transposition of the scrotum). The external opening of the urethra is wide. The head and cavernous bodies of the penis are underdeveloped. The foreskin is split.
Perineal and scrotal forms of hypospadias are often combined with undescended testicles (cryptorchidism), which makes sex determination even more difficult. Children suffer from severe complexes. After puberty, complaints appear about the inability to have sexual intercourse.
“Hypospadias without hypospadias” or hypospadias of the chord type is underdevelopment and shortening of the urethra, manifested by downward curvature of the penis with a normal location of the external opening. The urethra, like a bowstring, bends the corpora cavernosa during erection of the urethra. There are defects with narrowing - urethral dysplasia and normal patency of the canal. There are embryonic scars around the urethra, increasing the curvature of the corpora cavernosa. The defect is very difficult to treat. The degree of curvature of the penis increases sharply during puberty and during erection.
Individual differences in patients with hypospadias include the degree and shape of the curvature of the penis, variants of narrowing of the urethra, and the shape of the scrotum. Sometimes, with the capitate and coronal form of the defect, there is no curvature of the penis or splitting of the foreskin.
How to make the correct diagnosis for hypospadias?
Diagnosis of capitate, coronal and truncal hypospadias does not cause difficulties for specialists. A careful examination will clear up most of the questions. To clarify the presence of narrowings in the urethra, the volumetric flow rate of urination is determined - uroflowmetry. If the rate of urination decreases, the entire urinary system is diagnosed. Impaired urine outflow caused by narrowing of the urethra during hypospadias may result in decreased sensitivity of the bladder and the occurrence of vesicoureteral reflux. Combined genitourinary anomalies also occur.
Severe cases of hypospadias are more difficult to diagnose, especially when one or both testicles are absent from the scrotum. In such cases, genetic analysis is mandatory - determination of the karyotype, ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder and internal genitalia. Cystoscopy is performed to diagnose the genitourinary sinus. For rare combined defects, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is performed. Laparoscopy is sometimes used as a final assessment of the internal genitalia. Examination of children with severe forms of hypospadias is possible only in multidisciplinary specialized centers.
Associated anomalies with hypospadias
Hypospadias can be combined with defects of the genitourinary system - undescended testicle, inguinal hernia, kidney anomalies; as well as other organs and systems - heart defects, pyloric stenosis, anal atresia, as well as with genetic abnormalities - hereditary syndromes, variants of hermaphroditism.
Hypospadias may be an external manifestation of more severe malformations of the reproductive system. More than 120 diseases are known that include hypospadias as a component, requiring in-depth diagnosis and combined treatment together with endocrinologists and geneticists. Sometimes such children need gender reassignment at an early age. An erroneously chosen treatment approach cripples the lives of patients and leads to family tragedies. Treatment of such patients should be carried out only in multidisciplinary centers.
Several times a year we encounter patients whose gender was incorrectly assigned at birth. We are currently seeing 4 boys with hypospadias who were raised as girls. One of them was a girl under 16 years old when she was admitted to us and the correct diagnosis was made. Diagnosis of such cases is difficult and requires a detailed, complex examination followed by difficult psychological and surgical correction.
Most often, the time to achieve the best result at the time of admission in such patients is lost. Such patients at an older age often have to undergo sex reassignment surgery, since it is no longer possible to recreate a penis of a decent size.
Is hypospadias dangerous? Why does hypospadias need to be treated at an early age?
Problems associated with hypospadias depend on the age of the patient. In the first years, complaints about urination arise - difficulty or inability to urinate while standing. At the age of 3, the child evaluates the appearance of his genitals and from that moment experiences his difference from the surrounding boys and men. In adulthood, difficulties or impossibility of sexual intercourse are added. The degree of dissatisfaction with oneself is difficult to overestimate, and many patients with hypospadias early begin to suffer from neuroses and severe chronic stress, with all the ensuing consequences for the patient himself and those around him. Incorrect position of the urethral opening in patients with hypospadias is one of the causes of infertility.
