Have you ever experienced heartburn? If not, then it’s a matter of time: almost every adult has felt an unpleasant burning sensation in the esophagus at least once in their life. Due to the widespread prevalence of the problem, heartburn remedies are a hot commodity in any pharmacy, especially during the New Year holidays and other holidays associated with feasts. And almost always the assortment is presented in a prominent place in the display case. All antacids belong to the OTC group of drugs, which places responsibility on the pharmacist, who is obliged to recommend this or that drug. What do you need to know about the nature of heartburn in order to choose an effective and safe drug for a particular buyer? What questions to the buyer will help the pharmacist make a choice?
Required knowledge
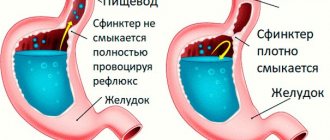
Heartburn is a symptom subjectively perceived as a feeling of burning or warmth of varying intensity and duration, occurring behind the sternum and/or in the epigastric region, spreading upward from the xiphoid process. In the domestic epidemiological study "MEGRE" (2011), it was demonstrated that this symptom is detected in 47.5% of Russians. Heartburn can occur both on an empty stomach and after a heavy meal (after 20–30 minutes), after eating a large amount of sweet foods and hot spices. Smoking, fatty foods, coffee, carbonated drinks, chocolate, tomatoes, onions, garlic, citrus fruits, mint and alcohol can also trigger heartburn. Most often it appears in a horizontal position and during physical activity (lifting weights, bending the body forward), during pregnancy. Also, heartburn can be caused by taking certain medications - these are reflex expectorants, antibiotics, NSAIDs, calcium channel blockers, estrogens, antispasmodics, β-blockers, nitrates, anticholinergic drugs.
Heartburn is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which involves inflammatory changes in the lining of the esophagus, but can also occur in healthy people.
Symptoms of GERD:
- belching air or sour;
- lump in the throat;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- Heartburn is the most common symptom, occurring in 81% of GERD cases.
Despite the apparent “frivolity” of the symptoms of GERD, a long-term uncontrolled course of the disease can lead to complications such as:
- esophageal ulcers;
- bleeding - when blood vessels are damaged due to the formation of an esophageal ulcer;
- strictures (narrowing) of the esophagus;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing);
- pharyngeal reflux - a condition when acid from the stomach enters not only the esophagus, but also higher into the pharynx, and from there into the larynx, which is manifested by hoarseness;
- pneumonia and bronchitis - develop when pharyngeal reflux worsens and acid enters the respiratory tract;
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition of the esophagus;
- esophageal carcinoma.
In this regard, timely consultation of the patient with a doctor for a complete examination and diagnosis is especially important even with minimal manifestations of the disease.
The basis of treatment for GERD is lifestyle changes: normalizing body weight, quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, fatty foods, coffee, chocolate, and carbonated drinks. Food should be taken in small portions, dinner no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime, stress associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure, as well as wearing tight clothing should be avoided. The most commonly used medications are proton pump inhibitors, H2-histamine receptor blockers, prokinetics, antacids and, more recently, alginates.
It is important to note that almost all drugs intended to treat GERD, except antacids and alginates, are prescription drugs and are prescribed only by a doctor!
Production
Sodium alginate is extracted from plant material, primarily brown algae. Production is quite labor-intensive and includes a number of successive stages:
- Collection of seaweed (both raw and dried), cleaning from foreign impurities.
- Fine and uniform grinding using a special machine, which ensures more complete extraction of alginate.
- In the reactor, a solution of sulfuric acid and water is heated to 45-50 °C.
- Add a portion of crushed algae (150-160 kg) to the prepared solution while stirring, stir, and leave for 1 hour without heating.
- The mixture is washed with water.
- The algae is poured with an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate and heated to 60-70 °C with constant stirring for 3 hours. A viscous boiled substance is formed - galerta.
- The mixture is mixed with water, then it is fed into special settling tanks, where compressed air is passed through it through tubes with holes, while water continues to be poured into it. This lasts no more than 20 minutes.
- The resulting solution is left to settle for 3 hours, after which it is filtered.
- The filtered liquid is collected by a pump and placed in precipitation baths, where sulfuric acid is added to separate alginic acid.
- The precipitated dense mixture of alginic acid in the washing baths is washed from sulfuric acid for 10-15 minutes.
- The resulting raw material is combined in a mixer with sodium bicarbonate, where sodium alginate is formed during the reaction.
- The solution is treated with steam in dryers at a temperature of 120 °C. Sodium alginate dries into a thin film, which is removed with scissors.
- The film is crushed into powder.
Typically, sodium alginate extraction plants are located in close proximity to coastal areas. The finished powder can be of different viscosities, mainly 500 and 1000. The main manufacturers of the food additive are the USA, Japan, France, and China. Some Russian factories also process brown algae into E401.
The role of the pharmacist
Unfortunately, in most cases of heartburn, the patient does not reach a doctor. When the first symptoms appear, people prefer to go to the pharmacy and pick up the drug there. Therefore, the pharmacist must know the features of all antacids, the rules for taking them and contraindications in order to give individual, competent advice to each buyer. In addition, the first-calculator needs to inform the client that timely consultation with a doctor in case of frequent heartburn is simply necessary! This will help identify the cause of the symptom, increase the likelihood of cure, and reduce the risk of developing serious complications such as Barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer.
So, what are antacids and alginates and what place do they occupy in the treatment of acid-related diseases? Let's figure it out.
Package
Manufacturers usually package the food additive E 401 in wound cardboard drums (volume 25 kg).
Chinese manufacturers use polypropylene bags with an additional inner liner that protects the product from moisture.
The container can serve as:
- multilayer paper bags;
- polypropylene bags;
- corrugated cardboard boxes.
A thick polyethylene bag is inserted inside.
All packaging must be marked “Keep away from moisture.”
Sodium alginate with a volume of up to 1 kg is packaged in foil or plastic bags.
Antacids
Antacids neutralize the effect of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. The abundance of dosage forms (tablets, lozenges, oral suspension in a bottle, oral suspension in bags, solutions, powders, gels), pleasant taste and almost complete absence of side effects with occasional use allows this group of drugs to retain one of the important positions in the treatment of acid-related diseases.
NB!
Antacids do not eliminate the cause of heartburn, but they temporarily relieve the discomfort! It is important to convey this to buyers, because only an integrated approach to treating the underlying disease can help get rid of unpleasant symptoms for a long time.
All antacid drugs are divided into absorbable and non-absorbable. Absorbed antacids can have systemic effects, while non-absorbable antacids act primarily in the gastrointestinal tract. This division of antacids is quite arbitrary and is based on the degree of absorption, so some drugs (for example, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide) are included by different authors in different groups.
Absorbable include :
- sodium bicarbonate (soda - NaHCO3);
- magnesium oxide (burnt magnesia);
- basic magnesium carbonate - a mixture of Mg(OH)2, 4MgCO3, H2O;
- main calcium carbonate - CaCO3;
- mixture - sodium sulfate, sodium phosphate, sodium bicarbonate;
- mixture: calcium carbonate + magnesium carbonate.
Products from this group are almost always present in pharmacy display cases, but they have a limited scope of application and are rarely prescribed by doctors. By entering into a neutralization reaction with hydrochloric acid, they give a very quick but short-lived effect, and the resulting carbon dioxide causes belching and bloating, which precludes their use for GERD. Also, taking absorbable antacids can lead to a secondary increase in the secretion of hydrochloric acid (the “rebound” phenomenon). In this regard, absorbable antacids have practically lost their clinical significance and are used mainly for self-medication. Antacid drugs from this list can be taken occasionally and once, since with long-term use they cause exacerbation and progression of diseases of the digestive tract, such as stomach ulcers.
A homemade antacid - soda - has a negative effect on water-salt metabolism, therefore, with intensive treatment, edema may appear, blood pressure may increase, and signs of heart failure may increase, which limits its use in patients with concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidney diseases and in old age .
The group of non-absorbable antacids includes primarily aluminum and magnesium preparations .
- 1st generation - aluminum salts of phosphoric acid - used limitedly due to the possible development of serious side effects;
- 2nd generation - aluminum-magnesium antacids - the most frequently prescribed drugs from the group of non-absorbable antacids, due to the combination of magnesium and aluminum salts, they have a more pronounced antacid effect and better tolerability;
- 3rd generation - aluminum-magnesium preparations with other components , prescribed in cases where a carminative or analgesic effect is additionally required.