Today, with the development of surgery, it has become possible to correct hypospadias already in the first year of life. This is the best age for treatment. The child does not understand that he is in the hospital. There is no trace of the disease left in his memory! Only complete reconstruction at an early age reliably saves a child from severe moral trauma for life.
Should a child with hypospadias be shown to a urologist during adolescence?
With the growth of the penis during adolescence and the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, a second wave of problems associated with previous operations often arises. Often the deformation of the penis increases due to limited growth of the created part of the urethra or preserved embryonic scars on the cavernous bodies. Hair can grow in the urethra if it was made, at least partially, from the skin of the scrotum, which contains hair follicles. Insoluble uric salts settle on the hair and form stones, which can serve as an obstacle to urination. A sharp expansion of the created urethra - a diverticulum accumulates urine and is manifested by leakage of urine after urination. Diverticula are sometimes combined with narrowing of the created urethra.
It is best to carry out examinations at the age of 13-14 years. If more than 10 years have passed from the time of the operation to the time of examination, it is likely that a hypospadiologist, having modern means and methods of correction, will find an opportunity to solve the patient’s problems. This can often be done through non-operative methods or simply advice.
Hormonal studies and spermogram analysis at the age of 16-17 years will help to correctly assess the characteristics of the reproductive system in a boy and his ability to fertilize.
Treatment of hypospadias.
In the process of surgical treatment of hypospadias, several main tasks are solved: 1. straightening the penis and giving it a natural appearance 2. forming the urethra from an elastic plastic material devoid of hair follicles 3. Forming the glans penis. 4. Extraction of the urethra to the apex of the head with the formation of the external opening of the urethra of normal location and shape. In severe forms of hypospadias, 5. elimination of transposition and splitting of the scrotum is additionally carried out.
The difficulty of surgical treatment of hypospadias lies in both achieving good patency of the urethra and the formation of a penis that has a normal appearance, as well as in preventing possible postoperative complications.
Stages of development of methods for treating hypospadias.
Urologists around the world have been solving the problem of treating hypospadias for more than a century. As a result, about 200 treatment methods and many options for their use were proposed. Until the mid-90s of the 20th century, almost every large clinic used its own modifications of surgical interventions, and in the hands of the authors they gave good results.
A fundamentally new stage in the treatment of hypospadias began in the 90s with the spread of digital technologies. At international urological conferences, video materials of operations and long-term results are shown. Many articles are supplied with high-quality photographic materials. Finally, it became possible to compare different treatment approaches and choose the truly best method.
If in the old days, evidence of the effectiveness of treatment for hypospadias was often words - statistically unproven statements about the advantages of certain methods, now the time has come for randomized multicenter studies and technologies that have proven their advantages in hundreds and even thousands of patients from different countries.
Urologists around the world exchange technologies and results. Today, not a single doctor can say my method is the best. Dozens of surgeons from different countries contributed to the improvement of technical techniques. The skill of a surgeon consists in mastering the entire arsenal of treatment methods and the ability to apply them creatively, in accordance with the characteristics of the pathology and the interests of the patient.
Anesthesia (anesthesia or anesthesia) for hypospadias operations.
The most modern type of anesthesia for hypospadias is combined anesthesia using local conduction anesthesia. Anesthesia with drugs such as marcaine and noropene allows you to achieve complete pain relief for 6-8 hours. Local remedies reduce the dose of general drugs and the load on the central nervous system.
Modern principles of operations for hypospadias.
Penis straightening
- usually performed by excision of embryonic scars on the lower (volar) surface of the penis, separating the urethra from the corpora cavernosa. Difficulty of the stage: on the one hand, it is important to prevent damage to the corpora cavernosa and shortening of the urethra; on the other hand, for complete straightening of the corpora cavernosa of the penis, it is necessary to completely excise the scar tissue.
- All subcutaneous adhesions are separated and the skin deficiency on the lower surface of the penis is eliminated.
- Sometimes, for minor curvatures, Nesbit straightening is performed by placing sutures on the tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa in the area of the dorsum of the penis.
Creation of the urethra
- We often form the missing part of the urethra - the urethra - from the foreskin, skin of the penis and tissues of the glans. The plastic material must be free of hair follicles, so the use of scrotal skin is undesirable. If there is a lack of penile skin material, we use the mucous membrane of the lip or cheek.
Own results of treatment of hypospadias. Original methods.
In our practice in the 80-90s, we went through a romantic stage of surgery, delusions and charm from our own developments. Based on the experience gained, as well as as a result of communication with colleagues from other countries and internships in foreign clinics, we have introduced the most reliable methods, which in most cases allow us to obtain perfect cosmetic and functional results.
The main components of success are an individual approach, effective methods, delicate microsurgical techniques, high-quality suture material and instruments, mastery of the entire modern arsenal of methods, extensive experience in reconstructive plastic surgery and the treatment of hypospadias, scrupulous management of the postoperative period.
Original modifications of surgical techniques allow us in some cases to significantly improve the cosmetic and functional results of treatment. For example, one of the most difficult stages of the operation is the formation of the capitate part of the urethra and especially the external opening of the urethra of a natural appearance.
Own results of operations for hypospadias
Operations for distal forms of hypospadias (capitate, coronal, stem without pronounced curvature of the penis) We have accumulated extensive experience in using various one-stage correction methods for coronary, stem and capitate hypospadias. Since 2000, we have been using our own modifications of one-stage Snodgrass-type operations for distal forms of hypospadias, which have been appreciated in recent years by leading hypospadiologists. These techniques allow you to achieve optimal functional and cosmetic results, fully preserve erectile function, while having a minimal risk of complications. At the same time, correction of curvatures and aesthetic correction of the penis is carried out.
Operations for perineal and scrotal forms of hypospadias.
Surgeries for severe forms of hypospadias are the most complex and responsible. Preservation of both blood supply and erectile function to the maximum length of the penis is achieved through careful, delicate technique and a creative approach to each patient.
We have proposed a number of modifications aimed at achieving maximum penis size, its normal function, appearance and preventing complications.
Is it worth using one-stage operations for complex types of hypospadias?
We see many problems in adolescents who come to us after inadequate interventions carried out in early childhood.
The main disadvantage of one-stage interventions for complex types of hypospadias is the high risk of postoperative deformations of the penis (curvatures) due to shortening of the created urethra, as a result of impaired blood circulation in the displaced skin flaps and increased scarring. There is no escape from them, and the only way out is repeated reconstruction.
Curvature of the penis in a teenager after a one-stage operation performed at the age of 2 years. The created scarred urethra prevents erections by bending the penis downwards. A complete reconstruction is required.
Symptoms of hypospadias in children
The main signs of pathology depend on its form. The farther the urethral opening is relative to the normal position, the more severe the symptoms. Classic manifestations include:
- a change in the direction of the stream of urine, due to which the child is forced to lift the penis upward during urination or urinate while sitting;
- deformation of the penis: especially common in the stem form of hypospadias in children; curvature increases as the penis grows, as well as during erection;
- painful erection due to deformation of the penis;
- thin and intermittent stream of urine, especially with concomitant narrowing of the external opening of the urethra.
Scrotal and perineal forms of hypospadias in children are usually accompanied by severe deformation of the external genitalia, cryptorchidism, inguinal hernia and other congenital developmental pathologies.
Parents
The optimal age for hypospadias correction is 10 months.
Correction of hypospadias is most often performed in one operation.
You may need to use hormonal ointment before surgery. The ointment is applied 3 weeks before surgery in the morning and evening. The ointment should be applied to the penis, the size of a drop is the size of the nail plate of the parent’s thumb.
Before the operation, you need to collect the necessary tests.
In the postoperative period, 2 diapers are used, the catheter is removed into the second (external) diaper. This technique allows the child to be active throughout the entire period of hospitalization.
Antibacterial therapy is prescribed for the entire postoperative period.
After the operation, a special compression bandage is applied to the penis, and a urethral catheter is installed for 10-12 days. After this period, the bandage is removed and the catheter is removed.