The main mechanism of action is associated with the adsorption of hydrochloric acid, so their effect develops more slowly than that of absorbed drugs, but lasts longer - 2.5–3 hours. They are superior to absorbed antacids in neutralizing capacity. Non-absorbable antacids have additional beneficial properties:
- can adsorb pepsin, reducing the proteolytic activity of gastric juice, preventing further destruction of the mucosa;
- bind bile acids that have a damaging effect on the gastric mucosa;
- have a pronounced enveloping effect, thereby protecting the mucous membrane and promoting better regeneration.
Aluminum-containing antacids can cause serious complications when used over a long period of time or when taken in high doses. In the small intestine, they form aluminum phosphate salts, due to which the absorption of phosphates is impaired and hypophosphatemia develops, manifested by malaise and muscle weakness. Severe phosphate deficiency causes osteomalacia and osteoporosis. Aluminum can interfere with bone mineralization, causing toxic effects on osteoblasts. Hypophosphatemia, in turn, promotes increased calcium absorption, the development of hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria and the formation of calcium stones. The accumulation of aluminum in the glomerular membranes of the kidneys can cause the development of renal failure or its aggravation. In this regard, it is undesirable to use aluminum-containing antacids in elderly patients, children, and pregnant women. Aluminum salts contribute to the development of constipation, and magnesium compounds weaken. In modern antacids, the ratio of aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide is well balanced, which helps to avoid bowel dysfunction.
Today, combined antacids with two or more active ingredients are most widely used. This allows you to vary the speed of onset of the therapeutic effect and duration of action, as well as reduce the number of side effects and improve tolerability.
To the delight of cosmetologists
Due to several special properties, the additive has now become practically the best friend of cosmetology center workers. The instructions for a cream with an anti-aging or moisture-retaining spectrum of action will most likely contain exactly this main ingredient.
Even if you simply make a mask at home, mixing the proportions correctly, after just a few procedures you will be able to achieve a visible effect. This happens due to the following features of the effect on the skin:
- activation of the protective barrier;
- regulation of water balance;
- moisture retention;
- toning;
- anti-stress therapy;
- strengthening collagen fibers;
- regulation of metabolism;
- stabilization of the sebaceous glands;
- increasing the tone of the subcutaneous layer.
It is most convenient to use all the beneficial qualities of the product as a mask. Moreover, it does not matter at all what type of skin the client has. Even people with signs of aging skin are allowed to use this type of therapy to freeze the loss of beauty. But most often they are prescribed to teenagers or simply people who have suffered for years due to problem skin without the opportunity to choose competent care on an ongoing basis.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
You can purchase the powder in pharmacy chains without a prescription or in specialized stores. It is best to dilute it with a special serum solvent. But if you don’t have such a liquid at hand, then even just warm water will do.
Next, you need to apply the mixture in an even layer in the place that most needs restoration. Immediately after application, an airtight film is formed on the area, which is designed to fix the contours of the face or body, depending on the selected treatment area.
As soon as the set time is up, the film can be removed. As a result, the consumer receives a pronounced lifting effect. This happens due to the fact that many skin irregularities are smoothed out. The effect works even in cases where you need to get rid of wrinkles on the neck, forehead or nasolabial fold.
Cosmetologists also value sodium alginate for its ability to structure a liquid solution, adding the viscosity necessary for a specific procedure. The slightly viscous consistency is ideal for the formation of irreversible gels. This property is used to create products in the household chemicals category, such as the production of shampoos, ready-made creams and soap solutions for intimate hygiene.
Alginates
According to the pharmacological index, alginates belong to antacids and adsorbents, although they have different mechanisms of action. Structurally, alginates are neutral polysaccharide polymers and belong to dietary fiber. Alginates stabilize viscous suspensions, forming films and turning into a gel form. Alginate reacts with gastric acid to form dioxide, which is captured by the gel. The dioxide gel foams and floats on the surface of the stomach contents (even when lying down), creating a kind of gel barrier, or “raft,” that prevents further acid and pepsin from entering the esophageal mucosa. It is this “raft” of alginate that prevents the reflux of both acidic gastric and alkaline duodenal contents into the esophagus. The alginate “raft” works for more than 4.5 hours. Another undeniable advantage of alginates is their proven safety at any stage of pregnancy, as well as during lactation.