To evaluate the result of the operation, it is necessary to videotape the process of urination.
Treatment of hypospadias
The only way to eliminate any form of hypospadias in a child is surgery. Currently, it is recommended to perform it at the age of 1–3 years, so that in the future the development of the reproductive system follows a normal path. Depending on the form of the pathology, single-stage and multi-stage interventions are used:
- meatotomy: the operation is used for capitate hypospadias in a child and consists of dissecting the edge of the urethra, followed by careful monitoring of fusion;
- urethroplasty: a more complex version of the intervention, the course of which depends on the position of the external opening of the urethra.
As a rule, after surgery for coronary, stem and posterior forms of hypospadias in children, a catheter is installed in the urethra, and if necessary, bougienage is performed.
Operation techniques
The general principles of the main stages are common to all methods. First, the corpora cavernosa is exposed from the skin of the penis. The fibrous cords and “notochord” present on the ventral surface are excised as much as possible. An “artificial erection” test is performed by injecting saline into the corpora cavernosa to detect any deviation of the penis. If the curvature is less than 45⁰, dorsal plication corporoplasty is performed under the neurovascular bundle. When the curvature is more than 45⁰, it is advisable to use patch corporoplasty or by applying multiple incisions on the ventral surface of the tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa. It is also possible to correct the curvature of the corpora cavernosa by intersecting the tunica albuginea at the point of maximum curvature and fixing a free graft (buccal mucosa, preputial skin or other grafts) to the resulting defect. This technique leads to the elimination of curvature and lengthening of the penis, in contrast to the plication method of correction.
If there is a pronounced fibrous “chord” or dysplasia of the corpus spongiosum of the urethra, it may require its intersection or excision. Various methods of urethroplasty can be used: tubularization of the urethral site itself, the use of local blood-supplied flaps, tissue grafts or urethral advancement procedures (GAP procedures).
The most commonly used technique for the correction of distal and mid-trunk hypospadias is TIP (tubularized incised plate, Snodgrass). This method allows you to create a urethra from local tissues according to the Duplay principle, but a distinctive feature is the dissection of the posterior wall of the urethra, which creates the opportunity for the formation of an artificial urethra of larger diameter. Current research shows that this technology is used by the majority of urologists worldwide to treat distal hypospadias.
Next, the wings of the head are mobilized to cover the formed urethra and give the head a more conical shape. Excess skin on the dorsal surface is mobilized to close the defect on the ventral part.
Various suture materials are used for urethroplasty, the most suitable for the requirements of modern plastic genital surgery are PDS 6-7/0 and Monocryl 6/0, as they are quite strong and quickly absorbable.
Many studies have shown that the use of additional layers of tissue (the foreskin, vaginal tunica, etc.) between the urethra and the skin reduces the risk of developing fistulas. The issue of using short urethral stents in combination with cystostomy and long-term catheterization of the bladder remains controversial. A retrospective study in 2015 showed that longer catheterizations of up to 3 weeks resulted in fewer complications than catheter placements of less than 1 week.
Repeated plastic surgeries for hypospadias, performed in conditions of insufficient plastic material, constitute a separate problem group of patients with a higher percentage of complications. To correct hypospadias in these patients, various free grafts are used: the mucous membrane of the cheek, lips, lower surface of the tongue, skin of the postauricular area, etc.
Correction of penis-scrotal transposition is usually performed as a separate stage, since additional incisions can cause ischemia of the skin flap from which the urethra is formed. It is usually performed six months after the main stage of the operation, when peripheral blood supply is restored.
Most forms of hypospadias can be corrected in one operation, but in case of severe curvature and removal of the dysplastic corpus spongiosum of the urethra, it is advisable to use a step-by-step approach. In this case, at the first stage, the penis is straightened, the urethral platform of the required diameter is created, and the urethra is formed at the second stage after 6 months. The diagram shows an algorithm for the treatment of proximal hypospadias:
Hormonal therapy before surgery
Many specialists use hormonal therapy to increase the size of the glans penis. Preoperative injections of testosterone or ointments (creams) based on testosterone or dehydrotestosterone, as well as injections of human chorionic gonadotropin are used. In a study of 182 children with distal hypospadias (mean age 30 months), Asgari et al. It has been shown that the use of parenteral testosterone can be effective in reducing the incidence of complications from 12 to 5%.
In our practice, we use Andractim Gel ointment or Androgel for preoperative preparation in patients with a small glans penis.
Forecast
Timely and correct surgery for hypospadias in boys allows you to completely restore the normal anatomy of the penis. Subsequently, urination, erection and ejaculation proceed without disturbance. After the intervention, regular examinations by a urologist are necessary, who will monitor the condition of the penis until its growth completely stops. In this case, if deformations occur during the maturation process, they can be quickly corrected.
Hypospadias is a defect that can and should be corrected. Only in this way will the boy be freed from his physical disability and the psychological complexes associated with it. Doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic will perform the necessary manipulations and help cope with the problem at an early stage of development.
Concomitant pathology&
Often, hypospadias in boys is combined with other developmental anomalies: inguinal hernia, cryptorchidism, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, myelomingocele, urogenital sinus, etc. Therefore, an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is recommended for all children to identify concomitant pathology of the urinary system before surgery. In the presence of hydronephrosis or vesicoureteral reflux, the first step is correction of the pathology of the upper or lower urinary tract, and after that, surgical treatment of hypospadias.
List of sources
- Marchenko A.S., Smirnov I.E., Zorkin S.N., Apakina A.V., Sukhodolsky A.A., Shakhnovsky D.S. Treatment of children with hypospadias. Pediatric surgery. 2013. No. 5. P. 40-44.
- Akranov N. R., Sharabidze G. G. Parasurgical aspects of the treatment of boys with hypospadias (literature review) // Reproductive health of children and adolescents. 2010, no. 5, p. 39–48.
- Fayzulin A.K., Prokopyev V.M., Demin N.V. Modern methods of treating hypospadias // Andrology and genital surgery. 2009. No. 2. 158 p.
- Volodko E.A. Main characteristics of disorders of sex formation in hypospadias in children // Materials of the VI Russian Forum “Mother and Child”, M., 2004. - P.554-555.
- Akranov N. R., Sharabidze G. G. Parasurgical aspects of the treatment of boys with hypospadias (literature review) // Reproductive health of children and adolescents. 2010, no. 5, p. 39–48.
Use of anesthesia or general anesthesia
During surgery, the most modern method is considered to be combined anesthesia, when local conduction anesthesia is used. The drugs “Marcain” and “Naropin” make it possible to anesthetize the child from 4 to 9 hours after the operation.
If such a need arises, traditional analgesics can be used in the future. The use of local anesthesia can reduce the load on the nervous system, since the amount of general drugs administered is reduced.
Prevention
No specific preventive measures have been developed for patients with hypospadias. Taking into account the risk factors for the development of this pathology, one should try to avoid them.
- Late birth.
- Avoid neuropsychic stress during pregnancy.
- Avoid infections, including influenza , and intrauterine infection of the fetus in the first trimester.
- Examine the father for spermatogenesis disorders.
- Avoid uncontrolled use of progesterone before pregnancy and oral contraceptives during pregnancy.
- Avoid alcohol, smoking and exposure to toxic substances, including pesticides/herbicides during pregnancy.
- Avoid using hairspray during pregnancy (it contains flalate, which is harmful to the body).
Pathogenesis
The development of the pathology is based on a violation of embryogenesis at 10–14 weeks of gestation, which leads to disruption of the normal process of differentiation of the embryonic epithelium. In this case, underdevelopment of the peripheral part of the urethra is noted and the urethral groove is closed. Deformation of the penis develops due to the inability of the urethral groove to transform into a tubular organ. Accordingly, a short/dense inelastic connective tissue cord (notochord) is formed in this area, which shortens the ventral surface of the genital organ, which leads to its bending down.