Positive effects of taking alginates:
- protect the esophagus from the pathological influence of gastric juice, without changing the acidity of the latter;
- act quickly;
- promote the healing of erosions, stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- with hyperacid gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa with high acidity) reduce increased appetite;
- adsorb harmful substances, excess hydrochloric and bile acids, pepsin;
- suppress the activity of pathological microflora;
- are an additional source of dietary fiber.
Antacids and alginates
| Tradename | INN | |||
| Antacids | Suction | Vikair | Magnesium carbonate + sodium bicarbonate + bismuth subnitrate + calamus rhizome + alder buckthorn bark | |
| Vikalin | Magnesium carbonate + sodium bicarbonate + bismuth subnitrate + coline + rutoside + calamus rhizomes + alder buckthorn bark | |||
| Bellalgin | Sodium bicarbonate + belladonna leaf extract + benzocaine + metamizole sodium | |||
| Becarbon | Sodium bicarbonate + belladonna leaf extract | |||
| Rumney | Calcium carbonate + magnesium carbonate | |||
| Rennie | ||||
| Inalan | ||||
| Non-absorbable | 1st generation (aluminum salts of phosphoric acid) | Phosphalugel | Aluminum phosphate | |
| 2nd generation (aluminum-magnesium antacids) | Almagel | Algeldrate + magnesium hydroxide | ||
| Gastal Likvo | ||||
| Gastracid | ||||
| Ajiflux | ||||
| Maalox | ||||
| Maalox mini | ||||
| Alumag | ||||
| Altacid | ||||
| 3rd generation (aluminum-magnesium antacids with additional components) | Simalgel-VM | Algeldrate + magnesium hydroxide + simethicone | ||
| Almagel Neo | ||||
| Relzer | ||||
| Almagel A | Algeldrate + magnesium hydroxide + benzocaine | |||
| Alma-Gal | Aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide + sorbitol | |||
| Alginates | Alginic acid salts | Gaviscon | Sodium alginate + sodium bicarbonate + calcium carbonate | |
| Gaviscon Forte | Sodium alginate + potassium bicarbonate | |||
| Gaviscon Double Action | Sodium alginate + sodium bicarbonate + calcium carbonate | |||
Chemical composition, nutritional value, calorie content
Sodium alginate has no significant nutritional value and is a low-calorie product. Due to the fact that it is carefully purified during extraction, it does not contain vitamin compounds. Sodium is of great importance, as it can change the balance of mineral elements in the body.
| BJU | Quantity | Calorie content, energy value |
| Squirrels | 0 g | 0.88 kcal, 3.68 kJ |
| Fats | 0 g | |
| Carbohydrates | 0.22 g | |
| Alimentary fiber | 0 g | |
| Dry matter | 98 g | |
| Water | 0 g |
It is important to understand that humans do not have enzymes that are capable of breaking down complex bonds in sodium alginate, so it is not absorbed, does not participate in metabolism and is released unchanged, without undergoing biotransformation in the liver.
Algorithm and questions
So, what questions should a buyer ask in order to correctly select a heartburn medication at a pharmacy or send it to a therapist on time?
- Are there any “worrying” complaints?
- abdominal pain (of any nature);
nausea, vomiting, obsessive belching;
- temperature increase;
- bloating, delayed gases;
- weakness;
- impurities of blood and/or mucus in the stool, traces of blood on toilet paper;
- black, tarry stool;
- constipation followed by loose stools;
- any sudden changes in bowel habits;
- sudden weight loss.
- Is heartburn new or recurring?
- If heartburn occurs for the first time, then we can recommend absorbable antacids (for example, calcium carbonate + magnesium carbonate) or non-absorbable 1st generation, which will help relieve unpleasant symptoms one-time.
If heartburn occurs not for the first time and the buyer has previously, according to him, already had some gastroenterological diseases, then preference should be given to non-absorbable antacids of the 2nd generation or alginates.
- How often do you experience heartburn?
- If episodes of heartburn occur once a week or less, then such a buyer should be recommended combined non-absorbable antacids of the 2nd generation * as the most effective (aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide) for use on an “on demand” basis.
If episodes of heartburn occur more often than twice a week, then it is advisable for such a buyer to be advised to undergo a medical examination, since in this case it may be necessary to regularly take other groups of drugs (proton pump inhibitors, prokinetics, H2-histamine receptor blockers), which only a doctor will prescribe .