Folk remedies
Photo: otravilsja.ru
Correcting the location of the exit of the urethra and the curvature of the penis can only be done surgically. Traditional methods are ineffective in this case. It is also not recommended to use traditional recipes to improve healing after surgery - all necessary drugs are applied to the wound during dressings.
Unauthorized use of lotions, compresses, ointments and other local remedies can disrupt the process of tissue restoration, cause inflammation, stricture formation or transplant rejection. The only safe folk method is universal auxiliary therapy, carried out to strengthen the immune system and increase the body's defenses.
The child needs to organize proper nutrition with sufficient content of meat, dairy products and vegetables in the diet. Vitamin drinks will help improve the immune system and provide the body with useful compounds: rosehip tea, cranberry juice, infusion of sea buckthorn, honey and lemon. When choosing drinks, you should take into account the presence of an allergic predisposition and the possibility of developing diathesis. You can use any traditional methods only after consultation with your doctor.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
SEARCH FOR TREATMENT AROUND THE WORLD WITH YELLMED
Diagnostics
Photo: doctors.am
In most cases, hypospadias is diagnosed immediately after the birth of the child, since the incorrect location of the urethral outlet is visible to the doctor during examination. In addition, the presence of pathology is indicated by the stream during urination.
In severe forms of the disease, when the external genitalia are greatly altered by the defect, a clinical study is required to confirm the karyotype. In addition, the child is given a full examination to detect concomitant diseases and pathologies of the urinary system.
General diagnostic principles
For stem, capitate and venous forms of hypospadias, the diagnosis is made by a doctor during the initial examination. Regardless of the form of the disease, a pelvic ultrasound is performed to detect chronic diseases and other congenital pathologies of the genitourinary system.
The patient also requires consultation with an endocrinologist and geneticist. Depending on the specifics of the case, these specialists may prescribe tests or clinical studies (blood test for sugar, blood test for sex hormones, and so on). A complete examination allows us to identify concomitant pathologies and conduct effective treatment.
Clinical researches
When diagnosing hypospadias, the doctor may prescribe the following clinical and instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- cytoscopy (examination of the bladder using an endoscope);
- MRI;
- uroflowmetry (the study allows you to determine the volumetric flow rate of urination).
In most cases, an examination is carried out not only of the penis, but also of the entire urinary system, since improper urination leads to stagnation of urine in the kidneys and ureters, which causes chronic and acute diseases.
Diagnosis of severe forms of hypospadias
With the perineal and scrotal form of the disease, the external genitalia often undergo significant changes, which makes it difficult to determine the sex of the child. To determine the sex of the newborn, in such cases a genetic analysis is performed to determine the karyotype.
Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging may not provide a complete picture of the development of the pathology, so laparoscopy of internal organs is sometimes prescribed. The study is carried out to detect the ovaries and other female genital organs.
The doctor also prescribes an examination of the endocrine system, which makes it possible to detect the cause of the development of the pathology. Often, disturbances in the production of hormones cause the appearance of abnormal genital organs and urination problems.
Severe forms of hypospadias are always accompanied by other pathologies, so a detailed examination of the internal organs is carried out for the purpose of early diagnosis and prescription of effective treatment.
If an abnormal exit of the urethra, a curved penis, or other signs of disease are detected, you should contact a urologist, who will schedule an examination. Please note that certain tests and examinations are prescribed depending on certain factors:
- features of the development of pathology;
- concomitant diseases;
- complaints from the patient or his parents (if we are talking about a small child);
- clinical capabilities of the clinic (available medical equipment) and so on.
In severe forms of the disease, it is necessary to contact a specialized clinic where appropriate specialists work and there is equipment to conduct a full examination, including rare tests and studies.
Urine drainage and wound dressing
Urine is drained using a transurethral drip stent or through a drainage tube placed above the pubis. Some surgeons do not perform drainage after repair of distal hypospadias. It is common to apply a circular bandage with light pressure, as well as prescribe antibiotics for prophylactic purposes. The duration of stenting and bandaging varied significantly between studies. Due to the low level of evidence, no recommendation can be made.