- Is the patient taking other medications?
- expectorants of reflex action;
antibiotics;
- NSAIDs;
- calcium channel blockers;
- estrogens;
- antispasmodics;
- β-blockers;
- nitrates;
- anticholinergic drugs.
- Is the woman pregnant or not?
- If heartburn is episodic (1-2 times a week or less), we recommend absorbable antacids (calcium carbonate + magnesium carbonate) once to quickly relieve symptoms.
If heartburn is systematic and causes severe discomfort, then preference should be given to alginates, as the safest means during pregnancy.
- Buyer's age?
In the group of elderly patients and children over 12 years of age, the safest use of alginates is to relieve heartburn, since they act quickly and do not have systemic effects. The use of absorbable and aluminum-containing antacids in elderly patients is undesirable due to possible side effects.
- Do you have a history of any inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, gastric or duodenal ulcers)?
- If the patient has not previously been seen by a gastroenterologist and has not taken antacids, then to start therapy, it is optimal to prescribe second-generation non-absorbable antacids.
If the buyer remembers that he was once registered with a gastroenterologist and underwent treatment, then the choice should be made on alginates, as they are the safest in this situation. Such a buyer should definitely be advised to consult a doctor so as not to miss an exacerbation or progression of the disease.
- Are you allergic to aluminum or magnesium?
An affirmative answer means refusing drugs with these components. Alginates will be a win-win option for such clients, as well as for those who doubt the answer.
Dear pharmacists, remember, if “habitual” heartburn is accompanied by at least one of the symptoms described above, this is a reason to immediately refer the buyer to a doctor. Delay in this case can be life-threatening!
In both cases, it is necessary to draw the buyer’s attention to the fact that long-term uncontrolled use of the drug is not safe and for optimal selection of the drug, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
All of these drugs can cause heartburn. In this case, we can recommend periodic use of antacids “on demand”, absorbable or non-absorbable, 1st generation.
The use of aluminum-containing drugs during pregnancy and lactation is strictly contraindicated!
Harm, contraindications, side effects
Sodium alginate as a food additive is approved in Russia and in all countries of the world. In food products, it performs its function when added in minimal quantities, so its content there is extremely low. In this regard, there is no restriction on the concentration of E401 in food in regulatory legal acts. Once in the body, it is broken down into sodium and alginic acid, which is excreted unchanged without causing harm to health.
The only contraindication to taking sodium alginate is individual intolerance, which is expressed in allergic reactions (rash, coughing, sneezing). There are no side effects; drug manufacturers indicate that if dosages are not observed, allergies may occur.
Summary
Let us remind you once again that the pharmacist’s task is not only to select the most effective and safe drug (which our article will help with), but also to motivate the buyer to see a doctor for a detailed examination.
Sources
- Vakil N., van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P., Dent J., Jones R; Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug.
- Maev I.V., Samsonov A.A., Bely P.A., Lebedeva E.G. GERD is the leader of acid-dependent pathology of the gastrointestinal tract // Appendix Consilium Medicum. Gastroenterology. No. 1. 2012. pp. 18–24.
- Minushkin O. N., Elizavetina G. A. Antacids in modern therapy of acid-related diseases // Gastroenterology of St. Petersburg. — 2010. — No. 2–3
- Yanova O. Modern understanding of the pathophysiological aspects of GERD and approaches to its pharmacotherapy // Doctor. 2013. No. 3.
- Bordin D.S., Masharova A.A., Kozhurina T.S. Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with alginates // Treating Doctor. 2008.
- Lazebnik L. B., Masharova A. A., Bordin D. S. et al. Results of the multicenter study “Epidemiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Russia” (“MEGRE”). Therapeutic archive. 2011.
- Isakov V. A. Analysis of the prevalence of heartburn: a national epidemiological study of the adult urban population (ARIADNA). Experimental clinical gastroenterology. 20089. Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease. 2006.
Type of substance
Food additive E 401 is the sodium salt of alginic acid.
The substance is an anionic polysaccharide of natural origin. Producers are brown algae (kelp, fucus, sargassum). Alginic acid is synthesized in plant cell walls in the form of salts. Industrial production of thickener E 401 is based on processing raw materials with alkali (caustic or baking soda) followed by purification.
Used as a thickener, stabilizer, emulsifier, and moisture-retaining agent.